Response to astronomical forcing of sedimentary record in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
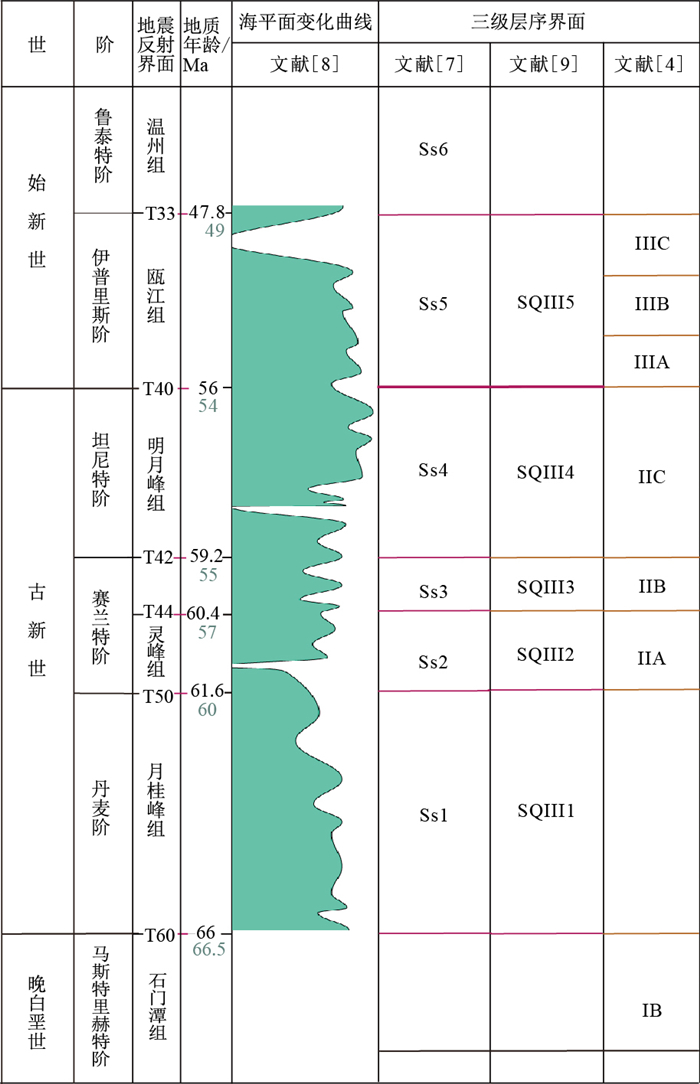
摘要: 基于东海陆架盆地古新世-始新世前人解释的三级层序成果,认为东海陆架盆地现有的三级层序划分不足以满足当下研究的需要,由此开展了旋回地层与层序地层研究,重新将三级层序界面的与基于对岩性及地震相特征变化的解释相结合,加入了天文旋回驱动的机制,阐明海平面变化驱动三级层序的特征。以东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷的BSH-1井及其相邻的NB-25-2-1井为研究对象,结合地层学研究基础,选取GR测井曲线为古气候替代指标,应用旋回地层学的理论及其时间序列分析、频谱分析技术的方法,对两口典型钻井进行了天文旋回分析,借助邻井时间锚点建立了有效的天文年代标尺,探讨了斜率周期信号变化的振幅调制的约1.2 Ma长周期与海平面变化以及三级层序发育的关系,认为东海陆架盆地三级层序受控于稳定的约1.2 Ma的斜率振幅调制周期。最终形成一套绝对天文年代标尺与一套三级层序划分方案。Abstract: In this study, we have investigated the third-order sequences interpreted by the previous researchers of Paleocene-Eocene in the East China Sea Basin, and believe that the interpretation of the third-order sequences is mainly based on the interpretation of seismic and lithologic changes, which is basically consistent with the previous interpretation of the stratigraphic stages, and cannot truly reflect the characteristics of the third-order sequences driven by the change of sea-level. This paper takes well BSH-1 and its adjacent well NB-25-2-1 in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin as the research objects and selects GR logging curve as the paleoclimate alternative index. Based on the theory of cyclostratigraphy, this study, combining with the previous stratigraphic research data, conducted spectrum analysis and time series analysis, and analyzed the astronomical cycle of the two wells. Then, the paper establishes an effective astronomical chronograph and discusses the slope cycle information.The relationship between the 1.2 Ma long period of amplitude modulation and sea level change and the development of the third-order sequence shows that the third-order sequence in East China Sea Basin is controlled by the stable 1.2 Ma slope amplitude modulation period. Finally, a set of absolute astronomical time scale and a set of third-order sequence division plan are formed.
-
Key words:
- Paleocene /
- Eocene /
- sea-level /
- astronomical time scale /
- Xihu Depression /
- East China Sea Basin
-
图 5 BSH-1井时间域斜率的振幅调制与调整到GTS2012的文献[8]中的海平面变化曲线对比
Figure 5. Amplitude modulation of time domain obliquity of well BSH-1 compared with sea-level change curve of Haq et al.(1987) adjusted to GTS2012
图 6 BSH-1井斜率的振幅调制频谱与文献[14]中的频谱以及La2004中的斜率理论曲线的振幅调制频谱对比
a.BSH-1井的时间域GR曲线的斜率滤波振幅调制曲线MTM频谱,斜率的滤波频带宽度(0.025 ± 0.006)旋回数/Ma,振幅的包络线用Taner-Hilbert方法提取;文献[14]的海平面变化曲线7.5~40.2 Ma范围的MTM频谱;c.数值解La2004中斜率曲线0.2~40.2 Ma范围的频谱的振幅调制曲线MTM频谱,斜率的滤波带宽(0.025±0.002)旋回数/Ma; 图中数字为横坐标的倒数
Figure 6. Comparison of amplitude modulation spectrum of obliquity of well BSH-1 with that of Miller et al.(2005) and obliquity theoretical curve in La2004
表 1 BSH-1井主要层序界面绝对ATS年龄与原定年对比
Table 1. Absolute ATS age of main sequence boundary of well BSH-1 compared with the original age
层段 顶深/m 底深/m 层厚/m 底界面 浮动ATS/ka 绝对ATS/Ma 原定年/Ma 调整到GTS2012/Ma 花港组上段 2 039.8 2 409 369.2 T21 24 796 24.996 - - 花港组下段 2 409 2 535 126 T30 26 755 26.955 - - 平湖组一二段 2 535 2 686.5 151.5 T32 28 517 28.717 - - 平湖组三段 2 686.5 2 844 157.5 T33 29 863 30.063 49 47.8 平湖组四段 2 844 3 135.5 291.5 T34 33 062 33.262 - - 平湖组五段 3 135.5 3 447.6 312.1 T35 36 155 36.355 - - 误差范围:±0.4 Ma;原定年据文献[5, 9] -
[1] 王鹏, 赵志刚, 张功成, 等.东海盆地钓鱼岛隆褶带构造演化分析及对西湖凹陷油气勘探的意义[J].地质科技情报, 2011, 30(4):65-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201104009 [2] 赵省民, 张正喜, 吴必豪, 等.东海陆架盆地古近-新近系高分辨率层序[J].地质力学学报, 2002, 8(3):239-247. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzlxxb200203007 [3] 侯国伟, 刘金水, 蔡坤, 等.东海丽水凹陷古新统源-汇系统及控砂模式[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):71-80. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902008 [4] 武法东, 陈建渝, 刘从印, 等.东营凹陷第三纪层序地层格架及沉积体系类型[J].现代地质, 1998, 12(4):559-566. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-XDDZ804.016.htm [5] 段九春, 赵英杰, 米慧芬.东海陆架盆地南部中生界及古近系层序地层格架[J].洁净煤技术, 2010, 16(6):100-104. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jjmjs201006028 [6] Hardenbol J, Thierry J, Farley M B, et al.Cretaceous sequence chronostratigraphy[C]//De Graciansky P C, Hardenbol J, Jacquin T, et al.Mesozoic and Cenozoic sequence stratigraphy of European basins: SEPM (Society for Sedimentary Geology).: Spec.Publ., 1998. [7] 刘景彦, 陈志勇, 林畅松, 等.东海丽水西次凹古新统明月峰组层序:体系域分析及沉积体系展布[J].沉积学报, 2004, 22(3):380-386. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjxb200403002 [8] Haq B U, Hardenbol J, Vail P R.Chronology of fluctuating sea levels since the Triassic[J].Science, 1987, 235:1156-1167. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4793.1156 [9] 张银国, 葛和平, 杨艳秋, 等.东海陆架盆地丽水凹陷古新统层序地层的划分及控制因素[J].海相油气地质, 2012, 17(3):37-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201203005 [10] Vail P R, Mitchum R M, Todd J R G, et al.Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level[C]//Payton C E.Seismic stratigraphy-applications to hydrocarbon exploration.: American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, 1977, 26: 49-212. [11] 陈忠云, 张建培, 张涛, 等.西湖凹陷层序划分及海平面变化响应[J].海洋地质前沿, 2013, 29(9):15-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201309003 [12] Boulila S, Galbrun B, Miller K G, et al.On the origin of Cenozoic and Mesozoic "third-order" eustatic sequences[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 109:94-112. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2011.09.003 [13] Laskar J.Long-term solution for the insolation quantities of the Earth[J].Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union, 2004, 2(14):101-106. http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=1432476&fulltextType=RA&fileId=S1743921307011404 [14] Laskar J, Fienga A, Gastineau M, et al.A new orbital solution for the long-term motion of the Earth[J].Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2011, 532(92):784-785. http://arxiv.org/abs/1103.1084 [15] Abels H A, Hilgen F J, Krijgsman W, et al.Long-period orbital control on middle Miocene global cooling:Integrated stratigraphy and astronomical tuning of the Blue Clay Formation on Malta[J].Paleoceanography, 2005, 20:PA4012. [16] Meyers S R, Sageman B B, Pagani M.Resolving Milankovitch:Consideration of signal and noise[J].American Journal of Science, 2008, 308(6):770-786. doi: 10.2475/06.2008.02 [17] Ruddiman W F.Orbital insolation, ice volume, and greenhouse gases[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22:1597-1629. doi: 10.1016/S0277-3791(03)00087-8 [18] Li M, Hinnov L A, Huang C, et al.Sedimentary noise and sea levels linked to land-ocean water exchange and obliquity forcing[J].Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1):1004. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-03454-y [19] Miller K G, Kominz M A, Browning J V, et al.The Phanerozoic record of global sea-level change[J].Science, 2005, 310:1293-1298. doi: 10.1126/science.1116412 [20] Lourens L J, Hilgen F J.Long-periodic variations in the earth's obliquity and their relation to third-order eustatic cycles and Late Neogene glaciations[J].Quaternary International, 1997, 40:43-52. doi: 10.1016/S1040-6182(96)00060-2 [21] Zachos J C, Shackleton N J, Revenaugh J S, et al.Climate response to orbital forcing across the Oligocene-Miocene boundary[J].Science, 2001, 292:274-278. doi: 10.1126/science.1058288 [22] Lourens L J, Sluijs A, Kroon D, et al.Astronomical pacing of late Palaeocene to early Eocene global warming events[J].Nature, 2005, 435:1083-1087. doi: 10.1038/nature03814 [23] Westerhold T, Röhl U, Laskar J, et al.On the duration of magnetochrons C24r and C25n and the timing of early Eocene global warming events:Implications from the Ocean Drilling Program Leg 208 Walvis Ridge depth transect[J].Paleoceanography, 2007, 22:1-19. doi: 10.1029/2006PA001322/full [24] Matthews R K, Frohlich C, Duffy A.Orbital forcing of global change throughout the Phanerozoic:A possible stratigraphic solution to the eccentricity phase problem[J].Geology, 1997, 25:807. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0807:OFOGCT>2.3.CO;2 -





 下载:
下载: