Origins of vein-forming fluid and hydrocarbon accumulation in Shiniulan Formation in Dingshan, southeast Sichuan Basin
-
摘要: 四川盆地东南部志留系油气成藏过程研究缺少成藏和破坏阶段的直接证据,丁山地区志留系石牛栏组储层内沥青和方解石脉体记录了储层内流体演化的信息,对研究油气藏油气成藏演化过程有重要的指示作用。运用显微岩相学、阴极发光、微区原位元素和流体包裹体分析方法,确定了古流体来源和活动时间,并恢复了甲烷包裹体古压力,结合烃源岩生烃演化史和地质特征揭示了石牛栏组油气成藏演化过程和主控因素。研究结果表明丁山地区石牛栏组储层内发育两期方解石脉体,原油充注发生在两期方解石脉形成之前。第一期方解石脉形成于距今约127 Ma,阴极发光颜色为褐红色,方解石脉形成于偏还原环境,成脉流体来源于同层位成岩流体。第二期方解石脉形成于距今约83 Ma,阴极发光颜色为褐黄色,方解石脉形成于偏氧化环境。龙马溪组烃源岩大量生油阶段在距今190~150 Ma之间,生成的石油充注到石牛栏组储层中并在距今约135 Ma裂解成气藏。甲烷包裹体捕获压力为51.77~57.46 MPa,储层压力系数为1.26~1.40。石牛栏组古气藏在燕山期以来,由于构造运动导致地层抬升剥蚀和断裂发育,促使天然气泄漏。Abstract: The Silurian hydrocarbon accumulation research in the southeastern Sichuan Basin lacks evidence of the hydrocarbon accumulation and destruction stages in reservoirs. Bitumen and calcite veins that were developed in the Shiniulan Formation had recorded the information of the fluid evolution in reservoirs and have important implications for fluid activities and hydrocarbon accumulation processes in the Dingshan area, southeast Sichuan Basin. Based on analysis of petrographic, trace element, fluid inclusion and laser Raman spectroscopy of the calcite veins, this research determines the timing and origin of the paleo-fluids formed the calcite veins; recovers the paleo-pressure of the methane inclusions, and reveals the petroleum system evolution and controlling factors of the Shiniulan Formation. The results indicate that two phases of calcite veins were developed in the Shiniulan Formation, and oil charging happened before the formation of the two phases of the calcite veins. The first phase of calcite veins were formed at ~127 Ma under relative reduction conditions, with the forming fluid sourcing from the diagenetic fluid of the same strata, which show brown-red cathode luminescence colors. The second phase calcite veins were formed at ~83 Ma under relative oxidation conditions, showing brown-yellow cathode luminescence colors. Oil generation peak of the Longmaxi source rocks, which were the main source of the Shiniulan reservoirs, was from ~190 Ma to ~150 Ma. Oil to gas cracking happened at ~135 Ma. The trapping pressure of methane inclusions is 51.77-57.46 MPa, and the pore fluid pressure coefficient is 1.26-1.40. Since the Yanshanian period, a series of tectonic movements have taken place in the Dingshan area, which uplifts and lead to erosion and fracturing of the Dingshan area is accounts for the destruction of the Shiniulan gas reservoirs.
-
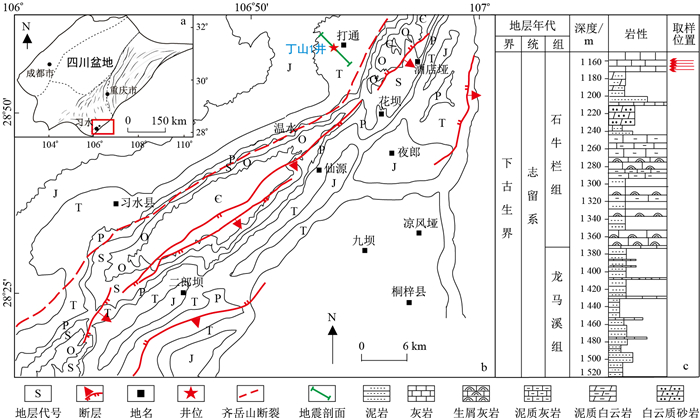
表 1 丁山1井石牛栏组方解石脉体微量元素特征参数
Table 1. Characteristic parameters of trace elements in calcite vein from Shiniulan Formation in Well Dingshan 1
编号 方解石脉期次 U/Th V/Cr Ni/Co 2×U/(U+Th/3) V/(V+Ni) δEu δCe S1-1 第一期 1.29 4.89 5.68 1.12 0.71 1.52 0.96 S1-2 第一期 2.31 5.62 11.62 3.26 1.02 3.88 0.92 S1-3 第一期 1.66 6.44 7.96 1.94 0.56 2.45 0.92 S1-4 第二期 0.12 0.03 4.89 0.52 0.56 0.75 0.73 S1-5 第二期 0.05 0.53 2.37 0.65 0.09 0.78 0.76 S1-6 第二期 0.78 1.02 3.12 0.35 0.32 0.68 0.84 S2-1 第二期 0.47 0.31 1.01 0.19 0.03 0.48 0.85 S2-2 第二期 0.12 1.16 2.90 0.51 0.14 0.85 0.81 S2-3 第二期 0.33 2.44 1.36 0.94 0.26 0.79 0.88 S2-4 第二期 0.68 1.69 3.77 0.75 0.11 0.84 0.79 表 2 丁山1井石牛栏组储层第一期方解石内甲烷包裹体拉曼散射峰、密度及压力计算结果
Table 2. Calculation results of Raman scattering peak, density and pressure of methane inclusions in the first phase calcites from Shiniulan Formation in Well Dingshan 1
编号 υmeans/cm-1 υcorr/cm-1 D/cm-1 ρ/(g·cm-3) 伴生盐水均一温度160℃条件下 捕获压力/MPa 压力系数 A-1 2 912.107 7 2 912.391 4 -5.188 6 0.205 57.46 1.40 A-2 2 912.136 4 2 912.549 9 -5.030 1 0.198 54.33 1.33 A-3 2 912.107 7 2 912.391 4 -5.188 6 0.205 57.46 1.40 A-4 2 912.107 7 2 912.391 4 -5.188 6 0.205 57.46 1.40 A-5 2 912.252 7 2 912.666 7 -4.913 3 0.192 51.77 1.26 A-6 2 912.252 7 2 912.666 7 -4.913 3 0.192 51.77 1.26 A-7 2 912.136 4 2 912.549 9 -5.030 1 0.198 54.33 1.33 A-8 2 912.198 7 2 912.616 3 -4.963 7 0.195 53.04 1.29 A-9 2 912.198 7 2 912.616 3 -4.963 7 0.195 53.04 1.29 A-10 2 912.136 4 2 912.549 9 -5.188 6 0.198 54.33 1.33 A-11 2 912.252 7 2 912.666 7 -4.913 3 0.192 51.77 1.26 注:υmeans为实测的甲烷散射峰;υcorr为真实的甲烷散射峰; D=υcorr-υ0, υ0为压力接近0时甲烷包裹体的甲烷拉曼散射峰波数。ρ为依据拉曼位移参数由式(1)计算的甲烷包裹体密度;捕获压力是依据ρ和甲烷包裹体伴生气-液两相盐水包裹体均一温度计算求得 -
[1] Gao J, He S, Zhao J X, et al. Sm-Nd isochron dating and geochemical (rare earth elements, 87Sr/86Sr, δ18O, δ13C) characterization of calcite veins in the Jiaoshiba shale gas field, China: Implications for the mechanisms of vein formation in shale gas systems[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2020, 132(7/8): 1722-1740. [2] 高键. 渝东地区五峰-龙马溪组页岩裂缝脉体古温压及古流体成因[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.Gao J. Paleo-temperature and pressure and origin of paleo-fluid of fracture veins in the Wufeng-Longmaxi shales of Yudong area[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 郭小文, 陈家旭, 袁圣强, 等. 含油气盆地激光原位方解石U-Pb年龄对油气成藏年代的约束: 以渤海湾盆地东营凹陷为例[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(3): 284-291. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202003005.htmGuo X W, Chen J X, Yuan S Q, et al. Constraint of in-situ calcite U-Pb dating by laser ablation on geochronology of hydrocarbon accumulation in petroliferous basins: A case study of Dongying Sag in the Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(3): 284-291(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202003005.htm [4] 吴忠锐, 何生, 何希鹏, 等. 涟源凹陷上二叠统大隆组泥页岩裂缝方解石脉体流体报告体特征及其启示[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 70-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904009.htmWu Z R, He S, He X P, et al. Characteristics of fluid inclusions in fracture calcite veins and implications of Upper Permain Dalong Formation shale at the Lianyuan Depression[J]. Geological Scinece and Technolody Information, 2019, 38(4): 70-81(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904009.htm [5] 胡文瑄, 陈琪, 王小林, 等. 白云岩储层形成演化过程中不同流体作用的稀土元素判别模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(6): 810-818. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201006017.htmHu W X, Chen Q, Wang X L, et al. REE models for the discrimination of fluids in the formation and evolution of dolomite reservoirs[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2010, 31(6): 810-818(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201006017.htm [6] 李月, 刘铮. 浮来山断裂带流体活动期次分析: 断裂带内方解石脉的阴极发光证据[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2017, 29(3): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.03.02Li Y, Liu Z. Fulaishan fault zone fluid activity phase analysis: Evidence from calcite vein cathodouminescence within fault zone[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2017, 29(3): 5-9(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2017.03.02 [7] Huang Y H, Tarantila A, Wang W J, et al. Charge history of CO2 in Lishui Sag, East China Sea Basin: Evidence from quantitative Raman analysis of CO2-bearing fluid inclusions[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2018, 98: 50-65. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.07.030 [8] 黄伟林, 冯明友, 刘小洪, 等. 渝东石柱地区龙马溪组页岩纤维状脉体成因[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 160-169. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10033.shtmlHuang W L, Feng M Y, Liu X H, et al. Gensis of fibrous veins the shales of Longmaxi Formation in Shizhu area, Eastern Chongqong[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 160-169(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10033.shtml [9] 杨兴业, 何生, 何治亮, 等. 京山地区方解石脉包裹体、同位素特征及古流体指示意义[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 37(1): 19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2013.01.004Yang X Y, He S, He Z L, et al. Characteristics and pale-fluid activity implications of fluid-inclusion and isotope of calcite veins in Jingshan area[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 37(1): 19-26(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2013.01.004 [10] 姜磊, 邓宾, 刘树根, 等. 焦石坝-武隆构造带古流体活动差异及对页岩气保存条件的影响[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2): 524-538. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902015.htmJiang L, Deng B, Liu S G, et al. Paleo-fluid migration and conservation conditions of shale gas in Jiaoshiba-Wulong area[J]. Earth Scinece, 2019, 44(2): 524-538(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902015.htm [11] 孙博. 川南长宁地区构造形变与流体活动特征[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2018.Sun B. Characteristics of structural deformation and fluid activity in Changning area and its' perphery, southern Sichuan[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [12] 范存辉, 李虎, 钟城, 等. 川东南丁山构造龙马溪组页岩构造裂缝期次及演化模式[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(4): 379-390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201804002.htmFan C H, Li H, Zhong C, et al. Tectonic fracture stages and evolution model of Longmaxi Formation shale, Dingshan structure, southeast Sichuan[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(4): 379-390(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201804002.htm [13] 高键, 何生, 何治亮, 等. 中扬子京山地区方解石脉成因及其对油气保存的指示意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(1): 33-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201401006.htmGao J, He S, He Z L, et al. Genesis of calcite vein and its implication to petroleum preservation in Jingshan region, Mid-Yangtze[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(1): 33-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201401006.htm [14] 刘力, 何生, 翟刚毅, 等. 黄陵背斜南翼牛蹄塘组二段页岩岩心裂缝脉体成岩环境演化与页岩气保存[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(11): 3583-3597. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911001.htmLiu L, He S, Zhao G Y, et al. Diagenetic environment evolution of fracture veins of the shale core in the second member of Niutitang Formation in southern limb of Huangling anticline and its connection with shale gas[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(11): 3583-3597(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201911001.htm [15] 李文. 涪陵与宜昌地区海相页岩裂缝脉体成因及流体包裹体古温压特征[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2018.Li W. Origins of fractured veins and characteristics of paleo-temperature and pressure of fluid inclusions in marine shales of Fuling and Yichang regions[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 王东. 川东南桑木场-酒店垭构造形成演化与多期流体充注[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009.Wang D. The evolution and multi-phase fluids injection of Sangmuchang-Jiudianya structure, southeast of Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 王勇, 施泽进, 彭俊, 等. 川东南地区石牛栏组碳、氧、锶同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2009, 28(4): 330-335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2009.04.003Wang Y, Shi Z J, Peng J, et al. The C, O, Sr isotope composition of Shiniulan Formation in southeast area of Sichuan and its geologic impolications[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2009, 28(4): 330-335(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2009.04.003 [18] 周大志. 川东南地区石牛栏组层序地层、沉积相及储层特征研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2010.Zhou D Z. Sequence stratigraphy, sedimentary facies and reservoir characteristics of Shiniulan Formation in southeast area of Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2010(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 肖开华, 李双建, 汪新伟, 等. 中、上扬子区志留系油气成藏特点与勘探前景[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(5): 589-596. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.05.007Xiao K H, Li S J, Wang X W, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation features and exploration direction in the Silurian of the Middle-Upper Yangtze Platform[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2008, 29(5): 589-596(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.05.007 [20] 李双建, 周雁, 肖开华, 等. 四川盆地东南缘习水吼滩志留系古油藏特征[J]. 石油学报, 2009, 30(6): 849-855. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.06.009Li S J, Zhou Y, Xiao K H, et al. Characteristics of Silurian destroyed oil reservoir in Houtan section of Xishui area in southeastern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2009, 30(6): 849-855(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2009.06.009 [21] 马文辛, 刘树根, 黄文明, 等. 四川盆地东南缘志留系古油藏特征及其油气勘探意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(3): 432-441. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201203015.htmMa W X, Liu S G, Huang W M, et al. Characteristics of Silurian paleo-oil reservoirs and their significance for petroleum exploration on the southeast margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(3): 432-441(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201203015.htm [22] 何顺, 秦启荣, 周吉羚, 等. 川东南DS地区龙马溪组页岩裂缝发育特征及期次解析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 101-109. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902012.htmHe S, Qin Q R, Zhou J L, et al. Shale fracture characteristics and its application of the Longmaxi Formation in DS area, Southeast Sichuan[J]. Geological Scinece and Technolody Information, 2019, 38(2): 101-109(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902012.htm [23] 胡东风, 张汉荣, 倪楷, 等. 四川盆地东南缘海相页岩气保存条件及其主控因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(6): 17-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406003.htmHu D F, Zhang H R, Ni K, et al. Main controlling factors for gas preservation conditions of marine shales in southeastern margins of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(6): 17-23(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201406003.htm [24] 朱梦月. 丁山地区五峰-龙马溪组构造特征与页岩气保存条件研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2018.Zhu M Y. Study on structural characteristics and shale gas preservation conditions of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation in Dingshan area[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] 唐永, 周立夫, 陈孔全, 等. 川东南构造应力场地质分析及构造变形成因机制讨论[J]. 地质论评, 2018, 64(1): 15-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201801004.htmTang Y, Zhou L F, Chen K Q, et al. Analysis of tectonic stress field of southeastern Sichuan and formation mechanism of tectonic deformation[J]. Geological Review, 2018, 64(1): 15-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201801004.htm [26] 黄为. 川东南丁山地区龙马溪组页岩气地质特征及有利目标优选[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2019.Huang W. Geological characteristics and favorable target selection of Longmaxi shale gas formation in Dingshan area, southeast Sichuan Basin[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [27] 贾小乐. 川东南构造几何学与运动学特征及其与雪峰山西段的构造关系探讨[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2016.Jia X L. Structural geometry and kinematics of southeast Sichuan Basin: Insights into tectonic relationship with the western segment of Xuefeng Mountain Orogenic Belt[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] 何顺, 秦启荣, 范存辉, 等. 川东南丁山地区页岩气保存条件分析[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(2): 24-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201902004.htmHe S, Qin Q R, Fan C H, et al. Shale gas preservation conditions in Dingshan area, southeastern Sichuan[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficience, 2019, 26(2): 24-31(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201902004.htm [29] 王瑞华, 谭钦银, 付建元, 等. 川东南志留系石牛栏组生物礁沉积特征[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2013, 33(2): 10-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2013.02.002Wang R H, Tan Q Y, Fu J Y, et al. Sedimentary characteristics of the Silurian organic reefs from the Shiniulan Formation in southeastern Sichuan[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2013, 33(2): 10-16(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2013.02.002 [30] 何利, 谭钦银, 王瑞华, 等. 川东南早志留世石牛栏期沉积相、沉积模式及其演化[J]. 矿物岩石, 2013, 33(4): 96-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2013.04.011He L, Tan Q Y, Wang R H, et al. Sedimentary facies, sedimentary model and evolution of the Shiniulan Formation of Early Silurian in the southeast Sichuan[J]. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 2013, 33(4): 96-106(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2013.04.011 [31] 袁玉松, 孙冬胜, 周雁, 等. 四川盆地川东南地区"源-盖"匹配关系研究[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(6): 831-838. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201006009.htmYuan Y S, Sun D S, Zhou Y, et al. Relationship between hydrocarbon generation history of source rocks and sealing history of mudstone cap-rocks in the southeast Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(6): 831-838(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201006009.htm [32] 李双建, 李建明, 周雁, 等. 四川盆地东南缘中新生代构造隆升的裂变径迹证据[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2011, 30(2): 225-233. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.02.007Li S J, Li J M, Zhou Y, et al. Fission track evidence for Mesozoic-Cenozoic uplifting in the southeastern margin of Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2011, 30(2): 225-233(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.02.007 [33] Bau M, Möller P. Rare earth element fractionation in metamorphogenic hydrothermal calcite, magnesite and siderite[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 1992, 45(3): 231-246. http://lib.gig.ac.cn/local/ejournal/MinePetr/MP1991/MP-1991-45(3-4)-231-246.pdf [34] Michael B. Rare-earth element mobility during hydrothermal and metamorphic fluid-rock interaction and the significance of the Oxidation State of Europium[J]. Chemical Geology, 1991, 93(3/4): 219-230. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009254191901158 [35] Lottermoser B G. Rare earth elements and hydrothermal ore formation processes[J]. Ore Geol. Rev., 1992, 7(1): 25-41. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(92)90017-F [36] 赵彦彦, 李三忠, 李达, 等. 碳酸盐(岩)的稀土元素特征及其古环境指示意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2019, 43(1): 141-167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901012.htmZhao Y Y, Li S Z, Li D, et al. Rare earth element geochemistry of carbonate and its paleoenvironmental implications[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2019, 43(1): 141-167(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DGYK201901012.htm [37] 林治家, 陈多福, 刘芊. 海相沉积氧化还原环境的地球化学识别指标[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(1): 72-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.01.012Lin Z J, Chen D F, Liu Q. Geochemical indices for redox conditions of marine sediments[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(1): 72-80(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.01.012 [38] 胡修棉, 王成善. 古海洋溶解氧研究方法综述[J]. 地球科学进展, 2001, 16(1): 65-71. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.01.013Hu X M, Wang C S. Summarization on the studying methods of the palaeo-ocean dissolved oxygen[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2001, 16(1): 65-71(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2001.01.013 [39] Sverjensky D A. Europium redox equilibria in aqueous solution[J]. Earth & Planetary Science Letters, 1984, 67(1): 70-78. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0012821X84900396 [40] Thieu V, Subramanian S, Colgate S O, et al. High-pressure optical cell for hydrate measurements using raman spectroscopy[J]. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 2000, 912(1): 983-992. [41] Liu W, Chou I M, Burruss R C, et al. A unified equation for calculating methane vapor pressures in the CH4-H2O system with measured Raman shifts[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2007, 71(16): 3969-3978. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2007.06.004 [42] Zhang J, Qiao S, Lu W, et al. An equation for determining methane densities in fluid inclusions with Raman shifts[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 171: 20-28. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.12.003 [43] Duan Z, Mølleri N, Weare J H. An equation of state for the CH4-CO2-H2O system: I. Pure systems from 0-1000℃ and 0 to 8000 bar[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1992, 56(7): 2605-2617. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(92)90347-L -





 下载:
下载: