Vertical heterogeneity and the main controlling factors of the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in the Middle Yangtze region
-
摘要:
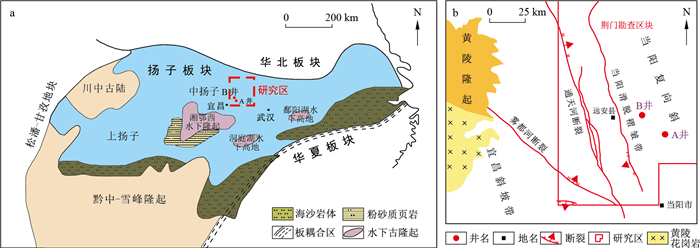
中扬子地区上奥陶统-下志留统五峰组-龙马溪组页岩在纵向上具有较强的非均质性, 影响着页岩储层含气性以及后期的可压裂性。本研究综合测井曲线、钻井岩心、薄片观察、有机碳测试、X衍射矿物测试以及主微量元素测试, 在建立研究区页岩等时地层层序格架的基础上, 剖析该套页岩在有机质丰度、矿物组分、页岩岩相等方面的非均质性特征, 结合恢复的古气候和古环境信息, 揭示控制非均质性的主控因素。研究结果表明: 五峰组-龙马溪组一段页岩识别出2个三级层序, 其中五峰组划分出海侵体系域(TST1)和高位体系域(HST), 龙马溪组一段划分出海侵体系域(TST2)和早期高位体系域(EHST)。海侵期页岩硅质含量高, 黏土含量较低, 有机碳含量高, 主要发育硅质页岩相和含黏土硅质页岩相; 早期高位域期, 页岩发育粉砂质条带和透镜状层理, 黏土含量较高, 有机碳含量较低, 主要发育含硅黏土质页岩相。古气候指标(CIA、Rb/Sr)、古生产力指标(Cu/Al、P/Al)、氧化还原条件指标(MoEF、UEF)以及陆源输入(Ti)指标在垂向上的变化表明研究区在海侵期具有较高古生产力, 缺氧的沉积环境、低陆源输入以及相对干燥寒冷的气候条件, 而高位体系域期, 研究区表现为古生产力较低、弱还原-氧化的沉积环境、高陆源输入以及相对温暖潮湿的气候条件。火山活动、底流作用、古气候、古生产力、氧化还原条件以及陆源输入是研究区五峰组-龙马溪一段页岩纵向非均质性的主控因素。最后通过与上扬子地区页岩层段参数对比, 发现研究区主要具有埋藏深度较深、富机质页岩层段明显偏薄、含气量偏低, 脆性矿物含量偏多等特征。
Abstract:The Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in the Middle Yangtze area have strong vertical heterogeneity, affecting the gas-bearing capacity of shale reservoirs and the fracturing ability.This study integrates wire-line logs, drilling cores, thin section observations, total organic carbon content, X-ray diffraction mineralogy measurement, and major, trace elements measurement.Under the stratigraphic sequence framework in the study area, the vertical variation of TOC content, mineralogical composition and shale lithofacies were studied.Combined with geochemical proxies for paleoclimate and paleoenvironmental conditions, the main factors controlling vertical heterogeneity were discussed.The results show that the Wufeng-Longmaxi shales have two 3rd-order sequences.The Wufeng Formation is divided into the transgressive systems tract(TST1) and high stand systems tract(HST), and the Longmaxi Formation is divided into the transgressive systems tract(TST2) and the early high stand systems tract(EHST).During the transgression period, the shale has high silica content, low clay content, and high organic carbon content, and mainly developed siliceous shale facies and clay-bearing siliceous shale facies.In the early high-stand systems tract period, shale developed silty bands and lenticular bedding, with high clay content, and low organic carbon content, and mainly developed siliceous-clay mixed shale lithofacies.The vertical changes of paleoclimate indicators(CIA, Rb/Sr), paleo-productivity indicators(Cu/Al, P/Al), redox environmental indicators(MoEF, UEF), and terrestrial input(Ti, Zr) indicators indicate a high productivity, anoxic sedimentary environment, low terrestrial input and relatively dry and cold climate conditions for the transgression period, while during the high-stand systems tract deposition, the study area has low productivity, oxic-dysoxic environment, high terrestrial input and relatively warm and humid climateconditions.The paleo climate, paleo productivity, redox conditions, volcanic activity, terrestrial input and bottom currents are the main factors controlling the stratigraphic heterogeneity of the Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in the study area.Finally, by comparing with some parameters of the shale in the Upper Yangtze region, it is found that the study area shows the differences in deeper burial depth, thinner organic shale, lower gas content and more brittle mineral content.
-
图 4 中扬子荆门地区内A井(a)、B井(b)和上扬子涪陵页岩气田(c)(据文献[28])页岩矿物组成三端元图解
硅质页岩相组合:S.硅质页岩相,S-1.含灰硅质页岩相,S-2.混合硅质页岩相,S-3.含黏土硅质页岩相;灰质页岩相组合:C.灰质页页岩相,C-1.含硅灰质页岩相,C-2.混合灰质页岩相,C-3.含黏土灰质页岩相;黏土质页岩相组合:CM.黏土质岩相,CM-1.含硅黏土质页岩相,CM-2.混合黏土质页岩相,CM-3.含灰黏土质页岩相;混合质页岩相组合:M.混合质页岩相,M-1.含灰/硅混合质页岩相,M-2.含黏土/硅混合质页岩相,M-3.含黏土/灰混合质页岩相
Figure 4. Ternary diagram showing the mineralogy compositions in Wells A and B in Jingmen area of the Middle Yangtze, and the Fuling shale gas field in the Upper Yangtze(a)
图 6 中扬子荆门地区上奥陶-下志留统五峰组-龙马溪组页岩岩心及薄片透射光照片
a.含硅黏土质页岩相,B井,见黑色泥岩和灰色粉砂质条带(黄色箭头)互层发育;b.见粉砂质条带(黄色箭头),B井;c.含硅黏土质页岩相,A井,见透镜状粉砂岩;d.含硅黏土质页岩相,B井,石英颗粒较多,水平层理和低角度交错层理(黄色实线);e.含硅黏土质页岩相,B井,见粉砂质条带,递变层理;f.含硅黏土质页岩相,见粉砂质条带(黄色箭头)和透镜状的黏土矿物(黄色虚线),B井,细小的粉砂状石英分散在富含黏土的基质中
Figure 6. Core photographs and thin-section images of Wufeng-Longmaxi shales in Jingmen area, Middle Yangtze Platform
图 8 中扬子荆门地区A井(a)、B井(b)五峰组-龙马溪组页岩的TOC质量浓度、古生产力指标(Cu/Al、P/Al)、氧化还原指标(UEF、MoEF)、陆源输入指标(Ti、Zr)以及古气候(CIA、Rb/Sr)的垂向变化特征
Figure 8. Vertical variation characteristics of TOC content, paleoproductivity proxies(Cu/Al, P/Al), redox proxies(UEF, MoEF), terrestrial input proxies(Ti) and paleoclimate proxies(CIA, Rb/Sr) of Wufeng-Longmaxi shales of Well A in Jingmen area, Middle Yangtze Platform
表 1 中扬子荆门地区和上扬子涪陵页岩气田和长宁-威远页岩示范区地质参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of geological parameters in Jingmen area, Fuling shale gas field and Changning-Weiyuan shale demonstration area of Middle Yangtze and Upper Yangtze regions
对比参数 荆门地区 涪陵页岩气田 长宁-威远页岩示范区 产层 五峰组-龙马溪组底部 五峰组-龙马溪组底部 五峰组-龙马溪组底部 埋藏深度/m 3 600~3 900 2 400~3 500 2 300~3 400 岩性特征 黑色硅质页岩、深灰色页岩和粉砂质页岩 炭质笔石页岩、粉砂质页岩 灰黑色粉砂质页岩 富有机质层段厚度/m 18~20 36~45 32~48 沉积特征 深水陆棚相 深水陆棚相 深水陆棚相 有机碳质量浓度[(最小值~ 最大值)/平均值]/% (1.78~4.53)/3.2 (1.5~6.1)/3.8 (1.9~7.3)/4.0 含气量[(最小值~ 最大值)/平均值]/(m3·t-1) (1.2~5.8)/3.5 (4.0~7.7)/6.1 (1.7~6.5)/4.1 岩相类型 硅质页岩相、含黏土硅质页岩相和含硅黏土质页岩相 含黏土硅质页岩相、含黏土/硅混合质页岩相和含硅黏土质页岩相 含黏土硅质页岩相、黏土质页岩相 注:表格数据来自于参考文献[25, 44-47] -
[1] 董大忠, 王玉满, 李新景, 等. 中国页岩气勘探开发新突破及发展前景思考[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(1): 19-32. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201601005.htmDong D Z, Wang Y M, Li X J, et al. Breakthrough and prospect of shale gas exploration and development in China[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(1): 19-32(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201601005.htm [2] 张福, 黄艺, 蓝宝锋, 等. 正安地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩储层特征及控制因素[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 49-56. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0016Zhang F, Huang Y, Lan B F, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of shale reservoir in Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation of the Zheng'an area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 49-56(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0016 [3] 陈孝红, 张保民, 张国涛, 等. 湖北宜昌地区奥陶系五峰组—志留系龙马溪组获页岩气高产工业气流[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(1): 199-200. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201801021.htmChen X H, Zhang B M, Zhang G T, et al. High shale gas industry flow obtained from the Ordovician Wufeng Formation and the Silurian Longmaxi Formation of Yichang area, Hubei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(1): 199-200(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201801021.htm [4] 卢双舫, 薛海涛, 王民, 等. 页岩油评价中的若干关键问题及研究趋势[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(10): 1309-1322. doi: 10.7623/syxb201610012Lu S F, Xue H T, Wang M, et al. Several key issues and research trends in evaluation of shale oil[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(10): 1309-1322(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201610012 [5] Zhang L, Li B, Jiang S, et al. Heterogeneity characterization of the lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in the Pengshui area, South China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2018, 195: 250-266. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2018.05.015 [6] 陈尚斌, 秦勇, 王阳, 等. 中上扬子区海相页岩气储层孔隙结构非均质性特征[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2015, 26(8): 1455-1463. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201508004.htmChen S B, Qin Y, Wang Y, et al. Pore structure and heterogeneity of marine shales in the Middle-Upper Yangtze[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2015, 26(8): 1455-1463(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201508004.htm [7] 孟志勇. 四川盆地涪陵地区五峰组-龙马溪组含气页岩段纵向非均质性及其发育主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6): 838-846. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201606007.htmMeng Z Y. Vertical heterogeneity and its controlling factors of the gas shale in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Fms in Fuling area, the Sichuan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(6): 838-846(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201606007.htm [8] Tang X, Jiang S, Jiang Z, et al. Heterogeneity of Paleozoic Wufeng-Longmaxi Formation shale and its effects on the shale gas accumulation in the Upper Yangtze Region, China[J]. Fuel, 2019, 239: 387-402. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.11.022 [9] 解经宇, 陆洪智, 陈磊, 等. 龙马溪组层状页岩微观非均质性及力学各向异性特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 67-77. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0302Xie J Y, Lu H Z, Chen L, et al. Micro scopic heterogeneity and mechanical anisotropy of the laminated shale in Longmaxi Formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 67-77(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0302 [10] Xiong F, Jiang Z, Tang X, et al. Characteristics and origin of the heterogeneity of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in southeastern Chongqing, SW China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2015, 27: 1389-1399. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.10.003 [11] Chen L, Lu Y, Jiang S, et al. Heterogeneity of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in the southeast Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2015, 65: 232-246. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2015.04.003 [12] 李玉喜, 何建华, 尹帅, 等. 页岩油气储层纵向多重非均质性及其对开发的影响[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 118-125. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602014.htmLi Y X, He J H, Yin S, et al. The multi-anisotropy of shale oil and gas reservoirs in vertical and its influence on oil-gas development[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2): 118-125(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602014.htm [13] 赵迪斐, 郭英海, 刘静, 等. 页岩储层非均质性地质理论的研究现状、进展与方向评述[J]. 非常规油气, 2020, 7(6): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2020.06.001Zhao D F, Guo Y H, Liu J, et al. Review on the current situation, progress and direction of the research on the geological theory of shale reservoir heterogeneity[J]. Unconventional Oil & Gas, 2020, 7(6): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-8471.2020.06.001 [14] Xu C, Jia Y R, Yue L, et al. Facies patterns and geography of the Yangtze region, South China, through the Ordovician and Silurian transition[J]. Paleogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Paleoecology, 2004, 204(3/4): 353-372. [15] 张君峰, 许浩, 周志, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区页岩气成藏地质特征[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(8): 887-899. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201908001.htmZhang J F, Xu H, Zhou Z, et al. Geological characteristics of shale gas reservoir in Yichang area, western Hubei[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(8): 887-899(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201908001.htm [16] 刘安, 陈孝红, 李培军, 等. 宜昌天阳坪断裂两侧页岩气保存条件对比研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 10-19. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0202Liu A, Chen X H, Li P J, et al. A comparative study of shale gas preservation conditions on both sides of Tianyangping fault in Yichang area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 10-19(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0202 [17] 张保民, 陈孝红, 蔡全升, 等. 鄂西宜昌斜坡带五峰组-龙马溪组含气页岩优势岩相[J]. 中国地质: 1-14[2022-05-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200420.1126.002.html.Zhang B M, Chen X H, Cai Q S, et al. Advantageous gas shale lithofacies of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in Yichang slope field of Western Hubei Province, China[J]. Geology in China: 1-14[2022-05-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.1167.P.20200420.1126.002.html [18] 陈林, 陈孝红, 张保民, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩储层特征及其脆性评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 54-61. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0206Chen L, Chen X H, Zhang B M, et al. Reservoir characteristics and brittleness evaluation of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation shale in Yichang area, Western Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 54-61(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0206 [19] 蔡全升, 陈孝红, 王传尚, 等. 上奥陶统五峰组-下志留统龙马溪组黑色岩系笔石赋存特征与堆积模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 43-53. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0205Cai Q S, Chen X H, Wang C S, et al. Occurrence characteristics and depositional model of graptolites from the black shale in the Upper Ordovician Wufeng Formation and Lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 43-53(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0205 [20] 陆扬博, 马义权, 王雨轩, 等. 上扬子地区五峰组-龙马溪组主要地质事件及岩相沉积响应[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1169-1184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707012.htmLu Y B, Ma Y Q, Wang Y X, et al. The sedimentary response to the major geological events and lithofacies characteristics of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in the Upper Yangtze Area[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1169-1184(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707012.htm [21] Wu L, Lu Y, Jiang S, et al. Relationship between the origin of organic-rich shale and geological events of the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian in the Upper Yangtze area[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102: 74-85. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.11.017 [22] 陈孔全, 李君军, 唐协华, 等. 中扬子地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气成藏关键地质因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(6): 18-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202006002.htmChen K Q, Li J J, Tang X H, et al. Key geological factors for shale gas accumulation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Fms in the central Yangtze area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(6): 18-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202006002.htm [23] 邹辰, 周松源, 梅珏, 等. 湖北当阳复向斜北部页岩气地质评价与有利区优选[J]. 海相油气地质, 2016, 21(2): 22-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2016.02.003Zou C, Zhou S Y, Mei Y, et al. Geological evaluation of upper ordovician-lower silurian gas-bearing shales and optional potential areas in the North of Dangyang Synclinorium, Hubei[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2016, 21(2): 22-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2016.02.003 [24] 陈孔全, 李君军, 唐协华, 等. 中扬子地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气成藏关键地质因素[J]. 天然气工业, 2020, 40(6): 18-30. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202006002.htmChen K Q, Li J J, Tang X H, et al. Key geological factors for shale gas accumulation in the Wufeng-Longmaxi Fms in the central Yangtze area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2020, 40(6): 18-30(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG202006002.htm [25] 蔡全升, 陈孝红, 张国涛, 等. 鄂西宜昌地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩气储层发育特征与勘探潜力[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2021(1): 1-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101011.htmCai Q S, Chen X H, Zhang G T, et al. Characteristics and exploration potential of the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale gas reservoirs of Lower Paleozoic in Yichang area, western Hubei Province, China[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2021(1): 1-20(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT202101011.htm [26] 罗胜元, 陈孝红, 岳勇, 等. 中扬子宜昌地区沉积-构造演化与寒武系页岩气富集规律[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2020, 31(8): 1052-1068. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202008002.htmLuo S Y, Chen X H, Yue Y, et al. Analysis of sedimentary tectonic evolution characteristics and shale gas enrichment in Yichang area, Middle Yangtze[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2020, 31(8): 1052-1068(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX202008002.htm [27] 苏文博, 李志明, 史晓颖, 等. 华南五峰组-龙马溪组与华北下马岭组的钾质斑脱岩及黑色岩系: 两个地史转折期板块构造运动的沉积响应[J]. 地学前缘, 2006, 13(3): 82-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606013.htmSu W B, Li Z M, Shi X Y, et al. K-bentonites and black shales from the Wufeng-Longmaxi formations(Early Paleozoic, South China) and Xiamaling formation(Early Neoproterozoic, North China): Implications for tectonic processes during two important transitions[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2006, 13(3): 82-95(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200606013.htm [28] 吴蓝宇, 胡东风, 陆永潮, 等. 四川盆地涪陵气田五峰组-龙马溪组页岩优势岩相[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(2): 189-197. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602005.htmWu L Y, Hu D F, Lu Y C, et al. Advantageous shale lithofacies of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation in Fuling gas field of Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2016, 43(2): 189-197(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201602005.htm [29] Ma Y, Fan M, Lu Y, et al. Geochemistry and sedimentology of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi mudstone in southwestern China: Implications for depositional controls on organic matter accumulation[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 75: 291-309. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.04.024 [30] Liu Y, Wu B, Gong Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics of the lower Silurian Longmaxi Formation on the Yangtze Platform, South China: Implications for depositional environment and accumulation of organic matters[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 184: 104003. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2019.104003 [31] Chen C, Mu C, Zhou K, et al. The geochemical characteristics and factors controlling the organic matter accumulation of the Late Ordovician-Early Silurian black shale in the Upper Yangtze Basin, South China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 76: 159-175. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.04.022 [32] 冯连君, 储雪蕾, 张启锐, 等. 化学蚀变指数(CIA)及其在新元古代碎屑岩中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2003(4): 539-544. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.019Feng L J, Chu X L, Zhang Q R, et al. CIA(Chemical Index of Alteration) and its applications in the Neoproterozoic clastic rocks[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003(4): 539-544(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2003.04.019 [33] Chen L, Jiang S, Chen P, et al. Relative sea-level changes and organic matter enrichment in the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Central Yangtze area, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 124: 104809. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2020.104809 [34] Liu S, Shi X, Liu Y, et al. Holocene paleoclimatic reconstruction based on mud deposits on the inner shelf of the East China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 69: 113-120. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.01.003 [35] 李艳芳, 邵德勇, 吕海刚, 等. 四川盆地五峰组-龙马溪组海相页岩元素地球化学特征与有机质富集的关系[J]. 石油学报, 2015, 36(12): 1470-1483. doi: 10.7623/syxb201512002Li Y F, Shao De Y, Lü H G, et al. A relationship between elemental geochemical characteristics and organic matter enrichment in marine shale of Wufeng Formation-Longmaxi Formation, Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2015, 36(12): 1470-1483(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201512002 [36] 何龙, 王云鹏, 陈多福, 等. 重庆南川地区五峰组-龙马溪组黑色页岩沉积环境与有机质富集关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2019, 30(2): 203-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201902005.htmHe L, Wang Y P, Chen D F, et al. Relationship between sedimentary environment and organic matter accumulation in the black shale of Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in Nanchuan area, Chongqing[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2019, 30(2): 203-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201902005.htm [37] 郭旭升. 上扬子地区五峰组-龙马溪组页岩层序地层及演化模式[J]. 地球科学, 2017, 42(7): 1069-1082. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707003.htmGuo X S. Sequence stratigraphy and evolution model of the Wufeng-Longmaxi shale in the Upper Yangtze Area[J]. Earth Science, 2017, 42(7): 1069-1082(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201707003.htm [38] Chen L, Jiang S, Chen P, et al. Relative sea-level changes and organic matter enrichment in the Upper Ordovician-Lower Silurian Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the Central Yangtze area, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020: 104809. [39] 何庆, 高键, 董田, 等. 鄂西地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积古环境恢复[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(3): 686-703. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202103014.htmHe Q, Gan J, Dong T, et al. Elemental geochemistry and paleo-environmental conditions of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang shale in western Hubei Province[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(3): 686-703(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202103014.htm [40] 韦恒叶. 古海洋生产力与氧化还原指标: 元素地球化学综述[J]. 沉积与特提斯地质, 2012, 32(2): 76-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2012.02.012Wei H Y. Productivity and redox proxies of palaeo-oceans: An overview of elementary geochemistry[J]. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 2012, 32(2): 76-88(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2012.02.012 [41] Xi Z, Tang S. Geochemical characteristics and organic matter accumulation of Late Ordovician shale in the Upper Yangtze Platform, South China[J]. Energy Reports, 2021, 7: 667-682. doi: 10.1016/j.egyr.2021.01.029 [42] Daniel J K R, R M B. Investigating the use of sedimentary geochemical proxies for paleoenvironment interpretation of thermally mature organic-rich strata: Examples from the Devonianâ Mississippian shales, Western Canadian Sedimentary Basin[J]. Chemical Geology, 2009, 260(1/2): 1-9. [43] Shanmugam G. 等深流沉积: 物理海洋学、过程沉积学和石油地质学[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2017, 44(2): 177-195. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201702003.htmShanmugam G. Contourites: Physical oceanography, process sedimentology, and petroleum geology[j]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(2): 177-195(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201702003.htm [44] 李艳芳. 上扬子地区晚奥陶世-早志留世页岩地球化学特征、有机质富集及古环境意义[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2017.Li Y F. Geochemical characteristics and organic matter accumulation of Late Ordovician-Early Silurian shale in the upper Ynagtze Platform, and implications for paleoenvironment[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [45] Calvert S E, Pedersen T F. Chapter fourteen elemental proxies for paleoclimatic and palaeoceanographic variability in marine sediments: Interpretation and application[M]. Elsevier Science & Technology, 2007, 1(14): 567-644. [46] Wei C, Dong T, He Z, et al. Major, trace-elemental and sedimentological characterization of the upper Ordovician Wufeng-lower Silurian Longmaxi formations, Sichuan Basin, south China: Insights into the effect of relative sea-level fluctuations on organic matter accumulation in shales[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2021, 126: 104905. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2021.104905 [47] 昝博文, 刘树根, 白志强, 等. 川西南威远地区龙马溪组页岩储层孔隙发育特征及控制因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2): 65-74. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201702008.htmZan B W, Liu S G, Bai Z Q, et al. Pore characteristics of shale gas reservoir of Longmaxi Formation in Weiyuan Area, soutjwest of Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(2): 65-74(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201702008.htm [48] 张靖宇, 陆永潮, 付孝悦, 等. 四川盆地涪陵地区五峰组-龙马溪组一段层序格架与沉积演化[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 65-72. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704009.htmZhang J Y, Lu Y C, Fu X Y, et al. Sequence stratigraphic framework and sedimentary evolution of Wufeng Formation -the 1st Member of Longmaxi Formation in Fuling Area, Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(4): 65-72(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704009.htm [49] 蒋裕强, 宋益滔, 漆麟, 等. 中国海相页岩岩相精细划分及测井预测: 以四川盆地南部威远地区龙马溪组为例[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(1): 107-118. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601012.htmJiang Y Q, Song Y T, Qi L, et al. Fine lithofacies of China's marine shale and its logging prediction: A case study of the Lower Silurian Longmaxi marine shale in Weiyuan area, southern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(1): 107-118(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201601012.htm [50] 王玉满, 黄金亮, 王淑芳, 等. 四川盆地长宁、焦石坝志留系龙马溪组页岩气刻度区精细解剖[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2016, 27(3): 423-432. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603006.htmWang Y M, Huang J L, Wang S F, et al. Dissection of two calibrated areas of the Silurian Longmaxi Formation, Changning and Jiaoshiba, Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2016, 27(3): 423-432(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201603006.htm -





 下载:
下载: