Evolution law of groundwater system with multiple seams mining in Nanliang Coal Mine
-
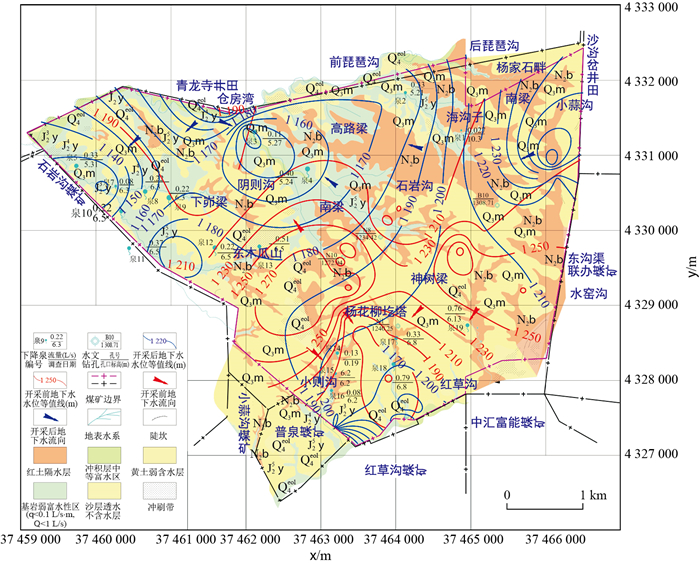
摘要: 煤层开采对所在矿区地下水系统有着重要影响。以往研究单煤层开采对地下水系统的影响较多,而对多煤层的影响研究甚少,特别对于我国西部缺水矿区。以南梁煤矿为例,运用地下水系统演化理论和岩石力学模拟等,对该矿井水文地质结构、矿井涌水变化规律、矿井地下水流场演变、矿井地下水化学成分变化等方面进行了综合分析研究,重构了多煤层开采条件下南梁矿井地下水系统流动模型,初步揭示了矿井水化学成分的演化机理。研究结果表明,2-2煤单煤层开采时,顶板导裂带的最大发育高度为42.1 m,而2-2和3-1煤层重复开采时则增大为83.1 m,相应地应力、位移、塑性区范围后者也比前者增大许多。这揭示出多煤层重复采动明显增大了顶板导裂带的发育高度,加剧了矿井水文地质结构变异,进一步地,导水裂隙带改变了天然地下水渗流路径,沟通了不同含水层之间的水力联系,增强了地下水流动速度和水文地球化学作用,整体扩大了地下水流动系统的规模,从降雨入渗→导裂带渗流→各煤层涌水→井底水仓排水构成了一个自然-人工复合地下水流动模式。研究成果可以为南梁煤矿的矿井水害防治及水资源高效利用提供科学依据,也为类似矿区提供研究参考。Abstract: Coal mining has an important impact on the groundwater system in the mining area.In the past, more research was distributed on the impact of single coal seam mining on the groundwater system, while the impact on multiple coal seams was rarely studied, especially for water-deficient mining areas in western China.Taking Nanliang Coal Mine as an example, groundwater system evolution theory and physical mechanics simulation method, etc.were used to study the mine hydrogeological structure, mine water inrush change law, mine groundwater flow field evolution, mine groundwater chemical composition change, etc., the groundwater flow system model of Nanliang Coal Mine was reconstructed under the condition of multi-coal mining, and the evolution mechanism of the chemical composition of mine water was initially revealed.The research results showed that when the 2-2 coal seam was mined, the maximum development height of the roof cracking zone was 42.1 m, while when the 2-2 and 3-1 coal seams were repeatedly mined, it increased to 83.1 m.The corresponding stress, displacement, and plastic zone range of the latter was also much larger than the former.This revealed that the repeated mining of multiple coal seams significantly increased the development height of the roof cracking zone, aggravated the variation of the mine's hydrogeological structure, and further, the water-conducting fracture zone changed the natural groundwater seepage paths and communicated the hydraulic connection between different aquifers.As a result, the groundwater flow rate and hydrogeochemical effects were enhanced, and the scale of the groundwater flow system was expanded as a whole, so a natural-artificial composite groundwater flow pattern from rainfall infiltration→seepage in the fracturing zone→water inrush from each coal seam→drainage from the bottom sump was formed.The research can provide a scientific basis for the prevention and control of mine water hazards and the efficient use of water resources in Nanliang Coal Mine, as well as a reference for similar mining areas.
-
表 1 模型岩石物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of rock in numerical simulation model
组号 岩性 厚度/m 累计厚度/m 容重/(kg·m-3) 抗拉强度/MPa 体积模量/MPa 泊松比 内摩擦角/(°) 内聚力/MPa 1 表土 10.00 10.00 1 800 0.80 1 111 0.26 16.00 2.10 2 黏土 10.00 20.00 1 800 0.80 3 111 0.26 36.00 3.10 3 中粗砂岩 28.00 48.00 2 290 5.54 9 980 0.26 44.90 3.52 4 细砂岩 13.80 61.80 2 430 5.04 14 277 0.20 42.40 3.39 5 中粒砂岩 16.00 77.80 2 330 0.90 3 070 0.21 43.30 2.80 6 2-2煤 2.20 80.00 1 350 0.60 1 890 0.29 32.90 1.30 7 粉砂岩 11.00 91.00 2 420 0.83 8 750 0.38 29.10 4.10 8 细砂岩 16.00 107.00 2 430 0.80 5 339 0.20 42.40 3.39 9 砂质泥岩 13.00 120.00 2 410 0.78 3 320 0.11 36.40 1.08 10 3-1煤 2.10 124.10 1 350 0.60 1 890 0.29 32.90 1.30 11 粉砂岩 19.58 143.60 2 420 0.83 5 750 0.38 29.10 6.10 12 中砂岩 26.32 170.00 2 330 1.04 2 066 0.21 43.30 5.80 -
[1] 彭苏萍, 毕银丽. 黄河流域煤矿区生态环境修复关键技术与战略思考[J]. 煤炭学报, 2020, 45(4): 1211-1221. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202004002.htmPeng S, Bi Y L. Strategic consideration and core technology about environmental ecological restoration in coal mine areas in the Yellow River basin of China[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2020, 45(4): 1211-1221(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB202004002.htm [2] Zhang J, Wang X S, Yin L H, et al. Inflection points on groundwater age and geochemical profiles along wellbores light up hierarchically nested flow systems[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2021, 48(16): 1-10. [3] Xu J, Ling H B, Zhang G P, et al. Variations in the dissolved carbon concentrations of the shallow groundwater in a desert inland river basin[J/OL]. (2021-11-01) 10.1016/J. J Hydrol. 2021.126774. [4] 张人权, 梁杏, 靳孟贵. 末次盛冰期以来河北平原第四系地下水流系统的演变[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(3): 217-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303026.htmZhang R Q, Liang X, Jin M G. Evolution of quaternary groundwater flow system in Hebei Plain since the Last Glacial Maximum[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(3): 217-226 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201303026.htm [5] 梁杏, 张人权, 牛宏, 等. 地下水流系统理论与研究方法的发展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5): 143-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205020.htmLiang X, Zhang R Q, Niu H, et al. Development of groundwater flow system theory and research methods[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(5): 143-151(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201205020.htm [6] 梁杏, 张婧玮, 蓝坤, 等. 江汉平原地下水化学特征及水流系统分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 21-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103Liang X, Zhang J W, Lan K, et al. Analysis of groundwater chemical characteristics and flow system in Jianghan Plain[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 21-33(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0103 [7] 程大伟, 詹红兵, 李洁, 等. 分层沉积物河流-地下水系统水力连通演化[J/OL]. 水科学进展(2020-9-29). http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1309.p.20210928.1541.005.html.Cheng D W, Zhan H B, Li J, et al. Hydraulic connectivity evolution of stratified sediment river groundwater system[J/OL]. Advances in Water Science, (2020-9-29) http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/32.1309.p.20210928.1541.005.html. (in Chinese with English abstract). [8] 叶慧君, 张瑞雪, 吴攀, 等. 六盘水矿区关键带岩溶水水化学演化特征及驱动因子[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(9): 2887-2898. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201909007.htmYe H J, Zhang R X, Wu P, et al. Hydrochemical evolution characteristics and driving factors of karst water in key zones of Liupanshui mining area[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(9): 2887-2898(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201909007.htm [9] 孙厚云, 毛启贵, 卫晓锋, 等. 哈密盆地地下水系统水化学特征及形成演化[J]. 中国地质, 2018, 45(6): 1128-1141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201806005.htmSun H Y, Mao Q G, Wei X F, et al. Hydrochemical characteristics and formation evolution of groundwater system in Hami Basin[J]. Geology in China, 2018, 45(6): 1128-1141(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201806005.htm [10] Rajput S, Singh M K. Off-diagonal dispersion effect with pollutant migration in groundwater system[J/OL]. (2021-10-16)[2021-11-03] 10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0002009. [11] Chen S, Peng H Y, Yang C, et al. Investigation of the iMPacts of tunnel excavation on karst groundwater and dependent geo-environment using hydrological observation and numerical simulation: A case from karst anticline mountains of southeastern Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2021, 28(30): 40203-40216. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13919-1 [12] Yin Z Y, Luo Q K, Wu J F, et al. Identification of the long-term variations of groundwater and their governing factors based on hydrochemical and isotopic data in a river basin[J/OL]. (2020-10-22)[2021-11-03] 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.125604. [13] 王焰新, 甘义群, 邓娅敏, 等. 海岸带海陆交互作用过程及其生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 1-10 doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101Wang Y X, Gan Y Q, Deng Y M, et al. Land-ocean interaction and their eco-environmental effects in the coastal zone: Current progress and future perspectives[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 1-10(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0101 [14] Qu S, Shi Z M, Liang X Y, et al. Multiple factors control groundwater chemistry and quality of multi-layer groundwater system in Northwest China coalfield: Using self-organizing maps (SOM)[J/OL]. (2021-04-20)[2021-11-03] 10.1016/J.GEXPLO.2021.106795. [15] 李亚昊. 采动影响下浅-中部地下水系统研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽理工大学, 2020.Li Y H. Research on the shallow-central groundwater system under the influence of mining[D]. Hefei: Anhui University of Science and Technology, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 张翼龙. 呼和浩特盆地开采胁迫下的地下水系统响应及适应性对策研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2012.Zhang Y L. Aquifer system response and its adaptability countermeasures to exploitation in the Hohhot Basin[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 隋旺华, 王丹丹, 孙亚军, 等. 矿山水文地质结构及其采动响应[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(1): 21-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201901003.htmSui W H, Wang D D, Sun Y J, et al. Mine hydrogeological structure and its responses to mining[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 21-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201901003.htm [18] 代锋刚, 张发旺, 王滨, 等. 含水层结构变异对区域地下水循环影响数值模拟[J]. 地球学报, 2017, 38(增刊1): 64-68. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.s1.17Dai F G, Zhang F W, Wang B, et al. Numerical simulation of structural variation of aquifer effect on regional groundwater circulation[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2017, 38(S1): 64-68(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2017.s1.17 [19] 齐跃明, 李民族, 许进鹏. 复杂地质条件下的突水疏放试验及水文地质意义[J]. 采矿与安全工程学报, 2016, 33(1): 140-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSYL201601022.htmQi Y M, Li M Z, Xu J P. Draining test of mine water inrush under complex geological conditions and its hydrogeological significance[J]. Journal of Mining & Safety Engineering, 2016, 33(1): 140-145(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KSYL201601022.htm -





 下载:
下载: