Fine characterization of the reservoir space in deep ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability glutenite in Bozhong Sag
-
摘要: 利用自动矿物定量识别系统(QEMSCAN)、二维大尺寸背散射图像拼接技术(MAPS)、多尺度微米CT、铸体薄片、恒速压汞等实验技术,对渤中凹陷深层孔店组特低孔特低渗砂砾岩储层的储集空间进行了二维、三维多尺度精细表征,并系统研究了砂砾岩储层渗流能力影响因素。实验结果显示,研究区砂砾岩孔隙毫米-微米-纳米级多尺度连续分布,孔隙度相对大的储层,孔径分布范围较宽,储层粒间原生孔、粒间溶蚀孔等大孔隙占比较高,粒内溶蚀孔、晶间孔占比较低。基于三维孔喉网络模型,孔隙主要半径分布区间为1.5~60 μm,喉道半径分布在0.5~8.0 μm之间,孔喉连通性的分布形态有条带状、连片状、孤立状,储集性较好的储层孔喉在三维空间多为连片状,渗透率相对较差的储层孤立状的大孔较多。孔隙型储层的渗透率与孔喉形态、喉道半径、配位数等参数密切相关。裂缝明显改善了砂砾岩的物性,也为酸性流体对储层的溶蚀提供了有效通道,导致溶蚀孔隙相对发育。综合研究认为,渤中凹陷深层砂砾岩储层的渗流能力受裂缝发育程度、孔喉连通性双重控制,储层中黏土矿物和碳酸盐矿物胶结对孔隙结构、储层渗流能力有重要影响。Abstract: With the application of automatic mineral quantitative identification system (QEMSCAN), modular automated processing system (MPAS), multi-scale micro CT, thin section identification, constant-rate mercury injection and other experimental techniques, the reservoir space in deep ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability glutenite of Kongdian Formation in the Bozhong Sag were characterized in two and three dimensions, and the influencing factors of the permeability of glutenite reservoir were studied in detail. The experimental results show that the glutenite in the study area has millimeter, micron and nanometer pores. For the samples with relatively large porosity, there are relatively more interparticle pores and interparticle dissolution pores in the reservoir. On the basis of the three-dimensional pore-throat network model, the most part of the pore radius ranges from 0.3 to 10 μm and the roar channel radius mainly ranges from 0.5 to 8.0 μm. The pore-throat distribution is mainly three forms: banded, contiguous and isolated. The pore throats of reservoirs with good reservoir properties are mostly continuous in three-dimensional space, and the reservoirs with relatively poor permeability contain more isolated large pores. The fluid mobility of porous reservoir is closely related to throat radius, pore-throat shape, coordination number and other parameters. Fractures improve the physical properties of glutenite obviously, and also provide a channel for the acid solution to the reservoir and promotes the formation of dissolution pores. Comprehensive study showed that the fluid flow of the glutenite in the Bozhong Sag is controlled by the fracture and the pore-throat connectivity. The cementation of clay and carbonate minerals in the reservoir has an important influence on the pore structure and permeability.
-
图 3 渤中凹陷孔店组砂砾岩储层储集空间类型
a.裂缝,全直径岩心, BZ-A-7井,4 532.30~4 532.47 m;b.裂缝和粒间大孔,旋转壁心, BZ-A-3井,3 944.00 m;c.粒间原生孔,单偏光, BZ-A-1井,3 595.00 m;d.粒间溶蚀孔,单偏光, BZ-A-1井,3 685.00 m;e.粒内溶蚀孔,单偏光, BZ-A-10井,4 427.57 m;f.铁白云石晶间孔,扫描电镜, BZ-A-3井,3 815.10 m;g.粒内裂隙,单偏光, BZ-A-10井,4 427.57 m;h.构造碎裂缝,MAPS,分辨率250 nm, BZ-A-7井,4 532.43 m;i.高岭石晶间孔,MAPS,分辨率250 nm, BZ-A-3井,3 850.47 m;j.粒间溶蚀孔,微米CT二维切片, BZ-A-7井,4 532.43 m;k.粒内溶蚀孔,微米CT二维切片, BZ-A-3井,4 050.29 m
Figure 3. Pore types of glutenite reservoir in Kongdian Formation of Bozhong Sag
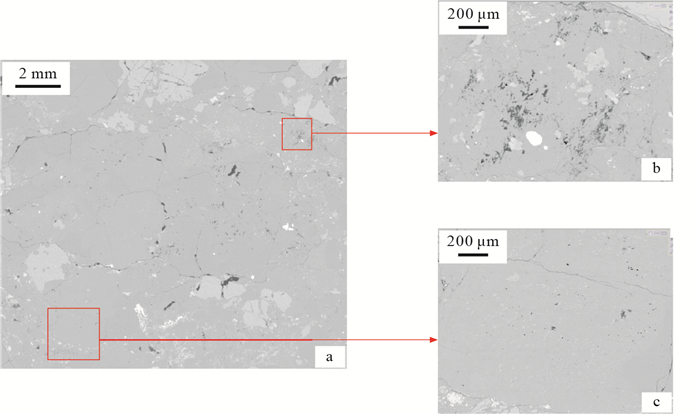
图 5 渤中凹陷孔店组砂砾岩数字岩心对比
a.孔隙连通性模型,A1号样品, BZ-A-7井,4 532.43 m;b.孔隙连通性模型,A2号样品, BZ-A-7井,4 537.30 m;c.孔隙连通性模型,A3号样品, BZ-A-3井,3 850.47 m;d.孔隙连通性模型,A4号样品, BZ-A-3井,4 050.29 m;e.三维孔喉网络模型(球为孔隙,管为喉道),A1号样品, BZ-A-7井,4 532.43 m;f.三维孔喉网络模型,A2号样品, BZ-A-7井,4 537.30 m;g.三维孔喉网络模型,A3号样品, BZ-A-3井,3 850.47 m;h.三维孔喉网络模型,A4号样品,BZ-A-3井,4 050.29 m
Figure 5. Micro-scale digital core model of glutenite in Kongdian Formation of Bozhong Sag
表 1 渤中凹陷BZ-A凝析气田孔店组砂砾岩数字岩心分析样品信息
Table 1. Digital core analysis of glutenite in Kongdian Formation of BZ-A condensate field, Bozhong Sag
样品编号 井号 取样深度/m 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10-3μm2) 岩性 储层类型 A1 BZ-A-7 4 532.43 8.00 19.44 砂质砾岩 裂缝-孔隙型 A2 BZ-A-7 4 537.30 5.50 0.73 砂质砾岩 孔隙型 A3 BZ-A-3 3 850.47 13.20 1.86 砂质砾岩 孔隙型 A4 BZ-A-3 4 050.29 12.70 0.52 砂质砾岩 孔隙型 表 2 不同表征方法识别BZ-A构造孔隙类型的主要孔径分布范围
Table 2. Different methods to identify the main pore diameter distribution range of pore type in BZ-A structure
孔隙类型 铸体薄片/μm 扫描电镜/μm MAPS/μm 微米CT/μm 粒间原生孔 30~1 000 5~1 000 10~1 000 20~1 000 粒间溶蚀孔 30~600 5~600 10~600 20~600 粒内溶蚀孔 30~200 0.5~200 1~200 10~200 晶间孔 20~50 0.5~50 1~50 5~50 表 3 基于QEMSCAN与MAPS叠加技术的孔隙类型面积百分比
Table 3. Pore type proportion based on QEMSCAN and MAPS superposition technology
样品编号 井号 取样深度/m 孔隙度/% 面孔率/% 裂缝占面孔率百分比/% 粒间孔百分比/% 晶间孔百分比/% 粒内溶孔百分比/% 粒内溶孔占总孔隙百分比/% 裂缝占总面孔率百分比/% A1 BZ-A-7 4 532.43 8.00 7.80 2.40 2.61 0.05 2.79 51.67 30.78 A2 BZ-A-7 4 537.30 5.50 5.12 0.44 1.97 0.70 2.71 57.91 8.59 A3 BZ-A-3 3 850.47 13.20 13.10 0.16 9.39 0.43 3.55 27.43 1.22 A4 BZ-A-3 4 050.29 12.70 12.40 0.20 9.26 1.56 2.94 24.10 1.61 表 4 渤中凹陷BZ-A凝析气田孔店组砂砾岩CT扫描孔喉参数统计
Table 4. Statistics of pore and throat structure parameters of CT scanning experiment samples of glutenite in Kongdian Formation of Bozhong Sag
样品编号 井号 孔隙度/% 渗透率/(10-3μm2) 平均孔隙半径/μm 平均孔隙体积/mm3 平均喉道半径/μm 平均喉道体积/mm3 平均配位数 死孔隙占比/% A1 BZ-A-7 8.00 19.44 47.56 0.33×10-3 6.46 4.34×10-7 2.53 87.45 A2 BZ-A-7 5.50 0.73 34.47 0.12×10-3 3.33 1.07×10-6 2.65 86.76 A3 BZ-A-3 13.20 1.86 80.56 1.62×10-3 13.40 1.56×10-5 3.83 88.89 A4 BZ-A-3 12.70 0.52 121.10 5.57×10-3 3.85 1.61×10-6 2.92 89.30 -
[1] Nelson P H.Pore-throat sizes in sandstones, tight sandstones, and shales[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(3):329-340. doi: 10.1306/10240808059 [2] 纪友亮.油气储层地质学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2015. [3] Zhang L, Lu S, Xiao D, et al.Pore structure characteristics of tight sandstones in the northern Songliao Basin, China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 88:170-180. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.08.005 [4] Andrä H, Combaret N, Dvorkin J, et al.Digital rock physics benchmarks, Part Ⅰ: Imaging and segmentation[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 2013, 50:25-32. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300412003147 [5] Mayo S, Josh M, Nesterests Y, et al.Quantitative micro-porosity characterization using synchrotron micro-CT and xenon K-edge subtraction in sandstones, carbonates, shales and coal[J]. Fuel, 2015, 154:167-173. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2015.03.046 [6] Loucks R G, Reed R M, Ruppel S C, et al.Morphology, genesis, and distribution of nanometer-scale pores in siliceous mudstones of the Mississippian Barnett Shale[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2009, 79(12):848-861. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2009.092 [7] Al-Kharusi A S, Blunt M J.Network extraction from sandstone and carbonate pore space images[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2007, 56(4): 219-231. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092041050600204X [8] Dewanckele J, Kock T D, Boone M A, et al.4D imaging and quantification of pore structure modifications inside natural building stones by means of high resolution X-ray CT[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2012, 416:436-448. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.11.018 [9] Tariq F, Haswell R, Lee P D, et al.Characterization of hierarchical pore structures in ceramics using multiscale tomography[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(5):2109-2120. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2010.12.012 [10] Sakdinawat A, Attwood D.Nanoscale X-ray imaging[J]. Nature Photonics, 2010, 4(12):840-848. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2010.267 [11] 李易霖, 张云峰, 尹淑丽, 等.致密砂岩储集空间多尺度表征:以松辽盆地齐家地区高台子油层为例[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(6):915-922. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95357X/201606/671030717.html [12] 李易霖, 张云峰, 丛琳, 等.X-CT扫描成像技术在致密砂岩微观孔隙结构表征中的应用:以大安油田扶余油层为例[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2016, 46(2):379-387. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-CCDZ201602007.htm [13] 赵丁丁, 孙卫, 杜堃, 等.特低-超低渗透砂岩储层微观水驱油特征及影响因素:以鄂尔多斯盆地马岭油田长81储层为例[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):163-170. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201903016.htm [14] 谢升洪, 李伟, 冷福, 等.致密砂岩储层可动流体赋存规律及制约因素研究:以鄂尔多斯盆地华庆油田长6段储层为例[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5):105-114. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201905011.htm [15] 刘春, 张荣虎, 张惠良, 等.致密砂岩储层微孔隙成因类型及地质意义:以库车前陆冲断带超深层储层为例[J].石油学报, 2017, 38(2):36-45. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SYXB201702003.htm [16] 林潼, 冉启贵, 魏红兴, 等.库车坳陷迪北地区致密砂岩孔喉形态特征及其对储层的影响[J].石油实验地质, 2015, 37(6):698-703. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201506004 [17] 朱伟林, 米立军, 龚再升, 等.渤海海域油气成藏与勘探[M].北京:科学出版社, 2009. [18] 魏刚, 杨海风, 冯冲, 等.渤海海域沙南凹陷沙二段储层成岩作用及其对储集层的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4):160-165. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201704020 [19] 王清斌, 牛成民, 刘晓健, 等.渤中凹陷深层砂砾岩气藏油气充注与储层致密化[J].天然气工业, 2019, 39(5):25-33. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201905003 [20] 李欢, 王清斌, 庞小军, 等.致密砂砾岩储层裂缝形成及储层评价:以黄河口凹陷沙二段为例[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1):182-191. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20191/68907581504849574849484957.html [21] Dong H, Blunt M J.Pore-network extraction from micro-computerized-tomography images[J]. Physical Review E, 2009, 80(3):036307. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.80.036307 [22] Dong H.Micor-CT imaging and pore network extraction[D]. London: Imperial College, 2007. -





 下载:
下载: