Grading evaluation of natural gas resources in the western sub-sag of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 东海西湖凹陷天然气资源丰富,呈现出常规、低渗和致密气并存的特点,但以往的资源评价仅预测总资源量,未区分常规、低渗和致密气资源量,不能满足油气勘探开发实践的需要。以西湖凹陷内油气勘探与发现程度相对较高的次级构造单元西次凹为研究对象,在合理求取各项参数的基础上,选用容积法对西次凹已发现气藏的常规、低渗及致密气资源分别进行了定量评价,并探究了资源分级分布规律及其主要控制因素。研究表明,西湖凹陷西次凹天然气资源丰富,总体呈现出"致密为主,少量低渗"及"中浅层低渗,中深层致密"的分级分布规律;资源分级分布受多种因素的联合控制,其中储层是基础,烃源是关键。研究成果有助于探索建立适用于西湖凹陷天然气资源分级评价的方法技术,并可为研究区天然气勘探开发部署与决策提供科学依据。Abstract: The discovery of abundant natural gas resources in Xihu Depression of East China Sea Shelf Basin revealed the characteristics of the coexistence of conventional, low-permeability and tight gas resources. However, the previous resource evaluation only predicted the total resources and did not distinguish among conventional, low-permeability and tight gas resources, thus failing to meet the needs of oil and gas exploration and development practices. This paper takes the western sub-sag as the study area, which is a secondary tectonic unit with relatively high oil and gas exploration and discovery in Xihu Depression. On the basis of reasonable selection of various parameters, the "volumetric method" is used to quantitatively evaluate the conventional, low-permeability and tight gas resources of the gas reservoirs discovered in the western sub-sag, and discusses the rules and the main controlling factors of the distribution and grading of natural gas resources. The research shows that the western sub-sag is rich in natural gas resources and the rules of "the tight gas content is the highest and contains a small amount of low-permeability" and "low-permeability gas is distributed in the middle and shallow layers when tight gas is distributed in the middle and deep layers". The distribution and grading of resources is controlled by a combination of factors, where the reservoir is the foundation and the source of hydrocarbons is the key. The research results will help to explore and establish the method and technology applicable to the grading evaluation of natural gas resources in Xihu Depression. It will provide scientific basis for natural gas exploration and development deployment and decision-making in the study area.
-
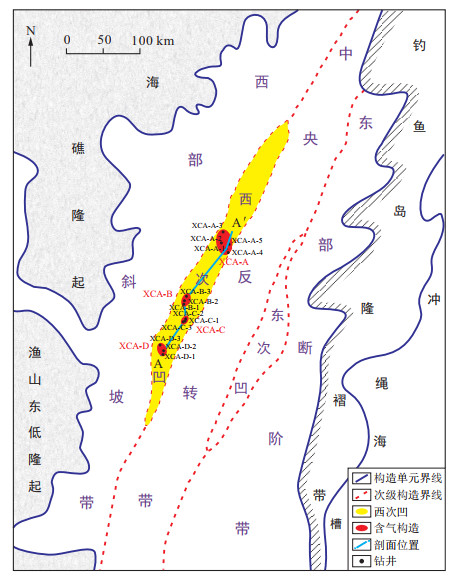
图 9 东海西湖凹陷西次凹天然气资源分级分布及成藏要素综合分析图(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 9. A comprehensive analysis chart of hydrocarbon accumulation elements and grading and distribution of gas resources in the western sub-depression of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
表 1 东海西湖凹陷花港组与平湖组储层分级评价标准
Table 1. Reservoir grading evaluation standard of Huagang and Pinghu formations in Xihu Depression of East China Sea Basin
级别 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ 渗透率/10-3μm2 ≥10 [1, 10) [0.1, 1) 孔隙度/% ≥15 [12, 15) [6.5, 12) 孔隙类型 大量溶蚀孔隙
大量原生孔隙大量溶蚀孔隙
一定原生孔隙少量溶蚀孔隙
少量原生孔隙岩石类型 长石岩屑质石英砂岩
岩屑砂岩长石岩屑质石英砂岩
长石质岩
屑砂岩长石岩屑质石英砂岩
岩屑质长石砂岩
岩屑砂岩
岩屑石英砂岩储层分级 常规 低渗 致密 -
[1] 金之钧, 张金川.油气资源评价技术[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 1999. [2] Lee P J, Wang P C.PRIMES:A petroleum resources information management and evaluation system[J].Oil and Gas Journal, 1984, 82(40):204-206. [3] Salazar J, McVay D A, Lee W J.Development of an improved methodology to asses potential gas resources[J].Natural Resources Research, 2010, 19(4):253-268. doi: 10.1007/s11053-010-9126-9 [4] Olea R A, Cook T A, Coleman J I.A methodology for the assessment of unconventional(continuous) resources with an application to the Greater Natural Buttes gas field, Utah[J].Natural Resources Research, 2010, 19(4):237-251. doi: 10.1007/s11053-010-9127-8 [5] Ahlbrandt T S, Klett T R.Comparison of methods used to estimate conventional undiscovered petroleum resources:World examples[J].Natural Resources Research, 2005, 14(3):187-209. doi: 10.1007/s11053-005-8076-0 [6] Attanasi E D, Charpentier R R.Comparison of two probability distributions used to model sizes of undiscoverd oil and gas accumulations:Does the tail wag the assessment[J].Mathematical Geology, 2002, 34(6):767-777. doi: 10.1023/A:1019809410934 [7] Chen Z H, Qsadetz K G.Undiscovered petroleum accumulation mapping using model-based stochastic simulation[J].Mathematical Geology, 2006, 38(1):1-16. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=65fc4c76e49168b0e1132359e5983b47 [8] Meneley R A, Calverley A E, Logan K G, et al.Resource assessment methodologies:Current status and future direction[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2003, 87(4):535-540. doi: 10.1306/10180202006 [9] 郑民, 李建忠, 吴晓智, 等.我国常规与非常规天然气资源潜力、重点领域与勘探方向[J].天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(10):1383-1397. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201810001 [10] 赵迎冬, 赵银军.油气资源评价方法的分类、内涵与外延[J].西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2019, 41(2):64-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnsyxyxb201902007 [11] 黄志超, 叶加仁.东海海域油气资源与选区评价[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(5):51-55. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201005008 [12] 杨传胜, 杨长清, 李刚, 等.东海陆架盆地中-新生界油气勘探研究进展与前景分析[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2018, 38(2):136-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201802014 [13] 李上卿, 李纯洁.东海西湖凹陷油气资源分布及勘探潜力分析[J].石油实验地质, 2003, 25(6):721-728. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200306015 [14] 彭己君, 张金川, 唐玄, 等.东海西湖凹陷非常规天然气分布序列与勘探潜力[J].中国海上油气, 2014, 26(6):21-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201406004 [15] 张建培, 余逸凡, 张田, 等.东海西湖凹陷深盆气勘探前景探讨[J].中国海上油气, 2013, 25(2):24-29. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201302005 [16] Ye J R, Qing H R, Stephen L B, et al.Petroleum systems in the offshore Xihu Basin on the continental shelf of the East China Sea[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(8):1167-1188. doi: 10.1306/02220705158 [17] 索艳慧, 李三忠, 戴黎明, 等.东海陆架盆地构造单元划分与特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2010, 30(6):49-58. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201006007 [18] 徐志星.西湖凹陷西次凹花港组低孔渗储层沉积相与成岩作用研究[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2012. [19] 刘广景, 宋荣彩, 何亮, 等.西湖凹陷三潭深凹南部异常高压分布层位及其主要成因[J].科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(16):21-26. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxjsygc201416005 [20] Shi H D.Research progress in calculation methods for single-well dynamic reserves of gas reservoirs[J].Advanced Materials Research, 2014, 3530(1044):401-405. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1044-1045.401 [21] Yang S D, Zhao J W, Tang W J, et al.New method to identify gas zones in low porosity and permeability reservoir[J].Well Logging Technology, 2005, 29(1):43-45. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjjs200501013 [22] 张中华, 佟颖, 吴永超.圈闭资源经济评价中开发概念方案关键参数研究[J].石油实验地质, 2018, 40(4):583-588. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201804019 [23] 陈晓智.致密气储量计算方法研究[J].中国矿业, 2018, 27(6):167-172. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgky201806035 [24] 中华人民共和国国土资源部.DZ/T 0217-2005石油天然气储量计算规范[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005. [25] 中华人民共和国国家能源局.SY/T 6098-2010天然气可采储量计算方法[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010. [26] 赵鹏飞, 李敬功, 王庆如, 等.我国现行油气资源储量分类修订的思考[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5):126-131. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201805017 [27] 钟韬, 李键, 曹冰, 等.西湖凹陷花港组储层致密化及其与油气成藏的关系[J].海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(1):20-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0120180802940887 [28] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 胡飞, 等.西湖凹陷中央构造带中南部油气成藏条件、特征及富集规律[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2):123-129. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201502017 [29] 彭己君, 张金川, 唐玄, 等.低渗透背景下西湖凹陷致密砂岩气藏的成藏条件[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3):107-112. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201503014 [30] 袁竞, 陆洋, 李喆.西湖凹陷深部储层物性特征及其影响因素[J].海洋石油, 2019, 39(2):12-17. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hysy201902003 [31] 陈林, 李珊珊, 游君君, 等.文昌B凹陷古近系低渗储层物性影响因素定量评价与应用[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):165-173. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201903017 [32] 王亦然, 徐国盛, 刘勇, 等.西湖凹陷西次凹花港组致密砂岩储层成岩环境与孔隙演化[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 47(1):35-49. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cdlgxyxb202001004 [33] Xu F H, Xu G S, Liu Y, et al.Factors controlling the development of tight sandstone reservoirs in the Huagang Formation of the central inverted structural belt in Xihu sag, East China Sea Basin[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development Online, 2020, 47(1):101-113. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(20)60009-X [34] 郑军.西湖凹陷中央背斜带中北部深部优质储层孔隙保存机理[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(3):173-179. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201603022 [35] 苏奥, 杜江民, 贺聪, 等.东海盆地西湖凹陷平湖构造带超压系统与油气成藏[J].中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 48(3):742-750. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201703024 [36] 侯志强, 于浩, 刘云, 等.西湖凹陷M气田区块低孔渗致密砂岩储层高精度三维孔隙压力场地震预测[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):267-274. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902032 [37] Guo X W, Liu K Y, Jia C Z, et al.Effects of early petroleum charge and overpressure on reservoir porosity preservation in the giant Kela-2 gas field, Kuqa depression, Tarim Basin, northwest China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2016, 100(2):191-212. doi: 10.1306/11181514223 -





 下载:
下载: