Sedimentary characteristics and hydrocarbon exploration potential of the upstream of the Central Canyon in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins
-
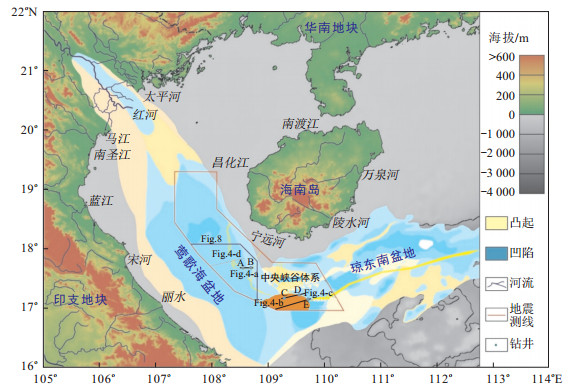
摘要: 深水油气勘探是近些年油气勘探取得重大发现的主要领域,我国已在琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷体系中发现并成功开发了首个深水大气田——陵水17-2气田。为进一步扩大油气勘探成果,急需阐明中央峡谷源头区沉积特征及其油气勘探前景。基于在多口钻井约束下覆盖整个研究区的三维地震资料综合解释建立的等时地层格架,系统总结了中央峡谷体系的形成演化过程,及各演化阶段中央峡谷源头区的沉积体系类型、空间展布和沉积模式,进而结合研究区天然气成藏条件和成藏模式分析,讨论了中央峡谷源头区油气勘探前景。研究结果表明,中央峡谷源头区在黄流组发育了深水水道、陆架边缘三角洲和水道化扇等沉积体系,来源于印支地块、红河和海南岛等多物源区的沉积体系总体以重力流方式呈汇聚型向盆地深水区搬运,并最终汇聚于中央峡谷体系内。在中央峡谷源头区沉积的轴向水道、陆坡水道和水道化扇内发育了优质储层,因此,来自深部的天然气在具有以泥-流体底辟构造作为天然气输导通道的区域,有望聚集形成大型整装天然气藏。该研究成果不但丰富和完善了中央峡谷沉积体系的认识,而且对南海北部深水油气勘探具有重要实际价值。Abstract: Hydrocarbon discoveries have been mainly focused on deep water areas during the past decade. The f-irst gas field in deep water area, Lingshui 17-2, has been discovered and successfully developed in the Central Canyon system of the Qiongdongnan Basin. In order to further expand the hydrocarbon exploration, it is urgent to clarify the sedimentary characteristics in the source area of the Central Canyon and its hyrocarbon exploration prospects. Based on the integration between 3D seismic data covering the whole study area and many drillings, the stratigraphic framework is established and the formation and evolution process of the Central Canyon system is illustrated. Furthermore, the types of sedimentary system, distribution and sedimentary models in the source area of the Central Canyon are systematically summarized. Combined with the natural gas accumulation conditions and reservoir forming models in the study area, the prospect of hydrocarbon exploration in the source area of the Central Canyon is discussed. The results show that deep water channels, shelf-edge delta and channelized fan are developed in the Huangliu Formation in the source area of the Central Canyon system. The sediments from Indosinian, Red River and Hainan Island are transported to the deep water area of the basin in the form of gravity flow, and finally converge in the Central Canyon system. High quality reservoirs are developed in the axial channels, slope channels and channelized fans deposited in the source area of the Central Canyon system.Therefore, natural gas from the deep strata is expected to be migrated and accumulated into large scale gas filed along mud-fluid diapirs.
-
图 3 A井所示黄流组二段低位体系域深水水道测井特征
(钻井位置见图 1)
Figure 3. Log characteristics of deep water channels in Well A showing the low-stand system tract of second member of Huangliu Formation
图 4 中央峡谷源头主要沉积类型地震反射特征
(地震剖面位置见图 1;FFS.初始海面)
Figure 4. Seismic profiles showing the sedimentary characteristics developed in the upstream of the Central Canyon system
图 8 中央峡谷源头区有利油气勘探区带
(位置见图 1)
Figure 8. Favorable hydrocarbon exploration zones in the upstream of the Central Canyon system
-
[1] Weimer P, Slatt R M.Introduction to petroleum geology of de-epwater settings[M].Tulsa:AAPG, 2006. [2] Crossey L J, Ficher, T P, Jonathan Patchett P, et al.Dissected hydrologic system at the Grand Canyon:Interaction between deeply derived fluids and plateau aquifer waters in modern springs and travertine[J].Geology, 2006, 34(1):25-28. http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2006Geo....34...25C [3] Mayall M, Jones E, Casey M.Turbidite channel reservoirs:Key elements in facies prediction and effective development[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(8):821-841. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.08.001 [4] Bouroullec R, Weimer P.Geometry and kinematics of Neogene allochthonous salt systems in the Mississippi Canyon, Atwater Valley, Western DeSoto Canyon protraction areas, northern deep-water Gulf of Mexico[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(7):1003-1037. doi: 10.1306/09011609186 [5] Weimer P, Bouroullec R, van den Berg A A, et al.Structural s-etting and evolution of the Mensa and Thunder Horse intraslope basins, northern deep-water Gulf of Mexico:A case study[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2017, 101(7):1045-1172. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=026681f0226a12d20e4ff1d01e9f7ef5 [6] 王振峰, 孙志鹏, 张迎朝, 等.南海北部琼东南盆地深水中央峡谷大气田分布与成藏规律[J].中国石油勘探, 2016, 21(4):54-64. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgsykt201604006 [7] 王振峰, 裴健翔, 郝德峰, 等.莺-琼盆地中新统大型重力流储集体发育条件、沉积特征及天然气勘探有利方向[J].中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4):13-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201504002 [8] Wang Zhenfeng, Jiang Tao, Zhang Daojun, et al.Evolution of deepwater sedimentary environments and its implication for hydroc-arbon exploration in Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(4):1-10. doi: 10.1007/s13131-015-0645-4 [9] Liang Chao, Xie Xinong, He Yunlong, et al.Multiple sediment sources and topographic changes controlled the depositional architecture of a palaeoslope-parallel canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, South China Sea[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2020, 113:104161. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.104161 [10] 谢玉洪.南海北部自营深水天然气勘探重大突破及其启示[J].天然气工业, 2014, 34(10):1-8. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201410001 [11] 王振峰, 孙志鹏, 朱继田, 等.南海西部深水区天然气地质与大气田重大发现[J].天然气工业, 2015, 35(10):11-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201510002 [12] 谢玉洪, 童传新, 裴健翔, 等.莺歌海盆地黄流组二段碎屑锆石年龄与储层物源分析[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2016, 40(3):517-529. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx201603010 [13] 谢玉洪, 范彩伟.莺歌海盆地东方区黄流组储层成因新认识[J].中国海上油气, 2010, 22(6):355-359. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201006001 [14] 谢玉洪, 王振峰, 解习农, 等.莺歌海盆地坡折带特征及其对沉积体系的控制[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2004, 29(5):569-573. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx200405011 [15] 李伟, 左倩媚, 张道军, 等.琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷黄流组储层特征及主控因素[J].海洋学报, 2016, 38(11):117-124. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201611011 [16] 张道军, 王亚辉, 赵鹏肖, 等.南海北部莺-琼盆地轴向水道沉积特征及成因演化[J].中国海上油气, 2015, 27(3):46-53. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201503007 [17] 苏明, 姜涛, 张翠梅, 等.琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系东段形态-充填特征及其地质意义[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2014, 44(6):1805-1815. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=663466818 [18] Cao Licheng.Jiang Tao, Wang Zhenfeng, et al.Provenance of Upper Miocene sediments in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan basins, northwestern South China Sea:Evidence from REE, heavy minerals and zircon U-Pb ages[J].Marine Geology, 2015, 361:136-146. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.007 [19] Jiang Tao, CaoLicheng, Xie Xinong, et al.Insights from heavy minerals and zircon U-Pb ages into the middle Miocene-Plioce-ne provenance evolution of the Yinggehai Basin, northwestern Sou-th China Sea[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2015, 327:32-42. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2015.07.011 [20] Fan Caiwei, Jiang Tao, Liu Kun, et al.Genesis of Miocene litho-stratigraphic trap and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J].Geoscience Letters, 2018, 5(1):1-13. doi: 10.1186/s40562-018-0112-0 [21] Jiang Tao, Zhang Yingzhao, Tang Sulin, et al.CFD simulation on the generation of turbidites in deepwater areas:A case study of turbidity current processes in Qiongdongnan Basin, northe-rn South China Sea[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2014, 33(12):127-137. doi: 10.1007/s13131-014-0582-7 [22] 罗进华, 朱培民.琼东南盆地陆坡区重力流沉积体系超高精度解析[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):42-50. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201906006 [23] 毛雪莲, 朱继田, 姚哲, 等.琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷砂体成因与展布规律[J].岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(6):60-68. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yxyqc201706008 [24] 何小胡, 张迎朝, 张道军, 等.莺-琼盆地轴向水道沉积演化及勘探前景[J].西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 39(3):66-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xnsyxyxb201703007 [25] 王亚辉, 张道军, 赵鹏肖, 等.南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷成因新认识[J].海洋学报, 2016, 38(11):97-104. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hyxb201611009 [26] 张道军, 张迎朝, 邵磊, 等.琼东南盆地中央峡谷沉积物源探讨[J].天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(10):1574-1581. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201710012 [27] 黄卫, 解习农, 何云龙, 等.琼东南盆地中央峡谷西段莺歌海组沉积演化及储层预测[J].沉积学报, 2015, 33(4):809-816. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201504019 [28] 王振峰, 裴健翔, 郝德峰, 等.莺-琼盆地中新统大型重力流储集体发育条件、沉积特征及天然气勘探有利方向[J].中国海上油气, 2015, 27(4):13-21. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201504002 [29] 张功成, 曾清波, 苏龙, 等.琼东南盆地深水区陵水17-2大气田成藏机理[J].石油学报, 2016, 37(增刊1):34-46. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syxb2016z1004 [30] 田冬梅, 姜涛, 张道军, 等.海底水道特征及其成因机制:以莺歌海盆地乐东区莺歌海组一段为例[J].地球科学, 2017, 42(1):130-141. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94035X/20171/671167276.html [31] 张建新, 党亚云, 何小胡, 等.莺歌海盆地乐东区峡谷水道成因及沉积特征[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2015, 35(5):29-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzydsjdz201505005 [32] 张建新, 范彩伟, 谭建财, 等.莺歌海盆地中新世沉积体系演化特征及勘探意义[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):51-59. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201906007 [33] 黄银涛, 文力, 姚光庆, 等.莺歌海盆地上中新统黄流组海底扇砂岩元素地球化学特征及地质意义[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4):90-99. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201804011 [34] Su Ming, Wu Chihua, Chen Hui, et al.Late Miocene provenance evolution at the head of Central Canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 110:787-796. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.07.053 [35] 王翠丽, 周文, 谢玉洪, 等.莺歌海盆地泥底辟带高温热事件与储层成岩作用[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(4):35-42. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201504006 -





 下载:
下载: