Characteristics of stable carbon isotopes and its implications on arsenic enrichment in shallow groundwater of the Jianghan Plain
-
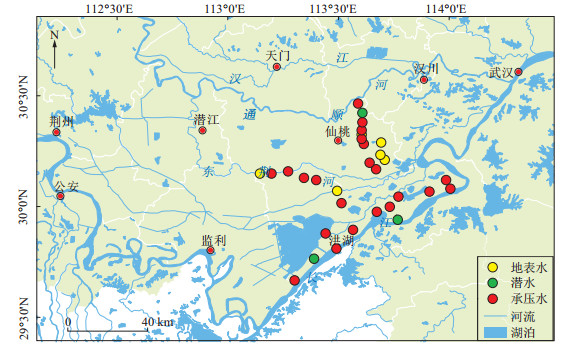
摘要: 溶解性有机碳(DOC)是地下水中砷释放过程的关键因素,为查明江汉平原高砷地下水稳定碳同位素特征,识别有机质的降解过程对砷富集的影响,采用稳定碳同位素分析测试技术并结合地下水化学特征,对江汉平原典型砷中毒病区的浅层地下水进行了区域采样分析。结果表明:浅层承压水的砷质量浓度为0.23~2 621 μg/L。地表水较地下水具有更负的δ13CDOC、δ13CDIC值。地下水中溶解性无机碳(DIC)的δ13CDIC值在-11.9‰~-3.99‰之间,溶解性有机碳的δ13CDOC值在-28.5‰~-19.6‰之间。地下水的δ13CDIC-δ13CDOC差值与ρ(As)呈一定负相关关系,表明微生物作用下有机质的降解促进了As的富集。δ13CDIC-δ13CDOC差值与δ13CDIC和ρ(DOC)均具有较显著的正相关关系,表明地下水中有机质的氧化分解是导致δ13CDIC贫化的重要过程,微生物作用下溶解性有机质的降解是地下水中无机碳的重要来源。此外,江汉平原少数高砷地下水呈现较大的δ13CDIC值,推断江汉平原高砷含水层强还原环境下可能存在的产甲烷过程导致了明显的碳同位素分馏。Abstract: Dissolved organic matter of groundwater is one of the most important factors controlling arsenic release. In order to elaborate the characteristics of stable carbon isotopes and the effects of degradation of organic matter on arsenic enrichment in groundwater, shallow groundwater samples were collected using hydrochemistry and stable carbon isotope analysis in typical arsenicosis areas of the Jianghan Plain. Results indicate that the concentration of As in the shallow groundwater range in 0.23-2621 μg/L. Surface water has lower values of δ13CDOC and δ13CDIC compared with groundwater. The value of δ13CDIC ranges from -11.9‰ to 3.99‰ and the values of δ13CDOC ranges from -28.5‰ to -19.6‰ in groundwater. There is a negative correlation between δ13CDIC-δ13CDOC and As concentration. It indicates that the degradation of organic matter promotes the enrichment of As. There is a positive correlation between δ13CDIC-δ13CDOC and δ13CDIC also between δ13CDIC-δ13CDOC and DOC concentration. It indicates that the microbially involving oxidative decomposition of organic carbon in groundwater leads to the fractionation of carbon isotopes, and the degradation of dissolved organic matter is the main source of inorganic carbon in groundwater. Moreover, some groundwater samples have high δ13CDIC values in the Jianghan Plain, which is significantly higher than other typical arsenic affected areas (Hetao Plain and Datong Basin). It is suggested that methanogenic process occurred in arsenic affected aquifer of the Jianghan Plain, which results in significant carbon isotope fractionation.
-
Key words:
- Jianghan Plain /
- arsenic /
- stable carbon isotope /
- dissolved organic matter
-
表 1 江汉平原地下水主要水化学指标统计
Table 1. Statistics of groundwater chemistry in the Jianghan Plain
指标 pH Ca+ Mg2+ K+ Na+ Cl- SO42- NO3- HCO3- DOC Fe2+ NH4+ As ρB/(mg·L-1) ρB/(mg·L-1) ρB/(μg·L-1) 浅层潜水 6.52~7.00
(6.84)104~190
(136)20.30~29.00
(23.90)1.42~2.18
(1.84)7.50~36.6
(18.60)7.68~39.8
(21.60)3.36~129
(45.40)0.24~121
(40.60)452~595
(534)1.86~5.61
(3.13)0.15~12.00
(5.88)0.10~6.50
(3.43)0.38~97.7
(60.10)浅层承压水 6.51~7.51
(7.02)58.50~180
(125)12.10~32.4
(24.20)0.31~5.54
(1.83)5.10~31.50
(16.70)4.07~37.50
(9.30)3.58~67.10
(7.18)0.16~0.62
(0.34)418~917
(646)0.72~22.90
(3.81)0.06~12.70
(6.69)0.04~13.70
(3.58)0.23~2 621
(193.00)注:括号中为平均值 表 2 江汉平原、大同盆地、河套平原地下水中δ13CDIC及As、Fe质量浓度范围
Table 2. δ13CDIC values and As, Fe concentrations in Jianghan Plain, Datong Basin and Hetao Plain
-
[1] Smedley P L, Kinniburgh D G.A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2002, 17:517-568. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(02)00018-5 [2] Hugh Brammer P R.Arsenic in groundwater:A threat to sustainable agriculture in South and Southeast Asia[J].Environment International, 2009, 35:647-654. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2008.10.004 [3] Nordstrom D K.Public health.Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water[J].Science, 2002, 296:2143-2145. doi: 10.1126/science.1072375 [4] Deng Y, Zheng T, Wang Y, et al.Effect of microbially mediated iron mineral transformation on temporal variation of arsenic in the Pleistocene aquifers of the central Yangtze River Basin[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 619/620:1247-1258. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.11.166 [5] Gan Y, Wang Y, Duan Y, et al.Hydrogeochemistry and arsenic contamination of groundwater in the Jianghan Plain, central China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2014, 138:81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.12.013 [6] 李红梅, 邓娅敏, 罗莉威, 等.江汉平原高砷含水层沉积物地球化学特征[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3):178-184. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201503025 [7] 段艳华, 甘义群, 郭欣欣, 等.江汉平原高砷地下水监测场水化学特征及砷富集影响因素分析[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(2):140-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201402023 [8] Chen Z, Wang Y, Jiang X, et al.Dual roles of AQDS as electron shuttles for microbes and dissolved organic matter involved in arsenic and iron mobilization in the arsenic-rich sediment[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2017, 574:1684-1694. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.006 [9] Mladenov N, Zheng Y, Miller M P, et al.Dissolved organic matter sources and consequences for iron and arsenic mobilization in Bangladesh aquifers[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(1):123-128. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=5648a6f9998b92db5697eda963337cde [10] Murphy E M, Schramke J A.Estimation of microbial respiration rates in groundwater by geochemical modeling constrained with stable isotopes[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1998, 62(21):3395-3406. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016703798002543 [11] Oremland R S, Stolz J F.The ecology of arsenic[J].Science, 2003, 300:939-944. doi: 10.1126/science.1081903 [12] Li X, Guo H, Zheng H, et al.Roles of different molecular weights of dissolved organic matter in arsenic enrichment in groundwater:Evidences from ultrafiltration and EEM-PARAFAC[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2019, 104:124-134. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0883292719300873 [13] 严怡君, 谢先军, 肖紫怡, 等.灌溉对非饱和带中砷迁移转化过程的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5):206-214. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201805028 [14] 鲁宗杰, 邓娅敏, 杜尧, 等.江汉平原高砷地下水中DOM三维荧光特征及其指示意义[J].地球科学, 2017, 42(5):771-782. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201705013 [15] Kulkarni H V, Mladenov N, Mcknight D M, et al.Dissolved fulvic acids from a high arsenic aquifer shuttle electrons to enhance microbial iron reduction[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2018, 615:1390-1395. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.164 [16] Wang S, Mulligan C N.Effect of natural organic matter on arsenic release from soils and sediments into groundwater[J].Environmental Geochemistry and Health, 2006, 28(3):197-214. doi: 10.1007/s10653-005-9032-y [17] Klitzke S, Lang F.Mobilization of Soluble and dispersible lead, arsenic, and antimony in a polluted, organic-rich soil-effects of pH increase and counterion valency[J].Journal of Environmental Quality, 2009, 38(3):933-939. doi: 10.2134/jeq2008.0239 [18] Mladenov N, Zheng Y, Simone B, et al.Dissolved organic matter quality in a shallow aquifer of Bangladesh:Implications for arsenic mobility[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(18):10815-10824. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b01962 [19] Fendorf S, Michael H A, Geen A V.Spatial and temporal variations of groundwater arsenic in South and Southeast Asia[J].Science, 2010, 328:1123-1127. doi: 10.1126/science.1172974 [20] Guo H, Zhang B, Zhang Y.Control of organic and iron colloids on arsenic partition and transport in high arsenic groundwaters in the Hetao Basin, Inner Mongolia[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2011, 26(3):360-370. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2010.12.009 [21] 贾永锋, 郭华明.高砷地下水研究的热点及发展趋势[J].地球科学进展, 2013, 28(1):51-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkxjz201301006 [22] Fonyuy E W, Atekwana E A.Dissolved inorganic carbon evolution and stable carbon isotope fractionation in acid mine drainage contaminated streams:Insights from a laboratory study[J].Applied Geochemistry, 2008, 23:2634-2648. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2008.05.012 [23] Slater G F, Sherwood Lollar B, Sleep B E, et al.Variability in carbon isotopic fractionation during biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes:Implications for field applications[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2001, 35(5):901-907. doi: 10.1021/es001583f [24] 李思亮, 刘丛强, 陶发祥, 等.碳同位素和水化学在示踪贵阳地下水碳的生物地球化学循环及污染中的应用[J].地球化学, 2004, 33(2):165-170. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqhx200402008 [25] 周殷竹.基于碳、铁稳定同位素的高砷地下水生物地球化学研究[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018. [26] 于凯.高砷地下水系统中有机质来源及其对砷动态变化的影响研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2016. [27] Yu K, Gan Y, Zhou A, et al.Organic carbon sources and controlling processes on aquifer arsenic cycling in the Jianghan Plain, central China[J].Chemosphere, 2018, 208:773-781. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.188 [28] 韩莉, 甘义群, 于凯.江汉平原高砷地下水中溶解性有机质来源的稳定碳同位素示踪研究[J].地质学报, 2015, 89(增刊1):266-268. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8771705 [29] Xie X, Wang Y, Ellis A, et al.Multiple isotope (O, S and C)approach elucidates the enrichment of arsenic in the groundwater from the Datong Basin, northern China[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 498:103-112. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2013.06.024 [30] Duan Y, Gan Y, Wang Y, et al.Temporal variation of groundwater level and arsenic concentration at Jianghan Plain, central China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 149:106-119. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.12.001 [31] Zheng T, Deng Y, Wang Y, et al.Seasonal microbial variation accounts for arsenic dynamics in shallow alluvial aquifer systems[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 367:109-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.087 [32] Wang J, Zeng X, Zhu X, et al.Sulfate enhances the dissimilatory arsenate-respiring prokaryotes-mediated mobilization, reduction and release of insoluble arsenic and iron from the arsenic-richs ediments into groundwater[J].Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 339:409-417. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.06.052 [33] Pi K, Wang Y, Xie X, et al.Geochemical effects of dissolved organic matter biodegradation on arsenic transport in groundwater systems[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 149:8-21. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.11.005 [34] Li X, Tang C, Cao Y, et al.Carbon, nitrogen and sulfur isotopic features and the associated geochemical processes in a coastal aquifer system of the Pearl River Delta, China[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 575:986-998. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.05.092 [35] Guo H, Zhang D, Wen D, et al.Arsenic mobilization in aquifers of the southwest Songnen Basin, P.R.China:Evidences from chemical and isotopic characteristics[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 490:590-602. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.05.050 [36] 周殷竹, 郭华明, 逯海.高砷地下水中溶解性有机碳和无机碳稳定同位素特征[J].现代地质, 2015, 29(2):252-259. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201502005 [37] 谢作明, 罗艳, 王焰新, 等.土著细菌对江汉平原浅层含水层沉积物中砷迁移的影响[J].生态毒理学报, 2013, 8(2):201-206. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cyyhj201302011 [38] 高杰, 郑天亮, 邓娅敏, 等.江汉平原高砷地下水原位微生物的铁还原及其对砷释放的影响[J].地球科学, 2017, 42(5):716-726. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201705007 [39] 吕航.地下水中石油烃生物降解的同位素地球化学研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2011. [40] 何哲峰.黄河河套段更新世晚期古湖问题的初步研究[D].北京: 中国地质科学院, 2009. [41] 何俊蓉, 谢先军, 池泽涌, 等.古气候变化对大同盆地第四纪沉积物中砷富集过程的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5):212-219. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201905022 [42] 周殷竹.内蒙古河套盆地地下水碳同位素特征及生物地球化学意义[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2014. [43] 黄爽兵, 王焰新, 刘昌蓉, 等.含水层中砷活化迁移的水化学与DOM三维荧光证据[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2013, 38(5):1091-1098. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201305019 [44] 顾延生, 管硕, 马腾, 等.江汉盆地东部第四纪钻孔地层与沉积环境[J].地球科学, 2018, 43(11):3989-4000. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dqkx201811015 [45] Huang S, Wang Y, Ma T, et al.Linking groundwater dissolved organic matter to sedimentary organic matter from a fluvio-lacustrine aquifer at Jianghan Plain, China by EEM-PARAFAC and hydrochemical analyses[J].Science of the Total Environment, 2015, 529:131-139. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2015.05.051 -





 下载:
下载: