Thinking and methods of intelligent supervision of urban geological environment based on big data
-
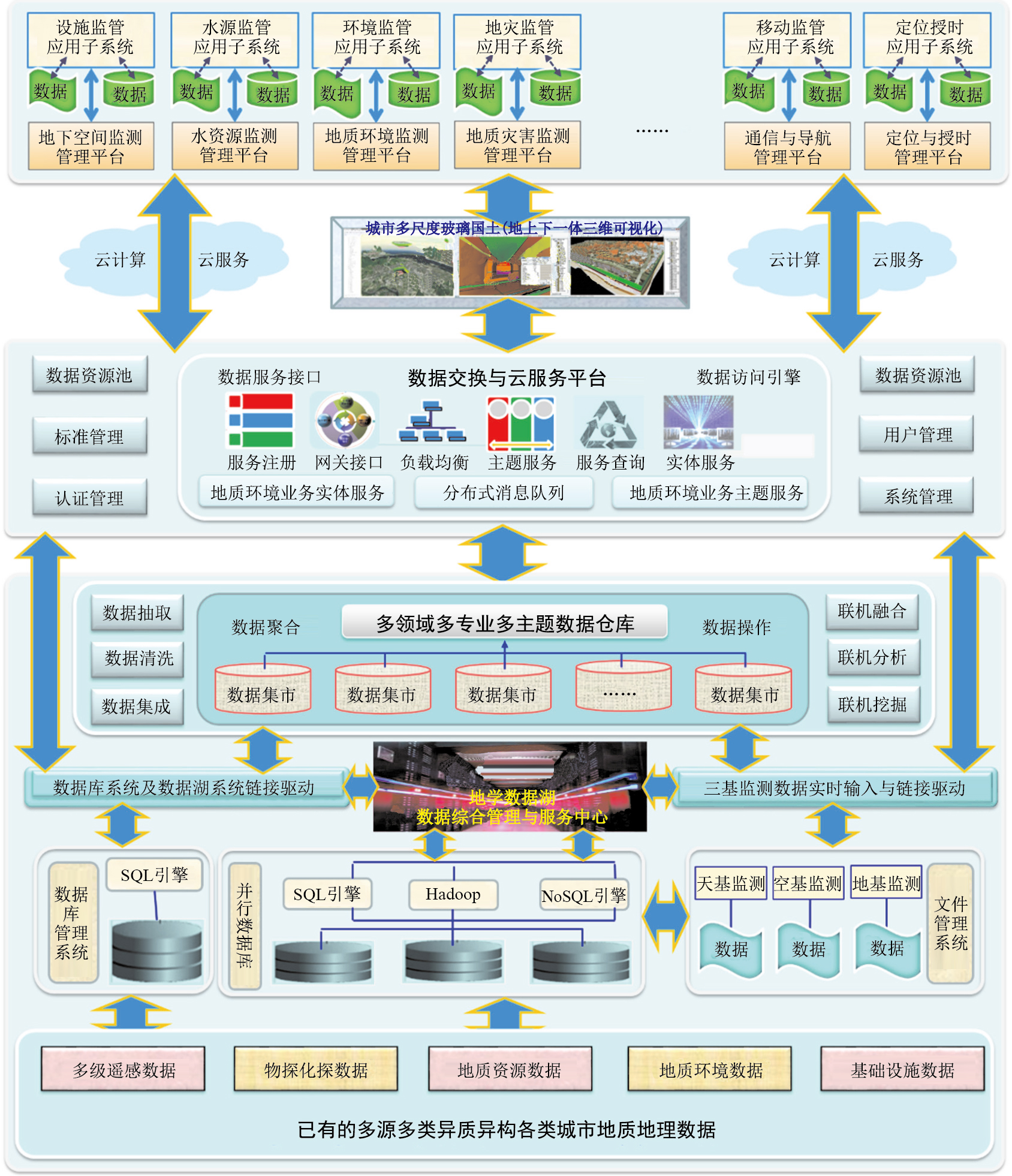
摘要: 随着城市化进程加速,城市范围迅猛扩大,人口急剧膨胀,高层建筑林立,地下空间开发规模化,面临着水资源贫化、地质环境恶化和地质灾害频发等巨大挑战。为了有效地应对挑战,迫切需要在城市多要素地质环境调查并建立完善的信息系统的基础上,开展面向"智慧城市"的精细、全息三维地质建模,即建立新型的城市"玻璃国土",实现城市地质环境时空透视,然后利用传感器、物联网和云技术,建立城市地质资源、地质环境和地质灾害动态监测数据链,最后基于地质科学大数据的同化、融合和挖掘技术,进行智能预警和管控。
-
关键词:
- 智慧城市 /
- 玻璃国土 /
- 三维地质建模 /
- 地学大数据 /
- 城市地质环境智能管控
Abstract: With the acceleration of urbanization, the rapid expansion of scope, the rapid expansion of population, the proliferation of high-rise buildings and the large-scale development of underground space, they are faced with great challenges, such as the dilution of water resources, the deterioration of geological environment and the frequent occurrence of geological disasters.In order to meet the challenge effectively, it is urgent to carry out fine and holographic three-dimensional geological modeling oriented to "intelligent city" on the basis of urban multi-factor geological environment survey and establishment of perfect information system, that is, to establish a new type of urban "glass land", to realize the temporal and spatial perspective of urban geological environment, and then to establish urban geological resources by using sensors, Internet of things and cloud technology.Finally, based on the assimilation, fusion and mining technology of geological science big data, intelligent early warning and control are carried out. -
-
[1] 尹秀莲.中国城市水资源的现状与出路[J].吉林省经济管理干部学院学报, 2008, 22(1):40-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0657.2008.01.011 [2] 黄春苑, 陈俊合, 苏晓波.深圳市水资源承载力与城市可持续发展研究[J].热带地理, 2006, 26(3):254-258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2006.03.012 [3] 陈桂荣, 王经武.中国城市建设与地质灾害综述[J].地质灾害与环境保护, 2002, 13(2):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2002.02.001 [4] 沈铭, 杨涛, 赵新建.武汉市岩溶地面塌陷监测技术探讨[J].资源环境与工程, 2014, 28(2):177-180. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1211.2014.02.013 [5] 深圳三年发生地面坍塌事故579起, 查出隐患2万个.深圳商报, 2016.2.18, http://sz.people.com.cn/n2/2016/0218/c202846-27756560.html. [6] 王家兵, 李平, 张百鸣, 等.天津平原地下水可开采量与确定依据[J].地学前缘, 2010, 17(6):221-226. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dxqy201006030 [7] 地面沉降的中国应对.国土资源2012年3月号 [8] 朱元武, 刘春香, 贺金强.采空区场地高层建筑地基稳定性评价[J].工业建筑, 2009, 39(增刊):738-740. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/spyzl201606091 [9] 毛小平, 吴冲龙, 师学明.天津高新技术产业园区海泰小区路面塌陷成因[J].工程地质学报, 2016, 24(2):299-307. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gcdzxb201602020 [10] Bristol S, Euliss N H, Booth N L.Science strategy for core science systems in the U.S.Geological Survey, 2013-2023-Public Review Release[R].Denver: U.S.Geological Survey, 2012. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271508464_Science_Strategy_for_Core_Science_Systems_in_the_US_Geological_Survey_2013-2023-Public_Review_Release [11] 张晓艺.农田土壤重金属污染状况及修复技术研究[J].中国资源综合利用, 2019, 37(4):86-88. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9500.2019.04.025 [12] 樊霆, 叶文玲, 陈海燕, 等.农田土壤重金属污染状况及修复技术研究[J].生态环境学报, 2013, 22(10):1727-1736. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5906.2013.10.015 [13] 彭诗杰.基于微服务体系结构和面向多地质主题的数据云服务关键技术研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2017. [14] 吴冲龙, 刘刚."玻璃地球"建设的现状、问题、趋势与对策[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1281-1287. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgqydz201507005 [15] Wikipedia Foundation, Inc.Data lake.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Data_lake. [16] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 田宜平, 等.论地质信息科学[J].地质科技情报, 2005, 24(3):1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200503001 [17] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 张夏林, 等.地质科学大数据及其利用的若干问题探讨[J].科学通报, 2015, 34(7):1280-1287. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201616010 [18] 吴冲龙, 牛瑞卿, 刘刚, 等.城市地质信息系统建设的目标与解决方案[J].地质科技情报, 2003, 22(3):67-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2003.03.013 -





 下载:
下载: