Data model for geological spatiotemporal big data expression and storage management
-
摘要: 随着传感器实时监测等高新技术在地质勘查或生产开发中的应用,形成了动态与静态并存、多源异构的地质时空大数据。然而,目前地质信息系统在地质数据组织管理方面,主要是静态地存储和表达出地质矿产勘查或生产开发在某个特定时期的状态,尚不能满足对勘查或生产开发过程中实时信息的存储管理,进而支持对地质过程的分析和研判。针对性开展了地质时空大数据表达与存储管理的数据模型研究,目标是能够融合数据多源与时空多维性,又能够支持时间关联与时间多粒性。针对地质大数据、地质过程的静态与动态数据紧密结合的特点,采用面向对象和基于事件的思想,提出了基于事件多因素驱动的地质时空大数据概念模型,并开展了相应的地质大数据存储管理逻辑模型、基于系统工程库的管理结构和地质时空对象管理模型设计。基于地质时空大数据逻辑组织管理模型和时空过程的非关系型分布式数据库架构,设计了地质大数据存储模型。融合三维地质建模技术、动态监测信息实时可视化等技术,构建了所需模型过程模拟的三维环境,通过绑定观测数据源,设计实现了基于OPC接口的模拟数据产生事件、作用对象响应的矿山动态开采流程。在王家岭煤矿首采区地质数据支持下开展了应用研究,实现地质时空事件条件下的矿山动态开采过程表达与数据管理,验证了本文模型的可行性和有效性。Abstract: Geological big data is a typical spatiotemporal big data.Most of present geological information systems only support the storage and expression of the static status of geological exploration or production in a specific period.However, with the development and application of multiple sensors, real-time monitoring and other high-tech in the geological exploration, which results in more and more dynamic and multi-source heterogeneous geological data being produced.In practical application, it is in urgent need to deal with the real-time increasing big data in the geological exploration and production, which can strongly support the analysis and judgement of the geological process.In this paper, we study the traditional data model for geological spatiotemporal expression and storage management with the target of a new hybrid model, which can not only deal with the multi-sources and multi-dimensional data, but also support the time associated and time granularity.According to the characteristics of geological big data and the combinations of static and dynamic geological process data, we took both the object-oriented and event based method and put forward a geological event multi-factors driven model.We also designed the corresponding geological data logic model for distributed storage.Based on the geological data logical model and NoSQL database technology, we designed a non-relational distributed database schema.With the use of 3D geological modeling technology, real-time dynamic monitoring information visualization technology, we build a necessary virtual simulation environment for the hybrid model.By binding the observation data source, which is operation as an events emitter based on the OPC interface, the dynamic mining process is simulating as the geological objects responding to their corresponding events.Under the support of geological modeling data and reports and other data in the first mining area of Wang Jialing coal mine, we tried to implement the model application with multi geological spatiotemporal events.The results show that the data model is feasible, applicable for the expression and data management of mine dynamic mining process.
-
空间信息技术在地质矿产勘查、地质学定量化研究、矿产预测评价等领域的广泛运用[1-4],为正在全世界范围内兴起和发展着的“玻璃地球”[5-6]建设带来了新的思路,推动了地质信息系统的建立和发展,促进了地质科学大数据的理论方法研究和地质科学研究新思路与方法的深入[4, 7-11]。目前大多数的地质信息系统,只是静态地记录和显示地质空间的地层结构、矿床分布、井巷开挖等情况,其实质是表达出地质矿产勘查或生产开发在某个特定时期的状态。然而,随着地质工作中大量传感器实时监测等高新技术的应用,在实际工作中通常要考虑一段时间内地质对象状态的空间和属性变化情况,或者需要及时地对勘查或开发过程中实时信息进行处理,构建实时的地质信息系统,加强对地质过程的分析和研判。这个过程中所形成的动态+静态、多源异构的海量数据构成了地质大数据的基础,并促使地质信息系统的研发和应用向智能化的阶段迈进[4, 8-12]。
地质科学大数据在形式上具有显著的多类、多维、多量、多尺度、多时态和多主题的显著特征,贴合4Ⅴ特征,即体量大而完整(volume)、类型多且关联(variety)、聚集快却杂乱(velocity)和价值大但稀疏(value)。地质数据既有结构化的,也有半结构化的和非结构化的。本文主要针对大规模地质时空数据的体量大、聚集快(地学传感网数据)的特点,研究具有基础意义的地质时空数据的表达模型和存储模型,实现结构化、半结构化和非结构化数据的一体化,以及静态数据与动态数据一体化存储管理。而建立面向大规模地质时空数据表达与存储管理的数据模型,是实现地质时空大数据存储管理的基础。历史上时空数据模型与时态GIS的研究,已经取得了丰硕的成果,例如:时空快照模型[13-14]、基态修正模型[13-14]、时空立方体模型[14-15]、时空复合模型[16-17]、基于事件的模型[18-20]、面向对象的数据模型[21-22],以及这些模型的改进模型[23-24]等。近年为满足动态目标与传感器等实时观测数据的获取、存储管理和应用需求促进了实时地理信息系统的发展,在实时数据表达与存储数据模型方面,龚健雅等[25]提出了一种实时GIS时空数据模型,将时空过程、地理对象、事件、事件类型、状态和观测等要素有机地结合在一起。然而,由于地质过程演化以逐步的、常年的缓慢变化与突然的灾难性变化相伴为特点,地质作用与时-空结构的表示形式随研究程度逐步深化,现有的时空数据模型难以描述地质过程“复杂性”、“非线性”特征[9],在实际矿山信息系统和地质灾害管理系统建设中却又迫切需要一种时空数据模型,以便为地质灾害实时监测、矿山开采过程及其安全动态监管、实时预警预报等提供基础支撑。
地质时空过程是指某个时间段内,某个地质对象或对象集合随着时间推进而演变的历程,是具有多时间粒度的产生事件和响应事件的过程。现有的基于事件和事件驱动的时空数据模型,在表达具体地质时空过程时,虽然能够表达时空变化的因果关系,却不能表达引起事件变化的诸多内部因素,不能描述发生事件间的关系,而且事件类型难以从具体过程中抽提。针对这些问题,本文研究团队开展了面向地质过程分析的时空数据模型研究,使其能够支持“动态过程模拟和实时表达”和大规模地质时空数据管理,具体包括:①建立能够描述在自然地质过程(地层构造演化、塌陷、滑坡、泥石流监测等)和地质矿产开发过程(金属、非金属、煤、油气等资源开采或地质工程)中,不同空间对象在时变空变条件下的统一概念模型和逻辑模型。②根据所设计的上述概念模型和逻辑模型,定制模型的物理存储方案,结合实际生产和应用的需求,开展模型的应用研究。本文即是在上述研究的基础上结合最新进展提炼而成[26-27]。
1. 地质时空大数据表达的概念模型
1.1 地质时空数据模型概念框架
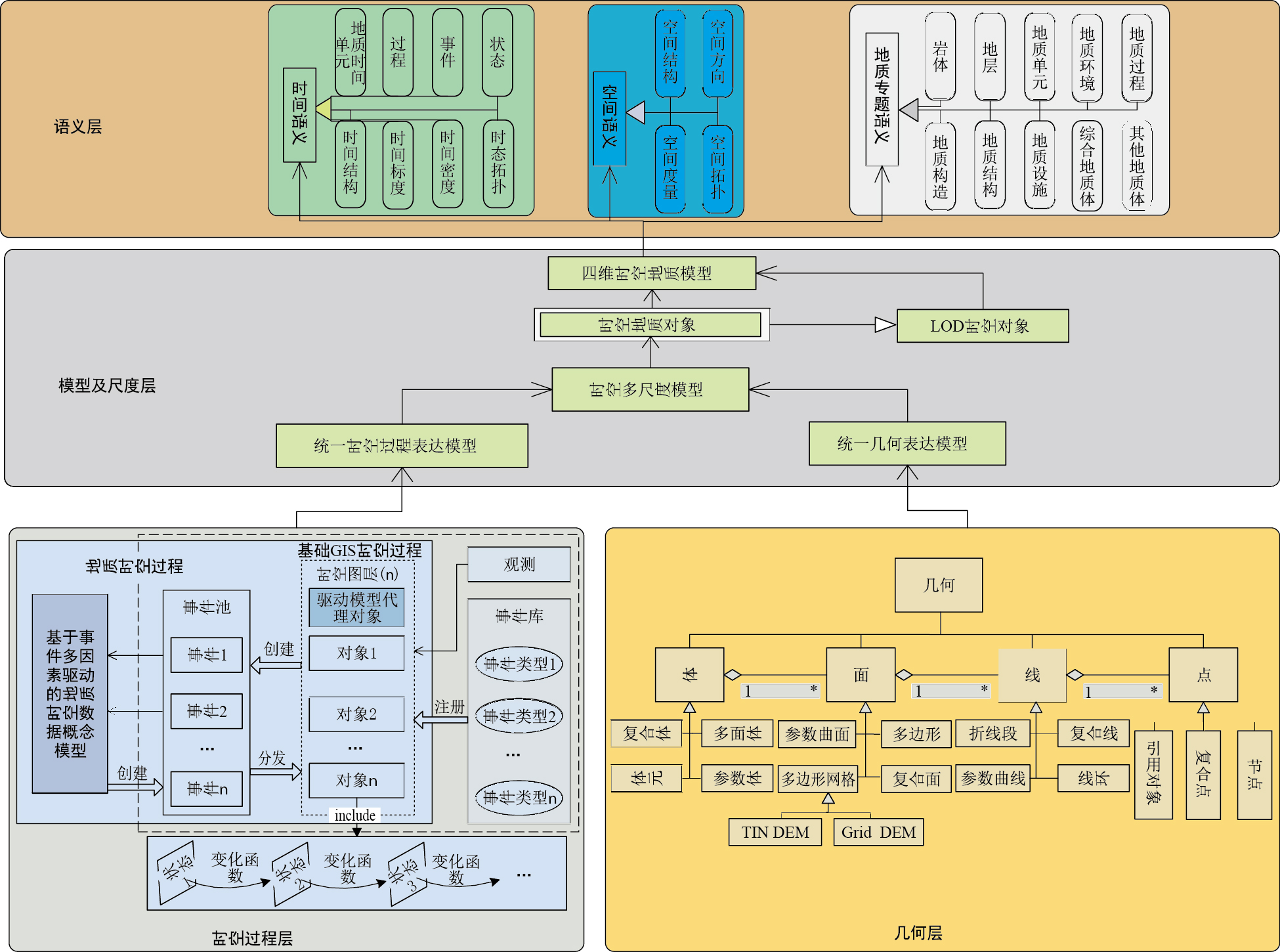
针对地质空间对象的几何、属性、空间关系、语义表达等综合表达问题,该概念模型由时空过程类、地质对象类、事件类、状态类、要素类、观测类以及地质模型类组成。事件是由对象定期或者不定期根据观测数据或者其他逻辑判断等条件产生的。结合地质时间、空间、变化及动态采掘和监测等一般地质过程的特点,提出一种面向动态过程模拟和实时表达的地质时空数据模型,其概念模型总共分为4层(图 1),分别为时空过程模型层、几何模型层、模型及尺度层、语义层。时空过程模型层:在通用时空GIS模型基础上,结合地质事件多因素驱动模型及其代理对象构成,为扩展模型核心部分。几何模型层:提供实体对象空间和形态的几何表示,为扩展模型基础部分。模型及尺度层:基于前两者,根据应用需求构建支持多时空尺度的四维时空地质模型。语义层:借助时空地质对象,表达时间、空间和地质专题语义。4个层次相互依赖、相互协调,自底向上逐步构建,能够较全面地支持多尺度的地质空间对象、多层次观测数据接入、多级别事件和多时间粒度的复合时空过程的表达。
时空过程模型层的主要概念描述如下。
(1) 地质对象 现实世界的地质空间环境中,作为地质现象分析、地质过程研究客体的人工或自然形成的、有明确或者不明确几何边界的物体或现象。
(2) 地质事件 是地质对象(集合)的非正常变化引起的地质时空过程演变。事件由地质对象或地质事件多因素模型触发,并由过程分发给注册的能对该事件响应的地质对象或多因素驱动模型代理对象,接受事件的对象根据接收的事件,按照一定的机理,做出响应。地质事件划分为原子事件和复合事件。原子事件是指在过程模拟中最先创建的未经过地质事件多因素驱动模型处理的事件(通常是直接监测到对象参数变化事件)。复合事件是指原子事件至少经过一次多因素驱动模型处理的,通过模拟运算或依据约束规则被其他事件触发的事件。每个地质事件都含有一个事件的层次计数器和广度计数器,记录该事件在模拟过程中的层次级别和广度级别。
(3) 地质事件多因素驱动模型对象 主要负责同事件池进行交互、维护事件队列,管理事件队列在地质事件驱动模型中的分发,以及维护模拟模型管理和约束规则管理所产生的发出事件队列。
(4) 地质时空过程 某个时间段内,所研究的某个地质对象(集合)或地质现象随着时间推进而演变的历程。地质时空过程大致分为三类:简单时空过程、关联时空过程和复合时空过程。
(5) 状态 空间对象变化过程中,某个时刻的特征集合。
(6) 特征 状态的组成部分,用于表达空间对象在该状态的空间和专题属性。
(7) 传感器 一种物理装置,能够探测、感受外接的信号、物理条件(如光、热、湿度)或化学组成(如烟雾),并将感知的信息传递给其他装置,通常由敏感元件和转换元件组成。
(8) 观测 观察属性的行为。
(9) 变化函数 根据行业科学计算或相关经验,利用已经观测的数值,在有效时间范围内,反映数值变化规律的函数。
1.2 基于事件多因素驱动的地质时空数据概念模型
龚建雅等[21]提出了实时GIS时空数据模型,分析借鉴了以往各种类型的时空数据模型的优缺点,全面考虑了地理时空过程中各种地理要素的特点以及存储管理要求。这一模型采用面向对象的设计思想,使得模型具有良好的可实现性和扩展性,为各个领域的扩展应用提供基本框架(如图 1中“基础GIS时空过程”的虚框线内模型所示)。笔者所提出的面向地质大数据表达的时空数据模型采用面向对象、基于事件的思想在其基础上进行了扩展。
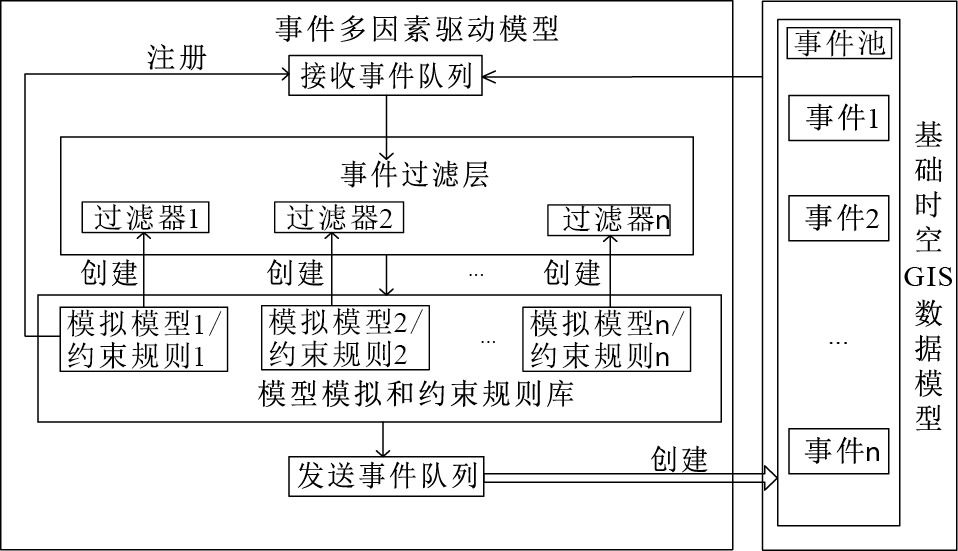
为增强对地质系统演化、地质过程模拟等地质现象、地质过程的语义表达,给出了基于事件多因素驱动的地质时空数据概念模型(event multi-factor driven geological spatio-temporal data model,简称EMDGSDM)。
多因素是指地质过程发展中所涉及的多种相关影响要素或者变化过程。不同的因素触发不同的事件,这些事件又会作用于相应的对象,促使其改变当前状态。该模型类似于地质过程模拟分析相关事件的加工厂。各类事件进入该模型后,经过过滤、约束、模拟运算等“工序”加工后,可以生成一些更高层次级别和广度级别的事件。各类事件由事件池按照时间的先后顺序进行统一存储管理,当事件池内的事件与事件接收队列中已注册的事件类型相符合时,将事件放入事件接收队列;事件接收队列中的事件经各个事件过滤器检验后记录;若某个事件过滤器需要的事件已经全部存在,从事件接收队列中提取相关事件,递交到模拟模型或者约束规则进行运算处理;模拟模型产生的结果以事件的形式存在,与其他事件一起由事件池进行存储管理。
该模型主要的运行机制描述如下:①由用户向模拟模型库中装载时空过程模拟需要的模拟模型和约束规则;②用户向模拟库装载模型和约束规则时创建相应的事件过滤器,并放入事件过滤层中;③根据模拟库中的模型需要输入的参数及约束规则需要的输入事件,向接收事件队列注册所需接收的相关事件;④当事件池中的事件满足接收事件队列需要的事件类型时,接收事件并放入接收事件队列中,并遍历事件过滤器事件到达;⑤当事件过滤器所需事件全部到达时,从接收事件队列中获取相应的事件,传入事件过滤器对应的模拟模型或约束运算产生相应的结果;⑥模拟结果以新事件的形式传出,如果属于接收事件队列已注册事件,则放回接收事件列表中,并放回到事件池中。⑦当多因素驱动模型发出一些特殊事件(一般对象无法响应该类型事件),对象层中的多因素驱动代理对象接收此类事件,并对相应的特殊事件进行处理。
与一般的时空数据模型相比,它不仅可以解决地质过程中多对象状态同时变化的问题,而且可以处理多层级事件产生问题。该模型可以支持解决事件的层次、粒度划分、事件触发新的子过程、复杂地质时空过程的定量评估等诸多问题,能支撑多层次语义表达(简单时空过程、关联时空过程和多层次复合时空过程)的时空数据模型,处理历史观测数据、实时监测和模拟数据,而且支持动态过程的监测管理和实时可视化。
2. 大规模地质时空数据存储管理的逻辑模型
2.1 基于对象与事件的地质时空数据存储管理逻辑模型
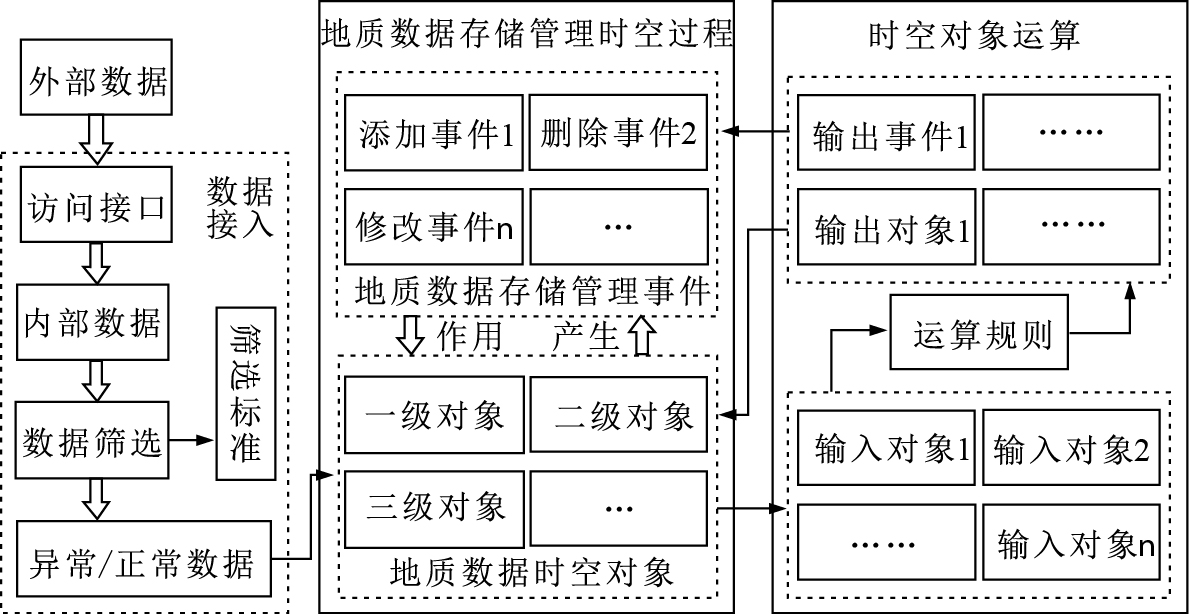
面向大规模地质数据存储管理的时空数据模型的首要任务是,同时适应于关系型数据库和非关系型数据库。时空数据模型的存在形式,应根据实际需要进行:有的用户可能不希望时空数据模型作为数据管理的唯一入口,则时空数据模型应作为一种方便挂载的模块存在;当系统功能的实现十分依赖于时空数据模型时,则时空数据模型可能需要嵌套在系统内部。分析地质数据的存储管理过程可以发现,只有在新的数据到来时,才需要对数据库进行添加、修改、删除等操作。这一机理与事件和对象的作用原理类似。
对于地质数据库而言,在没有新的地质数据产生时,地质数据库维持原有状态不变;通过接入新的地质数据,地质数据库进行添加、删除、更改等操作达到新的状态。因此,地质数据是驱动地质数据库产生时空变化的因素,是维持地质数据存储管理这一时空过程的动力。本文采用面向对象与事件的思路,地质大数据存储管理模型整体如图 3所示。
在时空数据模型中,地质数据时空对象对数据进行分层次的管理,不同级别的时空对象,负责管理不同层次的系统内部或数据库中的存储空间;3种地质数据对象分别为一级对象、二级对象和三级对象,分别对应着数据库中表/集合、行/文档、单元格/字段层次的数据。其中一级对象可以包含若干二级对象,并负责对二级对象进行管理。二级对象可以包含若干二级对象和三级对象,并负责管理。地质数据存储管理事件主要借助地质数据时空对象产生,包括添加事件、删除事件、修改事件等,并可以作用到其他的地质数据时空对象;地质数据存储管理事件被递交到系统内相关的地质数据时空对象后,时空对象可以根据所接收到的地质数据存储管理事件,对自己所管辖的数据库空间进行操作,完成地质数据的存储管理;地质数据时空对象和地质数据存储管理事件由地质数据存储管理时空过程进行统一管理,事件的传递、接收、响应,推动着整个数据存储管理过程的运转。时空对象的运算将根据现有时空对象,生成新的时空对象。可将时空对象的运算划分为数据层的运算和地理、地质实体对象的运算。数据的运算由数据库中各条数据的添加、修改、删除操作组合而成,是数据维护、筛选时的必要操作,也是提取新数据的手段;地理、地质实体对象由数据组成,但层次要高于单条的数据,因而不能直接使用数据运算的方式。实体对象几何形态上的变化,可视为当前地理、地质对象在某些规则的约束下,生成新的时空对象。
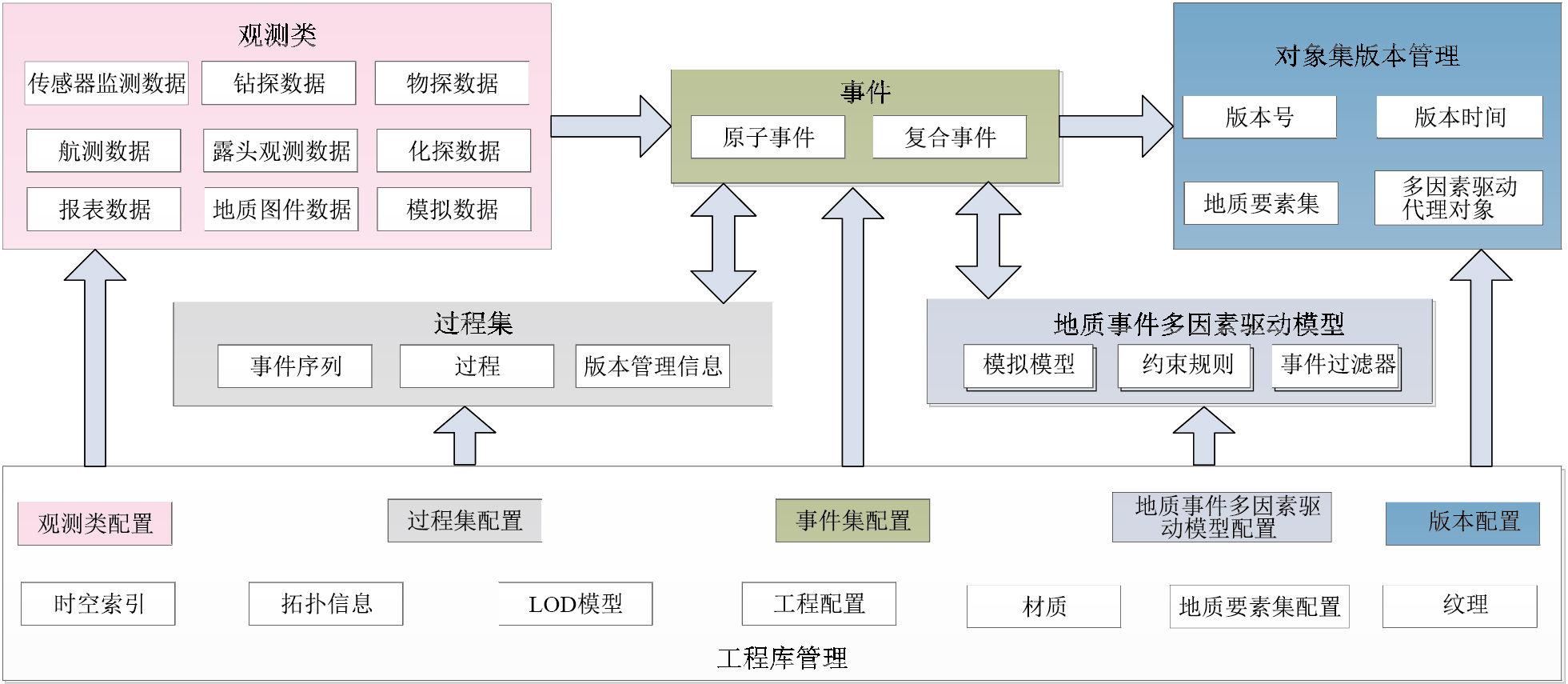
2.2 基于系统工程库的管理结构
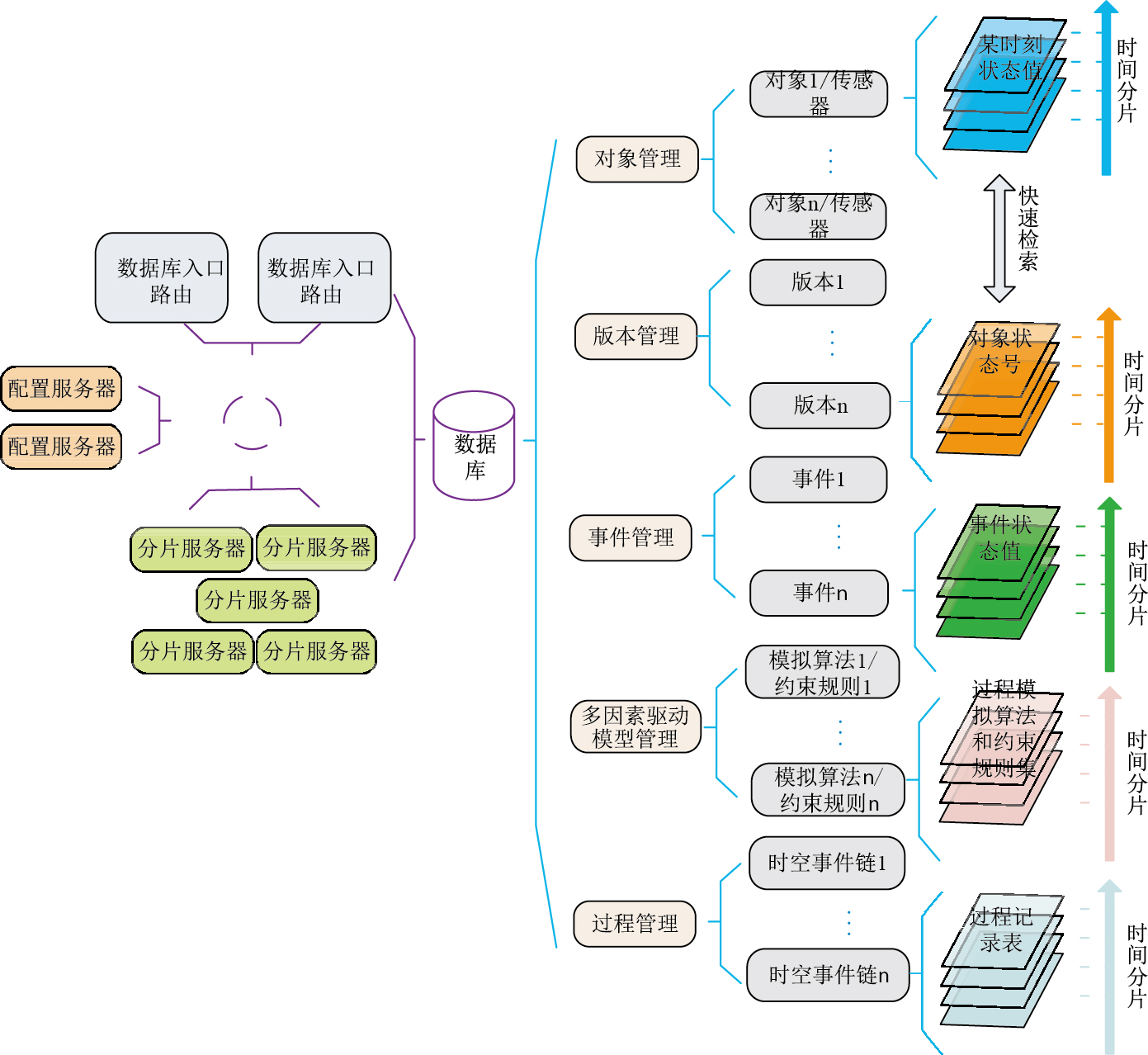
根据时空过程的概念模型框架,采用系统工程的思想,设计工程库管理结构(图 4),其主要功能为:总体上负责程序及各个过程协调运行,维护各种观测类信息、模型要素集和对象版本等配置数据。该设计结构能够使系统有效地利用观测类分发事件,保障事件经过多因素驱动模型加工后,作用于对象版本管理的地质要素集,并改变要素几何或属性状态这一流程顺利运行。从其管理内容上看,它除了能管理传统静态数据模型中的材质、纹理、地质要素、拓扑结构、LOD模型、索引等信息外,还可以支持动态变化信息管理。具体可分为:空间对象模型管理、过程管理、观测管理、事件管理、版本管理和多因素驱动管理六大部分。
2.3 地质时空对象管理
根据地质对象的空间特征及其在时空模型中的作用,将地质时空对象结构分为时空对象列表和时空对象操作两部分进行存储和管理。该结构具有两大特点:①时空对象管理,负责维护某时空范围内(或不同类型)的时空对象列表,并支持对象列表的状态操作、传感器观测绑定和事件响应等操作;②时空对象可以根据某一状态值快速检索相关联的几何模型和属性,操作相应地质对象模型。
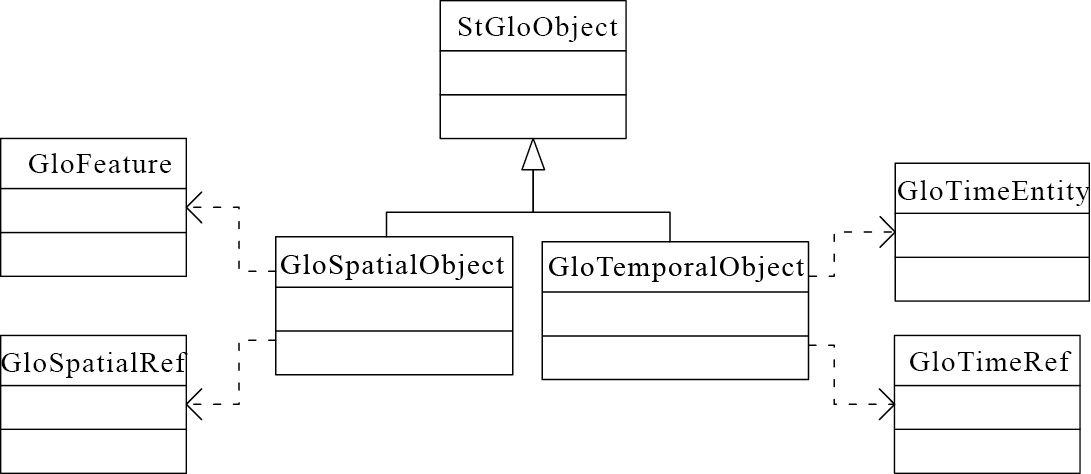
时空地质对象(StGloObject)(图 5)是由地质空间类(GloSpatialObject)和地质时间类(GloTemporalObject)构成。
地质空间对象GloSpatialObject是一个组合对象类,包含地质要素GloFeature和地质空间参考GlospatialRef,前者描述地质要素的几何、纹理、材质、多细节层次等信息,后者描述空间参考系信息。其中,几何要素信息只有在一定的空间参考下才具有定位意义。
地质时间GloTemporalObject是一组合对象类,包含地质时间实体GloTimeEntity和地质时间参考GloTimeRef,前者描述时间、日期、时间段或时间间隔等信息,后者描述时间参考系信息。考虑时间轴,GloTimeEntity表达时间轴的特定部分,时间域通过GloTimeRef定义,而时间轴上的取值由GloTimeEntity定义。
3. 地质时空数据模型存储结构设计及面向矿山生产过程的应用
在矿产开采过程中,一方面产生日常记录的生产进度数据、基础地质数据等静态或者长程变化更新数据,另一方面产生生产现场过程监控和安全监控数据等实时变化数据。所积累的数据是一类典型的地质时空大数据。针对矿山开采过程数据管理,结合典型的王家岭煤矿数据开展了应用研究。
3.1 基于非关系型数据库的主要存储结构设计
在存储组织模型方面,遵循简单要素原则,以地质对象和模型为中心,设计了包括大规模硬件在线添加件耦合和时空数据集成两方面的可伸缩体系(图 6)。在硬件耦合层面,通过分片、复制技术和管-运分离机制,动态构建存储节点、查询节点和管理节点,从而提供存储、检索到管理等方面的可伸缩性;在数据集成层面,基于对象、版本、事件、多因素驱动模型和过程的多层次存储方案结构,实现时空索引与时间分片存储,支持高效存储与查询。
针对本文矿山开采数据具有非结构化和结构化并存以及属性丰富的特点,本文选择面向文档的非关系型数据库MongoDB作为数据库平台,基于地质时空数据逻辑组织管理模型和时空过程的非关系型分布式数据库架构,开展物理存储模型设计。数据存储涉及到三维地质模型、时空对象版本信息、配置信息等。若以存储方式分类,可分为文件存储及MongoDB数据库存储。
(1) 文件系统
在文件存储方式下,主要针对三维地质模型与时空对象版本信息、配置信息进行分开存储,时空对象及版本信息存储格式如表 1所示。
表 1 文件系统中时空对象存储结构Table 1. Storage structure of spatio-temporal object in file system地质时空对象数量 对象1信息 时空对象1名称 时空对象1类型 开采点设置标志 开采点坐标 地质时空对象所包含的版本数量 版本a起始时间 版本a结束时间 版本a关联三维地质模型集合 版本b起始时间 版本b结束时间 版本b关联三维地质模型集合 … … … 对象2信息 … … … … … …… 对象n信息 …… (2) MongoDB数据库系统
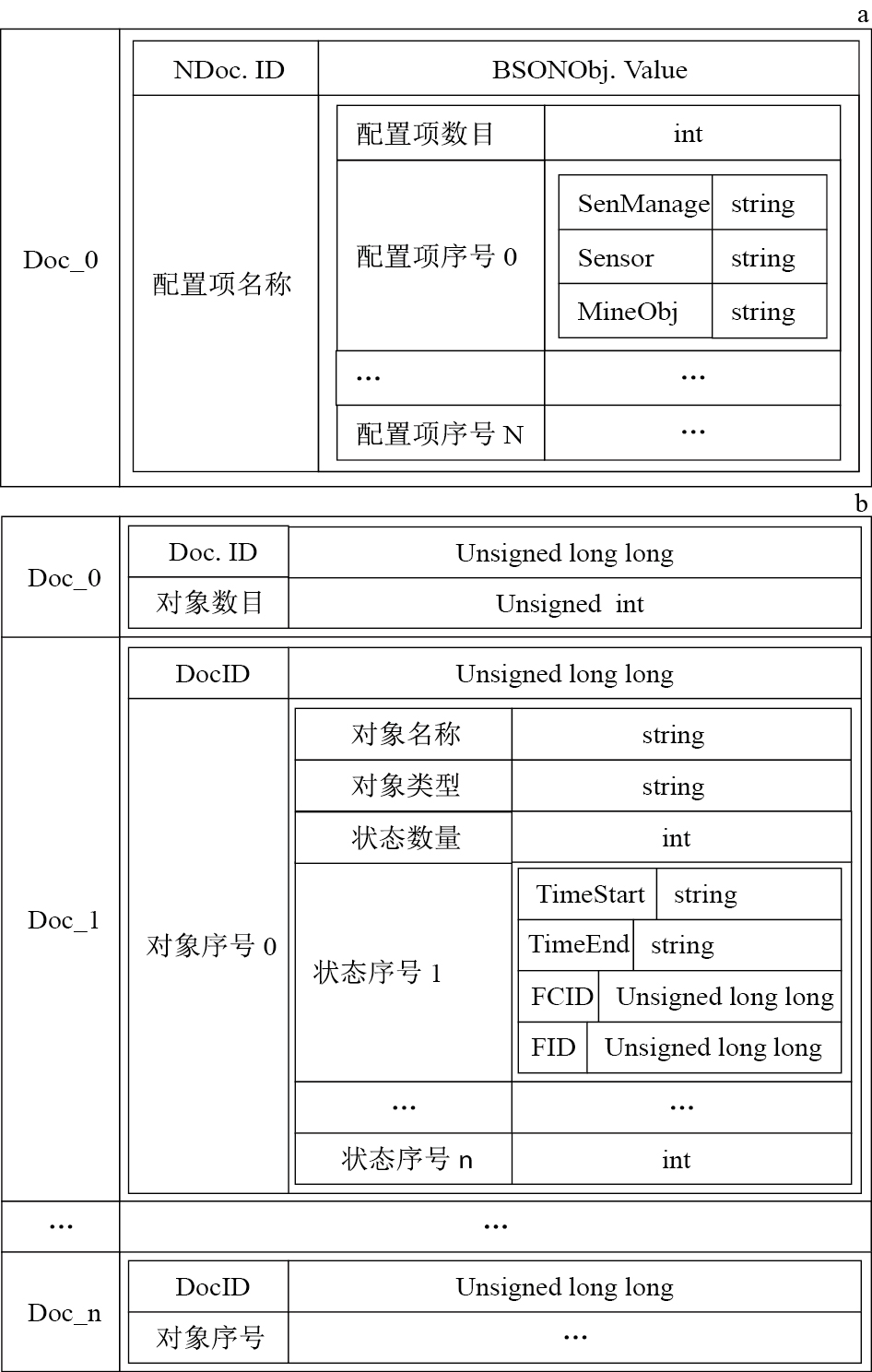
在MongoDB数据库中,数据分组存储在一系列集合中,每个集合由若干层次的文档组成。矿山动态开采监管系统的时空版本信息以及各类配置信息,都单独占用一个集合。时空对象数量信息及各对象信息分别存储于单个文档中,以BSON对象的形式存在,对象的具体信息及版本信息以较低层次的BSON对象存储。各类配置信息的配置项数目及各项配置具体信息分别占用一个独立的文档。每个观测对象都对应一个地质时空对象,对应关系在MongoDB数据库中的存储结构如图 7-a所示。在MongoDB数据库模式下,地质时空对象被存储在一个集合中,每个对象占用一个文档,版本作为子文档存储在对象文档的内部,具有可扩展性,整体的存储结构如图 7-b所示。
3.2 矿山开采过程数据应用实例
3.2.1 对象与版本综合管理三维地质模型
在地质信息系统中,矿体、岩层、巷道、采空区等地质对象或人工设施通过三维地质模型进行表达。随生产过程的推进,岩层、矿体等地质对象被开采的同时,采空区和巷道的长度逐渐增长,分布范围逐渐变广。在地质信息系统中可通过三维地质模型的替换、标记、增加、删除、修改等模拟这一过程。
根据三维地质模型在矿山开采过程中的变化趋势,可将其划分为增长型和削减型两类。增长型主要包括采空区、巷道,削减型主要包括矿体、岩层。一般情况下,某一区域的开采过程可按照时间划分为若干阶段。一个开采阶段内可能有多个不同类型的三维地质模型发生变化。可以针对某一类三维地质模型在某一开采阶段内的变化部分定义地质时空对象版本。版本只负责三维地质模型索引信息的管理,并无模型编辑功能。一个版本可以管理多个同类型的三维地质模型。因此,时空对象版本可以分为增长型和削减型。
3.2.2 基于OPC接口的动态过程构建方法
为实现模拟传感器数据接入效果,需构建OPC数据模拟模块。OPC数据模拟模块支持模拟数据读取、模拟数据的发送及停止,载入模拟数据后,根据预定义的规则、格式,将数据发送到OPC服务器端观测项。OPC服务器端最基本的数据结构单元是Item,每个Item都有各自的属性信息,包括Item的名称、数据类型、当前数据值等。选用Matrikon OPC Server for Simulation作为服务器端软件,用户定制服务器端观测项配置结构,并可以通过xml文件保存、打开和载入观测项配置信息。
当客户端连接到OPC的模拟服务器时,就能通过OPC提供的接口,对模拟数据进行访问,关键是建立OPC模拟数据源与传感器之间的关联。在关联之前需要保证安装有传感器,并配置传感器观测值的类型及其观测对象和作用范围等。基于OPC接口的传感器关联基本思路是:将传感器观测项与OPC的Item项进行绑定,一个传感器对象绑定一个或者多个观测项,可以是单个仪器设备的多个观测项,也可以是多个仪器设备的不同观测项(图 8)。
3.2.3 煤矿开采过程应用实例
利用王家岭煤矿首采区的钻孔数据、地质剖面图、采掘工程平面图、井上下对照图等,构建包括剖面(图 9)、地层、矿体、巷道在内的地质体和人工设施等三维地质模型,表现矿山某一时期的整体状态,包括地层结构、矿物分布、开采进度等。其中传感器数据和开采过程数据具有典型的地质时空数据特征。
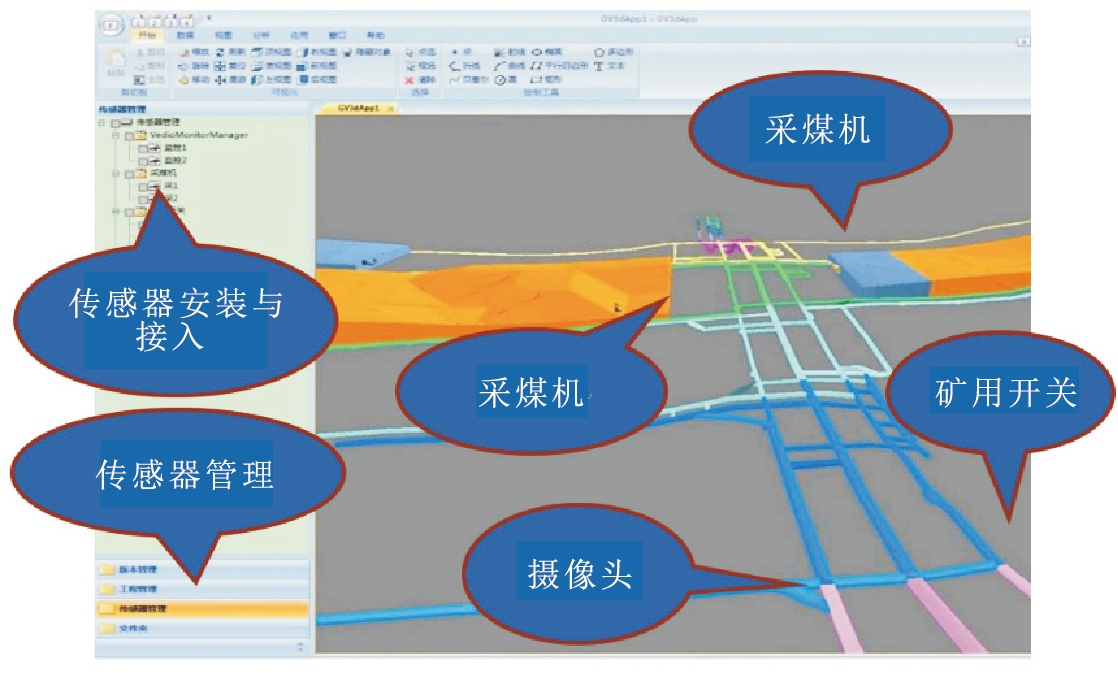
其次,利用系统实现三维传感器交互式安装与接入功能。在矿山动态开采监管动态监测中,都离不开各种传感器的运用,为了能真实反映各类传感器在三维空间中的分布,在三维煤矿开采场景中安装各类传感器(摄像头、挖煤机、采煤机、矿用开关等)(图 10)。
然后,利用OPC模拟服务器发送数据给传感器对象产生观测事件并驱动时空对象的演变,时空对象消费事件促使自身包含状态的增加、删除、修改,状态的变化导致其关联三维地质模型的变化,进而反映矿山的开采过程。实际采用了2012-2014年度共有3个计划采区,采区的开采宽度基本固定,每隔一个月记录一次当前进度位置。实验中提取的观测数据包含如下字段:开采起始位置、开采掘进方向、开采掘进距离、开采起始时间、开采终止时间,此外,需要根据观测数据所源自的计划采区,为每一条观测数据分配标识编码。如图 11-a所示,为矿山动态开采模拟初始阶段的矿山状态,可以清晰地看到矿山地下各类巷道的铺设情况、预开采矿体分布情况等。
如图 11-b所示,矿山开采在3个开采面同时进行,对应不同的时空地质对象,开采事件分别由3个预先绑定到OPC服务器的传感器对象(采煤机)接收后传递给时空对象,不同的时空地质对象只会响应和消费相关联的采煤机发出的事件。
伴随模拟过程的演变,时空对象版本管理发生变化(图 11-c),能够反映多个采煤机同时开采时的效果,矿山动态开采模拟持续一段时间后,采空区版本管理中版本的数量不断增加,各采煤机以不同的速率进行开采。在图 11各图的左边的时空对象树上可以看到时空对象的变化情况。
4. 结论与讨论
(1) 针对地质大数据、地质过程的静态与动态数据紧密结合的特点,采用面向对象和基于事件的思想,提出了事件多因素驱动的地质时空数据模型,并在此基础上开展了模型的基于对象与事件的地质大数据存储管理逻辑模型、基于系统工程库的管理结构和地质时空对象管理模型设计。
(2) 基于非关系型数据库和地质时空数据逻辑组织管理模型的非关系型分布式数据库架构,开展了物理存储模型设计,主要包括工程信息管理相关表、要素对象管理表、事件管理表、版本管理表和过程管理表等。
(3) 针对地质时空数据模型原型系统开发,融合三维地质建模、动态监测信息实时可视化等技术,构建了所需模型过程模拟的三维环境;结合实际的需求,通过交互安装传感器模型并绑定观测数据源,设计基于OPC接口的模拟数据产生事件、作用对象响应的矿山动态开采流程。利用王家岭煤矿首采区地质建模数据和报表数据等,开展模型的应用研究,实现多地质事件条件下矿山动态开采过程数据表达与记录,验证了模型的可行性和有效性。
该模型既可以融合数据多源与时空多维性,又能够支持时间关联与时间多粒性。具有支持复杂地质过程成因分析、动态模拟与实时响应等特点,不仅有助于地质时空大数据的表达与存储管理,而且可以支持地质专家和技术人员开展更为深入的地质时空过程推理和分析。
随着云计算、物联网及无线传感网等技术的兴起,大规模时空数据在地质信息领域的应用日益广泛,地质时空数据模型将会在其中发挥越来越重要的作用[28-33]。进一步的工作包括:①多源地质时空大数据的高维动态时空索引与动态调度问题,以及多用户动态调度过程中分布式数据节点负载平衡问题[34-36];②关于地质时空数据拓扑关系的定义、表达、存储以及地质模型发生改变时拓扑数据的自动更新与重构问题,也是模型研究相关的难点和热点问题。
-
表 1 文件系统中时空对象存储结构
Table 1. Storage structure of spatio-temporal object in file system
地质时空对象数量 对象1信息 时空对象1名称 时空对象1类型 开采点设置标志 开采点坐标 地质时空对象所包含的版本数量 版本a起始时间 版本a结束时间 版本a关联三维地质模型集合 版本b起始时间 版本b结束时间 版本b关联三维地质模型集合 … … … 对象2信息 … … … … … …… 对象n信息 …… -
[1] 严光生, 薛群威, 肖克炎, 等.地质调查大数据研究的主要问题分析[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1273-1279. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.004 [2] 肖克炎, 孙莉, 李楠, 等.大数据思维下的矿产资源评价[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1266-1272. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.003 [3] 王登红, 刘新星, 刘丽君.地质大数据的特点及其在成矿规律、成矿系列研究中的应用[J].矿床地质, 2015, 34(6):1143-1154. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kcdz201506005 [4] 周永章, 黎培兴, 王树功, 等.矿床大数据及智能矿床模型研究背景与进展[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2017, 36(2):334-339. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kwysdqhxtb201702016 [5] Carr G R, Andrew A S, Denton G J.The "Glass Earth":Geochemical frontiers in exploration through cover[J].Australian Institute of Geoscientists Bulletin, 1999, 28:33-40. https://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=7d2f0272938a957ebf839da4f81479d8&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [6] 吴冲龙, 刘刚."玻璃地球"建设的现状、问题、趋势与对策[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1280-1287. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.005 [7] 郭华东, 王力哲, 陈方, 等.科学大数据与数字地球[J].科学通报, 2014, 59(12):1047-1054. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/kjcgglyyj201608018 [8] Lake B, Salakhutdinov R, Tenenbaum J.Human-level concept learning through probabilistic program induction[J].Science, 2015, 266:1332-1338. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c50ea5bb88b1527b4c774daffe17c013 [9] 赵鹏大.大数据时代数字找矿与定量评价[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1255-1259. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.001 [10] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 张夏林, 等.地质科学大数据及其利用的若干问题探讨[J].科学通报, 2016, 61(16):1797-1807. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201616010 [11] 张旗, 周永章.大数据正在引发地球科学领域一场深刻的革命:《地质科学》2017年大数据专题代序[J].地质科学, 2017, 52(3):637-648. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkx201703001 [12] 黄少芳, 刘晓鸿, 孙玲, 等.初论大数据时代地质资料信息集成与服务[J].中国矿业, 2016, 25(2):170-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2016.02.033 [13] Langran G.Time in geographic information systems, technical issues in geographic information systems[M].Abington:Taylor & Francis, 1992. [14] 曹闻.时空数据模型及其应用研究[D].郑州: 解放军信息工程大学, 2011. [15] Koubarakis M.Spatio-temporal databases:The chorochronos approach[M].Berlin:Springer Science & Business Media, 2003. [16] Worboys M F.A unified model for spatial and temporal information[J].The Computer Journal, 1994, 37(1):26-34. doi: 10.1093/comjnl/37.1.26 [17] 郑扣根, 谭石禹, 潘云鹤.基于状态和变化的统一时空数据模型[J].软件学报, 2001, 12(9):1360-1365. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb200109013 [18] Peuquet D J, Duan N.An event-based spatiotemporal data model (ESTDM) for temporal analysis of geographical data[J].International Journal of Geographical Information Systems, 1995, 9(1):7-24. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1080/02693799508902022 [19] Chen J, Jiang J.An event-based approach to spatio-temporal data modeling in land subdivision systems[J].GeoInformatica, 2000, 4(4):387-402. doi: 10.1023/A:1026565929263 [20] 孟令奎, 赵春宇, 林志勇, 等.基于地理事件时变序列的时空数据模型研究与实现[J].武汉大学学报:信息科学版, 2003, 28(2):202-207. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/whchkjdxxb200302015 [21] 龚健雅, 李小龙, 吴华意.实时GIS时空数据模型[J].测绘学报, 2014, 43(3):226-232. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=chxb201403002 [22] 舒红, 陈军, 杜道生, 等.面向对象的时空数据模型[J].武汉测绘科技大学学报, 1997, 22(3):229-233. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1671-8860.1997.03.009 [23] 易宝林, 冯玉才, 曹忠升.2003.基于对象行为的时空拓扑模型[J].小型微型计算机系统, 2003, 24(6):1046-1049. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1220.2003.06.027 [24] 尹章才, 李霖, 艾自兴.基于图论的时空数据模型研究[J].测绘学报, 2003, 32(2):168-172. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.2003.02.015 [25] 龚健雅.GIS中面向对象时空数据模型[J].测绘学报, 1997, 26(4):289-298. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1595.1997.04.002 [26] 阙翔.面向动态过程模拟和实时表达的地质时空数据模型研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2015. [27] 田善君.面向地质大数据存储管理的时空数据模型研究[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2016. [28] Bristol S, Euliss N H, Booth N L.Science strategy for core science systems in the U.S.Geological Survey, 2013-2023-Public Review Release[R].Denver: U.S.Geological Survey, 2012. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/271508464_Science_Strategy_for_Core_Science_Systems_in_the_US_Geological_Survey_20132023Public_Review_Release [29] Wang L Z, Chen D, Hu Y, et al.Towards enabling cyberinfrastructure as a service in clouds[J].Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2013, 39:3-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=81bf0a5efdc4c0f540f7e7d0a2dc5715 [30] 吴冲龙, 刘刚, 田宜平, 等.论地质信息科学[J].地质科技情报, 2005, 24(3):1-8. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200503001 [31] 吕霞, 李健强, 龚爱华, 等.基于云架构的中国地质调查信息网格平台关键技术研究与实现[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1323-1332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.010 [32] 李超岭, 李健强, 张宏春, 等.智能地质调查大数据应用体系架构与关键技术[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1288-1299. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.006 [33] 陈建平, 李婧, 崔宁, 等.大数据背景下地质云的构建与应用[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):1260-1265. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.07.002 [34] 谭永杰.地质大数据与信息服务工程技术框架[J].地理信息世界, 2016, 23(1):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-1586.2016.01.001 [35] He Z, Wu C, Liu G, et al.Decomposition tree:A spatio-temporal indexing method for movement big data[J].Cluster Computing, 2015, 18:1481-1492. doi: 10.1007/s10586-015-0475-3 [36] 李婧, 陈建平, 王翔.地质大数据存储技术[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(8):1589-1594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2015.08.018 期刊类型引用(23)
1. 张利国,丁雨淋,朱庆,陈曦,李函侃,郭永欣,王玮. 铁路地理地质数据“本体域-变化域-状态域”三域关联的集成表达模型. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版). 2024(06): 1018-1027 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 张坤,花卫华,李叶繁,车文超,冯武超. 地质信息化平台发展综述与研究展望. 铁道建筑技术. 2024(07): 54-56+148 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 吴峥,王方建,董翔,翟颖,丁艳青. 地震观测数据融合存储技术研究. 地震地磁观测与研究. 2023(01): 115-119 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 明梓,刘伟,李旸,崔俊杰,刘刚,李佳惠,雷梦婷. 基于多层Voronoi图索引的非点型空间对象区域查询方法研究. 软件导刊. 2023(11): 49-56 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 刘刚,陈根深,陈麒玉,吴雪超. 基于Web的大规模三维空间模型高效可视化关键技术. 地理空间信息. 2023(12): 8-13 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 张颖,徐爱蓉,牟锴,沈星辰,曹沁愉. 基于多维大数据的长三角电力服务快速响应模型. 电子设计工程. 2022(03): 154-157+162 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 黄波. 矿井生产信息三维系统的设计与实现. 陕西煤炭. 2022(03): 106-109 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 王永庆,李山,杨真亮,刘彩杰,隋晓玲,刘向东. 胶东玲南-水旺庄巨型金矿床三维地质特征及断裂控矿规律. 地质通报. 2022(06): 977-985 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 刘文聪,张春菊,汪陈,张雪英,朱月琴,焦守涛,鲁艳旭. 基于BiLSTM-CRF的中文地质时间信息抽取. 地球科学进展. 2021(02): 211-220 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 李梅,姜展,姜龙飞,孙振明. 三维可视化技术在智慧矿山领域的研究进展. 煤炭科学技术. 2021(02): 153-162 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 彭晶晶,罗代洪,林锴,刘成海,尚颖. 基于文献资源的Re-Os同位素定年数据库建设研究. 岩矿测试. 2021(03): 425-434 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 刘江涛,赵洁,吴发富. 结构方程模型及其在地学数据建模中的回顾与展望. 地质力学学报. 2021(03): 350-364 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 程宇翔,梁均军,刘洪波,赵翔宇. 时空数据转换服务系统设计与应用. 地理空间信息. 2021(09): 116-118+8 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 袁焦,王珣,李高丰,刘勇,伏坤. 400km/h高速铁路地质灾害及基础设施监测系统研究. 高速铁路技术. 2021(05): 23-30 .  百度学术
百度学术15. 袁焦,王珣,伏坤,刘勇,邹文露. 艰险山区铁路地质灾害监测云平台的探讨与实现. 高速铁路技术. 2021(06): 20-25 .  百度学术
百度学术16. 张夏林,吴冲龙,周琦,翁正平,袁良军,何昆洋,张权莉,杨炳南. 基于勘查大数据和数据集市的锰矿床三维地质建模. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 12-20 .  本站查看
本站查看17. 徐凯,袁良军,杨炳南,孔春芳,张夏林,郑境,周琦,吴冲龙. 黔东北伴生-次生矿物遥感数据组合式挖掘与隐伏锰矿信息提取. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 37-43 .  本站查看
本站查看18. 张夏林,师志龙,吴冲龙,张明林,周琦,袁良军,胡郑斌,杨炳南. 基于移动设备的野外地质大数据智能采集和可视化技术. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 21-28 .  本站查看
本站查看19. 吴冲龙,刘刚,周琦,张夏林,徐凯. 地质科学大数据统合应用的基本问题. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 1-11 .  本站查看
本站查看20. 王统,田宜平,罗莹莹,张睿. 基于地质大数据与构造语义约束的断层建模. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 69-75 .  本站查看
本站查看21. 何珍文,吴冲龙,刘刚,田宜平,张夏林,陈麒玉. 地学时序大数据的相似性度量与索引方法综述. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 44-50 .  本站查看
本站查看22. 陈麒玉,刘刚,何珍文,张夏林,吴冲龙. 面向地质大数据的结构-属性一体化三维地质建模技术现状与展望. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 51-58 .  本站查看
本站查看23. 田宜平,吴冲龙,翁正平,刘刚,张志庭,陈麒玉. 地质大数据可视化关键技术探讨. 地质科技通报. 2020(04): 29-36 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(3)
-






 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:



 百度学术
百度学术













