Using CT scanning technology to investigate microscopic pore structure characteristics of low-permeability reservoir rocks after water sensitivity experiments
-
摘要:
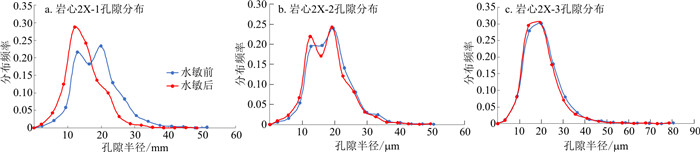
为了研究水敏效应对低渗油藏微观孔隙结构特征的影响,将CT在线扫描技术和岩心驱替实验相结合,开展了低渗油藏不同渗透率岩心水敏性评价实验,对水敏过程中孔、喉半径分布特征、配位数、孔隙变化特征、物性参数变化及对储层渗流能力的影响进行了实验研究,并绘制了水敏前后极限注采井距对比图版。结果表明,随着渗透率降低,水敏效应对孔隙、喉道伤害程度越大、平均孔喉配位数减少越多。两者共同作用是造成储层启动压力梯度增加的主要原因;水敏效应对储层喉道伤害程度远大于对孔隙伤害程度;水敏效应造成黏土膨胀、颗粒运移几乎发生在所有孔隙中,但对岩心整体孔隙结构和分布特征影响不大。通过极限注采井距可知,水敏效应造成新沟嘴组低渗油藏极限注采井距减少了153 m,需要通过加密井来调整注采井距,改善注水波及范围。该研究结果对长期注水的水敏性低渗储层开发调整具有现场指导意义。
Abstract:CT scanning and core flooding experiments were combined to investigate the change in microscopic pore structure of low-permeability reservoir rocks due to the water sensitivity effect. Water sensitivity experiments were conducted for low-permeability reservoirs using different permeability core plugs to study the pore throat radius distribution, coordination number, pore structure variation, physical property parameter variation, and effects on the seepage capacity. The comparison plates of the limit injection-production spacing were drawn. The results indicate that the pore throat damage increases while the mean coordination number decreases with the reduction of permeability, which leads to a higher flow resistance and a stronger damage to the microscopic pore structure. These combined effects lead to an increase in the starting pressure gradient. In addition, the damage extent of reservoir throats is much larger than that of pores in the reservoir. Moreover, the swelling of clay minerals and the particle migration mostly present in the pore space due to the water sensitivity effect, which would hardly influence the whole pore structure and distribution feature of the core plug. Furthermore, according to the limit injection-production spacing plates, the limit injection-production spacing of the Xingouzuizu Formation low-permeability reservoir decreases by 153 m, which is caused by the effect of water sensitivity. The injection-production well spacing must be adjusted by the infill well, which can be used to improve the injected water swept volume. This research could provide certain practical guidance for the development adjustment of low-permeability reservoirs featuring the water sensitivity effect under a long period of waterflooding.
-
表 1 实验岩心参数
Table 1. Physical properties of core plugs
岩样 气测渗透率/10-3 μm2 气测孔隙度/% 长度/cm 直径/cm 2X-1 2.76 9.84 7.06 2.48 2X-2 12.71 15.91 4.13 2.48 2X-3 55.91 17.35 6.97 2.48 表 2 模拟地层水离子组成数据
Table 2. Ionic composition of the simulated brine
Ca2+ Mg2+ OH- SO42- CO32- K++Na+ Cl- ρB/(mg·L-1) 1 503.0 243.0 25.5 480.3 60.0 47 857.5 29 175.5 表 3 水敏实验岩心基础物性参数对比
Table 3. Comparison of the physical properties of core plugs before and after water sensitivity tests
岩心编号 气测渗透率/10-3 μm2 气测孔隙度/% 水敏后渗透率/10-3 μm2 水敏程度/% 水敏前CT孔隙度/% 水敏后CT孔隙度/% 孔隙度损害率/% 2X-1 2.76 9.84 1.00 63.91 9.82 8.94 8.96 2X-2 12.71 15.91 8.92 29.83 15.80 14.68 7.09 2X-3 55.91 17.35 47.39 15.24 17.45 16.47 5.62 -
[1] 程亮, 刘德华, 夏志刚, 等. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷新沟嘴组致密油成藏模式与分布规律[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 39(6): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.06.004Cheng L, Liu D H, Xia Z G, et al. Accumulation model and distribution regularity of Xingouzui Formation tight oil in Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Edition of Natural Science, 2015, 39(6): 34-41(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.06.004 [2] Tang Y J, Zhang J Z, Li M J, et al. Origin of crude oils from the Paleogene Xingouzui Formation in the Jiangling Depression of Jianghan Basin, Central China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2020, 195: 107976. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107976 [3] 唐洪明, 龚小平, 唐浩轩, 等. 页岩敏感性损害评价方法及损害机理[J]. 中南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2016, 47(4): 1227-1235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201604020.htmTang H M, Gong X P, Tang H X, et al. Evaluation method and damage mechanism of shale formation sensitivity damage[J]. Journal of Central South University: Edition of Science and Technology, 2016, 47(4): 1227-1235(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNGD201604020.htm [4] 廖纪佳, 唐洪明, 朱筱敏, 等. 特低渗透砂岩储层水敏实验及损害机理研究: 以鄂尔多斯盆地西峰油田延长组第8油层为例[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2012, 33(2): 321-328. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201202023.htmLiao J J, Tang H M, Zhu X M, et al. Water sensitivity experiment and damage mechanism of sandstone reservoirs with ultra-low permeability: A case study of the eighth oil layer in the Yanchang Formation of Xifeng Oilfield, Ordos Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2012, 33(2): 321-328(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201202023.htm [5] Wang B Y, Qin Y, Shen J, et al. Experimental study on water sensitivity and salt sensitivity of lignite reservoir under different pH[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 172: 1202-1214. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.09.036 [6] 祝琦. 利用核磁共振研究致密砂岩油气藏水敏性伤害[J]. 石油化工应用, 2014, 33(5): 25-27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2014.05.007Zhu Q. An application study on water sensitivity damage of tight sandstone reservoir by nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)[J]. Petrochemical Industry Application, 2014, 33(5): 25-27(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5285.2014.05.007 [7] 冷振鹏, 马德胜, 吕伟峰, 等. CT扫描技术在水敏伤害评价中的应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2015, 22(5): 100-103. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201505021.htmLeng Z P, Ma D S, Lü W F, et al. Application of CT scanning technology in water-sensitivity damage evaluation[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2015, 22(5): 100-103(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201505021.htm [8] 李俊键, 成宝洋, 刘仁静, 等. 基于数字岩心的孔隙尺度砂砾岩水敏微观机理[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(5): 594-603. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905009.htmLi J J, Chen B Y, Liu R J, et al. Microscopic mechanism of water sensitivity of pore-scale sandy conglomerate based on digital core[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(5): 594-603(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201905009.htm [9] Al-Yaseri A Z, Lebedev M, Vogt S J, et al. Pore-scale analysis of formation damage in Bentheimer sandstone with in-situ NMR and micro-computed tomography experiments[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2015, 129: 48-57. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2015.01.018 [10] Fang W C, Jiang H Q, Li J, et al. A new experimental methodology to investigate formation damage in clay-bearing reservoirs[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 143: 226-234. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.02.023 [11] 王伟, 宋渊娟, 黄静, 等. 利用高压压汞实验研究致密砂岩孔喉结构分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 22-30. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402Wang W, Song Y J, Huang J, et al. Fractal characteristics of pore-throat structure in tight sandstone using high-pressure mercury intrusion porosimetry[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 22-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0402 [12] 孟子园, 孙卫, 刘登科, 等. 联合压汞法的致密储层微观孔隙结构及孔径分布特征: 以鄂尔多斯盆地吴起地区长6储层为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 208-216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902024.htmMeng Z Y, Sun W, Liu D K, et al. Combined mercury porosimetry to characterize the microscopic pore structure and pore size distribution of tight reservoirs: A case of Chang 6 reservoir in Wuqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 208-216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902024.htm [13] 曾宏斌, 王芙蓉, 罗京, 等. 基于低温氮气吸附和高压压汞表征潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层孔隙结构特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(5): 1-12. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022Zeng H B, Wang F R, Luo J, et al. Characterization of pore structure of intersalt shale oil reservoir by low temperature nitrogen adsorption and high pressure mercury pressure methods in Qianjiang Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(5): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0022 [14] 冷振鹏, 杨胜建, 吕伟峰, 等. 致密油孔隙结构表征方法: 以川中致密油储层岩心为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2016, 23(2): 161-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201602007.htmLeng Z P, Yang S J, Lü W F, et al. Pore structure characterization for tight oil reservoirs: Taking Chuanzhong tight oil reservoir cores as examples[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2016, 23(2): 161-165(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201602007.htm [15] 雷浩, 何建华, 胡振国. 潜江凹陷页岩油藏渗流特征物理模拟机影响因素分析[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(3): 94-98. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201903017.htmLei H, He J H, Hu Z G. Physical simulation and influencing factor analysis of the flow characteristics in the shale oil reservoir of Qianjiang Depression[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(3): 94-98(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201903017.htm [16] Lei H, He L, Li R S, et al. Effects of boundary layer and stress sensitivity on the performance of low-velocity and one-phase flow in a shale oil reservoir[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2019, 180: 186-196. [17] 操应长, 葸克来, 刘可禹, 等. 陆相湖盆致密砂岩油气储层储集性能表征与成储机制: 以松辽盆地南部下白垩统泉头组四段为例[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(3): 247-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201803001.htmCao Y C, Xi K L, Liu K Y, et al. Reservoir properties characterization and its genetic mechanism for tight sandstone oil and gas reservoir in lacustrine basin: The case of the Fourth Member of Lower Cretaceous Quantou Formation in the southern Songliao Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(3): 247-265(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201803001.htm [18] 高树生, 胡志明, 刘华勋, 等. 不同岩性储层的微观孔隙特征[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 248-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602012.htmGao S S, Hu Z M, Liu H X, et al. Microscopic pore characteristics of different lithological reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 248-256(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201602012.htm [19] 邓世冠, 吕伟峰, 刘庆杰, 等. 利用CT技术研究砾岩驱油机理[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(3): 330-335. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403011.htmDeng S G, Lv W F, Liu Q J, et al. Research on displacement mechanism in conglomerate using CT scanning method[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(3): 330-335(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201403011.htm [20] 韩文学, 高长海, 韩霞. 核磁共振及微、纳米CT技术在致密储层研究中的应用: 以鄂尔多斯盆地长7段为例[J]. 断块油气田, 2015, 22(1): 62-66. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201501013.htmHan W X, Gao C H, Han X. Application of NMR micrometer and nanometer CT technology in research of tight reservoir: Taking Chang 7 Member in Ordos Basin as an example[J]. Fault-Block Oil & Gas Field, 2015, 22(1): 62-66(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DKYT201501013.htm [21] 李芳芳, 高旺来, 杨胜来, 等. 安塞油田高52区低渗油藏储层敏感性研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 2012, 19(4): 126-129, 157. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201204033.htmLi F F, Gao W L, Yang S L, et al. Study on reservoir sensitivity for low permeability reservoirs in the Gao 52 block of Ansai Oilfield[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2012, 19(4): 126-129, 157(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201204033.htm [22] 宋金波, 张雨晨, 贾维霞, 等. 高泥质砂岩油藏防膨控砂体系性能评价与应用[J]. 特种油气藏, 2019, 26(4): 160-164. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201904028.htmSong J B, Zhang Y C, Jia W X, et al. Performance evaluation and application of anti-swelling and sand-control system in high argillaceous sandstone reservoir[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 2019, 26(4): 160-164(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TZCZ201904028.htm [23] 江建林, 岳湘安, 高震, 等. 特低渗透油藏注水黏土稳定剂及评价方法: 以海拉尔盆地贝尔油田为例[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2011, 18(2): 105-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201102029.htmJiang J L, Yue X A, Gao Z, et al. Study on clay stabilizer and evaluation method for extra-low permeability oil field: A case study of Beier Oilfield[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2011, 18(2): 105-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201102029.htm [24] 汪新光, 张冲, 张辉, 等. 基于微观孔隙结构的低渗透砂岩储层分类评价[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 93-103. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429Wang X G, Zhang C, Zhang H, et al. Classification and evaluation of low-permeability sand reservoir based on micro-pore structure[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 93-103(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0429 -





 下载:
下载: