Pore characteristics and its controlling factors in the Middle Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs of the Shengbei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin
-
摘要:
吐哈盆地中侏罗统致密砂岩储层是非常规致密油气勘探开发的主要目的层。以胜北洼陷8口井中侏罗统致密砂岩样品为主要研究对象,从储层岩石学特征、成岩作用、物性、孔隙结构等方面系统刻画了研究区中侏罗统致密砂岩储层特征,探讨了影响储层孔隙发育的主要因素。研究结果表明胜北洼陷中侏罗统低孔-特低渗致密砂岩储层以长石岩屑砂岩为主,岩屑砂岩次之;该储层遭受了强烈的压实作用,矿物胶结、交代和溶蚀现象明显,孔隙类型以次生长石溶蚀孔为主,同时发育矿物残余粒间孔、石英粒内溶蚀孔、黏土矿物层间孔和微裂缝等;储层内5~50 nm孔喉最为发育,然而储层物性则主要受50 nm~1 μm和100~800 μm孔喉发育程度控制,主要体现在两者孔喉体积与孔隙度和渗透率呈良好的正相关关系。储层物性与石英和长石含量呈正相关关系,与黏土矿物和碳酸盐矿物含量呈负相关关系,其原因一方面是该储层遭受了强烈压实,石英颗粒破裂导致其内微裂缝较发育,刚性石英含量增加有利于保存部分原始粒间孔,其内溶蚀孔也较发育,含有机酸的烃类流体运移至中侏罗统地层内促使长石发生了大规模溶蚀,形成大量次生长石溶蚀孔,孔径50 nm~1 μm和100~800 μm孔喉相对发育,储层物性因此得以改善;另一方面黏土矿物和碳酸盐矿物多以胶结物形式充填在原始粒间孔和次生微裂缝内,方解石交代长石降低了长石溶蚀的增孔效应,不利于孔径50 nm~1 μm和100~800 μm孔喉发育和储层物性改善。因此,研究区储层孔隙发育与早期原始沉积环境和后期成岩作用关系密切,压实作用、长石溶蚀和自生矿物胶结对储层孔隙发育及物性具有关键控制效应。该研究对吐哈盆地胜北洼陷中侏罗统致密砂岩油气有利勘探区分布预测具有指导意义。
Abstract:The Middle Jurassic sandstone reservoirs of the Turpan-Hami Basin are the main targets for unconventional tight oil and gas exploration and development.To better understanding the main controlling factors of pore characteristics in the Middle Jurassic tight sandstones of the Shengbei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin, a comprehensive investigation referring to lithology, diagenesis, physical properties, and pore structure was conducted on samples obtained from 8 wells. The results indicate that the Middle Jurassic tight sandstone reservoir characterized by low porosity and ultralow permeability primarily contains feldspar lithic sandstones, followed by lithic sandstones.These sandstone reservoirs suffered strong compaction and complicated mineral cementation, replacement, and dissolution. These sandstone reservoirs are dominated by the secondary pores generated by feldspar dissolution, with some residual interparticle pores, quartz dissolution pores, clay mineral interlayer pores, and microfractures.Pore throat of 5-50 nm most widely appears in these reservoirs, while the porosity and permeability of these reservoirs mainly depend on the pore throats of 50 nm-1 μm and 100-800 μm, as indicated by the good positive correlations between pore throats and volumes. Both porosity and permeability correlate positively with the quartz and feldspar contents but negatively with the clay and carbonate contents. These correlations were supposed to be caused by two factors: ①strong compaction led to the loss of most interparticle pores but kept the residual interparticle pores associated with rigid quartz, and caused the occurrence of microfractures and dissolution pores within the quartz; the migration of hydrocarbon fluids containing organic acids into the Middle Jurassic reservoirs resulted in the significant dissolution of feldspar and generation of secondary dissolution pores. This process promoted theoccurrence of pore throats of 50 nm-1 μm and 100-800 μm and improved the porosity and permeability. ②The primary interparticle pores and secondary microfractures were filled with authigenic clay or carbonate cement; the replacement of feldspar by calcite disturbed the positive effects of feldspar dissolution on the porosity and permeability, which reduced the occurrence of 50 nm-1 μm and 100-800 μm pore throats and the physical properties of these reservoirs.Therefore, the occurrence of pores was closely related to the early sedimentary environments and the later diagenesis after deposition.More importantly, mechanical compaction, feldspar dissolution, and authigenic mineral cementation played crucial roles in regulating the occurrence of pores and the physical properties of these sandstone reservoirs in the study area.This study should be helpful in predicting the favorable exploration areas of tight oil and gas in the Middle Jurassic sandstone reservoirs in the Shengbei Sag, Turpan-Hami Basin.
-
Key words:
- Turpan-Hami Basin /
- Shengbei Sag /
- tight sandstone /
- pore /
- compacting action /
- feldspar corrosion
-
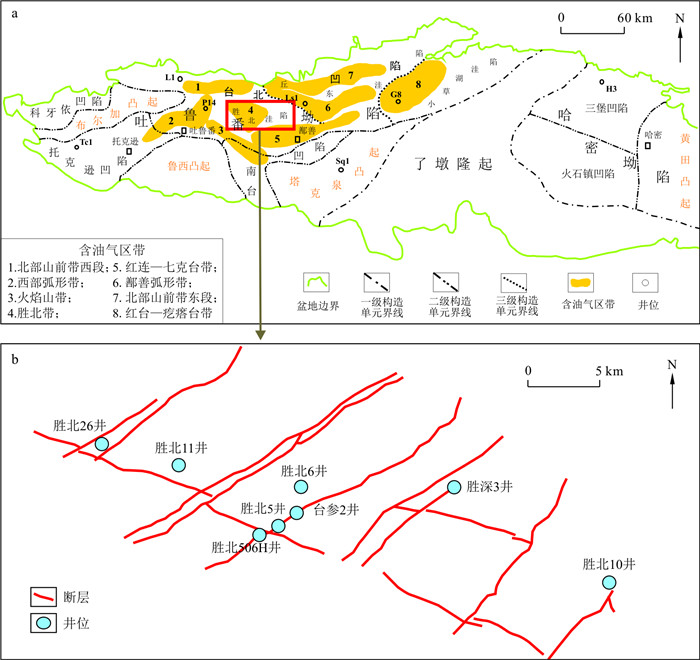
图 1 吐哈盆地含油气区带分布(a)和胜北洼陷研究井位分布图(b)(据文献[21]修改)
Figure 1. Distribution map of petroleum regions of Turpan-Hami Basin (a) and well locations (b) in Shengbei Sag
图 2 吐哈盆地地层综合柱状图(据文献[21]修改)
Figure 2. Comprehensive stratigraphic column of the Turpan-Hami Basin
图 4 胜北洼陷中侏罗统致密砂岩储层薄片观测
a.胜深3井,J2s,4 624.16 m,正交光下刚性颗粒石英破裂,粒内可见清晰裂纹,碎屑颗粒间呈线接触与线-凹凸接触;b.台参2井,J2s,4 481.84 m,塑性矿物云母挤压弯曲变形;c.胜深3井,J2x,4 891.62 m,颗粒间呈线-凹凸接触,颗粒定向排列;d.胜北11井,J2q,4 208.80 m,正交光下含铁方解石胶结在碎屑颗粒间;e.台参2井,J2x,4 768.68 m,正交光下可见长石溶蚀,方解石交代长石颗粒,沥青质充填溶蚀孔;f.胜北6井,J2s,4 323.09 m,含铁方解石呈锯齿状或港湾状交代长石颗粒
Figure 4. Thin section observations of the Middle Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs in the Shengbei Sag
图 5 胜北洼陷中侏罗统致密砂岩储层孔隙类型
a.胜北5井,J2q,4 002.13 m,灰色中细砂岩,长石粒内溶蚀孔普遍发育;b.胜深3井,J2s,4 452.01 m,灰色中砂岩,长石粒内溶蚀孔发育;c.胜北11井,J2s,4 386.62 m,浅灰色中砂岩,长石粒内溶蚀孔普遍发育;d.胜深3井,J2s,4 452.01 m,灰色中砂岩,发育石英粒内溶蚀孔;e.胜北10井,J2s,3 900.00 m,灰色荧光粗-中砂岩,发育书页状或鳞片状高岭石,并充填粒间孔中;f.胜深3井,J2s,4 452.01 m,灰色中-细砂岩,粒间孔中充填呈玫瑰花瓣状绿泥石;g.台参2井,J2q,4 069.40 m,灰绿色细砂岩,发育细丝状伊利石;h. 台参2井,J2q,4 069.40 m,灰绿色细砂岩,微裂缝发育;i.胜深3井,J2x,4 891.62 m,灰色粗砂岩,粒间微裂缝发育
Figure 5. Types of pores in Middle Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs Shengbei Sag
图 9 胜北洼陷中侏罗统致密砂岩储层不同直径的孔喉体积分布
a.灰色荧光中砂岩,J2q,4 038.27 m,偏光下可见石英颗粒内溶蚀孔发育;b.灰色荧光细砂岩,J2s,4 138.11 m,石英颗粒内溶蚀孔发育,并存在微裂缝;c.灰色荧光中砂岩,J2s,4 141.01 m,镜下可见颗粒间残余粒间孔,以及碳酸盐矿物内部溶蚀孔;d.灰色荧光中砂岩,J2s,4 235.70 m,单偏光下可见碎屑颗粒间残余粒间孔发育;e.灰色荧光粗砂岩,J2s,4 236.86 m,碎屑颗粒间与颗粒接触边缘发育残余粒间孔;f.灰色荧光粗砂岩,J2s,4 236.86 m,长石粒内溶蚀孔发育
Figure 9. Pore throat volumes distributions with different diameters in Middle Jurassic tight sandstone reservoirs in Shengbei Sag
表 1 胜北洼陷中侏罗统致密砂岩孔隙度、渗透率、高压压汞总孔体积以及不同直径孔喉体积与矿物组成相关性分析统计
Table 1. Statistical table of correlations analysis of porosity, permeability, total pore volume of high-pressure mercury penetration and volume of pore throats with different diameters, and mineral compositions of tight sandstone samples from the Middle Jurassic, Shengbei Sag
相关性 孔隙度/% 渗透率/10-3 μm2 TV 孔喉直径 石英 长石 黏土矿物 碳酸盐矿物 < 5 nm [5, 10)nm [10, 50)nm [50, 100)nm [100, 1 000)nm [1, 10)μm [10, 100)μm [100, 800]μm 孔隙度 1.00 渗透率 0.53 1.00 TV 0.45 0.80 1.00 孔喉 < 5 nm -0.35 -0.13 -0.02 1.00 [5, 10) nm 0.02 -0.15 -0.23 0.18 1.00 [10, 50) nm 0.45 -0.02 0.15 -0.26 0.32 1.00 [50, 100) nm 0.50 0.56 0.65 -0.38 -0.29 0.53 1.00 [100, 1 000) nm 0.52 0.72 0.68 -0.36 -0.25 0.32 0.84 1.00 [1, 10) μm 0.13 0.45 0.48 0.02 -0.43 -0.04 0.32 0.04 1.00 [10, 100) μm 0.31 0.06 -0.08 -0.21 0.29 -0.10 -0.11 -0.02 -0.34 1.00 [100, 800] μm 0.51 0.48 0.62 -0.35 -0.28 -0.04 0.21 0.08 0.36 0.15 1.00 石英 0.33 0.21 0.22 -0.17 -0.10 0.43 0.30 0.32 0.17 -0.11 0.14 1.00 长石 0.14 0.04 0.16 -0.18 -0.14 0.10 0.40 0.29 0.15 0.04 0.12 -0.34 1.00 黏土矿物 -0.30 -0.14 -0.19 0.01 0.26 -0.38 -0.38 -0.28 -0.49 -0.15 0.14 -0.71 -0.15 1.00 碳酸盐矿物 -0.22 -0.14 -0.31 0.55 0.07 -0.18 -0.36 -0.25 -0.07 0.15 -0.51 -0.11 -0.23 -0.22 1.00 注:相关系数在0.5以上定义为显著相关;TV.总孔隙体积,单位μm3 -
[1] 邹才能, 张光亚, 陶士振, 等. 全球油气勘探领域地质特征、重大发现及非常规石油地质[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(2): 129-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201002002.htmZou C N, Zhang G Y, Tao S Z, et al. Geological features, major discoveries and unconventional petroleum geology in the global petroleum exploration[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2010, 37(2): 129-145(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201002002.htm [2] 邹才能, 陶士振, 侯连华, 等. 非常规油气地质[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2011.Zou C N, Tao S Z, Hou L H, et al. Unconventional petroleum geology[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2011(in Chinese). [3] 邹才能, 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 等. 常规与非常规油气聚集类型、特征、机理及展望: 以中国致密油和致密气为例[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(2): 173-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htmZou C N, Zhu R K, Wu S T, et al. Types, characteristics, genesis and prospects of conventional and unconventional hydrocarbon accumulations: Taking tight oil and tight gas in China as an instance[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 173-187(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201202002.htm [4] Nelson P H. Pore-throat sizes in sandstones, tight sandstones, and shales[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(3): 329-340. doi: 10.1306/10240808059 [5] Jiang Z X, Li Z, Li F, et al. Tight sandstone gas accumulation mechanism and development models[J]. Petroleum Science, 2015, 12: 587-605. doi: 10.1007/s12182-015-0061-6 [6] Zhu S F, Zhu X M, Jia Y, et al. Diagenetic alteration, pore-throat network, and reservoir quality of tight gas sandstone reservoirs: A case study of the Upper Paleozoic sequence in the northern Tianhuan Depression in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2020, 104(11): 2297-2324. doi: 10.1306/08151919058 [7] Spencer C W. Geologic aspects of tight gas reservoirs in the Rocky Mountain region[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1985, 37(7): 1308-1314. doi: 10.2118/11647-PA [8] Surdam R C. A new paradigm for gas exploration in anomalously pressured "tight-gas sands" in the Rocky Mountain Laramide basins[C]//Surdam R C. Seals, traps, and the petroleum system: AAPG Memoir 67. Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, 1997: 283-298. [9] 张哨楠. 致密天然气砂岩储层: 成因和讨论[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2008, 29(1): 1-10, 18. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.01.001Zhang X N. Tight sandstone gas reservoirs: Their origin and discussion[J]. Oil and Gas Geology, 2008, 29(1): 1-10, 18(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-9985.2008.01.001 [10] 王芙蓉, 何生, 何治亮, 等. 准噶尔盆地腹部地区深层砂岩储层孔隙特征研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2010, 32(6): 547-552. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.06.006Wang F R, He S, He Z L, et al. The reservoir characteristic of deeply-buried sandstone in the center of Junggar Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology and Experiment, 2010, 32(6): 547-552(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6112.2010.06.006 [11] Zou C N, Zhu R K, Liu K Y, et al. Tight gas sandstone reservoirs in China: Characteristics and recognition criteria[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2012, 88/89: 82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2012.02.001 [12] 朱如凯, 吴松涛, 苏玲, 等. 中国致密储层孔隙结构表征需注意的问题及未来发展方向[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(11): 1323-1336. doi: 10.7623/syxb201611001Zhu R K, Wu S T, Su L, et al. Problems and future works of porous texture characterization of tight reservoirs in China[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(11): 1323-1336(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.7623/syxb201611001 [13] 高文杰, 李贤庆, 张光武, 等. 塔里木盆地库车坳陷克拉苏构造带深层致密砂岩气藏储层致密化与成藏关系[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(2): 226-235. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201802008.htmGao W J, Li X Q, Zhang G W, et al. The relationship research between densification of reservoir and accumulation of the deep tight sandstone gas reservoirs of the Kelasu tectonic zone in Kuqa Depression, Tarim Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2018, 29(2): 226-235(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201802008.htm [14] 张莉, 舒志国, 何生, 等. 川东建南地区须家河组储层特征及其差异演化过程[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(9): 3139-3156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202109008.htmZhang L, Shu Z G, He S, et al. Reservoir characteristics and differential evolution process of Xujiahe Formation in Jiannan area, East Sichuan[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(9): 3139-3156(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202109008.htm [15] 罗静兰, 李弛, 雷川, 等. 碎屑岩储集层成岩作用研究进展与热点问题讨论[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(6): 1021-1040. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202006001.htmLuo J L, Li C, Lei C, et al. Discussion on research advances and hot issues in diagenesis of clastic-rock reservoirs[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2020, 22(6): 1021-1040(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202006001.htm [16] 宫雪, 胡新友, 李文厚, 等. 成岩作用对储层致密化的影响差异及定量表述: 以苏里格气田苏77区块致密砂岩为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2020, 38(6): 1338-1348. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202006018.htmGong X, Hu X Y, Li W H, et al. Different influences and quantitative description of effect of diagenesis on reservoir densification: Case study of tight sandstone in Su77 block, Sulige Gas Field[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2020, 38(6): 1338-1348(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202006018.htm [17] 徐国盛, 崔恒远, 刘勇, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷古近系花港组砂岩储层致密化与油气充注关系[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 20-29. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0303Xu G S, Cui H Y, Liu Y, et al. Relationship between sandstone reservoirs densification and hydrocarbon charging in the Paleogene Huagang Formation of Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 20-29(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0303 [18] 张铜耀, 郝鹏. 渤中凹陷深层特低孔特低渗砂砾岩储层储集空间精细表征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 117-124. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0415Zhang T Y, Hao P. Fine characterization of the reservoir space in deep ultra-low porosity and ultra-low permeability glutenite in Bozhong Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 117-124 (in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0415 [19] Qian W D, Yin T J, Zhang C M, et al. Diagenetic evolution of the Oligocene Huagang Formation in Xihu Sag, the East China Sea Shelf Basin[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 1-16. http://www.socolar.com/Article/Index?aid=200259935745&jid=200000073720 [20] 李智, 叶加仁, 曹强, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地杭锦旗独贵加汗区带下石盒子组储层特征及孔隙演化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(4): 49-60. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0404Li Z, Ye J R, Cao Q, et al. Reservoir characteristics and pore evolution of the Lower Shihezi Formation in Duguijiahan zone, Hangjinqi area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(4): 49-60(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0404 [21] 苟红光, 张品, 佘家朝, 等. 吐哈盆地石油地质条件、资源潜力及勘探方向[J]. 海相油气地质, 2019, 24(2): 85-96. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201902009.htmGou H G, Zhang P, She J C, et al. Petroleum geological conditions, resource potential and exploration direction in Turpan-Hami Basin[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2019, 24(2): 85-96(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HXYQ201902009.htm [22] 袁明生, 梁世君, 燕列灿, 等. 吐哈油气地质与勘探实践[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2002.Yuan M S, Liang S J, Yan L C, et al. Tuha petroleum geology and exploration practice[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2002(in Chinese). [23] 翟亚梅, 余水生, 张志更, 等. 吐哈盆地胜北洼陷致密砂岩气勘探潜力与方向[J]. 新疆石油天然气, 2012, 8(4): 7-11, 5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201204001.htmZhai Y M, Yu S S, Zhang Z G, et al. The exploration potential and direction of tight sandstone gas in Shengbei Sag of Tuha Basin[J]. Xinjiang Oil and Gas, 2012, 8(4): 7-11, 5(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJSY201204001.htm [24] 杨占龙, 陈启林, 郭精义. 胜北洼陷岩性油气藏成藏条件特殊性分析[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2005, 16(2): 181-185, 189. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200502009.htmYang Z L, Chen Q L, Guo J Y. The particularity analysis of stratigraphy reservoirs in Shengbei Depression[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2005, 16(2): 181-185, 189(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200502009.htm [25] Sun M D, Zhao J L, Pan Z J, et al. Pore characterization of shales: A review of small angle scattering technique[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 78: 103294. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875510020301487 [26] Yang R, Hao F, He S, et al. Experimental investigations on the geometry and connectivity of pore space in organic-rich Wufeng and Longmaxi shales[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 84: 225-242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817217301198 [27] Meyer K, Klobes P. Comparison between different presentations of pore size distribution in porous materials[J]. Fresenius Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 1999, 363(2): 174-178. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034442854710_03e6.html [28] Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark A V, et al. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report)[J]. Pure and Applied Chemistry, 2015, 87(9/10): 1051-1069. [29] Tian H, Pan L, Xiao X M, et al. A preliminary study on the pore characterization of Lower Silurian black shales in the Chuandong thrust fold belt, southwestern China using low pressure N2 adsorption and FE-SEM methods[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 48: 8-19. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0264817213001761 [30] Surdam R C, Crossey L J, Hagen E S, et al. Organic-inorganic interactions and sandstone diagenesis[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1989, 73(1): 1-23. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Laura_Crossey/publication/237072808_Organic-inorganic_interactions_and_Sandstone_diagenesis/links/5c0d5472a6fdcc494fe87bd7/Organic-inorganic-interactions-and-Sandstone-diagenesis.pdf [31] Surdam R C, Jiao Z S, MacGowan D B. Redox reactions involving hydrocarbons and mineral oxidants: A mechanism for significant porosity enhancement in sandstones[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1993, 77(9): 1509-1518. http://www.osti.gov/scitech/biblio/140969-redox-reactions-involving-hydrocarbons-mineral-oxidants-mechanism-porosity-enhancement [32] Milliken K L. Late diagenesis and mass transfer in sandstone-shale sequences[J]. Treatise on Geochemistry, 2003, 7: 159-190. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B0080437516070912 -





 下载:
下载: