Characteristics, classification and genetic mechanism of pockmarks
-
摘要:
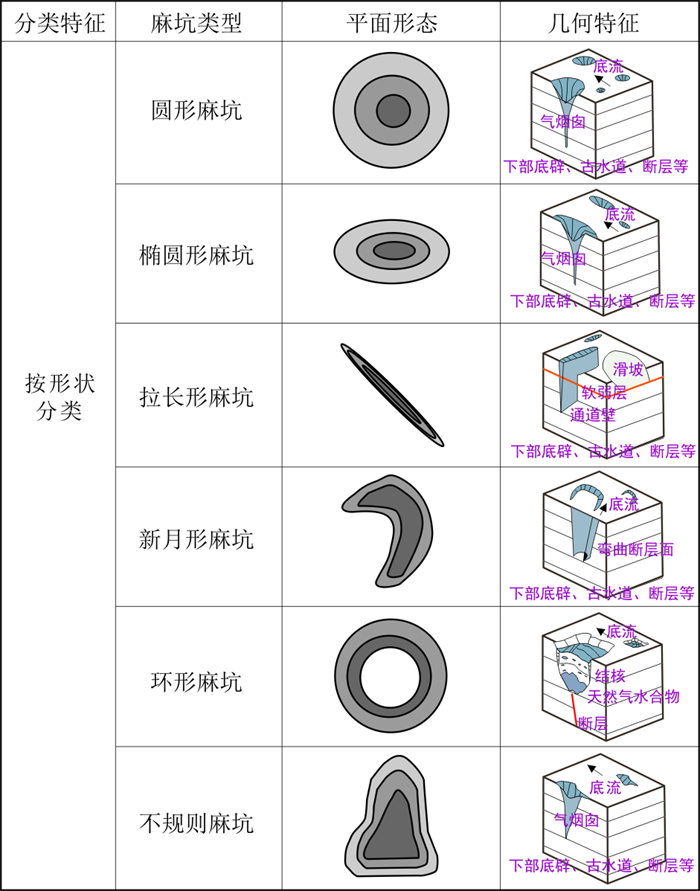
海底麻坑是由超压流体溢出海底时侵蚀海底沉积物所形成的一种负地貌, 其广泛分布于各种水下构造环境(如大陆边缘盆地和增生楔等)。综合近年有关海底麻坑的研究成果, 依据麻坑形状、直径、长宽比、空间分布以及垂向充填方式等特征, 对其类型进行了系统划分, 详细介绍了麻坑形成的主要条件及影响因素(如底辟、断层等), 深入阐释了麻坑的成因机制。麻坑形成过程中, 地层中的局部异常流体压力(超压)是最为关键的条件和驱动因素。根据地层中超压形成和释放过程的快慢, 可以将麻坑的成因机制划分为渐进型、突发型和混合型3类。渐进型麻坑形成过程中, 地层超压的形成和释放的过程较为缓慢; 突发型麻坑形成过程中地层超压形成和释放的过程较快; 混合型麻坑的形成过程介于二者之间。鉴于麻坑在形成过程中受到海水和下伏地层等多种因素的共同影响, 未来十分有必要对海底深部地层中“超压形成-流体聚集-垂向运移至海底表面并逸散-形成麻坑”的整个动态过程展开物理和数值模拟研究, 进一步建立海底麻坑形成模式。
Abstract:Pockmarks are a kind of negative geomorphology formed by overpressure fluid spilling from the seabed. They are widely distributed in various underwater tectonic environments (such as continental margin basins and accretion wedges). Based on the recent research progress and achievements of pockmarks, this paper systematically divides the types of pockmarks according to their shapes, diameters, length width ratios, distribution characteristics and vertical filling modes. Moreover, this paper detailed introduces the main conditions and influence factors (such as diapir and fault)and deeply analyzes the genetic mechanisms of pockmarks. The local abnormal fluid pressure (overpressure) is the key factor to trigger the formation of pockmarks. According to the formation and leakage speed of overpressure during pockmark formation, the genetic mechanisms of pockmarks can bedivided into progressive, sudden and transitional three types. In the progressive formation model, both the formation and leakage processes of overpressure are slow. Whilst in the sudden formation model, the formation and leakage processes of overpressure are fast. For the transitional model, the formation and leakage processes of overpressure are faster than those of the progressive model but slower than those of the sudden model. The formation of pockmarks is affected by many factors, such as seawater and underlying strata. The physical and numerical simulation of dynamic overpressure formation and vertical migration to the seabed may be the future study directions of pockmarks.
-
Key words:
- pockmark /
- classification /
- influencing factor /
- genetic mechanism
-
图 3 拉长形麻坑的形成过程(据文献[13]修改)
Figure 3. Formation processes of elongated pockmarks
图 4 环形麻坑的形成过程示意图(据文献[36]修改)
Figure 4. Formation processes of ring-shape pockmarks
图 5 链状麻坑示意图(据文献[46]修改)
Figure 5. The schematic diagram of chain pockmarks
图 6 麻坑的地震剖面及解释图(据文献[53]修改)
Figure 6. Seismic sections and their interpreted drawings of pockmarks
图 8 巴西桑托斯盆地盐底辟构造上方麻坑的地震剖面图(据文献[66]修改)
Figure 8. Seismic section of pockmarks above salt diapir structure in the Santos Basin, Brazil
图 9 南海中建盆地岩浆底辟构造上方麻坑的地震剖面图(据文献[51]修改)
Figure 9. Seismic section of pockmarks above the magmatic structure in the Zhongjian Basin of South China Sea
图 10 流体输运系统和麻坑模型(据文献[67]修改)
Figure 10. Model of fluid transport system and pockmark
图 11 尼日尔三角洲西部斜坡上海底峡谷内形成麻坑的地震剖面图(据文献[68]修改)
Figure 11. Seismic section of canyon-confined pockmarks on the western Niger Delta slope
图 12 推进型麻坑形成过程模型(据文献[53]修改)
a.初始基底麻坑的形成; b.基底麻坑被充填; c.麻坑上游侧细粒沉积物因底部涡流作用而重新悬浮,粗泥沙在下游侧积累; d.底流强度减弱,半深海物质沉积,麻坑堆叠前进
Figure 12. Model for the development of advancing pockmarks
-
[1] Hovland M, Talbot M R, Quale H, et al. Methane-related carbonate cements in pockmarks of the North Sea[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1987, 57: 881-892. [2] Webb K E, Hammer Ø, Lepland A, et al. Pockmarks in the inner Oslofjord, Norway[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2008, 29: 111-124. [3] Ramos R B, Santos R F, Schattner U, et al. Deep pockmarks as natural sediment traps: A case study from southern Santos Basin(SW Atlantic upper slope)[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2019, 41: 1-2. [4] King L H, MacLean B. Pockmarks on the Scotian Shelf[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1970, 81: 3141-3148. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1970)81[3141:POTSS]2.0.CO;2 [5] Harrington P K. Formation of pockmarks by pore-water escape[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1985, 5: 193-197. doi: 10.1007/BF02281638 [6] Hovland M, Svensen H, Forsberg C F, et al. Complex pockmarks with carbonate-ridges off mid-Norway: Products of sediment degassing[J]. Marine Geology, 2005, 218: 191-206. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.04.005 [7] Hovland M, Heggland R, De Vries M H, et al. Unit-pockmarks and their potential significance for predicting fluid flow[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27: 1190-1199. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.02.005 [8] Ondréas H, Olu K, Fouquet Y, et al. ROV study of a giant pockmark on the Gabon continental margin[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2005, 25: 281-292. doi: 10.1007/s00367-005-0213-6 [9] Gay A, Lopez M, Berndt C, et al. Geological controls on focused fluid flow associated with seafloor seeps in the Lower Congo Basin[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 244: 68-92. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.06.003 [10] Nakajima T, Kakuwa Y, Yasudomi Y, et al. Formation of pockmarks and submarine canyons associated with dissociation of gas hydrates on the Joetsu Knoll, eastern margin of the Sea of Japan[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 90: 228-242. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.10.011 [11] León R, Somoza L, Medialdea T, et al. Pockmarks, collapses and blind valleys in the Gulf of Cádiz[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2010, 30(3/4): 231-247. [12] Szpak M T, Monteys X, O'Reilly S, et al. Geophysical and geochemical survey of a large marine pockmark on the Malin Shelf, Ireland[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2012, 13: 1-18. doi: 10.1029/2011GC003955 [13] Xu C, Greinert J, Haeckel M, et al. The character and formation of elongated depressions on the upper Bulgarian Slope[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2018, 17: 555-562. doi: 10.1007/s11802-018-3460-7 [14] Sun Q L, Wu S G, Hovland M, et al. The morphologies and genesis of mega-pockmarks near the Xisha uplift, South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28: 1146-1156. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.03.003 [15] Dandapath S, Chakraborty B, Karisiddaiah S M, et al. Morphology of pockmarks along the western continental margin of India: Employing multibeam bathymetry and backscatter data[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27: 2107-2117. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2010.09.005 [16] Hovland M, Judd A G. Seabed pockmarks and seepages impact on geology, biology and the marine environment[M]. London: Graham & Trotman Ltd., 1988. [17] Gay A, Lopez M, Ondreas H, et al. Seafloor facies related to upward methane flux within a giant pockmark of the Lower Congo Basin[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 226: 81-95. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.09.011 [18] Rise L, Bellec V K, Chand S, et al. Pockmarks in the southwestern Barents Sea and Finnmark fjords[J]. Norwegian Journal of Geology, 2015, 94: 263-282. [19] Gay A, Lopez M, Cochonat P, et al. Isolated seafloor pockmarks linked to BSRs, fluid chimneys, polygonal faults and stacked Oligocene-Miocene turbiditic palaeochannels in the Lower Congo Basin[J]. Marine Geology, 2006, 226: 25-40. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2005.09.018 [20] 李磊, 裴都, 都鹏燕, 等. 海底麻坑的构型、特征、演化及成因: 以西非木尼河盆地陆坡为例[J]. 海相油气地质, 2013, 18(4): 53-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.04.008Li L, Pei D, Du P Y, et al. Architecture, character, evolution and genesis of seabed pockmarks: A case study to the continental slope in Rio Muni Basin, west Africa[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology, 2013, 18(4): 53-58(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.04.008 [21] Bøe R, Rise L, Ottesen D. Elongate depressions on the southern slope of the Norwegian Trench(Skagerrak): Morphology and evolution[J]. Marine Geology, 1998, 146: 191-203. doi: 10.1016/S0025-3227(97)00133-3 [22] Cathles L M, Su Z, Chen D. The physics of gas chimney and pockmark formation, with implications for assessment of seafloor hazards and gas sequestration[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27: 82-91. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2009.09.010 [23] Judd A G, Hovland M. Seabed fluid flow: The impact on geology, biology and the marine environment[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007. [24] Robin J, Pilcher R. Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 244: 15-32. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2007.05.002 [25] Sun Q L, Leslie S. Tsunamigenic potential of an incipient submarine slope failure in the northern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 112: 104-111. [26] Judd A G, Hovland M, Dimitrov L I, et al. The geological methane budget at continental margins and its influence on climate change[J]. Geofluids, 2002, 2: 109-126. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00027.x [27] MacDonald I, Leifer I, Sassen R, et al. Transfer of hydrocarbons from natural seeps to the water column and atmosphere[J]. Geofluids, 2002, 2: 95-107. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00023.x [28] Newman K R, Cormier M H, Weissel J K, et al. Active methane venting observed at giant pockmarks along the U.S. mid-Atlantic shelf break[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 267: 341-352. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.11.053 [29] Xu C, Xu G Q, Xing J H, et al. Research progress of seafloor pockmarks in spatio-temporal distribution and classification[J]. Journal of Ocean University of China, 2020, 19(1): 69-80. doi: 10.1007/s11802-020-3878-6 [30] Pilcher R, Argent J. Mega-pockmarks and linear pockmark trains on the West African continental margin[J]. Marine Geology, 2007, 244(1/4): 15-32. [31] Dimitrov L, Woodside J. Deep sea pockmark environments in the eastern Mediterranean[J]. Marine Geology, 2002, 195: 263-276. [32] Hovland M, Gardner J V, Judd A G. The significance of pockmarks to understanding fluid flow processes and geohazards[J]. Geofluids, 2002, 2: 127-136. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-8123.2002.00028.x [33] 曹超, 潘翔, 蔡锋, 等. 天然气水合物赋存区麻坑地貌特征及其地质灾害意义[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2018, 241(7): 52-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.07.009Cao C, Pan X, Cai F, et al. Characteristics of pockmark geomorphology in gas hydrate occurrence area and its geological hazards significance[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2018, 241(7): 52-55(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2018.07.009 [34] Chen J, Song H, Guan Y, et al. Morphologies, classification and genesis of pockmarks, mud volcanoes and associated fluid escape features in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Deep Sea Research, Part Ⅱ, Tropical Studies in Oceanography, 2015, 122: 106-117. doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2015.11.007 [35] Koch S, Berndt C, Bialas J, et al. Gas-controlled seafloor doming[J]. Geology, 2015, 43(7): 571-574. doi: 10.1130/G36596.1 [36] Riboulot V, Cattaneo A, Sultan N, et al. Sea-level change and free gas occurrence influencing a submarine landslide and pockmark formation and distribution in deep-water Nigeria[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2013, 375: 78-91. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2013.05.013 [37] Hammer Ø, Webb K E, Depreiter D. Numerical simulation of upwelling currents in pockmarks, and data from the Inner Oslofjord, Norway[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2009, 29: 269-275. doi: 10.1007/s00367-009-0140-z [38] Bulat J, Long D. Images of the seabed in the Faroee Shetland channel from commercial 3D seismic data[J]. Marine Geophysical Researches, 2001, 22: 345-367. doi: 10.1023/A:1016343431386 [39] Stow D A V, Pudsey C J, Howe J A, et al. Deep-water contourite systems: Modern drifts and ancient series, seismic and sedimentary characteristics[M]. London: Geological Society of London, 2002. [40] Duarte J C, Terrinha P, Rosas F M, et al. Crescent-shaped morphotectonic features in the Gulf of Cadiz(offshore SW Iberia)[J]. Marine Geology, 2010, 271: 236-249. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2010.02.017 [41] 拜阳, 宋海斌, 关永贤, 等. 利用反射地震和多波束资料研究南海西北部麻坑的结构特征与成因[J]. 地球物理学报, 2014, 57(7): 2208-2222. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201407016.htmBai Y, Song H B, Guan Y X, et al. Structural characteristics and genesis of pockmarks in the northwest of the South China Sea derived from reflective seismic and multibeam data[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2014, 57(7): 2208-2222(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201407016.htm [42] Chen J, Song H, Guan Y, et al. Geological and oceanographic controls on seabed fluid escape structures in the northern Zhongjiannan Basin, South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2018, 168: 38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.04.027 [43] Hill J C, Driscoll N W, Weissel J, et al. Large-scale elongated gas blowouts along the U.S. Atlantic margin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 2004, 109: 1-14. [44] Moss J L, Cartwright J, Cartwright A, et al. The spatial pattern and drainage cell characteristics of a pockmark field, Nile Deep Sea Fan[J]. Marine & Petroleum Geology, 2012, 35(1): 321-336. [45] 刘晓瑜, 冯秀丽, 陈义兰, 等. 北黄海海底麻坑群形态的定量研究及控制因素[J]. 海洋学报, 2018, 40(3): 36-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.03.004Liu X Y, Feng X L, Chen Y L, et al. Quantitative study of morphological features and control factors of seabed pockmarks in the North Yellow Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2018, 40(3): 36-49(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2018.03.004 [46] 张田升, 吴自银, 赵荻能, 等. 南海礼乐盆地海底麻坑地貌及成因分析[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(3): 106-120. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.03.011Zhang T S, Wu Z Y, Zhao D N, et al. The morphologies and genesis of pockmarks in the Reed Basin, South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2019, 41(3): 106-120(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.03.011 [47] Berndt C, Jacobs C, Evans A, et al. Kilometre-scale polygonal seabed depressions in the Hatton Basin, NE Atlantic Ocean: Constraints on the origin of polygonal faulting[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 332/334(12): 126-133. [48] Zhang K, Guan Y X, Song H B, et al. A preliminary study on morphology and genesis of giant and mega pockmarks near Andu Seamount, Nansha Region(South China Sea)[J]. Marine Geophysical Research, 2020, 41(1): 2. doi: 10.1007/s11001-020-09404-y [49] Brrothers L L, Kelly J T, Bellknap D F, et al. Shallow stratigraphic control on pockmark distribution in north temperate estuaries[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 329/331(6): 34-45. [50] 陈江欣, 关永贤, 宋海斌, 等. 麻坑、泥火山在南海北部与西部陆缘的分布特征和地质意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2015, 58(3): 919-938. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201503019.htmChen J X, Guan Y X, Song H B, et al. Distribution characteristics and geological implications of pockmarks and mud volcanoes in the northern and western continental margins of the South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2015, 58(3): 919-938(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWX201503019.htm [51] 杨志力, 王彬, 李丽, 等. 南海中建海域麻坑发育特征及成因机制[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(1): 42-49. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202001005.htmYang Z L, Wang B, Li L, et al. Characteristics of pockmarks and their genesis Zhongjian Offshore area, South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(1): 42-49(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202001005.htm [52] Ho S, Cartwright J A, Imbert P. Vertical evolution of fluid venting structures in relation to gas flux, in the Neogene-Quaternary of the Lower Congo Basin, Offshore Angola[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 332: 40-55. [53] Ho S, Imbert P, Hovland M, et al. Downslope-shifting pockmarks: Interplay between hydrocarbon leakage, sedimentations, currents and slope's topography[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 2018, 107(8): 1-23. [54] Moss J L. The spatial and temporal distribution of pipe and pockmark formation[D]. Cardiff: Cardiff University, 2010. [55] Ho S, Cartwright J A, Imbert P. The formation of advancing pockmarks arrays: An interplay between hydrocarbon leakage and slope sedimentation[C]//Anon. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Annual Convention and Exhibition. Long Beach: [s. n. ], 2012: 22-25. [56] Sangree J, Widmier J. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea level. Part 9: Seismic interpretation of clastic depositional facies[J]. Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull., 1978, 62: 752-771. [57] Ivanov M, Blinova V, Kozlova E, et al. First sampling of gas hydrate from the V-ring Plateau[J]. Eos Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2007, 88(19): 209-212. [58] 苏正, 刘丽华. 南海北部陆坡天然气水合物成藏特征研究进展分析[J]. 新能源进展, 2020, 8(1): 35-41. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNYJ202001006.htmSu Z, Liu L H. Research progress on gas hydrate accumulation in the northern slope of the South China Sea[J]. Advances in New and Renewable Energy, 2020, 8(1): 35-41(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XNYJ202001006.htm [59] Taylor M H, Dillon W P, Pecher I A. Trapping and migration of methane associated with the gas hydrate stability zone at the Blake Ridge Diapir: New insights from seismic data[J]. Marine Geology, 2000, 164: 79-89. [60] 赖冬, 范彩伟, 罗强, 等. 砂箱物理模型浅表底辟构造研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 103-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903010.htmLai D, Fan C W, Luo Q, et al. A review of tectonic sandbox modeling of diapir structure in shallow crust[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 103-119(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903010.htm [61] Sayago-Gil M, Long D, Hitchen K, et al. Evidence for current-controlled morphology along the western slope of Hatton Bank(Rockall Plateau, NE Atlantic Ocean)[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2010, 30: 99-111. [62] 王健, 邱文弦, 赵俐红. 天然气水合物发育的构造背景分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(2): 100-106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201002020.htmWang J, Qiu W X, Zhao L H. Tectonic settings analysis of gas hydrate deposits development[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(2): 100-106(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201002020.htm [63] Masoumi S, Reuning L, Back S, et al. Buried pockmarks on the top chalk surface of the Danish North Sea and their potential significance for interpreting palaeocirculation patterns[J]. International Journal of Earth Science, 2014, 103: 563-578. [64] Luo M, Chen L, Wang S, et al. Pockmark activity inferred from pore water geochemistry in shallow sediments of the pockmark field in southwestern Xisha Uplift, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2013, 48: 247-259. [65] Wu S, Yang Z, Wang D, et al. Architecture, development and geological control of the Xisha carbonate platforms, northwestern South China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 2014, 350: 71-83. [66] De Mahiques M M, Schattner U, Lazar M, et al. An extensive pockmark field on the upper Atlantic margin of Southeast Brazil: Spatial analysis and its relationship with salt diapirism[J]. Heliyon, 2017, 3(2): e00257. [67] Maia R A, Cartwright J, Andersen E. Shallow plumbing systems inferred from spatial analysis of pockmark arrays[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 865-881. [68] Benjamin U, Huuse M, Hodgetts D. Canyon-confined pockmarks on the western Niger Delta slope[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2015, 107: 15-21. [69] Jobe Z R, Lowe D R, Uchytil S J. Two fundamentally different types of submarine canyons along the continental margin of Equatorial Guinea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(3): 843-860. [70] Sultan N, Marsset B, Ker S, et al. Hydrate dissolution as a potential mechanism for pockmark formation in the Niger Delta[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Atmospheres, 2010, 115: B8. [71] 罗敏, 吴庐山, 陈多福. 海底麻坑研究现状及进展[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2012, 28(5): 33-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201205007.htmLuo M, Wu L S, Chen D F. Research status and progress of seabed pockmarks[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2012, 28(5): 33-42(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201205007.htm [72] 刘睿, 刘建章, 田金强, 等. 盆地异常流体压力-应力耦合过程研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(3): 87-95. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503011.htmLiu R, Liu J Z, Tian J Q, et al. Reviews of sedimentary basin abnormal fluid pressure/stress coupling process[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(3): 87-95(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201503011.htm [73] Rozhko A Y, Podladchikov Y Y, Renard F. Failure patterns caused by localized rise in pore-fluid overpressure and effective strength of rocks[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2007, 34(22): 315-324. [74] 罗敏. 南海西沙西南海底麻坑区生物地球化学过程、麻坑活动性以及麻坑形成时间研究[D]. 广州: 中国科学院广州地球化学研究所, 2015.Luo M. The biogeochemical processes, the activity, and the formation time of the pockmarks in the southwestern Xisha Uplift, northwestern South China Sea[D]. Guangzhou: Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry, Chinese Academy of Science, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [75] 孙启良. 南海北部深水盆地流体逸散系统与沉积物变形[D]. 山东青岛: 中国科学院海洋研究所, 2011.Sun Q L. Focused fliud-flow escape system and sediments deformation in deep-water basins of northern South China Sea[D]. Qingdao Shandong: Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Science, 2011(in Chinese with English abstract). [76] Paull C K, Iii WU, Borowski W S. Freshwater ice rafting: An additional mechanism for the formation of some high-latitude submarine pockmarks[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 1999, 19(1/2): 164-168. [77] Iglesias J, Ercilla G, García-Gil S, et al. Pockforms: An evaluation of pockmark-like seabed features on the Landes Plateau, Bay of Biscay[J]. Geo-Marine Letters, 2010, 30(3/4): 207-219. [78] 程聪, 姜涛, 匡增桂, 等. 天然气水合物系统特征及其对我国水合物勘查的启示[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4): 30-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904005.htmCheng C, Jiang T, Kuang Z G, et al. Characteristics of gas hydrate system and its enlightenment to gas hydrate exploration in China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(4): 30-40(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904005.htm [79] 张金华, 苏明, 魏伟, 等. 含气流体运移与天然气水合物成藏[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2): 176-185. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201702023.htmZhang J H, Su M, Wei W, et al. Relationship between gas-bearing fluids migration and accumulation of natural gas hydrate[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(2): 176-185(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201702023.htm -





 下载:
下载: