Deformation factors and failure modes of bedrock landslides in Yangxin County, Hubei Province
-
摘要:
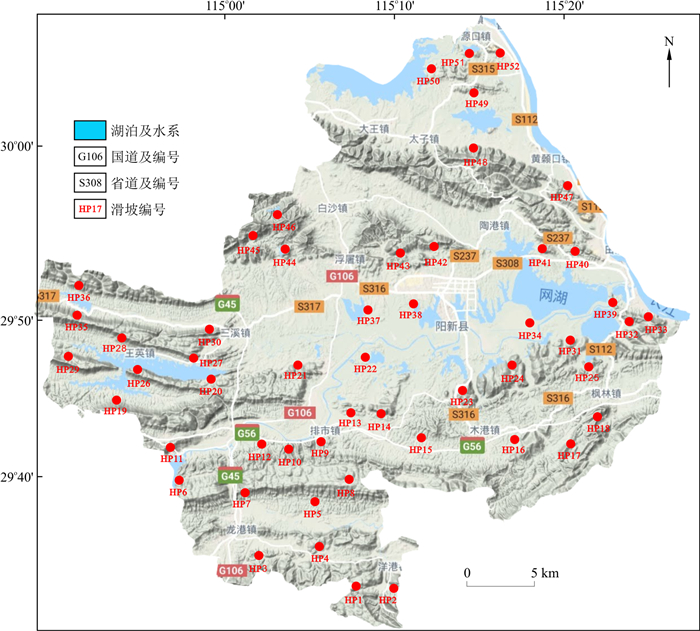
斜坡变形受众多因子综合控制, 不同因子的敏感性与作用规律在变形过程中差异明显。以湖北省阳新县顺层基岩滑坡为研究对象, 通过正交试验结合离散元数值模拟的方法, 研究多个影响因子对应顺层滑坡变形的敏感性并确立主导因素, 随后基于响应面拟合主导因素与滑坡不同部位变形程度间的量化关系, 揭示主导因素交互作用对滑坡变形破坏模式的影响规律。结果表明, 在研究区内坡度与岩层倾角分别为影响顺层滑坡变形的主导与次主导因素, 滑坡的变形破坏模式受控于二者的交互作用。在中-陡倾顺层滑坡中, 当坡度小于岩层倾角时, 滑坡变形主要集中在坡顶, 且变形程度随岩层倾角的增加而增大, 表现出滑移-弯曲的变形破坏模式; 在缓倾顺层滑坡中, 当坡度大于岩层倾角时, 滑坡坡脚位移较坡顶显著, 其坡脚变形程度随坡度的增加而增大, 以滑移-拉裂变形为主。研究成果可为该类滑坡的防治工作提供参考。
Abstract:The deformation of slopes is comprehensively controlled by many factors, and the sensitivity and action rules of different factors are obviously different in the deformation process. This article takes the bedding landslide in Yangxin County, Hubei Province as the research object. Through orthogonal experimental design combined with 3DEC (distinct element method, DEM), the sensitivity of multiple influencing factors to the deformation of bedding landslides is studied, and the dominant factors are established. Then, based on the response surface method to fit the quantitative relationship between the dominant factors and the deformation degree of different parts of the landslide, the influence law of the interaction of dominant factors on the deformation and failure mode of landslides is revealed. The study of the slope in the Yangxin County area shows that the slope and the strata dip are the dominant and secondary dominant factors affecting the bedding landslide, and the interaction between the two has a significant impact on the slope deformation. In the medium-steep bedding landslide, when the slope is less than the angle of rock, the slope deformation mainly concentrates on the slope top, and the degree of deformation increases with increasing rock dip, showing the slip-bending deformation failure mode. In a gently dipping bedding slope, when the slope is larger than the angle of rock, the displacement of the slope toe is more significant than that of the slope top, and the deformation degree of the slope toe increases with increasing slope, showing the slip-rupture deformation failure mode. This study can provide guidances for the prevention and control of such landslides.
-
表 1 岩体物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of the rock mass
岩层类型 密度/(kg·m-3) 内聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 抗拉强度/MPa 泊松比 泥质粉砂岩 2 480 0.8 38 0.2 0.25 结构面 抗拉强度/MPa 内聚力/MPa 内摩擦角/(°) 法向刚度/(kPa·m-1) 切向刚度/(kPa·m-1) 层面 0.02 14 15 150 150 节理面 0.016 9 15 120 120 表 2 影响因子范围区间
Table 2. Range of impact factors
影响因子 范围区间 斜坡高度/m 15~65 岩层倾角/(°) 15~65 斜坡坡度/(°) 15~75 弹性模量/GPa 2.5~5.5 层厚/m 0.5~2.0 表 3 试验因素与水平设计
Table 3. Experimental factors and level design
因素 水平 坡高/m 15 30 45 60 坡度/(°) 30 45 60 75 倾角/(°) 15 30 45 60 层厚/m 0.5 1 1.5 2 弹性模量/GPa 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 表 4 正交表L16(45)
Table 4. Orthogonal table L16(45)
方案序号 坡高/m 坡度/(°) 倾角/(°) 层厚/m 弹性模量 总位移/m 1 1 1 1 1 1 4.7×10-3 2 1 2 2 2 2 0.37 3 1 3 3 3 3 1.03 4 1 4 4 4 4 1.18 5 2 1 2 3 4 1.34×10-2 6 2 2 1 4 3 7.5×10-3 7 2 3 4 1 2 2.54×10-2 8 2 4 3 2 1 0.46 9 3 1 3 4 2 2.8×10-3 10 3 2 4 3 1 9.44×10-2 11 3 3 1 2 4 4×10-3 12 3 4 2 1 3 0.63 13 4 1 4 2 3 0.05 14 4 2 3 1 4 0.12 15 4 3 2 4 1 0.22 16 4 4 1 3 2 0.12 极差R 0.52 0.58 0.37 0.16 0.32 表 4 响应面试验变量与水平
Table 4. Response surface test variables and levels
因素 水平 -1 0 1 坡度 30 52.5 75 坡高 15 37.5 60 倾角 15 37.5 60 表 5 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 5. Response surface test design and results
方案 坡高/m 坡度/(°) 倾角/(°) 坡顶水平位移/m 坡脚水平位移/m 1 15 30 37.5 7×10-2 1×10-2 2 60 30 37.5 1.13×10-1 2.8×10-2 3 15 75 37.5 1.2×10-1 5.17×10-1 4 60 75 37.5 5.3×10-3 2.97×10-2 5 15 52.5 15 4×10-3 1.3×10-2 6 60 52.5 15 2×10-3 1.28×10-2 7 15 52.5 60 1.7×10-2 4.1×10-3 8 60 52.5 60 5×10-2 6.5×10-2 9 37.5 30 15 2×10-3 6×10-3 10 37.5 75 15 4×10-3 1.1×10-2 11 37.5 30 60 6.25×10-1 5×10-3 12 37.5 75 60 1.5×10-1 8×10-1 13 37.5 52.5 37.5 6×10-1 9.5×10-1 14 37.5 52.5 37.5 6×10-1 9.5×10-1 15 37.5 52.5 37.5 6×10-1 9.5×10-1 表 6 坡顶最大水平位移响应面模型的方差分析
Table 6. Variance analysis of the response surface model at the slope top
来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 P值 模型 0.87 9 0.096 8 5.29 0.040 6 A-坡高 0.000 1 1 0.000 1 0.003 4 0.955 8 B-坡度 0.027 3 1 0.027 3 1.49 0.275 9 C-倾角 0.086 1 1 0.086 1 4.71 0.082 2 AB 0.012 2 1 0.0122 0.665 8 0.451 6 AC 3×10-4 1 3×10-4 0.016 7 0.902 1 BC 0.0056 9 1 0.056 9 3.11 0.138 1 A2 0.472 8 1 0.472 8 25.85 0.003 8 B2 0.120 7 1 0.120 7 6.60 0.050 1 C2 0.185 1 1 0.185 1 10.12 0.024 5 R2=0.905 RAdj2=0.864 RPred2=0.858 表 7 坡脚最大水平位移响应面模型的方差分析
Table 7. Variance analysis of the response surface model at the slope toe
来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 P值 模型 2.25 9 0.2501 11.04 0.008 3 A-坡高 0.02 1 0.02 0.880 7 0.391 1 B-坡度 0.216 8 1 0.216 8 9.57 0.027 1 C-倾角 0.086 5 1 0.086 5 3.82 0.108 1 AB 0.066 1 1 0.006 61 2.92 0.148 3 AC 9×10-4 1 9×10-4 0.041 2 0.847 1 BC 0.156 3 1 0.156 3 6.90 0.046 7 A2 0.900 4 1 0.900 4 39.73 0.001 5 B2 0.36 1 0.36 15.88 0.010 5 C2 0.690 5 1 0.690 5 30.47 0.002 7 R2=0.952 1 RAdj2=0.923 RPred2=0.905 -
[1] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htmHuang R Q. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th Century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(6): 433-454(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200703000.htm [2] Hu Q J, Shi R D N, Zheng L N. Progressive failure mechanism of a large bedding slope with atrain-softening interface[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2018, 77(1): 443-454. [3] 王飞, 唐辉明, 宁奕冰, 等. 基于演化过程的互层斜坡深层倾倒稳定性评价[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 186-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905020.htmWang F, Tang H M, Ning Y B, et al. Stability analysis of deep-seated toppling in interlayered rock slopes based on evolution process[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 192-200 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905020.htm [4] 丁戈媛, 胡新丽. 大奔流顺层岩质滑坡溃屈型破坏力学机制研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 186-190. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0220Ding G Y, Hu X L. Mechanical mechanism of bucking failure of Dabenliu consequent bedding rockslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 186-190(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0220 [5] 杜毅, 晏鄂川, 肖尚德, 等. 恩施盆地典型红砂岩斜坡破坏机理试验研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1): 196-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201801027.htmDu Y, Yan E C, Xiao S D, et al. Experimental study on failure mechanism of typical red sandstone slope in Enshi Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2018, 37(1): 196-203(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201801027.htm [6] 朱冬雪, 许强, 李松林. 三峡库区大型-特大型层状岩质滑坡成因模式及地质特征分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 158-167. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0217Zhu D X, Xu Q, Li S L. Gentic types and geological features of large scale and extra-large scale layerd landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 158-167(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0217 [7] 王兰生. 意大利瓦依昂水库滑坡考察[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报, 2007, 41(3): 158-159. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200703034.htmWang L S. Investigation of the landslide of the Vaiang Reservoir in Italy[J]. Chinese Journal of Geological Hazards and Prevention, 2007, 41(3): 158-159(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDH200703034.htm [8] Zhao LH, Li D J, Tan H H, Cheng X, Zuo S. Characteristics of failure area and failure mechanism of a bedding rockslide in Libo County, Guizhou, China[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(7): 1367-1374. [9] 张倬元, 王士天, 王兰生, 等. 工程地质分析原理[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2016.Zhang Z Y, Wang S T, Wang L S. Principle of engineering geology analysis[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016(in Chinese). [10] 邹宗兴, 唐辉明, 熊承仁. 大型顺层岩质滑坡渐进破坏地质力学模型与稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(11): 2222-2231. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201211009.htmZou Z X, Tang H M, Xiong C R. Geomechanical model of progressive failure for large consequent bedding rockslide and its stability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(11): 2222-2231(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201211009.htm [11] 李云鹏, 杨治林, 王芝银. 顺层边坡岩体结构稳定性位移理论[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(6): 747-750. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200006012.htmLi Y P, Yang Z L, Wang Z Y. Displacement theory of structure stability for rock mass bedding slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(6): 747-750(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200006012.htm [12] Chi E A, Tao T J, Zhao M S. Failure mode analysis of bedding rock slope affected by rock mass structural plane[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials, 2014, 602/605: 594-597. [13] Saito M. Research on forecasting the time of occurrence of slope failure[J]. Soils and Foundations, 1969, 17(2): 29-38. [14] Mason R L, Gunst R F, Hess J L. Statistical design and experiments with applications to engineering and science[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons Publication, 2003. [15] Freire L, Carmezim M J, Ferreira M G S, et al. The passive behaviors of aisi 316 in alkaline media and the effect of pH: A combined electrochemical and analytical study[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2010, 55(21): 61-74. [16] Du Y, Yan E C, Gao X. Identification of the main control factors and failure modes for the failure of Baiyuzui landslide control project[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering, 2021(2): 1-18. [17] 蔡跃, 三谷泰浩, 江琦哲郎. 反倾层状岩体边坡稳定性的数值分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(12): 2517-2522. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200812022.htmCai Y, Yasuhiro M, Tetsuro E. Numerical analysis of stability for an antidip stratified rock slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(12): 2517-2522(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200812022.htm [18] 蔡静森. 均质等厚反倾层状岩质边坡倾倒变形机理研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2013.Cai J S. Mechanism research of toppling deformation for homo-geneous equal thickness anti-dip layered rock slopes[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [19] 黄少平, 晏鄂川, 尹晓萌, 等. 不同临空条件的层状反倾岩质边坡倾倒变形几何特征参数影响规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 159-165. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0111Huang S P, Yan E C, Yin X M, et al. Action law geometrical characteristic parameters in the anti-dip rock slopes under different free face condition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 40(1): 159-165(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0111 [20] Cambio D, Hicks D D, Moffitt K, et al. Back-analysis of the Bingham Canyon South Wall: A quasi-static complex slope movement mechanism[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 2019, 52(3): 4953-4977. [21] 龙建辉, 赵邦强, 李坤. 顺层岩质边坡多级滑动模式及成因机理分析[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(6): 1156-1163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201606011.htmLong J H, Zhao B Q, Li K. Multistage sliding mode and formation mechanism of bedding rock slope[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology, 2016, 45(6): 1156-1163(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201606011.htm [22] 张令非, 陈忠辉, 唐岳松. 含弱层边坡分区滑动破坏模式及演化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(6): 1145-1154. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202106007.htmZhang L F, Chen Z H, Tang Y S. Study on regional slideing failure modes and evolution regularity of slopes with weak layers[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(6): 1145-1154(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX202106007.htm [23] 蒋良潍, 黄润秋. 层状结构岩体顺层斜坡滑移-弯曲失稳计算探讨[J]. 山地学报, 2006, 24(1): 88-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200601011.htmJiang L W, Huang R Q. Studies on estimation of sliding-bending rupture of bedded rock slopes[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2006, 24(1): 88-94(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYA200601011.htm [24] 章涛. 顺层岩质边坡滑移-拉裂破坏机理研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2019.Zhang T. Study on the mechanism of sliding and cracking failure of the rock slope in the smooth layer[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: