Study of loess pore structure characteristics based on CT scanning
-
摘要:
孔隙特征作为反映黄土微观结构的重要特征之一, 直接影响黄土的水敏性、渗透性和强度等物理力学性质。为了研究水力耦合作用下黄土微观孔隙结构特征, 使用CT技术对天然原状、原状饱和与重塑黄土的初始结构以及不固结不排水剪切试验后的土体结构进行了扫描, 通过建立黄土三维结构模型, 分析了剪切试验前后孔隙结构的演变特征。结果表明: 饱和与重塑作用使天然原状黄土的大孔隙减少, 剪切作用使天然原状黄土和重塑黄土发生剪切破坏, 原状饱和黄土发生压缩破坏, 局部孔隙率增加。天然原状黄土与原状饱和黄土在剪切前后均表现为微孔和小孔数量较多, 其孔隙倾角主要分布在50°~90°之间, 解释了黄土亚稳态结构形成的主要原因。扰动作用使重塑黄土的孔隙尺寸分布均匀, 且重塑黄土与原状饱和黄土在水力作用下更易失稳屈服。揭示了黄土剪切变形破坏的微观结构主要表现为粒间胶结物的溶解、孔隙的坍塌与填充以及颗粒旋转、破碎和滑移。试验结果可为黄土剪切强度降低和湿陷机理研究提供依据。
Abstract:Porosity is one of the important characteristics reflecting the microstructure of loess and directly affects the physical and mechanical properties of loess, such as water sensitivity, permeability and strength. To study the micropore structure characteristics of loess under hydraulic coupling, micro CT technology was used to scan the initial structure of natural undisturbed, undisturbed saturated and remolded loess and the soil structure after unconsolidated-undrained shear tests. The evolution characteristics of the pore structure before and after shear tests are analyzed through the three-dimensional structure model of loess. The results show that the pore structures of the natural undisturbed loess, the saturated undisturbed loess and the remolded loess are significantly different, and the pore structures of the samples have a significant impact on the shear failure process. The process of saturation and remodeling can reduce the macropores of undisturbed soil.Shear stress can cause shear failure of natural undisturbed and remolded loess, compression failure of undisturbed saturated loess, and the increases of local porosity. The natural undisturbed and undisturbed saturated loess show a large number of micropores and small pores before and after shear, and the pore dip angle is mainly distributed between 50°-90°, which explains the main reason for the formation of the metastable structure of loess. The remodeled loess has a uniform pore size distribution due to the disturbance effect, and the remodeled and saturated loess is more prone to buckling and yielding under hydraulic action. It is revealed that the microstructure of shear deformation and failure of loess is mainly manifested in the dissolution of intergranular cement, the collapse and filling of pores, and the rotation, fragmentation and slip of particles. The test results can provide a basis for the mechanism of shear strength reduction and collapsibility of loess.
-
Key words:
- loess shear /
- pore structure /
- CT test /
- pore three dimensional model
-
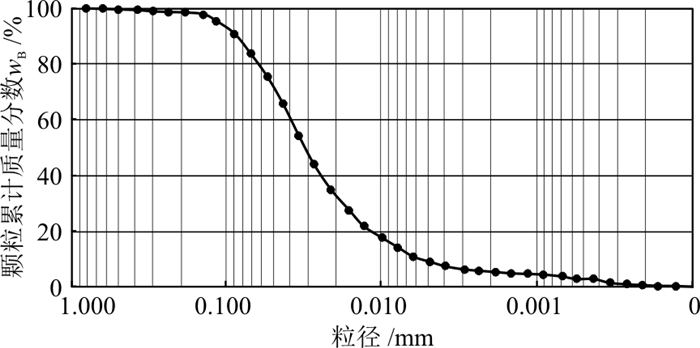
表 1 试样黄土的基本物理性质参数
Table 1. Physical property parameters of the loess samples
含水率
w/%密度
ρ/(g·cm-3)塑限
Wp/%液限
Wl/%塑性指数
Ip/%颗粒组成wB/% >0.075 mm [0.005, 0.075] mm < 0.005 mm 6.2 1.46 18.3 27.5 9.2 17.22 74.22 8.56 表 2 孔隙参数计算方法及定义
Table 2. Calculation method and definition of pore parameters
参数名称 计算方法 注释 孔隙率n2D n2D=AV/AT AV为孔隙面积;AT为土体总面积 孔隙等效直径d3D $d_{3 \mathrm{D}}=\sum\limits_{i=1}^J d_i / J$ di代表孔径;J代表测量值的数量 孔隙体积V3D V3D=N×V0 V0是最小体素单元体的体积;N是三维孔隙所包含的体素单元数目 球度SPH $S P H=\sqrt{\frac{4 V_{3 \mathrm{D}}}{\pi L_{3 \mathrm{D}}}}$ L3D为孔隙长轴直径 倾角θ/(°) $\theta=\sin ^{-1} \frac{\left|z_k-z_i\right|}{\sqrt{\left(x_k-x_i\right)^2+\left(y_k-y_i\right)^2+\left(z_k-z_i\right)^2}}$ (xi, yi, zi)和(xk, yk, zk)代表孔隙片段两端点的三维坐标 倾向φ/(°) $\varphi=\tan ^{-1} \frac{y_k-y_i}{x_k-x_i}$ -
[1] 刘东升. 黄土与环境[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1985.Liu D S. Loess and environment[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1985(in Chinese). [2] Li Y R, Shi W H, Aydin A, et al. Loess genesis and worldwide distribution[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2020, 201: 102947. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.102947 [3] Derbyshire E. Geological hazards in loess terrain, with particular reference to the loess regions of China[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2001, 54(1/3): 231-260. [4] Zhuang J Q, Peng J B, Wang G H, et al. Distribution and characteristics of landslide in Loess Plateau: A case study in Shaanxi Province[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 236: 89-96. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.001 [5] Peng J B, Wang S K, Wang Q Y, et al. Distribution and genetic types of loess landslides in China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2019, 170: 329-350. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.11.015 [6] Zhuang J Q, Peng J B, Xu C, et al. Distribution and characteristics of loess landslides triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan Earthquake, Northwest of China[J]. Geomorphology, 2018, 314: 1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.04.012 [7] Juang C H, Dijkstra T, Wasowski J, et al. Loess geohazards research in China: Advances and challenges for mega engineering projects[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 251: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2019.01.019 [8] 李同录, 范江文, 习羽, 等. 击实黄土孔隙结构对土水特征的影响分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2019, 27(5): 1019-1026. doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019045Li T L, Fan J W, Xi Y, et al. Analysis for effect of microstructure onswcc of compacted loess[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(5): 1019-1026(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019045 [9] 罗浩, 伍法权, 常金源, 等. 马兰黄土孔隙结构特征: 以赵家岸地区黄土为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2021, 29(5): 1366-1372. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202105013.htmLuo H, Wu F Q, Chang J Y, et al. Pore characteristics ofmalan loess: A case study at Zhaojia's landslide[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2021, 29(5): 1366-1372(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202105013.htm [10] Shao X X, Zhang H Y, Tan Y. Collapse behavior and microstructural alteration of remolded loess under graded wetting tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 233: 11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.11.025 [11] Wang H M, Ni W K, Yuan K Z, et al. Microstructure evolution of loess under multiple collapsibility based on nuclear magnetic resonance and scanning electron microscopy[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2021, 18(10): 2612-2625. doi: 10.1007/s11629-021-6838-8 [12] Li X A, Li L C, Song Y X, et al. Characterization of the mechanisms underlying loess collapsibility for land-creation project in Shaanxi Province, China: A study from a micro perspective[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 249: 77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.12.024 [13] Jiang M J, Zhang F G, Hu H J, et al. Structural characterization of natural loess and remolded loess under triaxial tests[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 181: 249-260. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.07.021 [14] Li P, Shao S J, Vanapalli S K. Characterizing and modeling the pore-size distribution evolution of a compacted loess during consolidation and shearing[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2020, 20(7): 2855-2867. doi: 10.1007/s11368-020-02621-3 [15] Li Z Q, Qi Z Y, Qi S W, et al. Microstructural changes and micro-macro-relationships of an intact, compacted and remolded loess for land-creation project from the Loess Plateau[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80(17): 593. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09872-4 [16] Li T C, Shao M A, Jia Y H. Application of X-ray tomography to quantify macropore characteristics of loess soil under two perennial plants[J]. European Journal of Soil Science, 2016, 67(3): 266-275. doi: 10.1111/ejss.12330 [17] 赵建鹏, 崔利凯, 陈惠, 等. 基于CT扫描数字岩心的岩石微观结构定量表征方法[J]. 现代地质, 2020, 34(6): 1205-1213. doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.044Zhao J P, Cui L K, Chen H, et al. Quantitative characterization of rock microstructure of digital core based on CT scanning[J]. Geoscience, 2020, 34(6): 1205-1213(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19657/j.geoscience.1000-8527.2020.044 [18] 蒲毅彬, 陈万业, 廖全荣. 陇东黄土湿陷过程的CT结构变化研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2000, 22(1): 52-57. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200001008.htmPu Y B, Chen W Y, Liao Q R. Research on CT structure changing for damping process of loess in Longdong[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2000, 22(1): 52-57(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC200001008.htm [19] Li Y R, He S D, Deng X H, et al. Characterization of macropore structure of Malan loess in NW China based on 3D pipe models constructed by using computed tomography technology[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 154: 271-279. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.12.028 [20] Li Y R, Zhang T, Zhang Y B, et al. Geometrical appearance and spatial arrangement of structural blocks of the Malan loess in NW China: Implications for the formation of loess columns[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2018, 158: 18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.02.007 [21] Wei T T, Fan W, Yuan W N, et al. Three dimensional pore network characterization of loess and paleosol stratigraphy from South Jingyang Plateau, China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2019, 78(11): 333. doi: 10.1007/s12665-019-8331-z [22] Zhang L X, Qi S W, Ma L N, et al. Three-dimensional pore characterization of intact loess and compacted loess with micron scale computed tomography and mercury intrusionporosimetry[J]. Scientific Reports, 2020, 10(1): 8511. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-65302-8 [23] 邵帅, 邵生俊, 朱丹丹, 等. 黄土的细观结构演变与宏观结构性变化规律[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2021, 43(增刊1): 64-70. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2021S1014.htmShao S, Shao S J, Zhu D D, et al. Evolution of micro-structure and macro-structural property of loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(S1): 64-70(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2021S1014.htm [24] 李鑫. 基于CT的黄土微细观空隙结构及优先流特性研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020.Li X. Research on micro and meso void structure and preferential flow characteristics of loess based on CT[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [25] Xu P P, Lin T, Qian H, et al. Anisotropic microstructure of loess-paleosol sequence and its significance for engineering and paleoclimate: A case study from Xiushidu(XSD) profile, southern Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 286(1): 106092. [26] 蒋明镜, 胡海军, 彭建兵, 等. 应力路径试验前后黄土孔隙变化及与力学特性的联系[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2012, 34(8): 1369-1378. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201208004.htmJiang M J, Hu H J, Peng J B, et al. Pore changes of loess before and after stress path tests and their links with mechanical behaviors[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2012, 34(8): 1369-1378(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201208004.htm [27] 魏婷婷. 荷载作用下黄土三维微结构演化及变形破坏机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020.Wei T T. Research on three-dimensional microstructure evolution and deformation mechanism of loess during loading[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [28] 井旭, 谢婉丽, 单帅. 原状及重塑黄土双轴试验微观力学特征离散元模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(3): 184-193. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0311Jing X, Xie W L, Shan S. Discrete element simulation study on micromechanical characteristics of undisturbed and remolded loess in biaxial test[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(3): 184-193(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0311 [29] Rezaee M, Jafari A, Kazemzadeh E. Relationships between permeability, porosity and pore throat size in carbonate rocks using regression analysis and neural networks[J]. Journal of Geophysics and Engineering, 2006, 3(4): 370-376. doi: 10.1088/1742-2132/3/4/008 [30] 雷祥义. 中国黄土的孔隙类型与湿陷性[J]. 中国科学: B辑, 1987(12): 1309-1318. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK198712008.htmLei X Y. Pore types and collapsibility of loess in China[J]. Science in China Series B, 1987(12): 1309-1318(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JBXK198712008.htm [31] 张瑜婷. 温度对重塑马兰黄土渗透性的影响研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019.Zhang Y T. Study on the influence of temperature on thepremeability of remolded Malan loess[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [32] 任晓虎, 许强, 赵宽耀, 等. 反复入渗对重塑黄土渗透特性的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 130-138. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0214Ren X H, Xu Q, Zhao K Y, et al. Effect of repeated infiltration on permeability characteristics of remolded loess[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 130-138(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0214 [33] 井彦林, 李洁茹, 张志权, 等. 陕西渭北黄土浸水饱和前后孔隙变化规律[J]. 水电能源科学, 2021, 39(10): 160-163. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY202110039.htmJing Y L, Li J R, Zhang Z Q, et al. Pore changes of loess before and after water saturation in Weibei, Shaanxi Province[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39(10): 160-163(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY202110039.htm [34] Wen B P, Yan Y J. Influence of structure on shear characteristics of the unsaturated loess in Lanzhou, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2014, 168: 46-58. [35] Xu P P, Zhang Q Y, Qian H, et al. An investigation into the relationship between saturated permeability and microstructure of remolded loess: A case study from Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geoderma, 2021, 382: 114774. [36] 魏亚妮. 水作用下黄土三维微结构演化及湿陷机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2019.Wei Y N. Research on three-dimensional microstructure evolution during wetting and collapsible mechanism of loess[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [37] 樊家豪. 黄土三维微结构演化动态表征[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021.Fan J H. Dynamic characterization of three-dimensional micro-structural evolution of loess[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). [38] Pulido-Moncada M, Katuwal S, Ren L, et al. Impact of potential bio-subsoilers on pore network of a severely compacted subsoil[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 363: 114154. [39] Kang D H, Yun T, Matthew E T. Evolution of pore orientation in granular media under biaxial compression[C]//Anon. Geo-Congress 2014: Geo-characterization and modeling for sustainability. [S. l. ]: Geotechnical Special Publication, 2014: 2830-2838. [40] Li Y R, Mo P, Wang Y F, et al. Strength anisotropy of Malan loess and the implications for the formation of loess walls and columns: Science direct[J]. Catena, 2020b, 194. [41] Liu Z, Liu F Y, Ma F L, et al. Collapsibility, composition, and microstructure of loess in China[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2016, 53(4): 673-686. [42] Peng D L, Xu Q, Liu F Z, et al. Distribution and failure modes of the landslides inHeitai terrace, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 236: 97-110. [43] 张宁宁, 骆亚生, 沙磊. 含水率对非饱和原状黄土强度的影响[J]. 水土保持通报, 2013, 33(5): 101-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201305022.htmZhang N N, Luo Y S, Sha L. Effect of water content on strength of undisturbed unsaturated loess[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation, 2013, 33(5): 101-104(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STTB201305022.htm [44] 方瑾瑾, 邵生俊, 冯以鑫. 真三轴条件下原状黄土的强度与含水率的关系[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 2016, 32(3): 314-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XALD201603011.htmFang J J, Shao S J, Feng Y X. Relationship between strength and water content of unsaturated intact loess based on true tri-axial tests[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Technology, 2016, 32(3): 314-320(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XALD201603011.htm [45] 蔡国庆, 张策, 黄哲文, 等. 含水率对砂质Q3黄土抗剪强度影响的试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(增刊2): 32-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2020S2006.htmCai G Q, Zhang C, Huang Z W, et al. Experimental study on influence of moisture content on shear strength of unsaturated loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(S2): 32-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC2020S2006.htm [46] 南静静. 湿载作用下黄土力学特性及微结构演变研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2021.Nan J J. Study on mechanical behavior and microstructural variation in loess under loading and wetting[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2021(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: