Experimental study on the effect of rainfall patterns on the failure mode of debris flows after earthquakes: A case study of Tiantanggou, Jiuzhai
-
摘要:
降雨过程中降雨强度的变化会影响土体渗透率及饱和过程, 从而改变土体的力学性质, 影响泥石流起动模式及破坏规模。为探究不同降雨模式对震后泥石流起动机制的影响, 自制了小比例模型槽, 结合可控雨型的降雨模拟系统, 进行了人工降雨诱发泥石流的室内模型试验; 基于不同降雨模式下泥石流的起动过程分析, 对坡体内部含水率和孔隙水压力的变化规律进行了研究。研究结果表明: 递增型降雨模式下泥石流发生突然, 呈整体滑坡转化为泥石流起动模式, 坡体破坏规模最大; 递减型降雨模式下表现为后退式溃散失稳起动模式; 均匀型降雨模式下则表现为溯源侵蚀起动模式; 中峰型降雨模式下以局部滑坡转化为泥石流起动模式; Ⅴ型降雨模式下则由坡面侵蚀加剧转化为泥石流启动模式, 破坏规模最小。研究结果可以为九寨沟地区泥石流的预报预警提供参考。
Abstract:Variable rainfall intensity can influence soil permeability and saturation processes, change the mechanical properties of soil, and affect the initiation mode and damage scale of debris flows. To explore the response mechanism of debris flows under different rainfall modes after earthquakes, laboratory tests of artificial rainfall-induced debris flows was performed through a small-scale model trough and rainfall simulation system. Based on the starting process of debris flow under different rainfall patterns, the variation of water content and pore water pressure in the slope was studied. The results show that the landslide transforms to a debris flow under the increasing rainfall model, and the damage scale of the accumulation is the largest; the debris flow under the decreasing rainfall occurs after the backward breaking instability; the initiation of debris flow under uniform rainfall mode results from traceable erosion; local landslides are transformed into debris flows under the middle-peak rainfall pattern; under the Ⅴ-shaped rainfall pattern, the slope erosion is intensified and transformed into debris flow, with the smallest damage scale.The research results can provide reference for the forecast and warning of debris flow in Jiuzhaigou area.
-
Key words:
- rainfall pattern /
- debris flow /
- physical model experimentation /
- water content
-
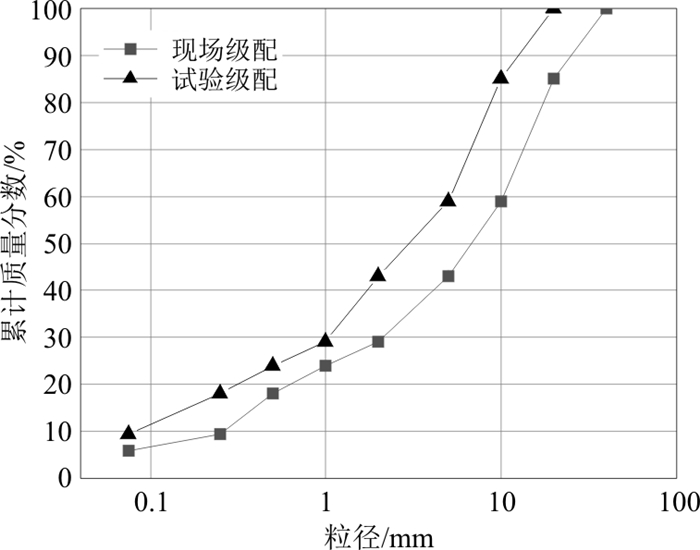
表 1 各降雨模式下坡体破坏过程汇总
Table 1. Summary of slope body failure process under different rainfall patterns
试验编号 1 2 3 4 5 降雨类型 递增型 递减型 均匀型 中峰型 V型 泥石流起动时间/min 16 9 22 25 35 最大侵蚀速率/(kg·min-1) 12.86 10.55 3.87 4.92 2.16 累计侵蚀量/kg 80.95 61.03 63.95 41.9 19.97 -
[1] Fan X M, Domenech G, Scaringi G, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution of mass wasting after the 2008 Mw 7.9 Wenchuan earthquake revealed by a detailed multi-temporal inventory[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(12): 2325-2341. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-1054-5 [2] 崔鹏, 庄建琦, 陈兴长, 等. 汶川地震区震后泥石流活动特征与防治对策[J]. 四川大学学报: 工程科学版, 2010, 42(5): 10-19. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201005005.htmCui P, Zhuang J Q, Chen X C, et al. Characteristics and countermeasures of debris flow in Wenchuan area after the earthquake[J]. Advanced Engineering Sciences, 2010, 42(5): 10-19(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SCLH201005005.htm [3] Fan X M, Scaringi G, Xu Q, et al. Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake(Sichuan, China): Factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(5): 967-983. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0960-x [4] 黄发明, 汪洋, 董志良, 等. 基于灰色关联度模型的区域滑坡敏感性评价[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(2): 664-676. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902027.htmHuang F M, Wang Y, Dong Z L, et al. Regional landslide susceptibility mapping based on grey relational degree model[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(2): 664-676(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201902027.htm [5] 李宁, 唐川, 卜祥航, 等. "5·12"地震后汶川县泥石流特征与演化分析[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(6): 1233-1245. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202006010.htmLi N, Tang C, Bu X H, et al. Characteristics and evolution of debris flows in wenchuan county after "5·12" earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(6): 1233-1245(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202006010.htm [6] 崔鹏, 刘世建, 谭万沛. 中国泥石流监测预报研究现状与展望[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2000, 9(2): 10-15. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2000.02.002Cui P, Liu S J, Tan W P. Progress of debris flow forecast in china[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2000, 9(2): 10-15(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2000.02.002 [7] 李继兴, 严松, 杨春建, 等. 泥质砂岩残积土边坡降雨冲刷特性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 26-33. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0051Li J X, Yan S, Yang C J, et al. Rainfall erosion characteristics of argillaceous sandstone residual soil slopes[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 10-15(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0051 [8] 缪海波, 王功辉. 风振影响下乔木坡地暴雨型浅层滑坡演化机制[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 60-70. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0011Miao H B, Wang G H. Evolution mechanism of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides on slopes covered by arbors considering the influence of wind-induced vibration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 60-70(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0011 [9] Chen N S, Gao Y C, Yang C L, et al. Effect of clay content to the strength of gravel soil in the source region of debris flow[J]. Journal of Mountain Science, 2018, 15(10): 2320-2334. doi: 10.1007/s11629-018-4911-8 [10] Timilsina S, Jeffrey D, Niemann, et al. Modeling hydrologic processes associated with soil saturation and debris flow initiation during the September 2013 storm, Colorado Front Range[J]. Landslides, 2021, 18(5): 1741-1759. doi: 10.1007/s10346-020-01582-5 [11] 栗倩倩, 史绪山, 柴波, 等. 台风-非台风降雨型滑坡的多时段临界雨量值预测模型[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 267-273. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0076Li Q Q, Shi X S, Chai B, et al. Multiduration critical rainfall prediction model for typhoons and non-typhoon rainfall landslides[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 267-273(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0076 [12] 陈晓清, 崔鹏, 冯自立, 等. 滑坡转化泥石流起动的人工降雨试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(1): 106-116. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200601020.htmChen X C, Cui P, Feng Z L, et al. Artificial rainfall experimental study on landslide translation to debris flow[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(1): 106-116(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200601020.htm [13] Chen N S, Zhou W, Yang C L, et al. The processes and mechanism of failure and debris flow initiation for gravel soil with different clay content[J]. Geomorphology, 2010, 121(3/4): 222-230. [14] 高冰, 周健, 张姣. 泥石流起动过程中水土作用机制的宏细观分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2011, 30(12): 2567-2573. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201112023.htmGao B, Zhou J, Zhang J. Macro-meso analysis of water-soil interaction mechanism of debris flow starting process[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2011, 30(12): 2567-2573(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201112023.htm [15] 周健, 杜强, 李翠娜. 降雨强度对泥石流起动影响的模型试验研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2016, 25(3): 104-113. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201603012.htmZhou J, Du Q, Li C N. Model test of rainfall intensity influence on debris flow starting[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2016, 25(3): 104-113(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201603012.htm [16] 罗渝, 何思明, 何尽川. 降雨类型对浅层滑坡稳定性的影响[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2014, 39(9): 1357-1363. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201409012.htmLuo Y, He S M, He J C. Effect of rainfall patterns on stability of shallow landslide[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2014, 39(9): 1357-1363(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201409012.htm [17] 常鸣, 窦向阳, 范宣梅, 等. 汶川震区暴雨泥石流激发雨型特征[J]. 现代地质, 2018, 32(3): 623-630. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803020.htmChang M, Dou X Y, Fan X M, et al. Critical rainfall patterns for rainfall-induced debris flows in the Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Geoscience, 2018, 32(3): 623-630(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XDDZ201803020.htm [18] Fan L F, Lehmann P, Zheng C M, et al. Rainfall intensity temporal patterns affect shallow landslide triggering and hazard evolution[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 2020, 47(1): 2019GL085994. [19] Ng C, Wang B, Tung Y K. Three-dimensional numerical investigations of groundwater responses in an unsaturated slope subjected to various rainfall patterns[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2001, 38(5): 1049-1062. [20] Ran Q H, Wang F, Gao Y H, et al. Modelling effects of rainfall patterns on runoff generation and soil erosion processes on slopes[J]. Water, 2019, 11(11): 2221. [21] Ran Q H, Hong Y Y, Li, W, et al, A modelling study of rainfall-induced shallow landslide mechanisms under different rainfall characteristics[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2018, 563: 790-801. [22] Tsai T L. The influence of rainstorm pattern on shallow landslide[J]. Environmental Geology, 2007, 53(7): 1563-1569. [23] Tsai T L, Wang J K. Examination of influences of rainfall patterns on shallow landslides due to dissipation of matric suction[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2010, 63(1): 65-75. [24] 朱煦. 前期降雨对强震区泥石流启动模式的影响研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.Zhu X. Study on the influence of prophase fainfall to the initation model of Debris flow in meizoseismal area[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014. [25] 翟淑花, 冒建, 安立伟, 等. 不同雨型下泥石流松散物源体降雨入渗及衰减规律[J]. 人民长江, 2019, 50(7): 22-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201907004.htmZhai S H, Mao J, An L W, et al. Rainfall infiltration and attenuation regularity analysis of debris flow loose material under different rainfall pattern[J]. Yangtze River, 2019, 50(7): 22-27(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-RIVE201907004.htm [26] 朱颖彦, 崔鹏, 陈晓晴. 泥石流堆积体边坡失稳机理的试验与稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(21): 129-136.Zhu Y H, Cui P, Che X Q. Experiment on mechanism of slope failure of debris flow fan and stability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(21): 129-136(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: