Investigation of the kinematic characteristic of Lijie Beishan landslide through surface displacement monitoring and rainfall response numerical simulation
-
摘要:
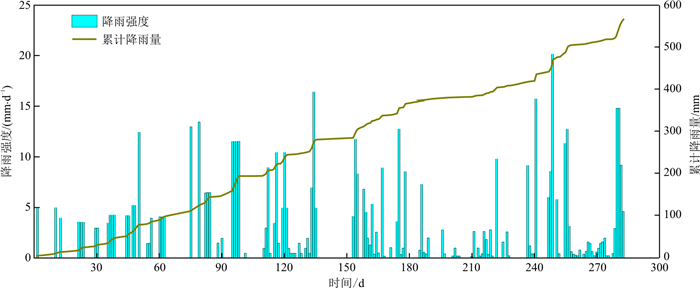
速度倒数法(INV)是基于坡表变形特征的滑坡启滑预测工具, 其与滑坡内部多物理场演化的关系仍需进一步明晰。开展了甘肃省舟曲县立节北山滑坡的勘察与坡表变形监测, 采用基于速度倒数法、速度阈值法、以非饱和土理论为基础的边坡降雨响应模拟3种方法, 对该滑坡的运动特征与失稳的内在机制展开了研究。研究结果表明: 边坡变形速度倒数-时间曲线有明显的加速起始点。速度倒数在2021年6月3日达到最低值后, 进入约60 d的平稳期, 在9月20日突然加速, 并在20 d内速度达到200 mm/d以上, 变形不再收敛。基于速度倒数法得到的滑坡生命周期结束点, 与实际的失稳点相差8 d, 提前约130 d对该突发性滑坡进行了预报。根据全过程速度时程曲线, 存在20, 60, 100 mm/d的多级速度阈值。边坡应力场、变形场、渗流场的数值模拟结果显示, 变形时程曲线的拐点与降雨强度的增加相关, 累计降雨量与安全系数呈指数负相关。数值模拟得到的累计变形为2 250 mm, 变形速度为10~35 mm/d, 速度倒数为0.03~0.12 d/mm, 与实际监测数据接近。综上所述, 速度倒数法对立节北山滑坡的生命周期进行了有效预测, 基于速度的预警阈值受长时序变形时程曲线波动的影响, 采用以非饱和土理论为基础的数值模拟明晰了立节北山滑坡变形对降雨的响应机制。
Abstract:Slope kinematics is normally used to evaluate the temporal and spatial evolution of landslides. The inverse velocity method (INV) is an important tool for predicting the initiation of landslide, but its correlation with the physical and mechanical mechanisms of multiple physical fields inside the landslide need to be further clarified. In this paper, the slope deformation and geological characteristics of the Lijie Beishan landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province was investigated. The inverse velocity method, velocity threshold method and numerical simulation based on unsaturated soil theory were used to study the kinematic characteristic of slope. The results showed that after the lowest value of the inverse velocity on June 3, 2021, a stable stage lasted for approximately 60 days and then suddenly accelerated on September 20. The velocity became more than 200 mm/d over 20 days, and the deformation did not converged. There was an obvious acceleration point in the time-dependent inverse velocity curve. The end of the landslide life cycle was obtained by extending the straight line after the onset of the acceleration point. The prediction period was within 8 days compared to the actual instability startup, and the landslide was predicted 130 days in advance. According to the post analysis of the whole time-dependent velocity curve, the multi-level speed thresholds of
v 1=20 mm/d,v 2=60 mm/d, andv 3=100 mm/d were set up. Because there were two peaks of velocity, the prediction of landslide triggering was lagging compared to the inverse velocity method. The coupling of slope stresses, deformation and pore water transportation was simulated. The results showed that the inflection point of the time-dependent deformation curve was correlated with the increase in precipitation intensity, and the cumulative precipitation was negatively exponentially correlated with the safety factor. The cumulative deformation obtained by numerical simulation was 2 250 mm, the velocity of deformation was 10-35 mm/d, and the inverse velocity was 0.03-0.12 d/mm, which were close to the actual monitoring data. However, there was still a deviation between the prediction of the inflection point of slope deformation and the actual situation. -
表 1 速度阈值预警等级
Table 1. Warning level and velocity threshold
变形速度 v < v1 v≥v1 v≥v2 v2≥v≥v3 v≥v3,Δv>0 预警等级 正常监测级 注意级 警示级 警戒级 警报级 注:v1用于识别滑坡开始出现异常变形时的状态;v2用于判断滑坡异常变形是否进入加速阶段;v3用于判断变形是否达到临界状态。另外, 采用速度增量Δv来判断滑坡变形趋势 表 2 岩土体物理力学参数取值
Table 2. Mechanical and physical parameters of the soil and rocks
名称 重度/(kN·m-3) 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 饱和含水率/% 渗透系数/(m·s-1) 泊松比 弹性模量/MPa 堆积体 15~18 15 10~15 45 2.2×10-6 0.30~0.35 10~20 基岩 26~27 6×103 — — 0.20~0.25 4×104 -
[1] Carlà T, Intrieri E, Traglia F D, et al. Guidelines on the use of inverse velocity method as a tool for setting alarm thresholds and forecasting landslides and structure collapses[J]. Landslides, 2017, 14(2): 517-534. doi: 10.1007/s10346-016-0731-5 [2] Intrieri E, Carlà T, Gigli G. Forecasting the time of failure of landslides at slope-scale: A literature review[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2019, 193: 333-349. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2019.03.019 [3] 马海涛, 张亦海, 于正兴. 滑坡速度倒数法预测模型加速开始点识别及临滑时间预测研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2021, 40(2): 355-364. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0522Ma H T, Zhang Y H, Yu Z X. Research on the identification of acceleration starting point in inverse velocity method and the prediction of sliding time[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(2): 355-364(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2020.0522 [4] Mufundirwa A, Fujii Y, Kodama J. A new practical method for prediction of geomechanical failure-time[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 2010, 47(7): 1079-1090. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.07.001 [5] Cruden D M, Masoumzadeh S. Accelerating creep of the slopes of a coal mine[J]. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering, 1987, 20(2): 123-135. doi: 10.1007/BF01410043 [6] Crosta G B, Agliardi F. Failure forecast for large rock slides by surface displacement measurements[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2003, 40(1): 176-191. doi: 10.1139/t02-085 [7] 许强, 彭大雷, 何朝阳, 等. 突发型黄土滑坡监测预警理论方法研究: 以甘肃黑方台为例[J]. 工程地质学报, 2020, 28(1): 111-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202001013.htmXu Q, Peng D L, He C Y, et al. Theory and method of monitoring and early warningfor sudden loess landslide: A case study at Heifangtai terrace[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(1): 111-121(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ202001013.htm [8] 方汕澳, 许强, 修德皓, 等. 基于斜率模型的突发型黄土滑坡失稳时间预测[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2021, 48(4): 169-179. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202009012Fang S A, Xu Q, Xiu D H, et al. A study of the predicted instability time of sudden loess landslides based on the SLO model[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(4): 169-179(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202009012 [9] Petley D N, Bulmer M H, Murphy W. Patterns of movement in rotational and translational landslides[J]. Geology, 2002, 30(8): 719-722. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0719:POMIRA>2.0.CO;2 [10] Rose N D, Hungr O. Forecasting potential rock slope failure in open pit mines using the inverse-velocity method[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics & Mining Sciences, 2007, 44(2): 308-320. [11] Dick G J, Eberhardt E, Cabrejoliévano A G, et al. Development of an early-warning time-of-failure analysis methodology for open-pit mine slopes utilizing ground-based slope stability radar monitoring data[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal, 2014, 52(4): 515-529. [12] Carlà T, Intrieri E, Traglia F D, et al. Reply to discussion on "Guidelines on the use of inverse velocity method as a tool for setting alarm thresholds and forecasting landslides and structure collapses" by F. Bozzano, P. Mazzanti, and S. Moretto[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(7): 1443-1444. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0991-3 [13] Zhou X P, Liu L J, Xu C. A modified inverse-velocity method for predicting the failure time of landslides[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 268(3): 105521. [14] Bozzano F, Mazzanti P, Moretto S. Discussion to: 'Guidelines on the use of inverse velocity method as a tool for setting alarm thresholds and forecasting landslides and structure collapses'[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(7): 1437-1441. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0976-2 [15] 杨背背, 殷坤龙, 梁鑫, 等. 三峡库区麻柳林滑坡变形特征及演化模拟[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 122-129. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0213Yang B B, Yin K L, Liang X, et al. Deformation characteristics and evolution simulation of the Maliulin landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 122-129(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0213 [16] 张怡悦, 殷坤龙, 陈丽霞, 等. 奉节县曾家棚滑坡时空差异性变形特征与成因机制分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 148-157. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0216Zhang Y Y, Yin K L, Chen L X, et al. Characteristics and mechanism of spatio-temporal difference deformation of Zengjiapeng landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 148-157(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0216 [17] 兰恒星, 伍法权, 周成虎, 等. GIS支持下的降雨型滑坡危险性空间分析预测[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(5): 507-512. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.05.021Lan H X, Wu F Q, Zhou C H, et al. Spatial analysis and prediction of rainfall-induced landslide hazard based on GIS[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2003, 48(5): 507-512(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.05.021 [18] Caine N. The rainfall intensity-duration control of shallow landslides and debris flows[J]. Geografiska Annaler Series A: Physical Geography, 1980, 62(1/2): 23-27. doi: 10.2307/520449 [19] Glade T. Models of antecedent rainfall and soil water status applied to different regions in New Zealand[C]//Anon. Proceedings of the 23rd general assembly of the European Geophysical Society. Annales Geophysicae. Seville[S. l. ]: [s. n. ]1998: 24-70. [20] Lu N, Godt J. Infinite slope stability under steady unsaturated seepage conditions[J]. Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(11): 2276-2283. [21] Tsai T L, Chiang S J. Modeling of layered infinite slope failure triggered by rainfall[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 68(5): 1429-1434. [22] 阳帅, 谭泽颖, 陈宏信, 等. 基于修正Green-Ampt模型的降雨诱发区域浅层斜坡失稳灾害分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 219-227. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0048Yang S, Tan Z Y, Chen H X, et al. Analysis of instability disaster of rainfall-induced shallow landslides at the regional scale based on the modified Green-Ampt model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 219-227(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0048 [23] 许强, 曾裕平. 具有蠕变特点滑坡的加速度变化特征及临滑预警指标研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(6): 1099-1106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200906005.htmXu Q, Zeng Y P. Research on acceleration variation characteristics of creep landslide and early-warning prediction indicator of critical sliding[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(6): 1099-1106(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200906005.htm [24] 许强, 汤明高, 徐开祥, 等. 滑坡时空演化规律及预警预报研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2008, 27(6): 1104-1112. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200806005.htmXu Q, Tang M G, Xu K X, et al. Research on space-time evolution laws and early warning-prediction of landslides[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(6): 1104-1112(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200806005.htm -





 下载:
下载: