Improved slope unit method for fine evaluation of regional landslide susceptibility
-
摘要:
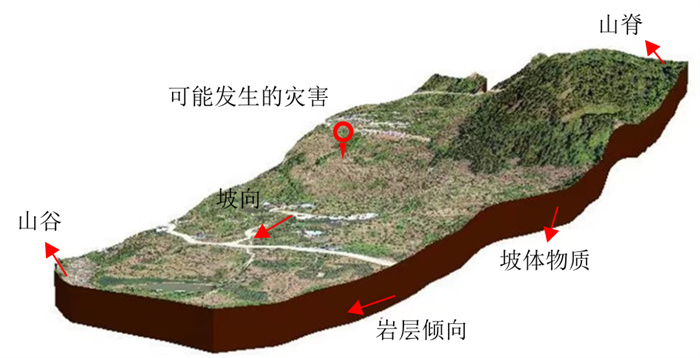
易发性评价是区域滑坡灾害风险预警与稳定性分析的基础,针对乡镇尺度的大比例尺精细化滑坡易发性评价,传统基于水文学和地貌学的斜坡单元划分方法难以满足评价精度。针对以上问题,以重庆市万州区大周镇为实例验证对象,形成了适用于精细化评价的改进斜坡单元划分方法。首先从斜坡地质环境孕灾规律出发,综合考虑地形地貌、物质组成、斜坡结构和灾害类型的均一性要求,提出了基于斜坡地质环境一致性的改进斜坡单元划分方法,选择重庆市万州区大周镇为实例验证对象,并与水文分析法、曲率分水岭法进行了对比分析。结果表明:①改进斜坡单元法划分的评价单元大小均匀性较好,未出现细碎单元或畸形长条状单元;②评价单元的总体形态特征更为合理,形态指数集中在1~2之间,呈现圆形或正方形斜坡形态;③改进斜坡单元划分的结果与已有灾害边界范围的叠加重合度最高,能更好地体现滑坡易发性评价或稳定性分析物理意义。研究结论对提高区域滑坡易发性评价的准确性与精度具有重要借鉴意义。
Abstract:Susceptibility evaluation is the basis of regional landslide risk early warning and stability analysis. Scientific and reasonable division of evaluation unit is the key to landslide susceptibility evaluation. For large-scale fine landslide susceptibility evaluation, the traditional slope unit division method based on hydrology and geomorphology generally results in low accuracy of the evaluation. In this paper, an improved slope unit method based on the slope geological environment is proposed. Dazhou Town was selected as an example and the obtained results from the proposed model were compared with the results from hydrological analysis method and curvature watershed method. The results show that the size uniformity of the evaluation units divided by the proposed method is better, and no fine units or deformed long strip units were generated. The overall morphological characteristics of the evaluation unit are more reasonable, and the morphological index is between 1 and 2, which generally presents circular-like or square-like shape. At the same time, the superposition degree between the results of the improved slope unit division and the range of the existing disaster boundary is the highest, which can better reflect the physical significance of landslide risk assessment. The proposed model has significant potential for improving the accuracy of regional landslide susceptibility evaluation.
-
Key words:
- regional landslide /
- susceptibility evaluation /
- slope unit /
- division method /
- ArcGIS
-
表 1 斜坡结构类型划分
Table 1. Division of slope structure type
斜坡结构类型 划分准则 水平坡 岩层倾角小于10° 非水平坡 顺向坡 岩层倾角大于10°且岩层倾向与斜坡坡向夹角在30°以内 斜交坡 岩层倾角大于10°且岩层倾向与斜坡坡向夹角在30°~150°之间 逆向坡 岩层倾角大于10°且岩层倾向与斜坡坡向夹角在150°~180°之间 表 2 3种斜坡单元划分结果统计表
Table 2. Division results of the three slope unit methods
水文分析法占比/% 曲率分水岭法占比/% 改进斜坡单元划分法占比/% 分布/ m2 [0, 103) 31.67 1.94 0 [103, 104) 18.51 10.53 1.87 [104, 105] 27.76 68.42 71.64 >105 22.06 19.11 26.49 形状指数 [1, 1.5) 13.17 43.77 29.10 [1.5, 2) 25.98 38.23 50.00 [2, 3) 22.06 13.30 19.03 [3, 5] 17.79 4.16 1.87 >5 21.35 0.55 0 灾害重合度/% < 50 27.27 39.39 3.03 [50, 75) 24.24 36.36 9.09 [75, 100) 6.06 12.12 15.15 100 42.42 12.12 72.73 -
[1] 殷坤龙, 韩再生, 李志中. 国际滑坡研究的新进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2000, 27(5): 1-4. doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2000.05.001Yin K L, Han Z S, Li Z Z. New progress in international landslide research[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2000, 27(5): 1-4(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2000.05.001 [2] 殷坤龙, 张宇, 汪洋. 水库滑坡涌浪风险研究现状和灾害链风险管控实践[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 1-12. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0064Yin K L, Zhang Y, Wang Y. A review of landslide-generated waves risk and practice of management of hazard chain risk from reservoir landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0064 [3] 王芳, 殷坤龙, 桂蕾, 等. 万州区滑坡灾害风险管理对策[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2017, 24(5): 31-36. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201705006.htmWang F, Yin K L, Gui L, et al. Risk management countermeasures for landslide disaster in Wanzhou District[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2017, 24(5): 31-36(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201705006.htm [4] Tengtrairat N, Woo W L, Parathai P, et al. Automated landslide-risk prediction using web GIS and machine learning models[J]. Sensors(Basel, Switzerland), 2021, 21(13): 4620. doi: 10.3390/s21134620 [5] Pawan G, Tetsuya K, Lok M S, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping with GIS in high mountain area of Nepal: A comparison of four methods[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2021, 80(9): 1-18. doi: 10.1007/s12665-021-09650-2 [6] Zhou H W, Yu J J, Feng H J, et al. A modelling tool for rainfall-triggered landslide susceptibility mapping and hazard warning based on GIS and machine learning[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science, 2021, 783(1): 012074. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/783/1/012074 [7] 周超, 殷坤龙, 曹颖, 等. 基于集成学习与径向基神经网络耦合模型的三峡库区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(6): 1865-1876. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006001.htmZhou C, Yin K L, Cao Y, et al. Landslide susceptibility assessment by applying the coupling method of radial basis neural network and adaboost: A case study from the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Sciences, 2020, 45(6): 1865-1876(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202006001.htm [8] 田述军, 张珊珊, 唐青松, 等. 基于不同评价单元的滑坡易发性评价对比研究[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2019, 28(6): 137-145. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201906015.htmTian S J, Zhang S S, Tang Q S, et al. Comparative study of landslide susceptibility assessment based on different evaluation units[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2019, 28(6): 137-145(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201906015.htm [9] 王凯, 张少杰, 韦方强. 斜坡单元提取方法研究进展和展望[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2020, 37(6): 85-93. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202006019.htmWang K, Zhang S J, Wei F Q. Slope unit extraction methods: Advances and prospects[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(6): 85-93(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202006019.htm [10] 张俊, 殷坤龙, 王佳佳, 等. 三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(2): 284-296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201404018.htmZhang J, Yin K L, Wang J J, et al. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility for Wanzhou District of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(2): 284-296(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201404018.htm [11] 薛强, 张茂省, 高波. 斜坡单元支持下基于土体含水率的陕西省清涧县城区黄土滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(6): 1904-1914. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006025.htmXue Q, Zhang M S, Gao B. Hazard assessment of loess landslide based on soil moisture content and supported by slope unit in Qingjian City, Shaanxi Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(6): 1904-1914(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI202006025.htm [12] 许晓露, 刘汉湖, 蒋川东. 基于斜坡单元的滑坡易发性评价: 以易贡地区为例[J]. 河南科学, 2019, 37(11): 1825-1832. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201911018.htmXu X L, Liu H H, Jiang C D. Evaluation of landslide susceptibility based on slope unitl: A case study of Yigong[J]. Henan Science, 2019, 37(11): 1825-1832(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201911018.htm [13] 黄启乐, 陈伟, 傅旭东. 斜坡单元支持下区域泥石流危险性AHP-RBF评价模型[J]. 浙江大学学报: 工学版, 2018, 52(9): 1667-1675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201809006.htmHuang Q L, Chen W, Fu X D. AHP-RBF evaluation model of regional debris flow hazard supported by slope unit[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University: Engineering, 2018, 52(9): 1667-1675(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZDZC201809006.htm [14] 宫清华, 黄光庆, 张冬良, 等. 基于斜坡单元的浅层滑坡风险区划: 以华南松岗河小流域为例[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(2): 615-620. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201702043.htmGong Q H, Huang G Q, Zhang D L, et al. Risk zoning of shallow landslides based on slope units: A case study of Songgang River watershed in South China[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(2): 615-620(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201702043.htm [15] 贾娟, 郭孟周, 姚昆, 等. 斜坡单元支持下基于信息量模型的地灾危险性评价[J]. 河南科学, 2017, 35(5): 787-792. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201705020.htmJia J, Guo M Z, Yao K, et al. Geo-hazard assessment based on information quantity model supported by slope unit[J]. Henan Science, 2017, 35(5): 787-792(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNKX201705020.htm [16] 易靖松, 张勇, 石胜伟, 等. 基于斜坡单元的山区城镇地质灾害风险快速评价研究: 以江口镇为例[J]. 探矿工程: 岩土钻掘工程, 2018, 45(8): 72-78. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TKGC201808015.htmYi J S, Zhang Y, Shi S W, et al. Study on the rapid evaluation of geological hazards in mountain towns based on slope unit: Taking Jiangkou Town for example[J]. Exploration Engineering: Rock &. Soil Drilling and Tunneling, 2018, 45(8): 72-78(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TKGC201808015.htm [17] 邱丹丹, 牛瑞卿. 基于斜坡单元的地震滑坡敏感性分析[J]. 自然灾害学报, 2017, 26(2): 144-151. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201702017.htmQiu D D, Niu R Q. Susceptibility analysis of earthquake-induced landslides based on slope units[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2017, 26(2): 144-151(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZH201702017.htm [18] 薛强, 张茂省, 李林. 基于斜坡单元与信息量法结合的宝塔区黄土滑坡易发性评价[J]. 地质通报, 2015, 34(11): 2108-2115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201511018.htmXue Q, Zhang M S, Li L. Loess landslide susceptibility evaluation based on slope unit and information value method in Baota District, Yan'an[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2015, 34(11): 2108-2115(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201511018.htm [19] 张曦, 陈丽霞, 徐勇, 等. 两种斜坡单元划分方法对滑坡灾害易发性评价的对比研究[J]. 安全与环境工程, 2018, 25(1): 12-17, 50. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201801003.htmZhang X, Chen L X, Xu Y, et al. Comparison of two methods for slope unit division in landslide susceptibility evaluation[J]. Safety and Environmental Engineering, 2018, 25(1): 12-17, 50(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KTAQ201801003.htm [20] Guzzetti F, Carrara A, Cardinali M, et al. Landslide hazard evaluation: A review of current techniques and their application in a multi-scale study, Central Italy[J]. Geomorphology, 1999, 31(1/4): 181-216. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0169555x99000781 [21] Xie M, Esaki T, Qiu C, et al. Spatial three-dimensional landslidesusceptibility mapping tool and its applications[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2007, 14(6): 73-84. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1872579108600044 [22] Jia N, Mitani Y, Xie M, et al. Shallow landslide hazard assessment using a three-dimensional deterministic model in a mountainous area[J]. Computers and Geotechnics, 2012, 45: 1-10. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035037350710_b64a.html [23] Wang K, Zhang S J, Tellez R D, et al. A new slope unit extraction method for regional landslide analysis based on morphological image analysis[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2019, 78: 4139-4151. doi: 10.1007/s10064-018-1389-0 [24] 颜阁, 梁收运, 赵红亮. 基于GIS的斜坡单元划分方法改进与实现[J]. 地理科学, 2017, 37(11): 1764-1770. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201711019.htmYan G, Liang S Y, Zhao H L. An approach to improving slope unit division using GIS technique[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2017, 37(11): 1764-1770(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201711019.htm [25] 李长安. 基于地貌过程的滑坡系统分析: 以三峡库区为例[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2020, 37(6): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202006003.htmLi C A. Systematic landslide analysis based on geomorphic process: An example from the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2020, 37(6): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJKB202006003.htm [26] Zhou T, Geng Y J, Chen J, et al. High-resolution digital mapping of soil organic carbon and soil total nitrogen using DEM derivatives, Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 data based on machine learning algorithms[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2020, 729: 138244. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32498148/ [27] 张福浩, 朱月月, 赵习枝, 等. 地理因子支持下的滑坡隐患点空间分布特征及识别研究[J]. 武汉大学学报: 信息科学版, 2020, 45(8): 1233-1244. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH202008014.htmZhang F H, Zhu Y Y, Zhao X Z, et al. Spatial distribution and identification of hidden danger points of landslides based on geographical factors[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2020, 45(8): 1233-1244(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WHCH202008014.htm [28] 李松林, 许强, 汤明高, 等. 三峡库区滑坡空间发育规律及其关键影响因子[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 45(1): 341-354.Li S L, Xu Q, Tang M G, et al. Study on spatial distribution and key influencing factors of landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 45(1): 341-354(in Chinese with English abstract). [29] 常中华, 伍法权, 刘海燕, 等. 三峡库区奉节新县城库岸边坡类型及岩体结构特征[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(17): 3057-3063. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200517008.htmChang Z H, Wu F Q, Liu H Y, et al. Bank slope types and rock mass structural features in new Fengjie County, Three Gorges Reservoir region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(17): 3057-3063(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX200517008.htm [30] 柴波, 殷坤龙, 陈丽霞, 等. 岩体结构控制下的斜坡变形特征[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(2): 521-525. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200902053.htmChai B, Yin K L, Chen L X, et al. Analysis of slope deformation under control of rock mass structure[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2009, 30(2): 521-525(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX200902053.htm [31] 黄发明, 胡松雁, 闫学涯, 等. 基于机器学习的滑坡易发性预测建模及其主控因子识别[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(2): 79-90. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0087Huang F M, Hu S Y, Yan X Y, et al. Landslide susceptibility prediction and identification of its main environmental factors based on machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 79-90(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0087 -





 下载:
下载: