-
摘要:
在西风带、东亚季风和印度季风的共同影响下,青藏高原不同区域全新世气候变化过程存在显著差异,加强不同区域古气候变化研究对重建青藏高原全新世气候变化过程及理解其变化机制具有重要意义。以青藏高原东部川西高原理塘县毛垭坝盆地全新世地层为研究对象,在14C测年的基础上,通过沉积环境和多个古气候代用指标的分析,重建了全新世气候变化过程。毛垭坝盆地早-中全新世冰水湖沉积物覆盖在末次冰期冰碛物之上,晚全新世为冲洪积物。全新世沉积物在筛除砾石(粒径>2 mm)后的粒度组成以中粉砂以下粒级(粒径 < 32 μm)为主,占比多>80%,是冰川磨蚀作用的产物。磁化率在古土壤层明显增大,结合粒径 < 1 μm粒度组分的出现,可能说明成壤作用生成的强磁性矿物是磁化率值增大的原因。在冰水湖还原环境中磁化率值显著减小,可能与磁性矿物溶解有关。结合总有机碳(TOC)和色度参数的综合分析表明,毛垭坝盆地早全新世气候温干,中全新世暖湿,晚全新世温干,这一变化过程与青藏高原东部全新世气候变化总的趋势相符。在晚全新世气候温干的趋势下,毛垭坝盆地在2 700 a BP古土壤发育,气候温湿。
Abstract:Objective The Holocene climate of the Tibetan Plateau (TP) is mainly controlled by midlatitude westerlies, the East Asian monsoon, and the Indian monsoon. Previous studies have identified different patterns of Holocene climate change in different regions of the TP. Holocene climate reconstructions for the entire TP help us comprehensively understand the internal linkages of different factors influencing the climate change in the TP.
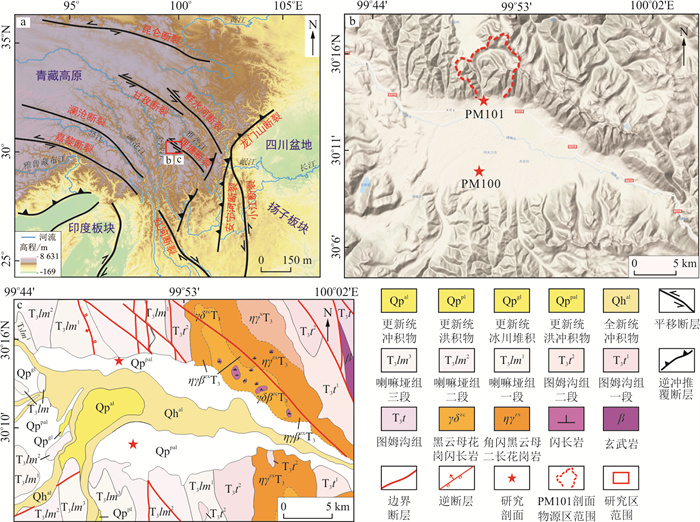
Methods In this paper, we study the Holocene climate in the eastern TP based on 14C dating, lithology and various proxies from the glaciolacustrine strata in the Maoyaba Basin in Litang County, western Sichuan Plateau.
Results The Early-Middle Holocene glaciolacustrine sediments covered the last glacial moraines, and then the alluvial-proluvial fans were common during the Late Holocene in the Maoyaba Basin. The grain size of all samples mainly shows a bimodal size distribution after sieving out >2 mm particles. The content of the grain size below medium silt (< 32 μm) is more than 80%, which may be produced by glacial abrasion. The magnetic susceptibility increases obviously in the paleosol, and the appearance of < 1 μm particle size components may indicate that the strong magnetic minerals were generated by pedogenesis. However, the magnetic susceptibility decreased significantly in the glaciolacustrine sediments, which may be related to the dissolution of magnetic minerals in the reducing environment.
Conclusion Comprehensive analysis of the sedimentary environment, grain size, magnetic susceptibility, total organic carbon (TOC) and color parameters indicates that the Maoyaba Basin was temperate and dry in the Early Holocene, warm and wet in the Middle Holocene, and temperate and dry in the Late Holocene. This pattern is consistent with the general trend of the Holocene climate in the eastern TP. The paleosol dated to~2 700 cal.yr. B.P. in the Maoyaba Basin indicates a relatively wet period against the background of cooling and a dry climate in the Late Holocene.
-
Key words:
- Tibetan Plateau /
- western Sichuan Plateau /
- Maoyaba Basin /
- Holocene /
- climate change
-
表 1 PM100和PM101剖面14C测年结果
Table 1. 14C dating results of the PM100 and PM101 profiles
实验室编号 野外编号 深度/cm AMS14C年龄/a BP 校正后年龄/a BP(2σ) Beta-563210 PM101-3 135 9 290±30 10 486±94 Beta-563211 PM101-4 118 4 980±30 5 697±56 Beta-563208 PM100-2-1 40 2 540±30 2 716±32 Beta-563209 PM100-4-1 10 110±0.4 -49±2 注:测试单位为美国Beta实验室;测试仪器为NEC加速器质谱仪和Thermo同位素比值质谱仪 -
[1] CHEN F, ZHANG J, LIU J, et al. Climate change, vegetation history, and landscape responses on the Tibetan Plateau during the Holocene: A comprehensive review[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 243: 106444. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106444 [2] GASSE F, ARNOLD M, FONTES J C, et al. A 13, 000-year climate record from western Tibet[J]. Nature, 1991, 353(6346): 742-745. doi: 10.1038/353742a0 [3] SHAH R A, ACHYUTHAN H, LONE A M, et al. Holocene palaeoenvironmental records from the high-altitude Wular Lake, western Himalayas[J]. The Holocene. 2020, 30(5): 733-743. doi: 10.1177/0959683619895592 [4] YAN T, ZHAO C, YAN H, et al. Elevational differences in Holocene thermal maximum revealed by quantitative temperature reconstructions at ~30° N on eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 570: 110364. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110364 [5] WU D, ZHOU A, ZHANG J, et al. Temperature-induced dry climate in basins in the northeastern Tibetan Plateau during the Early to Middle Holocene[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2020, 237: 106311. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2020.106311 [6] TANG L, SHEN C, LU H, et al. Fifty years of Quaternary palynology in the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2021, 64(11): 1825-1843. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9809-5 [7] 陈权亮, 刘晓冉, 范广洲, 等. 川西高原夏季降水变化特征及其异常年环流形势[J]. 中国沙漠, 2010, 30(3): 706-711.CHEN Q L, LIU X R, FAN G Z, et al. Features of summer precipitation change over the west Sichuan Plateau and its relationship with large-scale circulations[J]. Journal of Desert Research, 2010, 30(3): 706-711. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 马丹, 吴中海, 李家存, 等. 川西理塘断裂带的空间展布与第四纪左旋走滑活动的遥感影像标志[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(8): 1417-1435.MA D, WU Z H, LI J C, et al. Geometric distribution and the Quaternary activity of Litang active fault zone based on remote sensing[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(8): 1417-1435. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] PATERSON G A, HESLOP D. New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16(12): 4494-4506. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006070 [10] ZHANG Q, LIU X, LI H. Impact of hydrological conditions on the radiocarbon reservoir effect in lake sediment 14C dating: The case of Kusai Lake on the northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Quaternary Geochronology, 2021, 62: 101149. doi: 10.1016/j.quageo.2020.101149 [11] HOU J, D'ANDREA W J, LIU Z. The influence of 14C reservoir age on interpretation of paleolimnological records from the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 48: 67-79. doi: 10.1016/j.quascirev.2012.06.008 [12] HENDERSON A C G, HOLMES J A, LENG M J. Late Holocene isotope hydrology of Lake Qinghai, NE Tibetan Plateau: Effective moisture variability and atmospheric circulation changes[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2010, 29(17/18): 2215-2223. [13] CHEVALIER M, LELOUP P H, REPLUMAZ A, et al. Tectonic-geomorphology of the Litang fault system, SE Tibetan Plateau, and implication for regional seismic hazard[J]. Tectonophysics, 2016, 682: 278-292. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2016.05.039 [14] RAWAT S, GUPTA A K, SRIVASTAVA P, et al. A 13, 000 year record of environmental magnetic variations in the lake and peat deposits from the Chandra valley[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2015, 440: 116-127. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2015.08.044 [15] 李华勇. 青藏高原中部兹格塘错记录的末次冰消期以来气候变化[D]. 昆明: 云南师范大学, 2017.LI H Y. Climate change since the last deglaciation recorded by Lake Zigetang, central Tibetan Plateau[D]. Kunming: Yunnan Normal University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 巩雪娇, 王攀, 杨振京, 等. 粒度端元记录的靖边地区MIS 3以来的气候变化[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 184-191. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0113GONG X J, WANG P, YANG Z J, et al. Climate change recorded by the grain size end member since MIS 3 in Jingbian area[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 184-191. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0113 [17] 张延广, 方小敏, 毛子强, 等. 青藏高原古里雅冰帽冰碛和冰水沉积物粒度特征及其意义[J]. 冰川冻土, 2021, 43(3): 701-713.ZHANG Y G, FANG X M, MAO Z Q, et al. Grain-size characteristics of tills and glaciofluvial deposits in the Guliya ice cap, Tibetan Plateau and its implication[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 2021, 43(3): 701-713. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 陈安东. 云南大理点苍山末次冰期冰川地貌与冰碛物特征及其发育时代[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2015.CHEN A D. Diancang Mountain last glaciation geomorphic features and glacial deposits features and its ESR dating[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 谢远云, 李长安, 何葵, 等. 青海省民和黄土的粒度组成及气候含义[J]. 地质科技情报, 2002, 31(2): 41-44.XIE Y Y, LI C A, HE K, et al. Climatic implication and grain size composition from Minhe loess in Qinghai Provnice. [J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2002, 31(2): 41-44. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] AN Z, KUKLA G J, PORTER S C, et al. Magnetic susceptibility evidence of monsoon variation on the loess plateau of central China during the last 130000 years[J]. Quaternary Res., 1991, 36: 29-36. doi: 10.1016/0033-5894(91)90015-W [21] DEARING J A, LIVINGSTONE I P, BATEMAN M D, et al. Palaeoclimate records from OIS 8.0-5.4 recorded in loess-palaeosol sequences on the Matmata Plateau, southern Tunisia, based on mineral magnetism and new luminescence dating[J]. Quaternary International, 2001, 76(77): 43-56. [22] 刘青松, 邓成龙. 磁化率及其环境意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 2009, 52(4): 1041-1048. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021LIU Q S, DENG C L. Magnetic susceptibility and its environmental significances[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2009, 52(4): 1041-1048. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2009.04.021 [23] 刘秀铭, 刘东生, 夏敦胜, 等. 中国与西伯利亚黄土磁化率古气候记录-氧化和还原条件下的两种成土模式分析[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2007, 60(10): 1382-1391.LIU X M, LIU D S, XIA D S, et al. Paleoclimate record of susceptibility of loess from China and Siberia: Analysis of two soil-forming models under oxidation and reduction conditions[J]. Science China(Earth Sciences), 2007, 60(10): 1382-1391. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 昝金波, 方小敏, 聂军胜, 等. 塔里木盆地风积物表土磁学特征及其与物源物质、气候条件的关系[J]. 科学通报, 2011, 56(2): 153-160.ZAN J B, FANG X M, NIE J S, et al. Magnetic properties of surface soils across the southern Tarim Basin and their relationship with climate and source materials[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2011, 56(2): 153-160. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 陈梓炫, 吕镔, 郑兴芬, 等. 川西地区表土磁学性质及其环境意义[J]. 土壤学报, 2019, 56(3): 661-671.CHEN Z X, LÜ B, ZHENG X F, et al. Topsoil magnetic properties and its environmental significance in West Sichuan[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2019, 56(3): 661-671. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 沈吉, 张恩楼, 夏威岚. 青海湖近千年气候环境变化的湖泊沉积记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2001, 21(6): 508-513.SHEN J, ZHANG E L, XIA W L. Records from lake sediments of the Qinghai Lake to mirror climatic and environmental changes of the past about 1000 years[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2001, 21(6): 508-513. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] XU H, AI L, TAN L, et al. Stable isotopes in bulk carbonates and organic matter in recent sediments of Lake Qinghai and their climatic implications[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 235(3/4): 262-275. [28] KEMP D B, SUAN G, FANTASIA A, et al. Global organic carbon burial during the Toarcian oceanic anoxic event: Patterns and controls[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2022, 231: 104086. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2022.104086 [29] 杨胜利, 方小敏, 李吉均, 等. 表土颜色和气候定性至半定量关系研究[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 2001, 31(增刊1): 175-181.YANG S L, FANG X M, LI J J, et al. Qualitative to semi-quantitative relationship between topsoil color and climate[J]. Scientia Sinica Terrae, 2001, 31(S1): 175-181. (in Chinese with English abstract) [30] SUN Y, HE L, LIANG L, et al. Changing color of Chinese loess: Geochemical constraint and paleoclimatic significance[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2011, 40(6): 1131-1138. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.08.006 [31] 杜丁丁, SALEEM Mughal Muhammad, DEMBELE Blaise, 等. 青藏高原中部色林错湖泊沉积物色度反映末次冰盛期以来区域古气候演化[J]. 干旱区地理, 2019, 42(3): 551-558.DU D D, SALEEM M M, DEMBELE B, et al. Paleoclimatic changes reflected by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy since Last Glacial Maximum from Selin Co Lake sediments, central Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2019, 42(3): 551-558. (in Chinese with English abstract) [32] 李星波, 季军良, 曹展铭, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘古近纪-新近纪河湖相沉积物颜色的气候意义[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(9): 3278-3289.LI X B, JI J L, CAO Z M, et al. The climatic significance of the color of the paleo-Neogene fluvial and lacustrine sediments in the northern Qaidam Basin[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(9): 3278-3289. (in Chinese with English abstract) [33] JI J, SHEN J, BALSAM W, et al. Asian monsoon oscillations in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau since the late glacial as interpreted from visible reflectance of Qinghai Lake sediments[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 233(1/2): 61-70. [34] 吴艳宏, 李世杰. 湖泊沉积物色度在短尺度古气候研究中的应用[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(5): 789-792. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.05.016WU Y H, LI S J. Significance of lake sediment color for short time scale climate variation[J]. Advance in Earth Science, 2004, 19(5): 789-792. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.05.016 [35] 陈宗颜, 陈克龙, 罗正霞. 察尔汗地区130 ka BP以来湖相沉积物颜色记录的气候变化探讨[J]. 盐湖研究, 2011, 19(4): 1-14.CHEN Z Y, CHEN K L, LUO Z X. Climatic change recorded by the chroma of lacustrine sediments from 130 ka B.P. in Qarhan area[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research, 2011, 19(4): 1-14. (in Chinese with English abstract) [36] SAYEM A S M, GUO Z, WU H, et al. Sedimentary and geochemical evidence of Eocene climate change in the Xining Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2018, 61(9): 1292-1305. doi: 10.1007/s11430-018-9231-9 [37] 马兆颖. 清水河盆地晚更新世以来沉积特征及地质意义[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 2021.MA Z Y. Sedimentary characteristics and geological significance of Qingshuihe Basin since Late Pleistocene[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [38] YAN T, ZHAO C, YAN H, et al. Elevational differences in Holocene thermal maximum revealed by quantitative temperature reconstructions at ~30°N on eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2021, 570: 110364. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2021.110364 [39] SUN A, FENG Z. Holocene moisture variations across the Tibetan Plateau: A synthesis of pollen records[J]. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 2022, 297: 104581. doi: 10.1016/j.revpalbo.2021.104581 [40] WANG Y, CHENG H, EDWARDS R L, et al. The Holocene Asian Monsoon: Links to solar changes and North Atlantic climate[J]. Science, 2005, 308: 854-857. doi: 10.1126/science.1106296 [41] HU C, HENDERSON G M, HUANG J, et al. Quantification of Holocene Asian monsoon rainfall from spatially separatedcave records[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2008, 266(3/4): 221-232. [42] 李伟, 陈仕涛, 吴帅男, 等. 东亚季风"2.8 ka"事件高分辨率的石笋记录[J]. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34(6): 1256-1263.LI W, CHEN S T, WU S N, et al. A high-resolution east Asian Monsoon record around "2.8 ka" B.P. form Mt. Shennongjia, central China[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34(6): 1256-1263. (in Chinese with English abstract) -





 下载:
下载: