Indications of tunnel water inrush to the origin of large karst springs in Southwest China and water environmental effects
-
摘要:
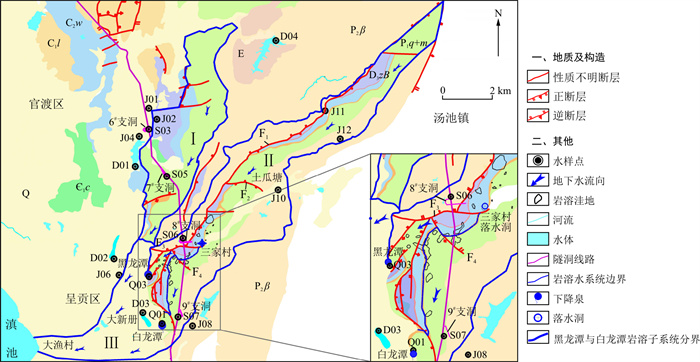
滇中引水工程昆呈隧洞横穿昆明市呈贡区主要的水源地——黑龙潭、白龙潭地区, 隧洞涌水可能严重威胁城市供水安全。综合隧洞施工水文动态数据和水化学数据, 分析岩溶水系统特征和隧洞施工的影响, 论证两泉的成因关系; 构建了昆呈隧洞黑龙潭—白龙潭段三维地下水流模型, 经模型识别验证后, 开展隧洞施工条件岩溶水系统的流场和泉流量变化的模拟预测, 分析评价其水环境效应。研究表明: 黑龙潭与白龙潭分别属于相对独立的2套岩溶水系统, 补给区均为P1
q +m 组强岩溶含水层, 但在三家村洼地下游, 两泉分别受P1d 组隔水地层和浑水塘断层的控制而形成稳定的岩溶通道; 昆呈隧洞掘进改变了区域地下水流场, 并袭夺白龙潭泉流量使其断流, 且泉流量恢复困难; 但隧洞掘进对黑龙潭影响较小。本研究对岩溶泉的成因关系进行探讨, 并定量分析隧道掘进的水环境影响, 对防止岩溶地区隧道建设中的突涌水等问题具有参考借鉴意义。Abstract:Objective The Kuncheng Tunnel of the Central Yunnan Water Diversion Project crosses the Heilongtan and Bailongtan areas, the major headwater regions in the Chenggong District of Kunming City.
Methods Tunnel water inrush may seriously threaten the safety of the urban water supply. In this paper, based on hydrodynamic data and hydrochemical data during tunnel construction, the characteristics of the karst water system, the origin of the springs, and the impact of tunnel construction were analysed. Then, a three-dimensional groundwater flow model for the Heilongtan-Bailongtan Section was developed and calibrated to simulate and predict groundwater level changes during the construction of the Kuncheng Tunnel, and the water environment effect of tunnel construction was evaluated.
Results The results show that both the Heilongtan and Bailongtan springs are mainly recharged by the same karst P1
q +m aquifer. However, controlled by aquitard P1d and the Hunshuitang fault downstream of the Sanjiacun Depression, the two springs actually belong to two relatively independent karst water systems. In addition, the excavation of the Kuncheng Tunnel has changed the regional groundwater flow field and cut off the flow of Bailongtan, while it has negligible impact on Heilongtan.Conclusion This study discusses the genetic relationship of karst spring, and quantitatively analyzes the impact of tunnel excavation on water environment, which has reference significance for preventing water inrush in tunnel construction.
-
表 1 黑龙潭-白龙潭岩溶水系统主要水化学数据
Table 1. Water chemistry data in the Heilongtan-Bailongtan karst water system
编号 位置 采样点 地层 宏量组分ρB/(mg·L-1) 微量组分ρB/(mg·L-1) δ18O/‰ δD/‰ TDS Na++K+ Ca2+ Mg2+ HCO3- Cl- SO42- Al3+ Sr2+ Ba2+ J10 补给区 头甸村水井 P2β 49.8 12.08 16.00 1.46 7.02 1.70 8.89 0.009 1 0.098 4 0.007 7 -11.59 -90.96 J11 一朵云村水井 P2β+ P1q+m 59.0 3.10 12.96 7.44 5.49 0.28 12.73 0.053 3 0.080 9 0.018 3 -10.93 -80.89 D04 宝象河水库 — 102.6 37.25 26.80 12.00 12.81 2.94 35.21 < 0.000 0.150 8 0.025 2 -8.12 -66.11 J01 果林水库排泄区 撒梅大道水井 ∈1l 289.0 13.27 71.20 39.90 34.16 17.30 33.09 0.148 6 0.078 6 0.045 5 -11.01 -82.75 J02 白水塘市场水井 ∈1l 289.0 15.90 74.88 37.13 39.04 16.24 29.63 < 0.000 0.082 5 0.057 8 -10.79 -81.51 J04 职业学院水井 ∈1l 328.0 24.10 77.60 40.24 39.89 34.49 31.94 < 0.000 0.051 4 0.133 8 -9.58 -73.74 D01 果林水库 — 167.2 22.04 28.00 18.86 13.91 30.42 47.89 0.030 2 0.162 0 0.118 2 -6.95 -57.45 S03 6#支洞 ∈1l 515.0 34.22 71.20 30.62 40.50 37.15 29.25 0.000 7 0.026 0 0.019 0 -11.65 -83.39 S05 7#支洞 D3zB 275.0 27.51 62.80 42.77 46.05 0.28 64.73 < 0.000 0.061 6 0.045 1 -10.99 -80.87 S06 黑龙潭排泄区 8#支洞 P2β 130.3 1.12 2.48 2.38 5.49 1.52 39.24 0.310 9 0.168 0 0.001 1 -12.10 -92.18 Q03 黑龙潭 P1q+m 298.1 15.51 70.24 10.55 25.62 11.45 23.10 0.161 1 0.129 7 0.037 3 -11.12 -83.09 J06 小新册社区水井 表层Q 207.4 8.03 35.84 22.21 20.37 0.82 30.02 0.003 9 0.281 5 0.368 8 -11.79 -91.70 D02 石龙坝水库 — 182.1 39.17 31.20 10.21 14.34 33.43 29.63 0.012 9 0.114 8 0.021 3 -7.43 -58.56 S07 白龙潭排泄区 9#支洞 P1q+m 175.9 34.20 61.76 13.32 23.91 4.71 73.44 0.067 3 0.078 0 0.008 1 -11.10 -84.12 Q01 白龙潭 P1q+m 248.3 8.88 60.80 10.69 22.26 6.66 21.95 0.009 9 0.083 2 0.003 7 -11.20 -84.60 J08 刘家营村机井 P1q+m 231.1 18.01 40.32 12.68 18.30 15.35 15.99 < 0.000 0.349 5 0.014 5 -10.84 -82.64 D03 白龙潭水库 — 211.6 8.06 49.76 9.23 18.91 7.37 12.92 < 0.000 0.064 2 0.025 6 -10.49 -80.70 -
[1] 杜宇本, 蒋良文, 胡卸文, 等. 高速铁路复杂岩溶地质勘察及灾害防治[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2021, 38(4): 16-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC202104004.htmDu Y B, Jiang L W, Hu X W, et al. Geological investigation and disaster prevention of complex karst on high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2021, 38(4): 16-21(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDGC202104004.htm [2] 罗明明, 周宏, 郭绪磊, 等. 峡口隧道间歇性岩溶涌突水过程及来源解析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(6): 246-254. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0054Luo M M, Zhou H, Guo X L, et al. Process and sources identification of intermittent karst water inrush in Xiakou Tunnel[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(6): 246-254(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0054 [3] 王宇. 断陷盆地岩溶水赋存规律[M]. 昆明: 云南科技出版社, 2003.Wang Y. Karst water storage law in fault basin[M]. Kunming: Yunnan Science and Technology Press, 2003(in Chinese). [4] 颜慧明, 常威, 郭绪磊, 等. 岩溶水流系统识别方法及其在引调水工程隧洞选线中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 127-136. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0008Yan H M, Chang W, Guo X L, et al. Identification of the karst water flow system and its application in the tunnel line selection of water diversion projects[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 127-136(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0008 [5] Li B, Li X. Characteristics of karst groundwater system in the northern basin of Laiyuan Spring area[J]. Journal of Groundwater Science and Engineering, 2018, 6(4): 261-269. [6] Rusjan S, Sapaĉ K, Petriĉ M, et al. Identifying the hydrological behavior of a complex karst system using stable isotopes[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 577: 123956. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.123956 [7] Luo M M, Chen Z H, Criss R E, et al. Dynamics and anthropogenic impacts of multiple karst flow systems in a mountainous area of South China[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2016, 24(8): 1993-2002. doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1462-3 [8] Vojtechovska A, Bruthans J, Krejca A F. Comparison of conduit volumes obtained from direct measurements and artificial tracer tests[J]. Journal of Cave & Karst Studies, 2011, 72(3): 156-160. [9] 彭红明, 袁有靖, 李铜邦, 等. 青海天峻新关角隧道涌排水水源识别与量化分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 60-70. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0026Peng H M, Yuan Y J, Li T B, et al. Identification and quantitative analysis of groundwater discharged from New Guanjiao Tunnel in Tianjun, Qinghai[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 60-70(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0026 [10] 常威, 谭家华, 黄琨, 等. 地下水多元示踪试验在岩溶隧道水害预测中的应用: 以张吉怀高铁兰花隧道为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2020, 39(3): 400-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003014.htmChang W, Tan J H, Huang K, et al. Application of groundwater multielement tracing tests to water hazard prediction of karst tunnels: An example of the Lanhua Tunnel on the Zhangjiajie-Jishou-Huaihua high-speed railway[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2020, 39(3): 400-408(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202003014.htm [11] Li D S, Cui B L, Wang Y, et al. Source and quality of groundwater surrounding the Qinghai Lake, NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Groundwater, 2021, 59(2): 245-255. doi: 10.1111/gwat.13042 [12] 林云, 曹飞龙, 武亚遵, 等. 北方典型岩溶泉域地下水水文地球化学特征分析: 以鹤壁许家沟泉域为例[J]. 地球与环境, 2020, 48(3): 294-306. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202003002.htmLin Y, Cao F L, Wu Y Z, et al. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of groundwater in typical karst spring areas of North China: A case study in the Xujiagou Spring area, Hebei[J]. Earth and Environment, 2020, 48(3): 294-306(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ202003002.htm [13] Nerantzaki S D, Nikolaidis N P. The response of three Mediterranean karst springs to drought and the impact of climate change[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 591(3): 125296. [14] Fiorillo F, Leone G, Pagnozzi M, et al. Long-term trends in karst spring discharge and relation to climate factors and changes[J]. Hydrogeology Journal, 2021, 29(1): 347-377. [15] Leone G, Pagnozzi M, Catani V, et al. A hundred years of Caposele spring discharge measurements: Trends and statistics for understanding water resource availability under climate change[J]. Stochastic Environmental Research and Risk Assessment, 2021, 35(2): 345-370. [16] 施佳会, 王锦国, 陈舟. 其宗岩溶泉成因简析[J]. 水电能源科学, 2014, 32(11): 58-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201411014.htmShi J H, Wang J G, Chen Z. A brief analysis of the origin of Qizong karst spring[J]. Hydropower Energy Science, 2014, 32(11): 58-62(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201411014.htm [17] 黄会, 张恺翔. 昆明呈贡黑、白龙潭地下水系统独立性研究[J]. 地下水, 2017, 39(4): 51-53, 56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201704016.htmHuang H, Zhang K X. Study on the Independence of groundwater system of Heilongtan and Bailongtan at Chenggong in Kunming[J]. Groundwater, 2017, 39(4): 51-53, 56(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201704016.htm [18] 王梅, 许模. 滇池盆地东侧黑龙潭与白龙潭水力关系研究[J]. 地下水, 2018, 40(2): 15-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201802005.htmWang M, Xu M. On the hydraulic connection between Heilongtan and Bailongtan in the eastern part of Dianchi Basin[J]. Groundwater, 2018, 40(2): 15-17(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXSU201802005.htm [19] 宁霞, 王增银, 杨建成. 桂林地区岩溶水中Ba元素的水文地球化学特征[J]. 中国岩溶, 2004, 23(4): 317-321. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200404010.htmNing X, Wang Z Y, Yang J C. Hydrogeochemical characteristics of Ba in karst water in Guilin area[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2004, 23(4): 317-321 (in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR200404010.htm [20] 陈余道, 程亚平, 王恒, 等. 岩溶地下河管道流和管道结构及参数的定量示踪: 以桂林寨底地下河为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2013, 40(5): 11-15. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201305006.htmChen Y D, Cheng Y P, Wang H, et al. Quantitative tracing study of hydraulic and geometric parameters of a karst underground river: Exemplified by the Zhaidi underground river in Guilin[J]. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 2013, 40(5): 11-15(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201305006.htm [21] 刘英俊. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984.Liu Y J. Elemental geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984(in Chinese). [22] 谈树成, 周家喜, 罗开, 等. 云南毛坪大型铅锌矿床成矿物质来源: 原位S和Pb同位素制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11): 3461-3476. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201911013.htmTan S C, Zhou J X, Luo K, et al. The sources of ore-forming elements of the Maoping large-scale Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan Province: Constrains from in-situ S and Pb isotopes[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(11): 3461-3476(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201911013.htm [23] 陈永权, 周新源, 赵葵东, 等. 塔里木盆地塔中19井奥陶系蓬莱坝组云灰互层段的岩性旋回特征与"顶侵型"埋藏云化模式的建立[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(2): 202-211. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200902002.htmChen Y Q, Zhou X Y, Zhao K D, et al. The petrologic rhythm of Lower Ordovician Penglaiba Formation encountered by Well Tazhong 19 and new dolomitization model Tarin Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentary Sinica, 2009, 27(2): 202-211(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200902002.htm [24] 孙超, 黄春阳, 梁爽. 广西崇左市江州区碳酸盐岩地层地下水锶富集规律及成因分析[J]. 南方国土资源, 2021(5): 33-38. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ202105009.htmSun C, Huang C Y, Liang S. Analysis of strontium enrichment law and genesis of groundwater strontium in carbonate formation in Jiangzhou District, Chongzuo City, Guangxi Province[J]. Southern Land and Resources, 2021(5): 33-38(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDZ202105009.htm [25] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 甘凤伟, 等. 滦河流域中上游富锶地下水成因类型与形成机制[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(1): 65-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202001006.htmSun H Y, Wei X F, Gan F W, et al. Genetic type and formation mechanism of strontium-rich groundwater in the upper and middle reaches of Luanhe River basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 41(1): 65-79(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB202001006.htm [26] Pu J, Yuan D, Zhang C, et al. Tracing the sources of strontium in karst groundwater in Chongqing, China: A combined hydrogeochemical approach and strontium isotope[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2012, 67(8): 2371-2381. doi: 10.1007%2Fs12665-012-1683-2.pdf [27] Keulegan G H. Laws of turbulent flow in open channels[M]. Gaithersburg, MD, USA: National Bureau of Standards, 1938. -





 下载:
下载: