Estimation of karst carbon sinks and analysis of their driving factors in Hubei Province from 2019 to 2021
-
摘要:
碳酸盐岩在水循环过程中的碳汇效应显著,加之岩溶地貌在我国分布广泛,所以探求岩溶碳汇潜力的研究对制定区域增汇策略具有重要意义。选取位于西南岩溶区的湖北省为重点研究区域,基于水化学径流法及入渗-平衡化学法进行定量化计算和比较,利用ArcGIS空间分析技术整体评估湖北省2019-2021年岩溶碳汇的空间格局与量级,探索更适宜应用于区域尺度的岩溶作用碳汇估算方法,综合分析岩溶碳汇的驱动因子,发掘更大的增汇潜力。研究结果表明:(1)采用入渗-平衡化学法估算3 a碳汇强度大小为2020年>2019年>2021年,丰水年(2020年)岩溶碳汇总量约为枯水年(2019年)的6倍,3 a年均碳汇强度为12.84 t/(km2·a),碳汇总量达163.89×104 t/a;(2)相较于水化学径流法,入渗-平衡化学法计算结果更为准确,获取数据资料较为简单,大小空间尺度都具有一定的普适性;(3)碳汇作用变化是高度动态的,气候变化下变化幅度主要由径流深决定,碳汇强度随径流深增大而变强,土地利用类型调控着岩溶作用碳汇强度;(4)鄂西南地区岩溶作用强烈,可建立岩溶碳汇试验区,定量评估人工干预所带来的增汇效果。研究结果不仅提供了精确易行的岩溶碳汇估算方法,而且确定了湖北省岩溶碳汇的量级与空间格局,摸清了碳汇强度驱动因子的共同耦合作用,体现了岩溶碳汇的人为可调控性以及复杂性,进一步为环境保护政策、人工增汇措施的制定提供了可靠的科学依据。
Abstract:Objective Carbonate rocks have a significant carbon sink effect in water cycle. Since karst landforms are widely distributed in China, research on the potential of karst carbon sinks plays an important role in formulating regional strategies for increasing carbon sinks.
Methods In this study, groundwater monitoring points in Hubei Province, which is located in the karst area of Southwest China, were selected. Quantitative calculations and method comparisons were performed based on the hydrochemical runoff method and the infiltration-equilibrium chemistry method. The spatial pattern and magnitude of karst carbon sinks in the hilly mountains of Hubei Province from 2019 to 2021 were evaluated via ArcGIS spatial analysis techniques. Additionally, the most suitable method for estimating karst carbon sinks at the regional scale were explored, the comprehensive analysis of the drivers of karst carbon sinks was performed, and the potential for increasing sinks were explored.
Results The results showed that: (1) the intensity of carbon sinks estimated by the infiltration-equilibrium chemistry method were 2020>2019>2021. The total amount of karst carbon sinks in wet year (2020) was approximately 6 times of that in dry year (2019). The average annual carbon sink intensity in the three years was 12.84 t/(km2·a) and the annual total amount of carbon reached 163.89×104 t/a; (2) the infiltration-equilibrium chemistry method was more accurate in calculation results and simpler in data acquisition than the hydrochemical runoff method, and had a certain universality at both large and small spatial scales; (3) the change in carbon sinks was highly dynamic. The extent of changes in carbon sinks under climate change was mainly determined by runoff depth, with the intensity of carbon sinks increasing with runoff depth, while land use regulated the intensity of carbon sinks in karst processes; and (4) the karstification is strong in southwestern Hubei Province, so a pilot field of karst carbon sinks could be established within the area to quantitatively evaluate artificial interventions to increase carbon sinks.
Conclusion This study not only provides an accurate and easy-to-use method for estimating karst carbon sinks, but also determines the magnitude and spatial pattern of karst carbon sinks in Hubei Province and figures out the coupling effect of the driving factors of carbon sink intensity, which demonstrates the complexity and anthropogenic control lability of karst carbon sinks. The results of this study provides a reliable scientific basis for the formulation of environmental protection policies and artificial sink increase measures.
-
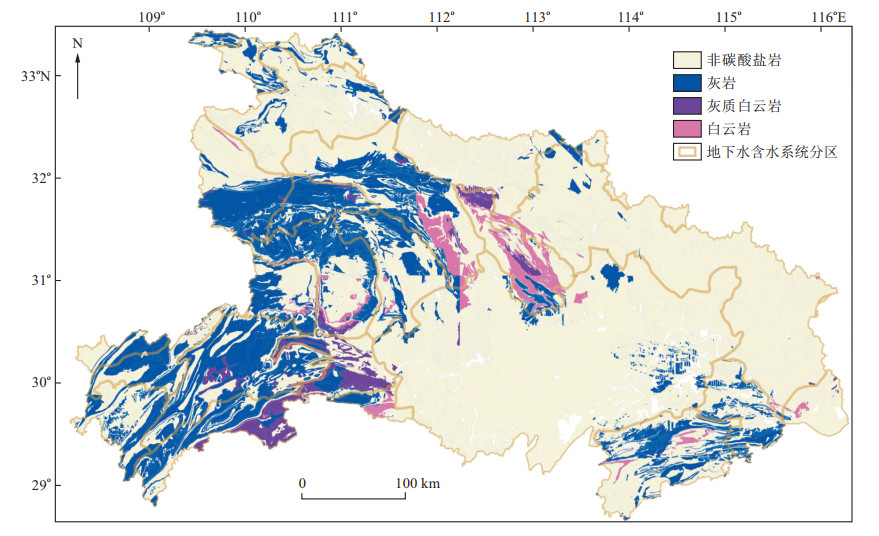
图 1 湖北省碳酸盐岩分布图(据文献[17]修改)
Figure 1. Map showing the distribution of different types of carbonate rock in Hubei Province
表 1 2021年湖北省岩溶碳汇计算
Table 1. Calculation of karst carbon sinks in Hubei Province for 2021
含水系统分区代码 含水系统分区 径流量/108 m3 分区面积/ km2 径流模数/ (s-1·km2) 碳汇强度/ (t·km-2·a-1) 碳酸盐岩面积/km2 碳汇总量/ (104 t·a-1) GF-2-3 长江中上游干流区 4.41 1 884.03 23.43 23.68 824.23 1.95 GF-2-4 乌江流域区 6.43 4 240.82 15.16 16.2 3 952.92 6.40 GF-3-1-1-2-1 丹江口以上镇安基岩裂隙含水系统区 0.04 599.25 0.69 0.78 403.68 0.03 GF-3-1-1-3-1 丹江口以上宁陕-白河寒武系-奥陶系岩溶含水系统区 1.33 3 691.38 3.60 8.22 2 554.78 2.10 GF-3-1-1-4-1 丹江口以上安康寒武岩溶含水系统区 0.65 6 645.41 0.98 1.02 2 178.51 0.22 GF-3-1-1-6-1 丹江口以上十堰基岩裂隙含水系统区 0.80 10 268.52 0.78 1.51 409.31 0.06 GF-3-1-2-1-1 巴东至宜昌巴东三叠系岩溶含水系统区 2.94 3 753.53 7.84 13.55 1 361.5 1.84 GF-3-1-2-2-1 巴东至宜昌兴山南华系裂隙含水系统区 2.37 7 364.95 3.22 4.55 4 733.4 2.15 GF-3-1-3-1-1 丹江口以下至荆门流马桥岩浆岩-变质岩基岩裂隙含水系统区 0.46 3 127.13 1.48 2.36 1 394.08 0.33 GF-3-1-3-2-1 丹江口以下荆门干流南漳碎屑岩裂隙含水系统区 1.39 11 366.48 1.23 3.18 3 467.13 1.10 GF-3-1-3-3-1 丹江口以下至荆门干流京山碎屑岩裂隙含水系统区 2.96 5 296.26 5.59 17.46 2 351.24 4.11 GF-3-1-4-1-1 清江利川三叠系岩溶含水系统区 5.30 3 435.46 15.43 17.56 621.54 1.09 GF-3-1-4-2-1 清江野三关三叠系岩溶含水系统区 21.76 9 944.01 21.89 18.33 6 038.67 11.07 GF-3-1-4-3-1 清江长阳-五峰寒武系岩溶含水系统区 6.79 3 911.67 17.36 27.93 1 751.98 4.89 GF-3-1-5-1-1 宜昌至荆门左岸远安岩溶含水系统区 4.81 6 400.79 7.51 12.7 999.56 1.27 GF-3-1-6-1-1 武汉至湖口左岸随州岩浆岩-变质岩基岩裂隙含水系统区 6.39 25 338.33 2.52 4.6 285.79 0.13 GF-3-1-7-1-1 城陵姬至湖口右岸咸宁碎屑岩裂隙含水系统区 4.59 8 831.46 5.20 7.53 2 061.77 1.55 GF-3-1-7-2-1 城陵姬至湖口右岸黄石碎屑岩裂隙含水系统区 2.20 4 422.41 4.99 6.91 844.9 0.58 GF-3-4 洞庭湖水系区 13.14 6 903.59 19.03 22.71 6 325.24 14.36 湖北省 88.76 127 425.48 8.31 12.98 42 560.23 55.23 表 2 2019-2021年湖北省岩溶碳汇计算
Table 2. Karst carbon sink calculations in Hubei Province from 2019 to 2021
年份 温度/℃ 径流深/(mm·a-1) 碳汇强度/(t·km-2·a-1) 碳酸盐岩面积/km2 碳汇总量/(104 t·a-1) 3 a年均碳汇强度/(t·km-2·a-1) 2019 17.1 172.46 4.28 42 560.23 18.21 2020 16.8 808.23 23.51 42 560.23 100.06 12.84 2021 17.4 350.82 10.72 42 560.23 45.62 -
[1] GOLDSCHEIDER N, CHEN Z, AULER A S, et al.Global distribution of carbonate rocks and karst water resources[J].Hydrogeology Journal, 2020, 28(5):1661-1677. doi: 10.1007/s10040-020-02139-5 [2] LIU Z, DREYBRODT W. Significance of the carbon sink produced by H2O-carbonate-CO2-aquatic phototroph interaction on land[J]. Ence Bulletin, 2015, 60(2): 182-191. [3] LI H W, WANG S J, BAI X Y, et al. Spatiotemporal distribution and national measurement of the global carbonate carbon sink[J]. Sci. Total. Environ., 2018, 643: 157-170. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.06.196 [4] 吴泽燕. 广西果化妙冠岩溶关键带碳汇效应研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2021.WU Z Y. Carbon sink effect of Miaoguang karst critical zone in Guohua, Guangxi[D]. Wuhan: China University Of Geosciences(Wuhan), 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] LIU Z, MACPHERSON G L, GROVES C, et al. Large and active CO2 uptake by coupled carbonate weathering[J]. Earth Science Reviews, 2018, 182: 42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.007 [6] 王文娟, 蓝芙宁, 蒋忠诚, 等. 湖南大龙洞流域不同岩性不同土地利用类型条件下碳酸盐岩试片的溶蚀速率[J]. 中国岩溶, 2013, 32(1): 29-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.01.005WANG W J, LAN F N, JIANG Z C, et al. Corrosion rate of carbonate tablet under diverse land use and lithology in the Dalongdong Basin, Hunan[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2013, 32(1): 29-33. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2013.01.005 [7] 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 黄奇波, 等. 珠江流域岩石风化作用消耗大气/土壤CO2量的估算[J]. 地球学报, 2013, 34(4): 455-462. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201304009.htmQIN X Q, LIU P Y, HUANG Q B, et al. Estimation of atmospheric/soil CO2 consumption by rock weathering in the Pearl River Valley[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2013, 34(4): 455-462. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXB201304009.htm [8] 曹星星, 吴攀, 杨诗笛, 等. 贵州威宁草海流域地下水水化学特征及无机碳通量估算[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(4): 1761-1771. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104019.htmCAO X X, WU P, YANG S D, et al. Hydrochemistry characteristics and estimation of the dissolved inorganic carbon flux in the Caohai Lake wetland catchment of Guizhou Province[J]. Environmental Sciences, 2021, 42(4): 1761-1771. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJKZ202104019.htm [9] 张连凯, 覃小群, 刘朋雨, 等. 硫酸参与的长江流域岩石化学风化与大气CO2消耗[J]. 地质学报, 2016, 90: 1933-1944. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201608021.htmZHANG L K, QIN X Q, LIU P Y, et al. Chemical denudation rate and atmospheric CO2 consumption by H2CO3 and H2SO4 in the Yangtze River catchment[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2016, 90: 1933-1944. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201608021.htm [10] DONG S C, LIU B W, LEI J H, et al. Carbon balance model of groundwater system: A field application[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2022, 610: 127845. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.127845 [11] YU J, YAN J, YANG W, et al. Hydrogeochemical characterization of a possible carbon sink from shallow saline-alkaline groundwater in the eastern Hetao Basin of Inner Mongolia in China[J]. Environmental Science(Processes and Impacts), 2021, 32: 344-356. [12] LIU J, XU Z, ZHANG D, et al. Effects of carbon dioxide enrichment and nitrogen addition on inorganic carbon leaching in subtropical model forest ecosystems[J]. Ecosystems, 2011, 14(5): 683-697. doi: 10.1007/s10021-011-9438-6 [13] 曾成, 赵敏, 杨睿, 等. 岩溶作用碳汇强度计算的溶蚀试片法和水化学径流法比较: 以陈旗岩溶泉域为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 2014, 41(1): 106-111. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201401020.htmZENG C, ZHAO M, YANG R, et al. Comparison of karst processes-related carbon sink intensity calculated by carbonate rock tablet test and solute load method: A case study in the Chenqi karst spring system[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2014, 41(1): 106-111. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWDG201401020.htm [14] 刘再华. 岩溶作用及其碳汇强度计算的"入渗-平衡化学法": 兼论水化学径流法和溶蚀试片法[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4): 379-382. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.005LIU Z H. "Method of maximum potential dissolution" to calculate the intensity of karst process and the relevant carbon sink: With discussions on methods of solute load and carbonate-rock-tablet test[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4): 379-382. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.005 [15] 范威, 于瑶, 江越潇, 等. 湖北省地下水流系统划分研究[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2020, 34(4): 565-570. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202004017.htmFAN W, YU Y, JIANG Y X, et al. Current situation and consideration of groundwater monitoring in Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2020, 34(4): 565-570. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202004017.htm [16] 牛俊强, 郭昆, 李寅, 等. 湖北省地下水监测现状及思考[J]. 资源环境与工程, 2021, 35(4): 467-471. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202104010.htmNIU J Q, GUO K, LI Y, et al. Study on groundwater flow system division in Hubei Province[J]. Resources Environment & Engineering, 2021, 35(4): 467-471. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HBDK202104010.htm [17] 李大通, 罗雁. 中国碳酸盐岩分布面积测量[J]. 中国岩溶, 1983, 12(2): 147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198302008.htmLI D T, LUO Y. Measurement of carbonate rocks distribution area in China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 1983, 12(2): 147. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR198302008.htm [18] DREYBRODT W. Processes in karst systems: Springer Series in Physical Environment[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 1988: 288. [19] GOMBERT P. Role of karstic dissolution in global carbon cycle[J]. Glob Planet Change, 2002, 33: 177-184. doi: 10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00069-3 [20] 邰治钦, 曾成, 肖时珍, 等. 近27a来典型白云岩流域岩溶碳汇变化及其调控机制: 以贵州施秉黄洲河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2021, 40(4): 625-635. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202104009.htmSHAN Z Q, ZENG C, XIAO S Z, et al. Variation and rgulation mechanism of karst carbon sink in typical dolomite Basin in recent 27 years: A case study of the Huangzhouhe Basin in Shibing, Guizhou[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2021, 40(4): 625-635. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR202104009.htm [21] GAILLARDET J, CALMELS D, ROMERO-MUJALLI G, et al. Global climate control on carbonate weathering intensity[J]. Chemical Geology, 2019, 527: 118762. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2018.05.009 [22] GODSEY S E, KIRCHNER J W, CLOW D W. Concentration-discharge relationships reflect chemostatic characteristics of US catchments[J]. Hydrological Processes, 2009, 23(13): 1844-1864. doi: 10.1002/hyp.7315 [23] 罗维均, 杨开萍, 王彦伟, 等. 喀斯特地区不同岩土组构对岩溶碳通量的影响[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(3): 208-214. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0088LUO W J, YANG K P, WANG Y W, et al. Influence of different rock-soil fabrics on carbonate weathering carbon sink flux in karst regions[J]. Bulletin of Geological Scienceand Technology, 2022, 41(3): 208-214. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0088 [24] ROMERO-MUJALLI G J, HARTMANN B. Temperature and CO2 dependency of global carbonate weathering fluxes: Implications for future carbonate weathering research[J]. Chemical Geology, 2018, 527: 118874. [25] 曾成, 赵敏, 杨睿, 等. 贵州典型岩溶流域水循环驱动的岩溶碳汇通量及其主控因素分析[J]. 地球与环境, 2017, 45(1): 74-83. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201701011.htmZENG C, ZHAO M, YANG R, et al. Karst related carbon sink flux driven by water cycle in typical karst catchments of Guizhou Province and its main controlling factors[J]. Earth and Environment, 2017, 45(1): 74-83. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ201701011.htm [26] 李汇文, 王世杰, 白晓永, 等. 气候变化及生态恢复对喀斯特槽谷碳酸盐岩风化碳汇的影响评估[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(16): 6158-6172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201916040.htmLI H W, WANG S J, BAI X Y, et al. Effects of climate change and ecological restoration on carbonate rock weathering carbon sequestration in the karst valley of Southwest China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2019, 39(16): 6158-6172. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STXB201916040.htm [27] 曾思博. 西南地区近40年气候变化及其对岩溶作用碳汇的影响研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2017.ZENG S B. Climate change characteristics of karst area in SW China and its impacts on karst-related carbon sink during recent 40 years[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract) [28] 孙从建, 郑振婧, 李新功, 等. 黄土塬面保护区潜在蒸发量时空变化及其与气象、环流因子关系分析[J]. 自然资源学报, 2020, 35(4): 857-868. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX202004009.htmSUN C J, ZHENG Z J, LI X G, et al. Spatio-temporal distribution of the potential evapotranspiration and its controlling factors in the tableland protected region of the Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 2020, 35(4): 857-868. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZRZX202004009.htm [29] 章程. 不同土地利用土下溶蚀速率季节差异及其影响因素[J]. 地质论评, 2010, 56(1): 136-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201001021.htmZHANG C. Seasonal variation of dissolution rate under the soil at different land uses and its influence factors[J]. Geological Review, 2010, 56(1): 136-140. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZLP201001021.htm [30] 覃小群, 蒙荣国, 莫日生. 土地覆盖对岩溶地下河碳汇的影响: 以广西打狗河流域为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4): 372-378. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.004QIN X Q, MENG R G, MO R S. Influence of land covers on carbon sink of underground river: A case in the Dagouhe Basin in Guangxi[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4): 372-378. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4810.2011.04.004 [31] ZENG C, LIU Z, ZHAO M, et al. Hydrologically-driven variations in the karstn-related carbon sink fluxes: Insights from high-resolution monitoring of three karst catchments in southwest China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2016, 533: 74-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.11.049 [32] LIU Z, LI Q, SUN H, et al. Seasonal, diurnal and storm-scale hydrochemical variations of typical epikarst springs in subtropical karst areas of SW China: Soil CO2 and dilution effects[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2007, 337: 207-223. [33] 曾思博, 蒋勇军. 土地利用对岩溶作用碳汇的影响研究综述[J]. 中国岩溶, 2016, 35(1): 1-4. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201602004.htmZENG S B, JIANG Y J. Impact of land-use and land-over change on the carbon sink produced by karst processes: A review[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2016, 35(1): 1-4. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201602004.htm [34] 赵敏, 曾成, 刘再华. 土地利用变化对岩溶地下水溶解无机碳及其稳定同位素组成的影响[J]. 地球化学, 2009, 38(6): 565-572. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906009.htmZHAO M, ZENG C, LIU Z H. Influence of land use change on dissolved inorganic carbon and stable isotopic compositions of karst groundwater[J]. Geochimica, 2009, 38(6): 565-572. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX200906009.htm [35] 罗明明, 姜光辉. 基于岩溶水动态模拟的补给面积计算方法[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(5): 293-300. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0184LUO M M, JIANG G H. Estimation method of recharge area based on hydrograph simulation of karst water[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(5): 293-300. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0184 [36] 张春来, 黄芬, 蒲俊兵, 等. 中国岩溶碳汇通量估算与人工干预增汇途径[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(4): 40-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC202104006.htmZHANG C L, HUANG F, PU J B, et al. Estimation of karst carbon sink fluxes and manual intervention to increase carbon sinks in China[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(4): 40-52. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDC202104006.htm [37] 黄芬, 唐伟, 汪进良, 等. 外源水对岩溶碳汇的影响: 以桂林毛村地下河为例[J]. 中国岩溶, 2011, 30(4): 417-421. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201104013.htmHUANG F, TANG W, WANG J L, et al. The influence of allogenic water on karst carbon sink: A case study in the Maocun subterranean river in Guilin, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica, 2011, 30(4): 417-421. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGYR201104013.htm [38] 刘再华. 碳酸酐酶对碳酸盐岩溶解的催化作用及其在大气CO2沉降中的意义[J]. 地质学报, 2001, 75(5): 477-480. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200103019.htmLIU Z H. The role of carbonic anhydrase as an activator in carbonate rock dissolution and its significance in atmospheric CO2 precipitation[J]. Journal of the Earth Magazine, 2001, 75(5): 477-480. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE200103019.htm [39] 曾思博, 刘再华. 我国岩溶碳汇和在非岩溶区播撒碳酸盐粉的碳中和潜力[J]. 科学通报, 2022, 67(34): 4116-4129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202234015.htmZENG S B, LIU Z H. Karst-related carbon sink and the carbon neutral potential by carbonate liming in non-karst areas in China[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2022, 67(34): 4116-4129. (in Chinese with English abstract) https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202234015.htm [40] 朱常坤. 基于信息熵的岩溶水监测网优化: 以徐州市典型水源地为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2022, 41(1): 168-176. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0030ZHU C K. Optimization of karst water monitoring network based on information entropy: A case study in typical groundwater source sites in Xuzhou[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 168-176. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2022.0030 -





 下载:
下载: