Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of source rocks of the Dongying Formation in southwest subsag of Bozhong Sag
-
摘要:
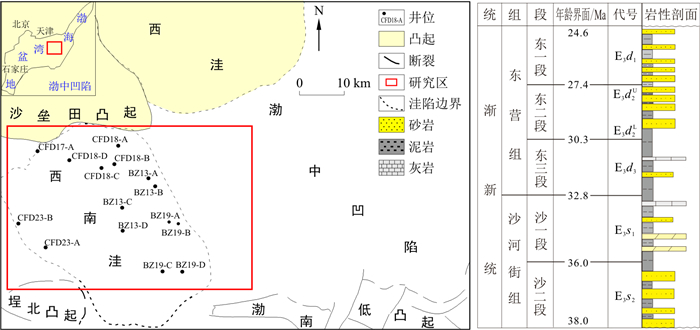
东营组烃源岩在渤中凹陷广泛分布, 明确该套烃源岩特征及其形成的古环境对于推动渤中凹陷常规-非常规油气勘探具有重要意义。通过对渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩样品进行有机、无机地球化学实验, 分析该套烃源岩品质、有机质来源和古沉积环境, 并与凹陷内主力烃源岩沙河街组进行对比分析。结果显示: ①东营组不同层段烃源岩特征差异显著, 且与沙一二段烃源岩呈现明显不同。东二下段与东三段有机质丰度高, 已达到成熟-高成熟阶段, 东营组整体有机质类型均以Ⅱ型为主; ②通过Pr/
n C17-Ph/n C18等图版以及干酪根类型判断东营组有机质来源为混合型, 与沙一二段的低等藻类输入明显不同; ③综合Sr/Cu、Mn/Fe等16种元素含量或比值以及Pr/Ph、伽马蜡烷指数分析烃源岩形成时期的古环境, 与沙一二段烃源岩干旱气候下强还原咸化湖盆的形成环境所不同, 东营组整体形成于温湿气候下, 伴随较强陆源输入, 受控于弱氧化淡水环境; 纵向上, 从东三段-东一段古气候变化不大, 水体盐度基本一致, 但水深逐渐变浅, 水体氧化条件呈现逐渐增强的趋势; ④利用Co、La含量定量恢复东营组沉积时的古水深, 认为东三段(50.4m)>东二段(35.7m)≈沙一二段(33.2m)≈东一段(31.7m), 计算结果与前面的古水深定性结果保持一致。东营组独特成源条件的揭示, 将大大促进针对该组为烃源灶的油气勘探。Abstract:Source rocks of the Dongying Formation are widely distributed in the Bozhong Sag. It is of great significance to clarify the characteristics and paleoenvironment of the source rocks to promote conventional and unconventional oil and gas exploration in the Bozhong Sag. In this study, organic and inorganic geochemical experiments were carried out on the source rock samples collected from the Dongying Formation in the Bozhong Sag, with aims to analyze the quality and paleoenvironment and compare it with the Shahejie Formation. The results show that: ①the characteristics of source rocks in different layers of the Dongying Formation are significantly different from those in E
s 1-2.The abundance of organic matter in the lower and third members of the Dongying Formation (Ed 2L and Ed 3) is high and has reached the mature-high maturity stage. The organic matter of the Dongying Formation is mainly type Ⅱ. ②According to the Pr/n C17-Ph/n C18 charts, the source of organic matter in the Dongying Formation is mixed type, which is obviously different from the low algae of Es 1-2.③The paleoenvironment during the formation of source rocks was analyzed by combining the contents or ratios of 16 elements, such as Sr/Cu, Mn/Fe, Pr/Ph and the gammacerane index. Different from the strong reduction-salinized lacustrine basin in the arid climate of Es 1-2, the Dongying Formation was formed in a warm and humid climate, accompanied by strong terrigenous input, and controlled in a weakly oxidized freshwater environment. Longitudinally, the paleoclimate changes little from Ed 3 to Ed 1, and the water salinity is basically the same, but the water depth becomes shallower and the water oxidation conditions show a trend of increasing gradually.④Using Co and La contents to quantitatively restore the paleo-water depth during the deposition of the Dongying Formation, and suggests that Ed 3 (50.4 m)>Ed 2 (35.7 m)≈Es 1-2(33.2 m)≈Ed 1(31.7 m). The calculated results are consistent with the previous qualitative results of paleo-water depth.-
Key words:
- Bozhong Sag /
- Dongying Formation /
- source rock /
- geochemical characteristics /
- paleoenvironment
-
表 1 渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩有机质丰度评价
Table 1. Organic matter abundance of the source rocks from the Dongying Formation in the southwest subsag of the Bozhong Sag
层段 w(TOC)/% “A”/% HC/10-6 (S1+S2)/(mg·g-1) 评价 东一段(E3d1) $\frac{\text { 范围}}{\text { 平均值}}$ $\frac{0.1 \sim 0.83}{0.33}$ $\frac{0.01 \sim 0.14}{0.07}$ $\frac{78 \sim 856.6}{413.8}$ $\frac{0.24 \sim 2.37}{0.98}$ 差 东二上段(E3d2U) $\frac{0.13 \sim 1.18}{0.5}$ $\frac{0.01 \sim 0.47}{0.134}$ $\frac{48.58 \sim 2681.42}{734.22}$ $\frac{0.14 \sim 3.79}{1.42}$ 差-中等 东二下段(E3d2L) $\frac{0.2 \sim 2.1}{0.78}$ $\frac{0.025 \sim 0.59}{0.15}$ $\frac{104.8 \sim 3966.6}{826.6}$ $\frac{0.26 \sim 11.46}{2.67}$ 中等-好 东三段(E3d3) $\frac{0.6 \sim 6.15}{2.37}$ $\frac{0.05 \sim 1.06}{0.39}$ $\frac{316.8 \sim 6857.66}{2 \ 560.5}$ $\frac{1.03 \sim 45.08}{9.79}$ 好-优质 沙一二段(E3s1-2) $\frac{1.28 \sim 6.9}{2.9}$ $\frac{0.02 \sim 1.43}{0.44}$ $\frac{331 \sim 6943.1}{2354.5}$ $\frac{1.47 \sim 59.8}{21.14}$ 好-优质 表 2 渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩有机质类型划分
Table 2. Classification of kerogen pyrolysis organic matter types of the source rocks from the Dongying Formation in southwest subsag of Bozhong Sag
层段 氢指数 H/C原子比 O/C原子比 KTI指数 干酪根类型 东一段(E3d1) $\frac{\text { 范围}}{\text { 平均值}}$ $\frac{30 \sim 382.1}{207.7}$ $\frac{0.85 \sim 1.09}{0.95}$ $\frac{0.13 \sim 0.25}{0.18}$ $\frac{35 \sim 54}{42.2}$ Ⅱ1-Ⅱ2 东二上段(E3d2U) $\frac{34.1 \sim 419}{211.6}$ $\frac{0.7 \sim 1.39}{1.02}$ $\frac{0.1 \sim 0.75}{0.21}$ $\frac{20 \sim 72.9}{40.3}$ Ⅱ1-Ⅱ2 东二下段(E3d2L) $\frac{55.6 \sim 581.8}{242.1}$ $\frac{0.67 \sim 1.47}{1.02}$ $\frac{0.1 \sim 0.75}{0.21}$ $\frac{15 \sim 80}{42.8}$ Ⅱ1-Ⅱ2 东三段(E3d3) $\frac{22.5 \sim 774.5}{344.18}$ $\frac{0.38 \sim 1.46}{0.97}$ $\frac{0.08 \sim 0.49}{0.16}$ $\frac{22 \sim 85.7}{45.9}$ Ⅱ1-Ⅱ2为主,少量Ⅰ型 沙一二段(E3s1-2) $\frac{90 \sim 1 325}{572}$ $\frac{1.31 \sim 1.89}{1.28}$ $\frac{0.1 \sim 0.2}{0.18}$ $\frac{44 \sim 86}{63}$ Ⅰ-Ⅱ1 表 3 渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩有机质类型划分
Table 3. Classification of kerogen pyrolysis organic matter types in the source rocks of the Dongying Formation in southwest subsag of Bozhong Sag
层段 Ro/% Tmax/℃ C29 20S/(20S+20R)甾烷 C29ββ/(ββ + αα) 甾烷 成熟度 东一段(E3d1) $\frac{\text { 范围}}{\text { 平均值}}$ $\frac{0.3~0.63}{ 0.5}$ $\frac{304~437}{ 404}$ $\frac{0.15~0.26}{ 0.22}$ $\frac{0.18~0.28}{ 0.24}$ 未熟-低熟阶段 东二上段(E3d2U) $\frac{0.42~0.84}{ 0.59}$ $\frac{387~445}{ 428}$ $\frac{0.11~0.36}{ 0.31}$ $\frac{0.27~0.39}{ 0.33}$ 低熟-成熟阶段 东二下段(E3d2L) $\frac{0.49~1.2}{ 0.7}$ $\frac{387~445}{ 437}$ $\frac{0.17~0.48}{ 0.36}$ $\frac{0.23~0.53}{ 0.38}$ 成熟阶段 东三段(E3d3) $\frac{0.53~1.48}{ 1.0}$ $\frac{407~449}{ 440}$ $\frac{0.17~0.56}{ 0.42}$ $\frac{0.25~0.7}{ 0.49}$ 成熟-高成熟阶段 沙一二段(E3s1-2) $\frac{0.61~1.67}{ 1.1}$ $\frac{423~450}{ 445}$ — — 成熟-高成熟阶段 表 4 渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩古水深计算
Table 4. Paleo water depth of the Dongying Formation in southwest subsag of Bozhong Sag
层段 井名 w(Co)/10-6 w(La)/10-6 水深h/m 单井平均水深h/m 层段平均水深H/m E3d1 BZ13-A 11.7~21.8 22.2~48.4 23.4~35.1 38.3 31.7 BZ13-B 14.5~16.4 39.2~45.9 21.4~26.0 23.4 BZ19-B 15.7~17.5 32.2~42.9 20.7~38.8 31.6 E3d2U CFD17-A 9.88~13.2 30.7~48.4 12.15~25.12 26.9 34.2 BZ19-A 14.4~16.3 33.9~36.8 27.8~36.9 31.7 BZ19-B 10.5~15.8 31~37.8 25~32.6 34.6 E3d2L CFD17-A 11.2~15.9 34.5~46.4 16.1~41.8 32.6 37.3 CFD18-A 11.6~14.4 41.2~47.4 14.7~32.0 26.9 BZ13-C 14.7~24.6 36.5~53.1 28.2~67.1 41.4 E3d3 CFD17-A 11.9~17.5 39.2~48.4 12.9~34.8 27.4 50.4 BZ13-C 21.2~22.9 44.4~48.8 51.8~63.5 57.7 BZ13-D 13.8~17.9 36.8~48.0 23.6~35.9 30.4 BZ19-A 16.8~31.7 22.8~41.6 35.4~109.4 76.2 BZ19-B 16.6~32.9 32.2~45.4 34.5~121.3 65.9 E3s1-2 CFD23-A 13.1 20.8 29.8 29.8 33.2 BZ19-A 6.35~16.7 36.3~51.5 11.23~39.63 36.67 -
[1] 张功成. 渤海海域构造格局与富生烃凹陷分布[J]. 中国海上油气地质, 2000, 14(2): 93-99, 2. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200002003.htmZhang G C. Tectonic framework and prolific hydrocarbon depressions in Bohai Bay[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2000, 14(2): 93-99, 2(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD200002003.htm [2] 姜福杰, 庞雄奇. 环渤中凹陷油气资源潜力与分布定量评价[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2011, 38(1): 23-29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201101005.htmJiang F J, Pang X Q. Quantitative evaluation of hydrocarbon resource potential and its distribution in the Bozhong Sag and surrounding areas, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2011, 38(1): 23-29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201101005.htm [3] 王昕, 王永利, 官大勇, 等. 环渤中凹陷斜坡区浅层油气地质特征与勘探潜力[J]. 中国海上油气, 2012, 24(3): 12-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2012.03.003Wang X, Wang Y L, Guan D Y, et al. Shallow petroleum geology and exploration potential in the slope area, circum-Bozhong Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2012, 24(3): 12-16(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1506.2012.03.003 [4] 王翔宇. 渤海湾盆地渤中凹陷渐新统东营组三段烃源岩预测及评价[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2019.Wang X Y. Prediction and evaluation of the source rocks of the third member of the Oligocene Dongying Formation in the Bozhong Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[D]. Wuhan: Yangtze University, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [5] 刘伟. 渤中凹陷湖相优质烃源岩形成机理与发育模式研究[D]. 武汉: 长江大学, 2020.Liu W. Study on the Formation mechanism and development model of lacustrine high quality source rocks in Bozhong sub-basin[D]. Wuhan: Yangtze University, 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [6] 张参, 阳宏, 王飞龙, 等. 渤中凹陷南洼东营组烃源岩有机地球化学特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2020, 36(11): 35-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202011006.htmZhang C, Yang H, Wang F L, et al. Organic geochemistry of the source rocks in the Dongying Formation of the South Bozhong subsag[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2020, 36(11): 35-44(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT202011006.htm [7] Patterson J H, Ramsden A R, Dale L S, et al. Geochemistry and mineralogical residences of trace elements in oil shales from Julia Creek, Queensland, Australia[J]. Chemical Geology, 1986, 55(1/2): 1-16. [8] Hatch J R, Leventhal J S. Relationship between inferred redox potential of the depositional environment and geochemistry of the Upper Pennsylvanian(Missourian) Stark Shale Member of the Dennis Limestone, Wabaunsee County, Kansas, U.S. A[J]. Chemical Geology, 1992, 99(1/3): 65-82. [9] Rimmer S, Thompson J, Goodnight S, et al. Multiple controls on the preservation of organic matter in Devonian-Mississippian marine black shales: Geochemical and petrographic evidence[J]. Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 2004, 215(1/2): 125-154. [10] Algeo T J, Maynard J B. Trace-element behavior and redox facies in core shales of Upper Pennsylvanian Kansas-type cyclothems[J]. Chemical Geology, 2004, 206(3/4): 289-318. [11] 邓宏文, 钱凯. 沉积地球化学与环境分析[M]. 兰州: 甘肃科学技术出版社, 1993.Deng H W, Qian K. Sedimentary geochemistry and environment analysis[M]. Lanzhou: Gansu Science and Technology Press, 1993: 95-104(in Chinese). [12] 李浩, 吴金涛, 黄建廷, 等. 断层垂向封闭性定量分析及其在渤海湾盆地A油田中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 125-131. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0416Li H, Wu J T, Huang J T, et al. Quantitative analysis of fault vertical sealing ability and its application in A Oilfield of Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 125-131(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0416 [13] 林旭, 赵希涛, 吴中海, 等. 渤海湾周缘主要河流钾长石物源示踪指标研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 10-18. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0602Lin X, Zhao X T, Wu Z H, et al. Source tracing elements of K-feldspars of main rivers around Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 10-18(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0602 [14] 王华, 陈思, 巩天浩, 等. 牵引流化重力流沉积过程与堆积机制: 以渤海湾盆地歧口凹陷为例[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 95-104. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111Wang H, Chen S, Gong T H, et al. Sedimentary process and accumulation mechanism of traction fluidzation gravity flow: An example from Qikou Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 95-104(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0111 [15] 杜雨佳. 渤中凹陷古近系烃源岩生烃潜力评价[D]. 山东青岛: 中国石油大学(华东), 2015.Du Y J. Hydrocarbon generation potential of Paleogene source rocks in Bozhong Depression[D]. Qingdao, Shandong: China University of Petroleum(East China), 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 牛成民, 王飞龙, 何将启, 等. 渤海海域渤中19-6潜山气藏成藏要素匹配及成藏模式[J]. 石油实验地质, 2021, 43(2): 259-267. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202102009.htmNiu C M, Wang F L, He J Q, et al. Accumulation factor matching and model of Bozhong 19-6buried hill gas reservoir, Bohai Sea area[J]. Prtroleum Geology & Experiment, 2021, 43(2): 259-267(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202102009.htm [17] 施和生, 王清斌, 王军, 等. 渤中凹陷深层渤中19-6构造大型凝析气田的发现及勘探意义[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2019, 24(1): 36-45. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.005Shi H S, Wang Q B, Wang J, et al. Discovery and exploration significance of large condensate gas fields in BZ19-6 structure in deep Bozhong Sag[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2019, 24(1): 36-45(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2019.01.005 [18] 何仕斌, 朱伟林, 李丽霞. 渤中坳陷沉积演化和上第三系储盖组合分析[J]. 石油学报, 2001, 22(2): 38-43, 121-122. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200102007.htmHe S B, Zhu W L, Li L X. Sedimentary evolution and Neogene reservoir-seal assemblage analysis of Bozhong Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22(2): 38-43, 121-122(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB200102007.htm [19] Fang H, Zhou X, Zhu Y, et al. Lacustrine source rock deposition in response to co-evolution of environments and organisms controlled by tectonic subsidence and climate, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J]. Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42(4): 323-339. [20] 黄志龙, 高岗. 石油地质综合研究方法[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2017.Huang Z L, Gao G. Comprehensive research method of petroleum geology[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2017(in Chinese). [21] 李福来, 曲希玉, 刘立, 等. 内蒙古东北部上二叠统林西组沉积环境[J]. 沉积学报, 2009, 27(2): 265-272. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200902009.htmLi F L, Qu X Y, Liu L, et al. Sedimentary enviorment on upper Permain Linxi Group in Inner Mongolia[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2009, 27(2): 265-272(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200902009.htm [22] Sarwar A R, Liu C, Gong H, et al. Paleo-sedimentary environment in relation to enrichment of organic matter of Early Cambrian black rocks of Niutitang Formation from Xiangxi area China[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 112: 104057. [23] Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Early Proterozoic climates and plate motions inferred from major element chemistry of lutites[J]. Nature, 1982, 299: 715-717. [24] Fedo C M, Nesbitt H W, Young G M. Unraveling the effects of potassium metasomatism in sedimentary rocks and paleosols, with implications for paleoweathering conditions and provenance[J]. Geology, 1995, 23(10): 921-924. [25] 魏永峰, 赵志强, 林美英, 等. 西昆仑尖山混杂岩带中硅质岩地球化学特征及沉积环境[J]. 新疆地质, 2016, 34(2): 197-203. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201602009.htmWei Y F, Zhao Z Q, Lin M Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and sedimentary environment of cherts from Jianshan melange belt in West Kunlun[J]. Xinjiang Geology, 2016, 34(2): 197-203(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJDI201602009.htm [26] 郑玉龙, 马志强, 王佰长, 等. 黑龙江省柳树河盆地始新统八虎力组油页岩元素地球化学特征及沉积环境[J]. 古地理学报, 2015, 17(5): 689-698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201505011.htmZheng Y L, Ma Z Q, Wang B Z, et al. Geochemistry characteristics and sedimentary environment of oil shale from the Eocene Bahuli Formation in Liushuhe Basin, Heilongjiang Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2015, 17(5): 689-698(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201505011.htm [27] 周洪瑞, 王自强, 崔新省, 等. 华北地台南部中新元古界层序地层研究[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1999.Zhou H R, Wang Z Q, Cui X S. et al. Study on stratigraphic characteristics of Mesoproterozoic in southern North China Platform[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1999(in Chinese). [28] 吴智平, 周瑶琪. 一种计算沉积速率的新方法: 宇宙尘埃特征元素法[J]. 沉积学报, 2000, 18(3): 395-399. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200003011.htmWu Z P, Zhou Y Q. Using the characteristic elements from meteoritic must in strata to calculate sedimentation rate[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinca, 2000, 18(3) : 395-399(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB200003011.htm [29] 王峰, 刘玄春, 邓秀芹, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地纸坊组微量元素地球化学特征及沉积环境指示意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2017, 35(6): 1265-1273. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706017.htmWang F, Liu X C, Deng X Q, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of trace elements of Zhifang Formation in Ordos Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinca, 2017, 35(6): 1265-1273(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201706017.htm [30] 范萌萌, 卜军, 赵筱艳, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地东南部延长组微量元素地球化学特征及环境指示意义[J]. 西北大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 49(4): 633-642. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201904016.htmFan M M, Bu J, Zhao X Y, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of trace elements of Yanchang Formation in southeastern Ordos Basin[J]. Journal of Northwest University: Natural Science Edition, 2019, 49(4): 633-642(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XBDZ201904016.htm [31] 朱伟林, 米立军, 龚再升, 等. 渤海海域油气成藏与勘探[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.Zhu W L, Mi L J, Gong Z S, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation and exploration in Bohai Sea[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009(in Chinese). [32] 黄梓桑, 王兴志, 杨西燕, 等. 沉积环境对页岩中有机质富集的约束: 以蜀南地区五峰组-龙马溪组为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2021, 39(3): 631-644. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202103010.htmHuang Z S, Wang X Z, Yang X Y, et al. Constraints of sedimentary environment on organic matter accumulation in shale: A case study of the Wufeng-Longmaxi Formations in the southern Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2021, 39(3): 631-644(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB202103010.htm [33] 李成凤, 肖继风. 用微量元素研究胜利油田东营盆地沙河街组的古盐度[J]. 沉积学报, 1988, 6(4): 100-107. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198804010.htmLi C F, Xiao J F. The application of trace element to the study on paleosalinities in Shahejie Formation of Dongying Basin Shengli Oilfield[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinca, 1998, 6(4): 100-107(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB198804010.htm [34] 钱焕菊, 陆现彩, 张雪芬, 等. 东营凹陷沙四段上部泥质烃源岩元素地球化学及其古盐度的空间差异性[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28(2): 161-168. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200902008.htmQian H J, Lu X C, Zhang X F, et al. Spatial paleosalinity distribution and element geochemistry of argillceous source rocks in the upper part of 4th Member of Tertiary Shehejie Formation in Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Petrologic et Mineralogica, 2009, 28(2): 161-168(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSKW200902008.htm [35] Piper D Z. Seawater as the source of minor elements in black shales, phosphorites and other sedimentary rocks[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 114(1/2): 95-114. [36] Emerson S R, Huested S S. Ocean anoxia and the concentrations of molybdenum and vanadium in seawater[J]. Marine Chemistry, 1991, 34(3/4): 177-196. [37] Bryn J, David M. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129. [38] Tribovillard N, Algeo T J, Lyons T, et al. Trace metals as paleoredox and paleoproductivity proxies: An update[J]. Chemical Geology, 2006, 232(1/2): 12-32. [39] 李广之, 胡斌, 邓天龙, 等. 微量元素V和Ni的油气地质意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2008, 19(1): 13-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200801007.htmLi G Z, Hu B, Deng T L, et al. Petroleum geological significance of microelements V and Ni[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2008, 19(1): 13-17(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX200801007.htm [40] Peters K E, Walters C C, Moldowan J M. The biomarker guide[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2013. -





 下载:
下载: