Susceptibility assessment of a translational rockslide considering the control mechanism and spatial uncertainty of a weak interlayer: Application study in Tiefeng Township, Wanzhou District
-
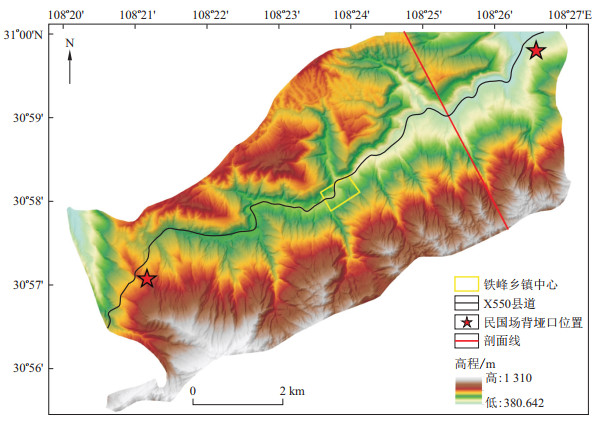
摘要: 顺层岩质滑坡突发性强, 破坏性大, 是危害山区城镇安全的重要灾害类型之一。发育软弱夹层的顺向斜坡是顺层岩质滑坡的高发区, 区域顺层岩质滑坡易发性评价应融入软弱夹层的控滑机制和空间分布不确定性分析。以万州区铁峰乡为研究区, 在软弱夹层物质结构及空间分布详细调查的基础上, 分析了原生沉积、构造变形和表生改造作用下区内页岩和泥岩两类软弱夹层发展为滑动面的演化机理, 总结了顺层岩质滑坡的变形破坏机理。考虑软弱夹层空间分布的不确定性, 提出了软弱夹层垂向分布和有效控滑深度范围内软弱夹层控滑贡献度的计算模型。提取了软弱夹层类型和控滑贡献度等表征顺层岩质滑坡控滑结构的关键指标, 结合地形地貌、斜坡结构、水文地质及人类工程活动4类要素, 构建了顺层岩质滑坡易发性评价指标体系。针对万州区铁峰乡河谷南侧的顺向坡区段, 以斜坡为评价单元, 采用层次分析法对研究区顺层岩质滑坡开展了易发性评价。结果显示研究区内侏罗系珍珠冲组泥化夹层和自流井组页岩层是顺层岩质滑坡的主要控滑层位, 极高易发区和高易发区占比分别为9.7%和25.8%, 岩质斜坡单元下伏软弱夹层分布情况和斜坡前缘开挖情况是影响滑坡灾害易发性的主要因素, 建房和道路开挖等人类工程活动极易诱发顺层岩质滑坡灾害。与不考虑软弱夹层相关指标的易发性评价结果相比, 本文方法的结果更符合实际情况。Abstract: Translational rockslides are an important disaster that endangers the safety of mountain towns. The dip slopes with weak interlayers are the areas prone to translational rockslides. The regional translational rockslide susceptibility assessment should consider the sliding mechanism and spatial distribution uncertainty analysis of the weak interlayer. Taking Tiefeng Town of Wanzhou District as the study area, based on the detailed investigation of the material, structure and spatial distribution of weak interlayers, this paper analysed the evolution mechanism of shale and mudstone developing into sliding surfaces under the action of primary deposition, tectonic deformation and supergene transformation and summarized the deformation and failure mechanism of translational rockslides. Considering the spatial distribution uncertainty of the weak interlayer, a calculation model of the vertical distribution of the weak interlayer and the contribution of the weak interlayer to slip control in the effective control depth are proposed. The key factors that characterize the sliding structure, including the type of weak interlayer and the contribution degree of the weak interlayer, are selected as susceptibility assessment factors. In addition, four elements, topography, slope structure, hydrogeology and human activities, are considered. The susceptibility of translational rockslides in the study area was assessed with slope units adopting the analytic hierarchy process. The investigation and assessment results show that the mud interlayers of the Jurassic Zhenzhuchong Formation and the shale layer of the Ziliujing Formation are the main potential slip surfaces of the translational rockslide in the study area. The extremely high susceptibility area and high susceptibility area accounted for 9.7% and 25.8%, respectively. The distribution of the underlying weak interlayer and the excavation of the slope units are the main factors affecting the susceptibility to landslide disasters. Human activities such as house building and road excavation are the main triggering factors of translational rockslides.Compared with the susceptibility assessment results without considering the factors of the weak interlayer, the results of the method proposed in this paper are more consistent with the facts.
-
图 3 研究区工程地质岩组剖面图(剖面位置见图 1)
J1z.珍珠冲组;J1-2z.自流井组;J2x.新田沟组;J2xs.下沙溪庙组;T2b.巴东组;T3xj.须家河组
Figure 3. Profile of engineering geological rock groups in the study area
表 1 软弱夹层平均厚度权重参数
Table 1. Weight parameters of average thickness of weak interlayers
软弱夹层类型 平均厚度/m 权重 自流井组 页岩 0.7 0.4 0.4 0.3 珍珠冲组 泥化夹层 0.3 0.2 煤层 0.1 0.1 表 2 软弱夹层埋藏深度权重参数
Table 2. Weight parameters of buried depth of the weak interlayer
深度范围/m 权重Wi [0, 10) 0.5 [10, 20) 0.4 [20, 30] 0.1 表 3 顺层岩质滑坡易发性指标
Table 3. Susceptibility indicators of translational rockslide
评价指标 权重系数
(考虑软弱夹层)权重系数
(不考虑软弱夹层)三级指标 分值 一级 二级 地形地貌 坡型 0.0146 0.04 凹型 0.33 直线型 0.67 凸型 1.00 平均坡度/(°) 0.023 6 0.064 7 <20 0.33 [20, 25) 0.67 [25, 30] 1.00 临空面数量 0.0687 0.188 4 1 0.33 2 0.67 3 1.00 河流侵蚀坡脚坡度/(°) 0.040 9 0.112 2 < 10 0.25 [10, 20) 0.50 [20, 30] 0.75 >30 1.00 斜坡结构 坡度与地层倾角比 0.018 8 0.051 6 < 1 0.33 [1, 1.2] 0.67 >1.2 1.00 斜坡坡向与岩层层面夹角/(°) 0.028 2 0.077 3 >40 0.25 [30, 40] 0.50 [20, 30) 0.75 <20 1.00 控滑结构 30 m深度范围内软弱层贡献度/% 0.313 3 / < 20 0.2 [20, 40) 0.4 [40, 60) 0.6 [60, 80] 0.8 >80 1.0 软弱层主要类型 0.134 3 / 煤线 0.33 泥化层 0.67 页岩层 1.00 水文地质条件 汇水面积与单元面积之比 0.014 6 0.004 [0, 0.2) 0.25 [0.2, 1) 0.50 [1, 2] 0.75 >2 1.00 上覆岩层渗透性 0.048 3 0.132 4 小/泥页岩 0.33 中/砂岩 0.67 大/粉砂岩 1.00 冲沟密度 0.026 6 0.072 9 [6, 8) 0.25 [8, 10) 0.50 [10, 12) 0.75 [12, 14] 1.00 人类工程活动 道路开挖切坡高度/m 0.080 4 0.220 5 < 5 0.25 [5, 10) 0.50 [10, 15] 0.75 >15 1.00 是否揭露软弱层 0.187 7 / 否 0 是 1 -
[1] 肖诗荣, 刘德富, 胡志宇. 世界三大典型水库型顺层岩质滑坡工程地质比较研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2010, 18(1): 52-59. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.01.007Xiao S R, Liu D R, Hu Z Y. Engineering geologic study of three actual dip bedding rockslides associated with reservoirs in the world[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2010, 18(1): 52-59(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.01.007 [2] 肖莉丽, 殷坤龙, 刘艺梁, 等. 高速库岸岩质滑坡运动过程及速度分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2012, 31(4): 117-122. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2012.04.010Xiao L L, Yin K L, Liu Y L, et al. Analysis of the velocity and process of high speed reservoir rockslide[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2012, 31(4): 117-122(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2012.04.010 [3] 殷跃平. 斜倾厚层山体滑坡视向滑动机制研究: 以重庆武隆鸡尾山滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2010, 29(2): 217-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002002.htmYin Y P. Mechanism of apparent dip slide of inclined of bedding rockslide: A case study of Jiweishan rockslide in Wulong, Chongqing[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2010, 29(2): 217-226(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX201002002.htm [4] Xue D, Li T, Zhang S, et al. Failure mechanism and stabilization of a basalt rock slide with weak layers[J]. Engineering Geology, 2018, 233: 213-224. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.12.005 [5] 李江, 许强, 王森, 等. 川东红层地区降雨入渗模式与岩质滑坡成因机制研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(增刊2): 4053-4062. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2016S2066.htmLi J, Xu Q, Wang S, et al. Research on rainfall infiltration models of slopes and formation mechanism of rock landslide in red stratum in the east of Sichuan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S2): 4053-4062(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2016S2066.htm [6] 柴波, 殷坤龙, 陈丽霞, 等. 岩体结构控制下的斜坡变形特征[J]. 岩土力学, 2009, 30(2): 521-525. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.02.041Chai B, Yin K L, Chen L X, et al. Analysis of slope deformation under control of rock mass structure[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics. 2009, 30(2): 521-525(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2009.02.041 [7] 黄少平, 晏鄂川, 尹晓萌, 等. 不同临空条件的层状反倾岩质边坡倾倒变形几何特征参数影响规律[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 159-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101017.htmHuang S P, Yan E C, Yi X M, et al. Action law of geometrical characteristic parameters in the anti-dip rock slopes under different free face condition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 159-165(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101017.htm [8] 谭明健, 周春梅, 孙东, 等. 软硬互层顺层岩质边坡破坏试验研究[J/OL]. 地质科技通报, 2021: 1-9[2021-12-02]. https://doi.org/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0096.Tan M J, Zhou C M, Sun D, et al. Model experimental study on failure of soft-hard alternant rock formation bedding slope and instability mechanism research[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021: 1-9[2021-12-02]. https://doi.org/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0096(in Chinese with English abstract). [9] 柴波, 殷坤龙, 李想. 巴东组岩石能量耗散规律的实验研究[J]. 工程地质学报, 2012, 20(6): 1013-1019. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.014Chai B, Yin K L, Li X. Experimental study on rock energy dissipation of the middle triassi Badong Formation[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(6): 1013-1019(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.014 [10] 秦四清. 斜坡失稳的突变模型与混沌机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2000, 19(4): 486-492. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.04.020Qing S Q. Nonlinear catastrophy model of slope instability and chaotic dynamics mechanism of slope ecolution process[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2000, 19(4): 486-492(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2000.04.020 [11] 郑迎凯, 陈建国, 王成彬, 等. 确定性系数与随机森林模型在云南芒市滑坡易发性评价中的应用[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 131-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006015.htmZheng Y K, Chen J G, Wang C B, et al. Application of certainty factor and random forests model in landslide susceptibility evaluation in Mangshi City, Yunnan Province[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 131-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202006015.htm [12] 黄发明, 胡松雁, 闫学涯, 等. 基于机器学习的滑坡易发性预测建模及其主控因子识别[J/OL]. 地质科技通报: 1-12[2021-10-18]. https://doi.org/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0087.Huang F M, Hu S Y, Yan X Y, et al. Landslide susceptibility prediction and its main environmental factors identification based on machine learning models[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology: 1-12[2021-10-18]. https://doi.org/10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2021.0087(in Chinese with English abstract). [13] Erener A, Mutlu A, Düzgün H S. A comparative study for landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS-based multi-criteria decision analysis(MCDA), logistic regression(LR) and association rule mining(ARM)[J]. Engineering Geology, 2016, 203: 45-55. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2015.09.007 [14] Lee D, Kim Y, Lee S. Shallow landslide susceptibility models based on artificial neural networks considering the factor selection method and various non-linear activation functions[J]. Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(7): 1194. doi: 10.3390/rs12071194 [15] Tsangaratos P, Ilia I. Comparison of a logistic regression and Naïve Bayes classifier in landslide susceptibility assessments: The influence of models complexity and training dataset size[J]. Catena, 2016, 145: 164-179. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2016.06.004 [16] 任杰. 含双软弱夹层顺层岩质滑坡的滑动模式及变形规律研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2019.Ren J. Study on sliding mode and deformation law of bedding rock landslide with double weak interlayers[D]. Taiyuan University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese with English abstract). [17] 柴波, 殷坤龙. 三峡库区巴东新城区库岸三叠系巴东组层间软弱带[J]. 工程地质学报, 2009, 17(6): 809-816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.06.011Chai B, Yin K L. Interlayer weakness zones in Badong Formation of middle Triassic forming bank slopes of Three Gorges Reservoir in new Badong County[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(6): 809-816(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.06.011 [18] 邹宗兴, 唐辉明, 熊承仁, 等. 大型顺层岩质滑坡渐进破坏地质力学模型与稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2012, 31(11): 2222-2231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.11.010Zhou Z X, Tang H M, Xiong C R, et al. Geomechanical model of progressive failure for large consequent bedding rockslide and its stability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2012, 31(11): 2222-2231(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6915.2012.11.010 [19] He K, Ma G, Hu X. Formation mechanisms and evolution model of the tectonic-related ancient giant basalt landslide in Yanyuan County, China[J]. Natural Hazards, 2021, 106(3): 2575-2597. doi: 10.1007/s11069-021-04555-6 [20] Jiang J, Xiang W, Rohn J, et al. Research on water-rock(soil) interaction by dynamic tracing method for Huangtupo landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, PR China[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2015, 74(1): 557-571. doi: 10.1007/s12665-015-4068-5 [21] Tannant D D, Giordan D, Morgenroth J. Characterization and analysis of a translational rockslide on a stepped-planar slip surface[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 220: 144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.02.004 [22] Carla T, Gigli G, Lombardi L, et al. Monitoring and analysis of the exceptional displacements affecting debris at the top of a highly disaggregated rockslide[J]. Engineering Geology, 2021, 294: 106345. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795221003562 [23] Furuki H, Chigira M. Structural features and the evolutionary mechanisms of the basal shear zone of a rockslide[J]. Engineering Geology, 2019, 260: 105214. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795219310622 [24] Dou J, Yunus A P, Bui D T, et al. Improved landslide assessment using support vector machine with bagging, boosting, and stacking ensemble machine learning framework in a mountainous watershed, Japan[J]. Landslides, 2020, 17(3): 641-658. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01286-5 [25] Regmi A D, Devkota K C, Yoshida K, et al. Application of frequency ratio, statistical index, and weights-of-evidence models and their comparison in landslide susceptibility mapping in Central Nepal Himalaya[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2014, 7(2): 725-742. -





 下载:
下载: