Discussion on the variation characteristics of paleo-water-depth of lake basin under the background of forced regression: An example in the Early Oligocene of west of Weixi'nan Sag
-
摘要:
强制水退在地质历史时期普遍存在, 但由于物源供应不匹配, 地质记录较少, 研究案例更少。以南海西北部北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷渐新世早期涠四段湖盆为研究对象, 利用地震反射结构法开展了湖盆古水深恢复研究, 明确了强制水退背景下古水深变化特征, 并进一步探讨了利用三角洲前积结构法研究古水深的恢复方法。研究表明, 渐新世早期涠四段沉积时, 涠西南凹陷物源充足, 周缘发育大型下切河谷, 凹陷内发育大型斜交前积反射结构, 具有典型的强制水退特征, 形成了较大规模的强制水退体系域。通过对典型前积剖面的精细解剖, 识别出了强制水退体系域中的6个典型前积反射层。结合地震、钻井与砂泥岩压实系数, 恢复出湖盆古水深介于111.2~286.5 m, 平均为218.5 m。自湖盆边缘向中心方向, 前积层的高度和倾角呈先缓慢增大后快速减小特征, 表明湖盆古水深具有相似的变化特征。其中水深方面早期在230 m左右, 至中晚期逐步加深至280 m左右, 末期快速下降至110 m, 相较最大水深变化幅度达61.5%;前积层倾角早期在10°左右, 至中期达14.5°后逐步下降, 末期快速变化至2.9°, 倾角变化幅度达79.8%。结合区域地质研究认为涠四段沉积时经历的地质时期小于2 Ma, 古水深与前积层倾角在不到2 Ma内快速剧烈变化, 与强制水退特征基本一致, 印证了地震反射结构的响应特征。从理论模型和恢复参数优化方面探讨了利用三角洲前积结构进行古水深恢复的可行性与未来研究方向。上述研究成果为丰富和完善强制水退背景下湖盆古水深变化特征的认识提供了重要参考。
Abstract:Forced regression is common during geological history, but due to mismatched sources andsupplies, there are fewer geological records and fewer research cases. Taking the 4th member of Weizhouformation in the Early Oligocene of Weixi'nan Sag in the Beibu Gulf Basin in the northwest of the South China Sea as the research object, the restoration of paleo-water-depth is carried out by using the seismic reflectionstructure method, the variation characteristics of paleowater depth under the background of forcedregression are clarified, and the restoration method of paleowater depth by using the delta progradationstructure method is further discussed. The research shows that during the deposition of 4th member of Weizhou Formation in the Early Oligocene, the provenance of Weixi'nan Sag was sufficient, a large incisedvalley was developed around it, and a large oblique progradation reflection structure was developed in thesag, which has typical Forced Regression characteristics, forming a large-scale forced regression systemtract. Through the fine dissection of typical progradation sections, six typical progradation reflection layersare identified. Combined with seismic, drilling and compaction coefficient, the paleo-water-depth of thelake basin is restored to be 111.2-286.5 m, with an average of 218.5 m. From the edge of the paleo-laketo the center, the height and dip angle of the progradation layers increase slowly and then decrease rapidly.In terms of water depth, it is about 230 m in the early stage, gradually deepened to about 280 m in themiddle and late stage, and rapidly decreased to 110 m in the last stage, with a change range of 61.5% comparedwith the maximum water depth; The dip angle of progradation layer is about 10° in the early stage, gradually decreases after reaching 14.5° in the middle stage, and changes rapidly to 2.9° in the final stage, with a change range of 79.8%. Combined with the regional geological research, it is considered that thegeological period experienced during the deposition of 4th member of Weizhou Formation is less than 2 Ma, and the paleowater depth and paleodip angle of progradation layers change rapidly and violently in lessthan 2 Ma, which is basically consistent with the characteristics of forced regression, which confirms theresponse characteristics of seismic reflection structure. Further, the feasibility and future research directionof paleo-water-depth restoration using delta progradation structure are discussed from the perspectiveof theoretical model simplification and restoration parameter optimization. The research results provide animportant reference for enriching the understanding of the variation characteristics of paleowater depth underthe background of forced regression.
-
Key words:
- forced regression /
- paleo-water-depth /
- Early Oligocene /
- western Weixi'nan Sag /
- lake basin
-
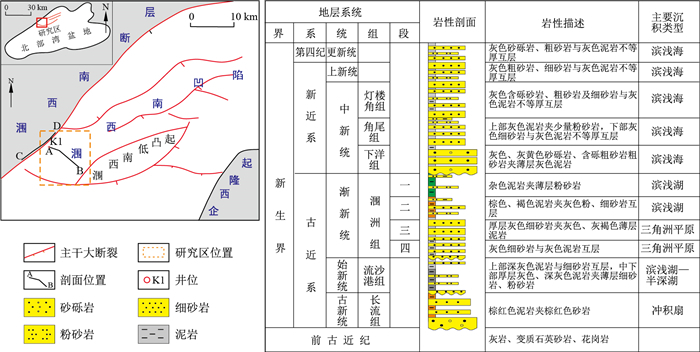
图 3 周缘下切谷发育特征(据文献[24])
Figure 3. Development characteristics of circumferentially incised valley
图 4 三角洲前积层高度与水体深度的关系(据文献[25])
细粒沉积:3°~5°; 中粒沉积:10余度; 粗粒沉积:20°~30°; 有的扇三角洲可达30余度
Figure 4. Relationship between delta foreset height and water depth
图 5 地震剖面发育典型的前积反射层结构与前积层(图 2-c局部放大)
Figure 5. Typical foreset reflector structure and foreset layer number
表 1 典型前积层计算参数统计
Table 1. Statistics of typical foreset layers calculation parameters
前积层编号 前积层长度/m 前积层高度 前积层角度 压实恢复系数 地震/m 压实恢复/m 地震/(°) 压实恢复/(°) 砂岩 泥岩 1 1 260 125 232.76 5.67 10.47 0.19 0.61 2 1 120 139 258.83 7.08 13.01 0.19 0.61 3 1 000 139 258.83 7.91 14.51 0.19 0.61 4 1 250 156 286.54 7.11 12.91 0.19 0.59 5 960 91 163.97 5.42 9.69 0.19 0.57 6 2 150 62 110.22 1.61 2.93 0.19 0.55 平均 1 290 118.7 218.5 5.80 10.58 0.19 0.59 -
[1] 梅冥相. 从正常海退与强迫型海退的辨别进行层序界面对比: 层序地层学进展之一[J]. 古地理学报, 2010, 12(5): 549-564. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201005008.htmMei M X. Correlation of sequence boundaries according to discerning between normal and forced regressions: The first advance in sequence stratigraphy[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2010, 12(5): 549-564(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201005008.htm [2] 操应长. 断陷湖盆中强制湖退沉积作用及其成因机制[J]. 沉积学报, 2005, 23(1): 84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.011Cao Y C. Sedimentation and its forming mechanism of the forced lacustrine regression in the rift lacustrine basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2005, 23(1): 84-90(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0550.2005.01.011 [3] 梅冥相, 杨欣德. 强迫型海退及强迫型海退楔体系域: 对传统Exxon层序地层学模式的修正[J]. 地质科技情报, 2000, 19(2): 17-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2000.02.004Mei M X, Yang X D. Forced regression and forced regressive wedge system tract: Revision on tradition Exxon model of sequence stratigraphy[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2000, 19(2): 17-21(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2000.02.004 [4] Thomas A L, Fujita K, Iryu Y, et al. Assessing subsidence rates and paleo-water depths for Tahiti Reefs using U-Th chronology of Altered Corals[J]. Marine Geology, 2012, 1(295/298): 86-94. [5] 潘文静, 刘士磊, 田德瑞, 等. 渤海海域新近纪湖盆萎缩期古水深恢复: 以渤东低凸起南端为例[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(4): 18-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201904003.htmPan W J, Liu S L, Tian D R, et al. Reconstruction of paleo-water depth of Neocene shrinking lake: An example from the south of Bodong Low Uplift, Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 2019, 35(4): 18-25(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT201904003.htm [6] 杨万芹, 蒋有录, 王勇. 东营凹陷沙三下-沙四上亚段泥页岩岩相沉积环境分析[J]. 中国石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 2015, 39(4): 19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.04.003Yang W Q, Jiang Y L, Wang Y. Study on shale facies sedimentary environment of lower Es3-upper Es4 in Dongying Sag[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum: Natural Science Edition, 2015, 39(4): 19-26(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.04.003 [7] 董刚, 何幼斌. 根据地层厚度恢复古水深的研究[J]. 长江大学学报: 自然科学版, 2010, 7(3): 484-486. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409-C.2010.03.164Dong G, He Y B. Study on restoring ancient water depth according to formation thickness[J]. Journal of Yangtze University: Natural Science Edition), 2010, 7(3): 484-486(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1409-C.2010.03.164 [8] 康波, 解习农, 杜学斌, 等. 基于滨线轨迹的古水深定量计算新方法: 以古近系沙三中段东营三角洲为例[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(3): 443-450. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201203005.htmKang B, Xie X N, Du X B, et al. A new paleobathymetric approach based on shoreline trajectory: An example from Dongying delta in the third member of Paleogene Shahejie Formation[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(3): 443-450(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201203005.htm [9] 李守军, 郑德顺, 姜在兴, 等. 用介形类优势分异度恢复古湖盆的水深: 以山东东营凹陷古近系沙河街组沙三段湖盆为例[J]. 古地理学报, 2005, 7(3): 399-404. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.03.010Li S J, Zheng D S, Jiang Z X, et al. Water depth of palaeo-lacustrine basin recovered by dominance diversity of ostracoda: An example from sedimentary period of the Member 3 of Shahejie Formation of Paleogene in Dongying Sag, Shandong Province[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2005, 7(3): 399-404(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1505.2005.03.010 [10] 苏新, 丁旋, 姜在兴, 等. 用微体古生物定量水深法对东营凹陷沙四上亚段沉积早期湖泊水深再造[J]. 地学前缘, 2012, 19(1): 188-199. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201022.htmSu X, Ding X, Jiang Z X, et al. Using of multi-microfossil proxies for reconstructing quantitative paleo-water depth during the deposit period of LST of Es4s in Dongying Depression[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2012, 19(1): 188-199(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201201022.htm [11] 阳宏, 刘成林, 王飞龙, 等. 渤中凹陷西南洼东营组烃源岩地球化学特征及环境指示意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, doi:10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq,2021.0077.Yang H, Liu C L, Wang F L, et al. Geochemical characteristics and environmental implications of source rocks of the Dongying Formation in southwest subsag of Bozhong Sag[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, doi:10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq,2021.0077 (in Chinese with English abstract). [12] Glϕrstad-Clark E, Birkeland E P, Nystuen J P, et al. Triassic platform-margin deltas in the western Barents Sea[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(7): 1294-1314. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.03.006 [13] 沙旭光, 刘健, 程新民, 等. 强制海退沉积作用及其地质意义[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2006, 22(11): 13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.11.003Sha X G, Liu J, Cheng X M, et al. Sedimentation and geologic significance of forced regression[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2006, 22(11): 13-17(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2722.2006.11.003 [14] 赵军, 洪庆玉, 董伟良. 北部湾涠西南凹陷物源方向及古地理景观分析[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2001, 28(5): 25-28. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.05.007Zhao J, Hong Q Y, Dong W L. Analysis on material sources and palaeogeographic landscapes of Weixi'nan Sag[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2001, 28(5): 25-28(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0747.2001.05.007 [15] 颜世永, 李月, 吴智平, 等. 北部湾盆地海中凹陷与涠西南凹陷构造特征及成因机制[J]. 石油学报, 2020, 41(6): 711-722. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202006008.htmYan S Y, Li Y, Wu Z P, et al. Structure characteristics and genetic mechanism of Haizhong Sag and Weixi'nan Sag in Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2020, 41(6): 711-722(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB202006008.htm [16] 陈奎, 周家雄, 张辉, 等. 涠西南凹陷二号断裂带断裂控藏研究及应用[J]. 海洋学报, 2019, 41(7): 92-102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.07.008Chen K, Zhou J X, Zhang H, et al. The research and application of the reservoir controlling mechanism for the No. 2 Fracture Zone, Weixi'nan Sag[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2019, 41(7): 92-102(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2019.07.008 [17] 张辉, 曾小明, 黄冬梅, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷富砾型和富砂型湖底扇沉积特征差异分析[J]. 石油实验地质, 2017, 39(5): 633-639. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201705008.htmZhang H, Zeng X M, Huang D M, et al. Differences of sedimentary characteristics of sublacustrine fans between conglomerate-rich and sand-rich types in the Weixi'nan Sag, Beibu Gulf Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2017, 39(5): 633-639(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201705008.htm [18] 杨希冰, 赵彦璞, 陆江, 等. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷C洼湖底扇沉积特征及控制因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 18-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901003.htmYang X B, Zhao Y P, Lu J, et al. Sedimentary characteristics and controlling factors of sublacustrine fan in Sag C, Weixi'nan Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 18-28(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901003.htm [19] 张洪洋. 涠洲A油田涠三段油层分布研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2018.Zhang H Y. Study on the distribution of W3 oil layer in Weizhou A Oilfield[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2018(in Chinese with English abstract). [20] 黄家琳, 万丽芬, 张萍, 等. 涠洲油田涠三段沉积特征分析[J]. 海洋石油, 2019, 39(1): 17-23, 44. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2019.01.017Huang J L, Wan L F, Zhang P, et al. Sedimentary characteristics in the 3rd Member of Weizhou Formation in Weizhou Oilfield[J]. Offshore Oil, 2019, 39(1): 17-23, 44(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2019.01.017 [21] 裴健翔, 董贵能, 朱其. 北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷流一段强制湖退沉积体的特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(4): 520-527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201604009.htmPei J X, Dong G N, Zhu Q. Characteristics and petroleum geological significance of lacustrine forced regressive deposits in the 1st Member of Liushagang Formation in Weixi'nan Sag, Beibuwan Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2016, 37(4): 520-527(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201604009.htm [22] 袁丙龙, 张辉, 张连枝, 等. 涠西南凹陷浅水三角洲前缘砂体类型及分布模式[J]. 中国海上油气, 2020, 32(2): 78-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202002009.htmYuan B L, Zhang H, Zhang L Z, et al. Types and distribution patterns of shallow water delta fronts and bodies in Weixi'nan Sag[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2020, 32(2): 78-87(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD202002009.htm [23] 蒲仁海. 前积反射的地质解释[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 1994, 29(4): 490-497. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ199404011.htmPu R H. Geological interpretation of progradation reflection[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 1994, 29(4): 490-497(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDQ199404011.htm [24] 黄建军, 张百涛, 张萍, 等. 涠西油气突破区古地貌演变和源汇体系特征及下步勘探方向[J]. 海洋石油, 2016, 36(2): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2016.02.001Huang J J, Zhang B T, Zhang P, et al. Palaeogeomorphology evolution, characteristics of source to sink system and exploration direction in the Weixi Block of Sinopec[J]. Offshore Oil, 2016, 36(2): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2016.02.001 [25] 钟建华, 李勇, 邵珠福, 等. 东营凹陷古近纪沙三中期超深水湖泊的研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2015, 21(2): 320-327. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201502016.htmZhong J H, Li Y, Shao Z F, et al. The Ultr-water lake of Middle Sha-3 Formation during Paleogene in Dongying Sag, NE China[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2015, 21(2): 320-327(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201502016.htm [26] 陈章明, 万龙贵. 古地层厚度计算方法的探讨[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 1984, 5(1): 47-54. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT198401008.htmChen Z M, Wan L G. Discussion on calculation method of paleostratigraphic thickness[J], Oil & Gas Geology, 1984, 5(1): 47-54(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT198401008.htm [27] 钟建华, 倪良田, 邵珠福, 等. 渤海湾盆地古近纪超深水与极超深水沉积及油气地质意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2017, 23(3): 521-532. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201703014.htmZhong J H, Ni L T, Shao Z F, et al. Identification of the ultradeep water deposition of the Bohai Bay Basin during the Paleogene and its significance for oil and gas geology[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2017, 23(3): 521-532(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX201703014.htm -





 下载:
下载: