Hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater and analysis of groundwater flow systems in Jianghan Plain
-
摘要: 江汉平原水质性缺水问题日益突出,识别江汉平原地下水流系统分布模式,对地下水资源的合理利用与保护具有重要意义。选取江汉平原典型区域,综合水文地质条件、水动力场及水化学同位素指标深入分析地下水补给过程、水岩作用及滞留时间。得出由于碳酸盐岩的溶解,研究区的地下水化学类型属于HCO3-Ca·(Mg)型。地下水中典型离子随深度增加逐渐降低,同位素随深度增加逐渐偏负,表现出地下水流系统呈局部与区域水流系统的特点,系统深度界限在10~20 m。独立而复杂的局部水流系统在平枯水期地下水向河渠地表水排泄。根据3H的含量,局部水流为现代水,水循环交替迅速。受地形控制,中深层地下水总体由西和西北向东和东南径流,汇入汉江和长江,为区域水流系统。由于补给源的高程效应,区域水流的18O值存在明显分区,指示不同的补给来源与水流路径。山前丘陵区基本为现代水,向平原腹地纵深至汉江和长江排泄区,地下水年龄在几百年至6 000 a不等,水循环交替缓慢。研究发现江汉平原低洼排泄区存在区域水流的顶托补给,可为原生劣质水的分布与聚集研究提供依据。Abstract: Based on increasingly serious groundwater quality problems in Jianghan Plain, the investigation of groundwater flow systems (GFSs) is vital for the sustainable management and protection of water resources. Hydrogeological conditions, hydrodynamic field and hydrogeochemistry were used to gain insight into the recharge process, water-rock interactions, and groundwater residence time in the typical area of Jianghan Plain. Because of carbonate mineral weathering, groundwater is predominantly of the HCO3-Ca·(Mg) type. The decrease of typical ions and the depletion of isotopic distributions with depth increasing indicate that the GFSs were divided into local and regional GFSs with a depth limitation of approximately 10~20 m. The complex and independent local GFSs exhibit a pattern in which groundwater discharged into surface waters during the nonflood season. Groundwater age of local GFSs is modern according to the 3H concentrations, indicating the hydrodynamic circulation is active. Furthermore, controlled by topography, the regional GFSs flow from west or northwest to east or southeast, eventually discharging into the Yangtze River and the Han River. The evident zonations of δ18O distribution in regional GFSs are dominated by the altitude effect of recharge areas, indicating different recharge sources and flow paths. The piedmont hilly area is basically modern water. Deep into the hinterland of the plain to the discharge area of the Han River and Yangtze River, groundwater age of regional GFSs varied from hundreds of years to 6 000 years estimated by 14C isotope data, elucidating that the hydrodynamic circulation is slow to relatively stagnant. The existence of regional GFSs driven by an upward hydraulic gradient in the low-lying discharge area of Jianghan Plain, can provide a theoretical basis for researching the distribution and aggregation of primary inferior groundwater.
-
Key words:
- groundwater flow systems /
- hydrogeochemistry /
- interfluve /
- Jianghan Plain
-
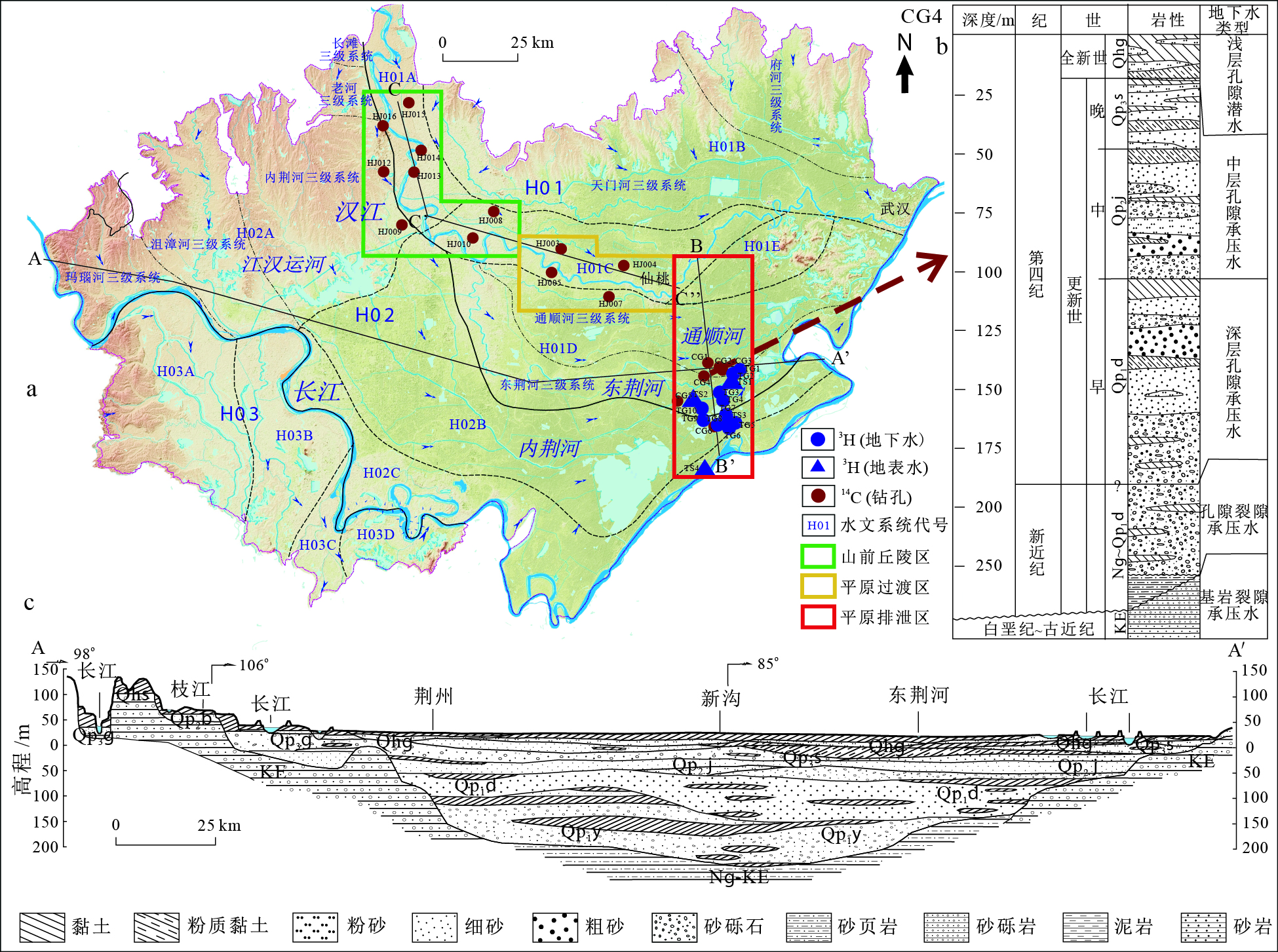
表 1 江汉平原水文系统划分
Table 1. Distribution of hydrological system in Jianghan Plain
区域 一级划分 二级划分 三级划分 名称 代码 面积/km2 名称 代码 面积/km2 名称 面积/km2 长江
干流
以北汉江
流域H01 14 608.2 汉江夹道区 H01A 1 118.68 汉北支流区 H01B 6 101.78 天门河三级系统 4 171.46 府河三级系统 1 930.32 汉江主干流区 H01C 1 949.50 汉江南分叉河流 H01D 4 671.78 通顺河三级系统 2 643.23 东荆河三级系统 2 028.55 汉江东长河 H01E 766.47 长江
干流长江
干流
区域H02 14 188.1 玛瑙河三级系统 1 153.81 沮漳河三级系统 1 782.76 荆北地区支流 H02A 6 218.85 内荆河三级系统 2 914.13 老河三级系统 296.61 长滩三级系统 71.54 四湖流域 H02B 5 125.97 长江主干流区 H02C 2 843.23 长江
干流
以南洞庭湖
流域松滋河流域 H03A 2 433.78 虎渡河流域 H03B 1 619.60 藕池河流域 H03C 422.50 调弦河流域 H03D 559.41 表 2 水样测试手段及方法
Table 2. Testing means and methods for water samples
测试指标 仪器或方法 最低检出浓度 测试单位 常规阳离子 电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICAP 6300,美国) 0.001 mg/L 中国地质大学(武汉)
地质调查研究院常规阴离子 离子色谱仪(ICS-2100,赛默飞,美国) 0.01 mg/L 氘氧同位素(δ2H和δ18O) 液态水同位素分析仪(LGR,IWA-45EP,美国) δ2H:0.5‰; δ18O:0.1‰ 氚(3H) 1220 Quantulus型超低本底液体闪烁谱仪 0.1 TU 中国地质大学(武汉)
环境学院实验中心放射性14C 加速器质谱仪 0.1 pMC 西安加速质谱中心 表 3 江汉平原研究区地下水化学指标统计结果
Table 3. The statistic results of hydrogeochemical indicators in the study area, Jianghan Plain
区域 含水岩组 K+ Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- NO3- TDS pH δ2H/
‰δ18O/
‰E 水化学
类型ρB/(mg·L-1) 山
前
丘
陵
区浅层孔隙潜水 最大值 156.5 125.5 327.8 86.6 229.4 266.9 745.4 351.8 1285.0 7.5 -27.5 -2.0 4.9 A, B (0~15m) 最小值 0.3 6.7 52.0 15.2 1.7 0.0 127.6 0.0 216.5 6.5 -54.5 -8.1 -4.9 (n=44) 平均值 16.5 33.8 161.0 40.0 64.0 84.1 504.9 93.7 660.2 7.0 -42.0 -6.4 0.2 中层孔隙承压水 最大值 32.9 77.0 244.0 58.8 159.0 456.0 799.0 220.3 1082.3 7.7 -30.9 -4.1 10.0 A, B (15~70m) 最小值 0.2 8.1 24.4 14.0 0.3 0.0 187.8 0.0 151.9 6.4 -54.8 -8.6 -9.9 (n=108) 平均值 2.0 23.7 120.0 34.0 15.5 22.9 523.3 14.6 485.3 6.9 -47.1 -7.0 1.6 平
原
过
渡
区浅层孔隙潜水 最大值 25.6 48.5 181.5 56.4 99.8 79.6 657.3 41.8 765.9 7.3 -30.1 -3.6 3.3 A, B (0~20m) 最小值 0.4 13.8 70.8 12.5 0.86 0.0 264.1 0.0 299.7 6.3 -20.9 -7.9 -3.0 (n=17) 平均值 3.2 23.9 118.0 34.4 25.1 19.4 221.5 4.8 484.7 6.9 -41.1 -6.3 0.5 中层孔隙承压水 最大值 3.5 67.1 172.2 68.8 68.8 66.0 831.3 8.8 664.8 7.9 -37.7 -5.4 4.9 A, B (20~80m) 最小值 0.5 9.4 51.9 11.3 0.0 0.0 180.1 0.0 187.1 6.2 -58.3 -8.6 -7.1 (n=88) 平均值 1.2 25.0 102.1 28.0 5.0 1.8 512.3 0.7 419.0 7.0 -47.4 -7.1 -0.3 平
原
排
泄
区浅层孔隙潜水 最大值 148.6 109.0 215.5 60.3 122.7 208.8 907.0 297.5 1037.0 8.3 -23.5 -3.2 10.7 A, B, C, D (0~20m) 最小值 0.4 7.8 53.9 13.7 0.0 0.0 160.0 0.0 270.0 6.3 -55.8 -8.1 0.1 (n=109) 平均值 5.3 27.5 128.1 28.2 19.3 30.1 552.0 23.2 523.0 6.9 -40.9 -6.5 1.1 中层孔隙承压水 最大值 14.6 64.9 172.7 45.3 29.7 12.2 850.0 12.3 665.0 7.5 -31.0 -4.6 9.8 A, B (20~100m) 最小值 0.7 2.1 23.0 12.3 0.0 0.0 171.0 0.0 187.0 6.3 -58.5 -8.6 0.0 (n=111) 平均值 1.9 18.9 120.7 24.8 3.3 1.4 576.0 0.26 457 6.9 -45.8 -7.2 3.2 E代表电荷平衡误差;水化学类型:A为HCO3-Ca型水,B为HCO3-Ca-Mg型水,C为HCO3-Cl-Ca型水,D为HCO3-SO4-Ca型水 表 4 汉江-长江剖面水样氚(3H)测试结果
Table 4. Results of the 3H analyses in water samples on profile of the Han River and the Yangtze River
样品编号 井深/m 3H/TU 水样类型 TG1 23 17.5 地下水 TG2 28 14.6 地下水 TG3 30 14.0 地下水 TG4 23 13.9 地下水 TG5 50 15.6 地下水 TG6 24 16.4 地下水 TG7 26 16.8 地下水 TG8 25 16.3 地下水 TG9 28 15.4 地下水 TG10 15 13.8 地下水 TS1 0 20.8 东荆河 TS2 0 18.4 东荆河 TS3 0 20.5 内荆河 TS4 0 21.3 长江 表 5 研究区地下水14C的测试结果与校正分析
Table 5. Results of the 14C test and calibration analyses for groundwater samples in the study area
区
域样品
编号井深/
m滤水管/
mδ13C/‰ 14C/
pMC视年龄/
(aB.P.)统计模型/
(aB.P.)化学混合模型/
(aB.P.)平均混合年龄/
(aB.P.)Pearson模型/
(aB.P.)IAEA模型/
(aB.P.)地下水
位/m汉
江
∣
长
江
地
块CG1 230 44~60 -6.6 64.5 3520 -809.7 -569.6 现代 -7 291.3 -3 765.0 21.57 130~150 -5.5 32.6 9 017 4 846.5 4 100.3 4 473.4 -3 120.1 406.2 21.59 CG2 50 45~50 -10.8 58.9 4 254 -53.5 -311.1 现代 -2 434.0 1 092.3 21.86 CG3 50 24~25 -6.3 64.8 3 488 -843.0 -602.9 现代 -7 607.3 -4 081.0 21.49 45~50 -9.0 59.2 4 206 -103.9 188.1 42.1 -3 918.2 -391.9 21.52 CG4 201 40~80 -6.5 52.3 5 209 927.7 126.9 527.3 -5 640.8 -2 114.5 22.04 138~160 -8.7 29.4 9 827 5 679.5 4 801.4 5 240.5 1 592.2 5 118.5 22.09 CG5 85 52~72 -11.8 45.3 6 356 2 108.6 1 721.4 1 915.0 501.8 4 028.0 22.17 CG6 87 54~75 -10.1 67.0 3 222 -1 116.6 -2 037.3 现代 -3 998.0 -471.7 23.93 汉
江
区
域HJ004 240 30~45 -9.9 61.3 3 930 -386.5 -1 255.6 现代 -3 428.6 93.9 22.89 64~80 -11.0 40.9 7 180 2 956.7 2 166.4 2 561.5 738.9 4 261.3 - 182~238 -12.1 3.8 26 250 22 580.5 22 303.6 22 442.0 21 160.1 24 682.6 - HJ007 185 40~70 -3.9 54.5 4 880 588.6 273.8 431.2 -10 171.4 -6 648.9 22.98 160~180 -10.7 9.6 18 830 14 940.6 13 921.2 14 430.9 12 516.6 16 039.0 - 53~72 -13.0 64.6 3 510 -816.1 -1 423.1 现代 -1 648.3 1 874.1 - HJ005 138 76~86 -10.1 44.2 6 560 2 321.0 1 256.7 1 788.8 -556.1 2 966.4 - HJ003 110 110~126 -11.8 18.5 13 540 9 508.5 8 232.2 8 870.4 7 929.1 11 451.6 - HJ008 186 44~76 -9.3 26.8 10 570 6 444.2 6 148.2 6 296.2 2 868.6 6 391.0 - 30~38 -12.9 95.2 400 -4 021.3 -3 954.4 现代 -4 885.4 -1 363.0 27.53 40~50 -12.8 88.5 985 -3 417.7 -3 635.7 现代 -4 352.5 -830.1 27.52 HJ010 73 150~180 -11.5 12.2 16 880 12 939.0 12 107.7 12 523.4 11 089.9 14 612.4 - HJ009 104 22~66 -11.9 84.4 1 370 -3 026.3 -2 430.3 现代 -4 570.8 -1 048.4 29.07 HJ013 78 30~42 -13.2 70.6 2 800 -1 548.4 -1 881.6 现代 -2 222.6 1 299.9 30.86 HJ012 40 44~60 -9.7 85.3 1 280 -3 115.9 -2 797.5 现代 -6 369.0 -2 846.6 - 25~37 -11.2 62.8 3 730 -591.6 -452.2 现代 -2 667.4 855.0 - -
[1] [1] 梁杏,张人权,靳孟贵.地下水流系统:理论、应用与调查[M].北京:地质出版社,2015. [2] 梁杏,张人权,牛宏,等.地下水流系统理论与研究方法的发展[J].地质科技情报,2012,31(5):143-151. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/201205/43592586.html [3] Goderniaux P,Davy P,Bresciani E,et al.Partitioning a regional groundwater flow system into shallow local and deep regional flow compartments[J].Water Resources Research,2013,49:2274-2286.doi: 10.1002/wrcr.20186 [4] Liang X,Quan D J,Jing M G,et al.Numerical simulation of groundwater flow patterns using flux as upper boundary[J].Hydrology Process,2013,27:3475-3483.doi: 10.1002/hpy.9477 [5] Currell M J,Han D M,Chen Z Y,et al.Sustainability of groundwater usage in northern China:Dependence on paleowaters and effects on water quality,quantity and ecosystem health[J].Hydrology Process,2012,26:4050-4066.doi: 10.1002/hyp.9028 [6] Wang J Z,Wörman A,Bresciani E,et al.On the use of late-time peaks of residence time distributions for the characterization of hierarchically nested groundwater flow systems[J].Journal of Hydrology,2016,543:47-58.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.04.034 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2016.04.034 [7] Niu B B,Wang H H,Loáiciga H A,et al.Temporal variations of groundwater quality in the western Jianghan Plain,China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2017,578:542-550.http//dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.10.225 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0391af89b9a85ccd188c0b887d54ed46 [8] Han D M,Liang X,Jin M G,et al.Hygrogeochemical indicators of groundwater flow systems in the Yangwu River alluvial fan,Xinzhou Basin,Shanxi,China[J].Environmental Management,2009,44:243-255.doi: 10.1007//s00267-009-9301-0 [9] Montcoudiol N,Molson J,Lemieux J M.Groundwater geochemistry of the Outaouais Region (Québec,Canada):A regional-scale study[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2014,23:377-396.doi: 10.1007/s10040-014-1190-5 [10] Han D M,Liang X,Currell M J,et al.Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical characteristics of groundwater systems in Daying and Qicun geothermal fields,Xinzhou Basin,Shanxi,China[J].Hydrology Process,2010,24:3157-3176.doi: 10.1002/hyp.7742 [11] Majumder R K,Halim M A,Saha B B,et al.Groundwater flow system in Bengal Delta,Bangladesh revealed by ebvironmental isotopes[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2011,64:1343-1352.doi: 10.1007/s12665-011-0959-2 [12] Koh D C,Ha K,Lee K S,et al.Flow paths and mixing properties of groundwater using hydrogeochemistry and environmental tracers in the southwestern area of Jeju volcanic island[J].Journal of Hydrology,2012,432/433:61-74.doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.02.030 [13] 张人权,梁杏,靳孟贵.末次盛冰期以来河北平原第四系地下水流系统的演变[J].地学前缘,2013,20(3):217-226. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Conference/8118544 [14] He J M,Ma J Z,Zhao W,et al.Groundwater evolution and recharge determination of the Quaternary aquifer in the Shule River basin,Northwest China[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2015,23:1745-1759.doi: 10.1007/s10040-015-1311-9 [15] Casique E M,Belmont J G,Guerrero A O.Regional groundwater flow and geochemical evolution in the Amacuzac River Basin,Mexico[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2016,24:1873-1890.doi: 10.1007/s10040-016-1423-x [16] Zhou Y,Wang Y X,Li Y L,et al.Hydrogeochemical characteristics of central Jianghan Plain,China[J].Environmental Earth Sciences,2013,68:765-778.doi: 10.1007/s12665-012-1778-9 [17] Zhou Y,Wang Y X,Zwahlen F,et al.Organochlorine pesticide residues in the environment of central Jianghan Plain,China[J].Environmental Forensics,2011,12:106-119.https://doi.org/10.1080/15275922.2010.547546 doi: 10.1080/15275922.2010.547546 [18] Yao L L,Wang Y X,Tong L,et al.Seasonal variation of antibiotics concentration in the aquatic environment:A case study at Jianghan Plain,central China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2015,527-528:56-64.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.scititenv.2015.04.091 doi: 10.1016/j.scititenv.2015.04.091 [19] 李红梅,邓亚敏,罗莉威,等.江汉平原高砷含水层沉积物地球化学特征[J].地质科技情报,2015,34(3):178-184. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb201901028 [20] 成东,廖鹏,袁松虎.FeS胶体对三价铁吸附态As(V)的解吸作用[J].地球科学,2016,41(2):325-330. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQKX201602012.htm [21] 沈帅,马腾,杜尧,等.江汉平原典型地区季节性水文条件影响下氮的动态变化规律[J].地球科学,2017,42(5):674-684. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201705003 [22] Gan Y Q,Zhao K,Deng Y M,et al.Groundwater flow and hydrogeochemical evolution in the Jianghan Plain,central China[J].Hydrogeology Journal,. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-018-1778-2 [23] Zhang J W,Liang X,Jin M G,et al.Indentifying the groundwater flow systems in a condensed river-network interfluve between the Han River and Yangtze River (China) using hydrogeochemical indicators[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2019,27:2415-2430. doi: 10.1007/s10040-019-01994-1 [24] 张婧玮,梁杏,葛勤,等.江汉平原第四系弱透水层渗透系数求算方法[J].地球科学,2017,42(5):761-770. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201705012 [25] 段艳华.浅层地下水系统中砷富集的季节性变化与机理研究[D].武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2016. [26] 段艳华,甘义群,郭欣欣,等.江汉平原高砷地下水监测场水化学特征及砷富集影响因素分析[J].地质科技情报,2014,33(2):140-147. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201402023 [27] 沈帅,马腾,杜尧,等.江汉平原东部浅层地下水氮的空间分布特征[J].环境科学与技术,2018,41(2):47-56.doi: 10.19672/j.cnki.1003-6504.2018.02.008 [28] Duan Y H,Gan Y Q,Wang Y X,et al.Arsenic speciation in aquifer sedment under varying groundwater regime and redox conditions at Jianghan Plain of Central China[J].Science of the Total Environment,2017,607/608:992-1000. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28724231 [29] Nisi B,Buccianti A,Vaselli O,et al.Hydrogeochemistry and strontium isotopes in the Arno River Basin (Tuscany,Italy):Constraints on natural controls by statistical modeling[J].Journal of Hydrology,2008,360:166-183.doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2008.07.030 [30] Liu F,Song X,Yang L,et al.Identifying the origin and geochemical evolution of groundwater using hydrochemistry and stable isotopes in Subei Lake Basin,Ordos energy base,Northwestern China[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2015,19:551-565. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=205f4177aea2f7eba927c1ea811821dc [31] Fisher R S,Mulican W F III.Hydrochemical evolution of sodium-sulphate and sodium-chloride groundwater beneath the Northern Chihuahuan desert Trans-Pecos,Texas,USA[J].Hydrogeol Journal,1997,5:4-16. doi: 10.1007-s100400050102/ [32] Krishnaraj S,Murugesan V,Vijayaraghavan K,et al.Use of hydrochemistry and stable isotopes as tools for groundwater evolution and contamination investigations[J].Geosciences,2011,1:16-25.doi: 10.5923/j.geo.20110101.02 [33] Farid I,Zouari K,Rigane A,et al.Origin of the groundwater salinity and geochemical processes in detrital and carbonate aquifers:case of Chougafiya basin (central Tunisia)[J].Journal of Hydrology,2015,530:508-532.http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.009 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.10.009 [34] 赵家成,魏宝华,肖尚斌.湖北宜昌地区大气降水中的稳定同位素特征[J].热带地理,2009,29(6):526-531. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rddl200906004 [35] Chen Z Y,Wei W,Liu J,et al.Identifying the recharge sources and age of groundwater in the Songnen Plain (Northeast China) using environmental isotopes[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2011,19:163-176.doi:10.1007//s 10040-010-0650-9 [36] Michel R L.Chapter 5 Radionuclides as tracers and timers in surface and groundwater[J].Radiocativity in the Environment,2009,16:139-230.doi: org/10.1016/S1569-480(09)01605-2 [37] Wang Y,Jiao JJ.Origin of groundwater salinity and hydrogeochemical processes in the confined Quaternary aquifer of the Pearl River Delta,China[J].Journal of Hydrology,2012,438/439:112-124.http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.008 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.008 [38] Geyh M A.Environmental isotopes in the hydrological cycle:Principles and applications- groundwater saturated and unsaturated zone//Mook W G.UNESCO and IAEA.Vienna:UNESCO and IAEA,2000,4:100-107. [39] Tamers M A.The validity of radiocarbon dates on groundwater[J].Survey in Geophysics,1975,2:217-239.doi: org/10.1007/BF01447909 [40] Pearson F J,White D E.Carbon 14 ages and flow rates of water in Carrizo Sand,Atascosa County,Texas[J].Water Resources Research,1967,3:251-261. doi: 10.1029-WR003i001p00251/ [41] Salem O,Visser J M,Deay M,et al.Groundwater flow patterns in the weastern Lybian Arab Jamahitiya evaluated from isotope data//IAEA.Arid zone hydrology:Investigations with Isotope Techniques.Vienna:IAEA 1980:165-179. [42] 于凯.高砷地下水系统中有机质来源及其对砷动态变化的影响研究:以江汉平原为例[D].武汉:中国地质大学(武汉),2016. [43] Du Y,Ma T,Deng Y M,et al.Characterizing groundwater/surface-water interactions in the interior of Jianghan Plain,central China[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2018,26(4):1047-1059.http://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-017-1709-7 doi: 10.1007/s10040-017-1709-7 [44] Clark I D,Fritz P.Environmental isotopes in hydrogeology[M].Lewis,New York:[s.n.],1997:328. [45] 陈宗宇.从华北平原地下水系统中古环境信息研究地下水资源演化[D].长春:吉林大学,2001. [46] Chen Z Y,Nie Z L,Zhang G H,et al.Environmental isotopic study on the recharge and residence time of groundwater in the Heihe River Basin,northwestern China[J].Hydrogeology Journal,2006,14:1635-1651.doi: 10.1007//s10040-006-0075-7 [47] Mook W G,Bommerson J C,Staverman W H.Carbon isotope fractionation between dissolved bicarbonate and gaseous carbon dioxide[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters,1974,22:169-176.http://doi.org/10.1016/0012-821X(74)90078-8 . doi: 10.1016/0012-821X(74)90078-8 [48] Atkinson A P,Cartwright I,Gilfedder B S,et al.Using 14C and 3H to understand groundwater flow and recharge in an aquifer window[J].Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,2014,18:4591-4964.doi: 10.5194/hess-18-4954-2014 -





 下载:
下载: