Semi-analytical solution for radial solute transport model with skin effect
-
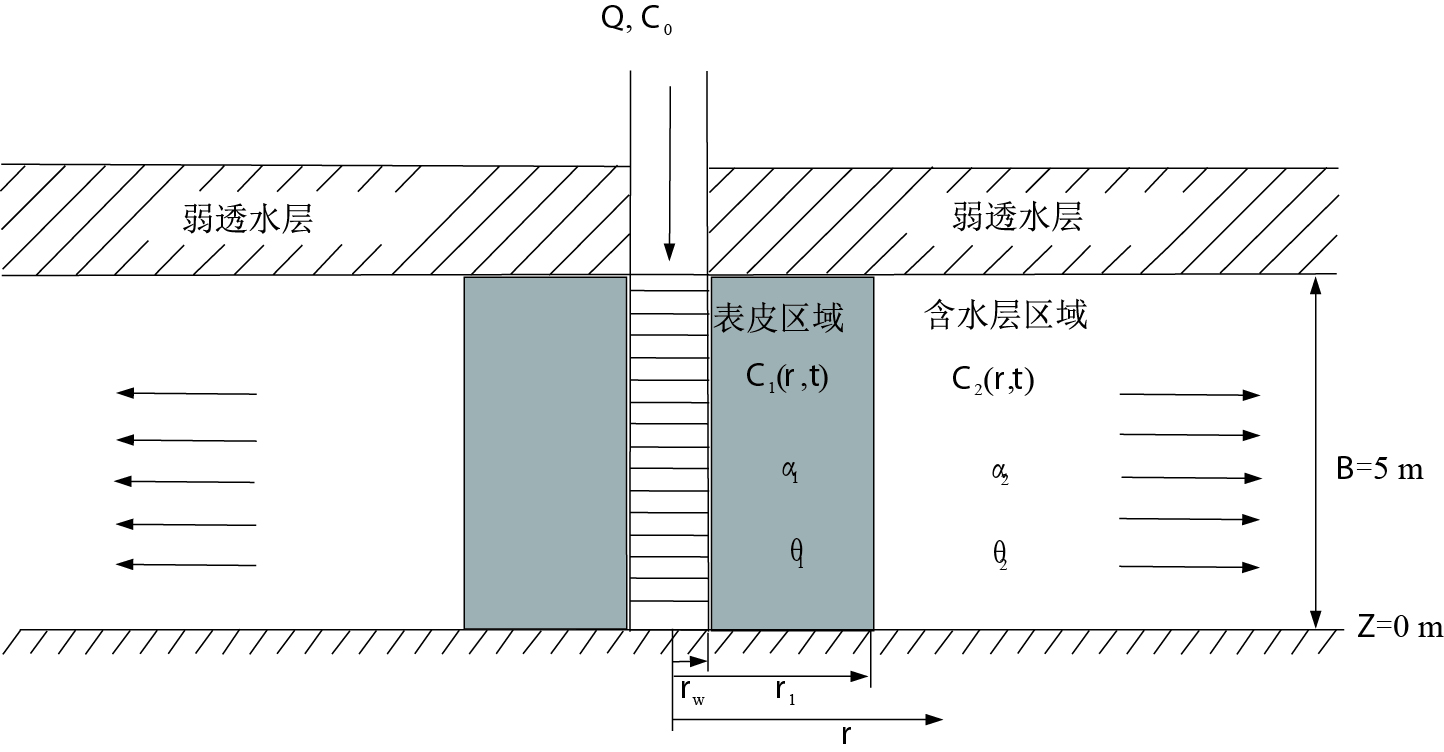
摘要: 径向示踪试验是一种非常有效的获取含水层弥散参数的试验方法,但传统径向示踪试验很少考虑抽水井附近的表皮效应(由于钻井施工工艺所导致抽水井附近一定区域水力性质发生变化)。建立了考虑表皮效应的单井注入示踪试验模型,并利用Lapalce变换以及数值逆变换获得了该模型的半解析解。系统分析了表皮区域水力性质对示踪试验穿透曲线的影响规律。研究结果表明:表皮区域的弥散度越大,穿透曲线早期的浓度越高,且峰值越高;表皮孔隙度越大,穿透曲线早期浓度越低,后期浓度越高;此外,散度差异也会导致浓度分布曲线在表皮区域与含水层界面处发生突变。总之,表皮效应对径向溶质迁移产生了较大的影响,有必要将表皮效应考虑到径向示踪试验中去。Abstract: Radial tracer test is one of the most effective ways to estimate aquifer transport parameters.However, traditional tracer tests usually neglect skin effect near a pumping well, due to extensive well development resulting in anomalous hydrogeological properties.A semi-analytical model for a confined aquifer was developed to analyze the effects of skin of hydrogeological properties on breakthrough curves.The Laplace transform and numerical inverse Laplace methods were used to solve the model.The results indicate that a larger dispersivity in the skin zone results in higher values of breakthrough curves (BTCs) at the early injection stage, and higher peak values of BTCs; however, larger effective porosity in the skin zone results in lower values of the BTCs at the early injection stage but generates higher values at the late stage; besides, an abrupt change for the spatial concentration distribution was observed at the interface of the skin and aquifer formation zones due to the change of dispersivity in the skin zone.The general conclusion is that the possible impacts of skin on radial solute transport are significant and should be taken into consideration in tracer-injection tests.
-
Key words:
- radial solute transport /
- skin effects /
- tracer test /
- the advection-dispersion equation
-
表 1 默认的模型参数
Table 1. Default parameter values used in this study
参数 符号 数值 含水层厚度/m B 5 井半径/m rw 0.1 表皮区半径/m r1 0.8 表皮区的有效孔隙度 θ1 0.3 含水层有效孔隙度 θ2 0.3 含水层的径向弥散度/m α2 0.5 表皮的径向弥散度/m α1 0.5 注入流量/(m3·h-1) Q 2.5 溶质注入时间/h t0 0.5 注入时间/h tinj 6 -
[1] 朱学愚, 冯绍元.用改进的特征有限元法确定抽水(注水)时的弥散参数[J].水动力学研究与进展:A辑, 1992, 7(2):206-211. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SDLJ199202011.htm [2] 任理.地下水溶质径向弥散问题的混合拉普拉斯变换有限单元解[J].水动力学研究与进展:A辑, 1994, 9(1):37-43. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400399541 [3] Moench A, Ogata A.A numerical inversion of the Laplace transform solution to radial dispersion in a porous medium[J].Water Resources Research, 1981, 17(1):250-252. doi: 10.1029/WR017i001p00250 [4] Chen J S, Liu C W, Liao C M.A novel analytical power series solution for solute transport in a radially convergent flow field[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2002, 266(1/2):120-138. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e615311224c8a049b05d550e8d1790cb [5] Wang Q R, Zhan H B.Radial reactive solute transport in an aquifer-aquitard system[J].Advance in Water Resources, 2013, 61:51-61. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.08.013 [6] 张效先.不动水体存在时求解径向弥散问题的一种有限单位法及其应用[J].水利学报, 1988(1):40-46. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0559-9350.1988.01.005 [7] Hoopes J A, Harleman D R F.Dispersion in radial flow from a recharge well[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1967, 72(14):3595-3607. doi: 10.1029/JZ072i014p03595 [8] 高光耀, 冯绍元, 霍再林, 等.考虑弥散尺度效应的溶质径向运移动力学模型及半解析解[J].水动力学研究与进展, 2009, 24(2):156-163. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sdlxyjyjz200902005 [9] Sharifi Haddad A, Hassanzadeh H, Abedi J, et al.Application of tracer injection tests to characterize rock matrix block size distribution and dispersivity in fractured aquifers[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 510:504-512. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.01.008 [10] Wang Q R, Shi W G, Zhan H B, et al.Models of single-well push-pull test with mixing effect in the wellbore[J].Water Resources Research, 2018, 54:10155-10171. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=47c425260a9df4fd1daa19af6d1e81c0 [11] de Hoog F R, Knight J, Stokes A.An improved method for numerical inversion of Laplace transforms.[J].SIAM Journal on Scientific and Statistical Computing, 1982, 3(3):357-366. doi: 10.1137/0903022 [12] Stehfest H.Algorithm 368 numerical inversion of Laplace transform[J].Communication of ACM, 1970, 13(1):47-49. doi: 10.1145-355598.362787/ [13] Li N, Wen Z, Zhan H B, et al.The single-well test dilemma:The skin effect and variable-rate pumping perspective[J].Hydrogeology Journal, 2018, 26:2521-2529. doi: 10.1007/s10040-018-1852-9 [14] Li X, Wen Z, Qi Zhu, et al.Numerical simulation of single-well push-pull tests in a radial two-zone confined aquifer[J].Hydrogeology Journal, 2019, 27(7):2645-2658. doi: 10.1007/s10040-019-02014-y [15] Yeh H D, Chen Y J.Determination of skin and aquifer parameters for a slug test with wellbore-skin effect[J].Journal of Hydrology:Amsterdam, 2007, 342(3/4):283-294. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=028b083ad0dfd7c969be981a00e5b98d [16] Malama B, Kuhlman K L, Barrash W, et al.Modeling slug tests in unconfined aquifers taking into account water table kinematics, wellbore skin and inertial effects[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 408(1/2):113-126. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d2dbcfbbdc25e901d689de8575a5a50e [17] Wen Z, Zhan H B, Huang, G H, et al.Constant-head test in a leaky aquifer with a finite-thickness skin[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2011, 399:326-334. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2011.01.010 [18] Feng Q, Zhan H B.Constant-head test at a partially penetrating well in an aquifer-aquitard system[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 569:495-505. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.018 [19] Chen Y J, Yeh H D, Chang K J.A mathematical solution and analysis of contaminant transport in a radial two-zone confined aquifer[J].Journal of Contaminant Hydrology, 2012, 139(2):75-82. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22814588/ [20] Hsieh P F, Yeh H D.Semi-analytical and approximate solutions for contaminant transport from an injection well in a two-zone confined aquifer system[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 519:1171-1176. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.08.046 -





 下载:
下载: