Productivity and development model of source rock of the Liushagang Formation in the Weixinan Sag
-
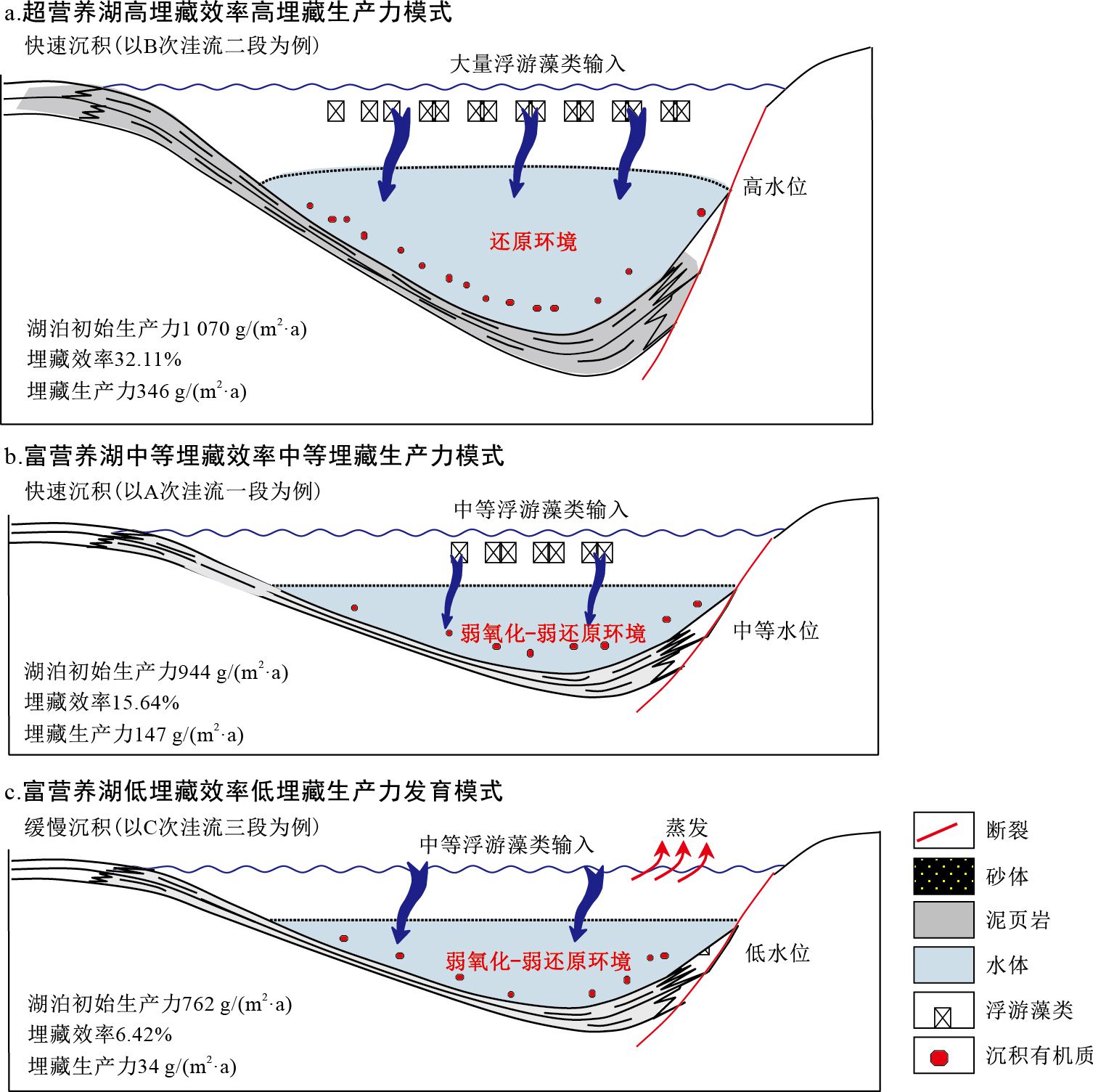
摘要: 涠西南凹陷是中国近海北部湾盆地已证实的富烃凹陷,始新统流沙港组是该凹陷主要烃源岩层系。为深入认识涠西南凹陷流沙港组烃源岩的生产力和发育特征,采用有机地球化学与地球生物学相结合、定性分析与定量计算相结合的方法正演恢复了涠西南凹陷不同次洼流沙港组不同层段烃源岩的古生产力、有机质埋藏效率和有机碳埋藏生产力,进而建立了研究区流沙港组烃源岩形成的地球生物学模式。结果表明,涠西南凹陷流沙港组烃源岩的古生产力、有机质埋藏效率及有机碳埋藏生产力在横向不同次洼和纵向不同层段上均存在差异,横向上以B次洼最优,纵向上以流二段最高;涠西南凹陷流沙港组烃源岩发育超营养湖高埋藏效率高埋藏生产力、富营养湖中等埋藏效率中等埋藏生产力及富营养湖低埋藏效率低埋藏生产力3种代表性的地球生物学模式。Abstract: The Weixinan Sag is a proven hydrocarbon-rich sag with the Eocene Liushagang Formation as main source rock system in the Beibuwan Basin, offshore China.In order to deepen the understanding of the productivity and development characteristics of the Liushagang Formation source rock, the paleo-productivity, organic matter burial efficiency and organic carbon burial productivity of each sub-sag in the Weixinan Sag and each member in the Liushagang Formation are restored forward by using the methods of organic geochemistry combined with geobiology and qualitative analysis combined with quantitative calculation, and the geobiological development models of the Liushagang Formation source rock are further established.The results show that there are differences in paleo-productivity, organic matter burial efficiency and organic carbon burial productivity among different sub-sags in lateral and vertical directions.The B sub-sag is the best in plane and the E2L2 is the highest in vertical sequence.Three representative geobiological development models of the Liushagang Formation source rocks can be summarized as the hypertrophic lake with high burial efficiency and burial productivity, the eutrophic lake with medium burial efficiency and burial productivity, and the eutrophic lake with low burial efficiency and burial productivity.
-
Key words:
- paleo-productivity /
- burial efficiency /
- burial productivity /
- geobiological model /
- Weixinan Sag
-
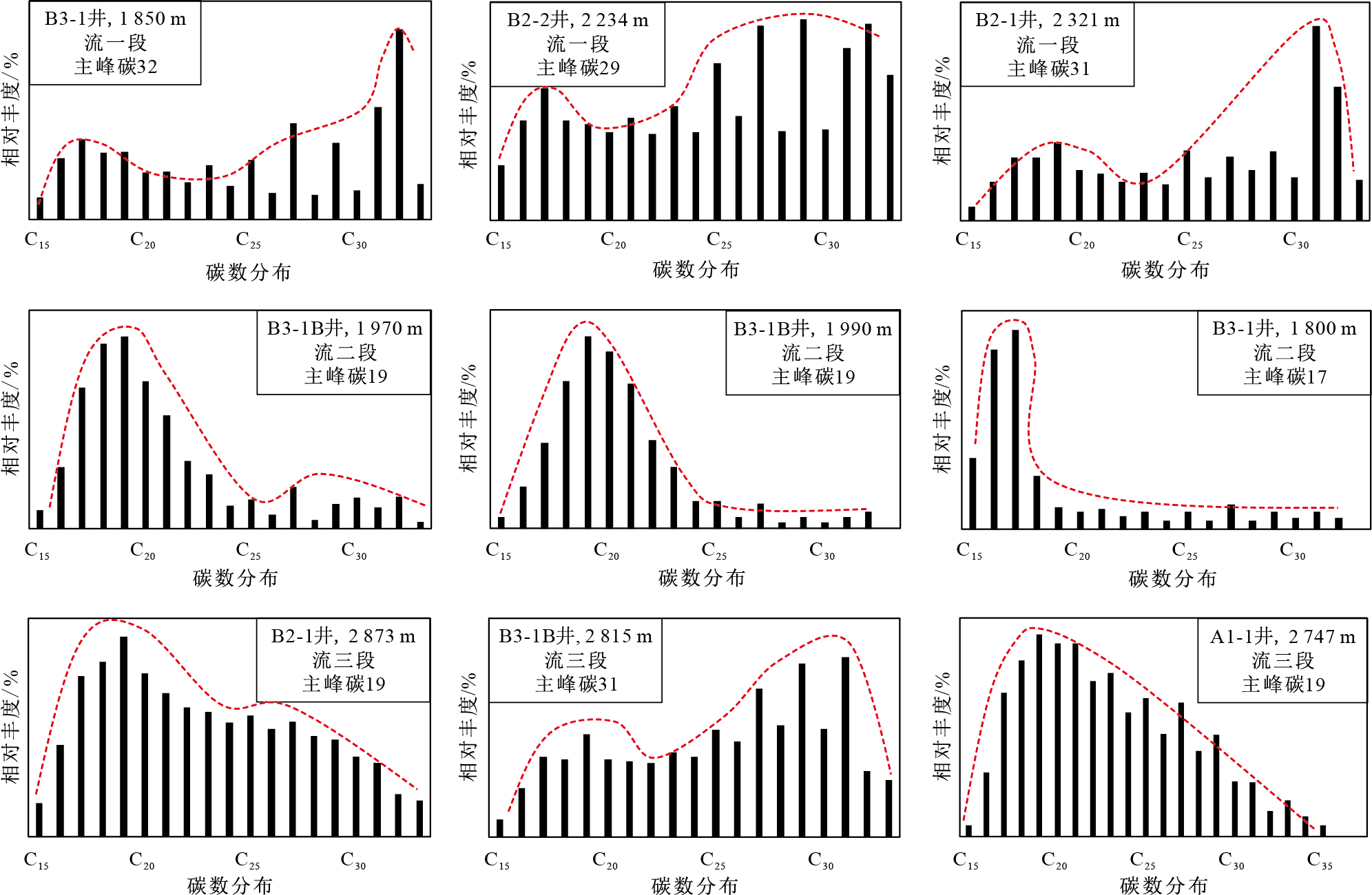
表 1 涠西南凹陷流沙港组烃源岩主峰碳、姥鲛烷/植烷、CPI、w(TOC)统计
Table 1. Statistics of the main peak carbon, pristane/phytane, CPI、w(TOC) of the Liushagang Formation source rock in Weixinan Sag
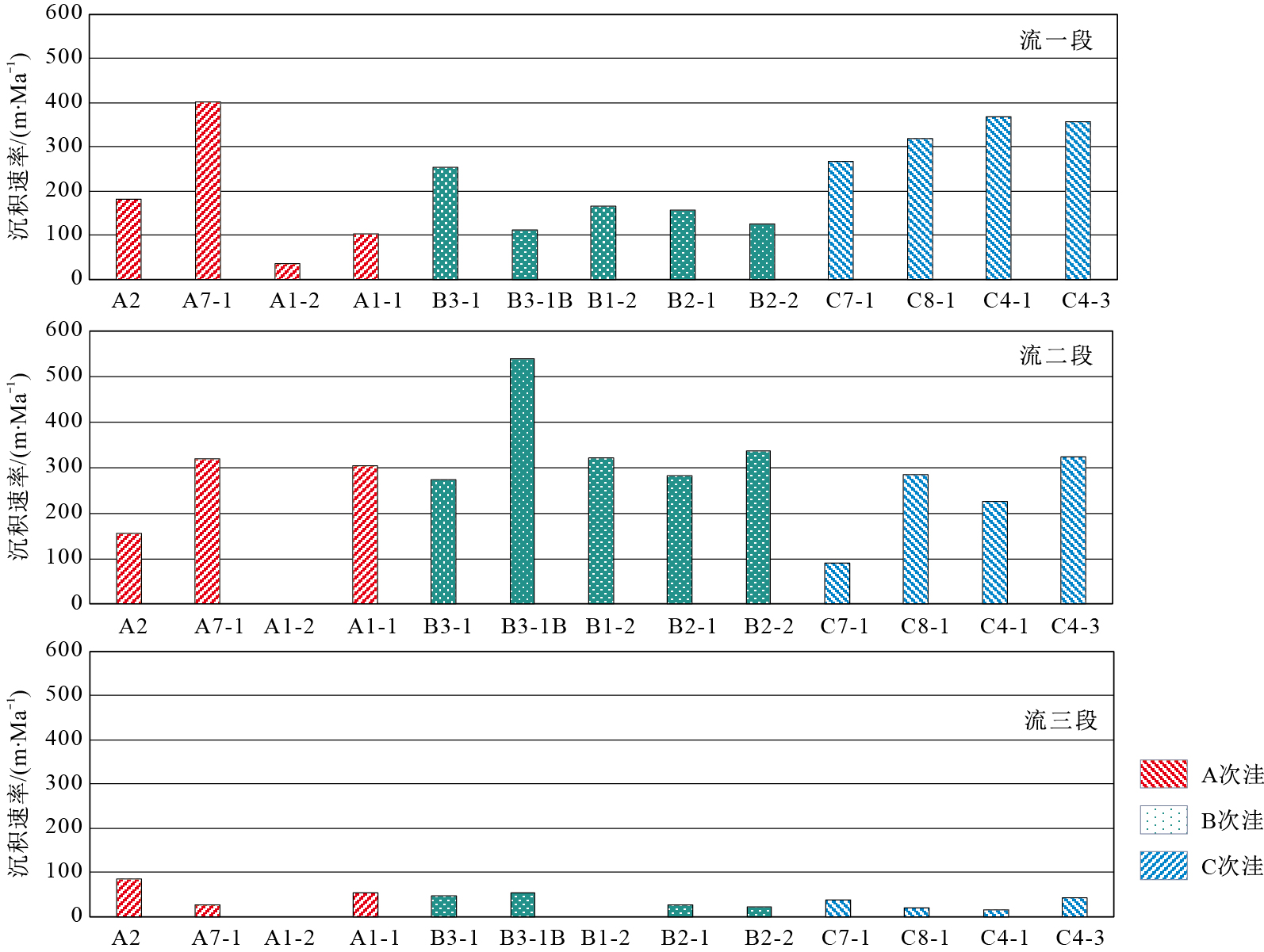
烃源岩层段 主峰碳 姥鲛烷/植烷 CPI/% w(TOC)/% 流一段 C29~C32 区间值 2.47~3.2 0.92~2.34 1.13~2.84 平均值 2.86 1.48 2.07 流二段 C17~C 19 区间值 1.18~2.41 0.97~3.27 1.81~3.28 平均值 1.98 1.67 3.06 流三段 C19~C 31 区间值 2.08~3.54 0.99~3.63 1.00~2.55 平均值 2.9 1.41 1.95 表 2 涠西南凹陷流沙港组湖泊古生产力、有机质埋藏效率、有机碳埋藏生产力计算参数、计算结果一览
Table 2. Calculation parameters and results of the lake paleo-productivity, organic matter burial efficiency and organic carbon burial productivity of the Liushagang Formation in Weixinan Sag
井位 洼
陷层
段沉积速率/
(m·Ma-1)w(TOC)/
%孔隙度φ/
%沉积物密度ρ/
(g·cm-3)湖泊古生产力/
(g·m-2·
a-1)湖泊古生产
力平均值/
(g·m-2·
a-1)有机质
埋藏
效率/%有机质埋
藏效率平均值/
%有机碳埋藏
生产力/
(g·m-2·
a-1)有机碳埋
藏生产力
平均值/
(g·m-2·
a-1)A7-1 A
次
洼流一
段82.70 1.79 0.11 2.47 785 944 17.78 15.64 140 147 A1-2 35.56 2.34 0.18 2.43 995 9.21 92 A1-1 102.34 2.69 0.15 2.35 1 053 19.94 210 A2 流二
段154.84 2.60 0.12 2.47 1 069 927 24.15 24.61 258 220 A7-1 90.40 2.30 0.09 2.51 1 040 18.68 194 A1-1 303.46 1.80 0.12 2.37 673 30.99 208 A2 流三
段86.13 2.32 0.11 2.49 1 023 890 18.19 15.89 186 144 A1-1 54.71 1.71 0.10 2.38 756 13.58 103 B3-1B B
次
洼流
一
段113.05 3.13 0.16 2.43 1 242 761 20.96 23.00 260 173 B1-2 165.00 2.45 0.10 2.52 1 045 24.80 259 B2-1 156.78 0.73 0.13 2.46 297 24.28 72 B2-2 125.10 1.14 0.14 2.44 461 21.98 101 B3-1 流
二
段273.16 3.39 0.18 2.47 1 240 1 070 29.92 32.11 371 346 B3-1B 539.47 3.41 0.11 2.47 1 279 36.83 471 B1-2 320.00 2.41 0.08 2.47 975 31.53 308 B2-1 282.00 1.67 0.11 2.51 673 30.24 2.30 B2-2 335.73 2.98 0.11 2.51 1 183 32.01 379 B3-1 流
三
段46.97 2.23 0.15 2.49 987 1 056 12.03 7.59 119 80 B2-1 27.71 2.45 0.10 2.54 1 220 6.67 81 B2-2 21.47 1.9 0.11 2.55 962 4.08 39 C7-1 C
次
洼流
一
段266.94 2.52 0.15 2.34 908 792 29.68 31.70 269 249 C8-1 319.09 2.73 0.14 2.43 1 018 31.50 320 C4-1 368.97 1.69 0.14 2.43 623 32.97 205 C4-3 357.14 1.65 0.14 2.47 620 32.64 202 C8-1 流
二
段282.95 3.12 0.12 2.47 1 220 1 022 30.28 29.93 369 308 C4-1 224.43 1.94 0.12 2.47 773 27.92 216 C4-3 322.06 2.7 0.11 2.50 1 0.10 31.59 338 C7-1 流
三
段38.52 1.34 0.12 2.48 619 762 10.02 6.42 62 34 C8-1 20.41 2.63 0.11 2.49 1 306 3.57 47 C4-1 16.10 1.96 0.12 2.49 982 1.16 11 C4-3 42.22 0.30 0.10 2.51 143 10.95 16 -
[1] 叶加仁, 任建业, 吴景富, 等.中国近海富烃凹陷特征及评价[M].北京:科学出版社, 2016:1-361. [2] 卢双舫, 张敏.油气有机地球化学[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2008:1-273. [3] Margarita A G, Rafael T.Trace metals and organic geochemistry of the Machiques Member (Aptian-Albian) and La Luna Formation (Cenomanian-Campanian), Venezuela[J].Chemical Geology, 1999, 160(1/2):19-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6b4657a898c89be435b85d28b75f59da [4] 黎彤, 饒紀龙.论化学元素在地壳及其基本构造单元中的丰度[J].地质学报, 1965, 45(1):82-92. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE196501006.htm [5] 田正隆, 陈绍勇, 龙爱民.以Ba为指标反演海洋古生产力的研究进展[J].热带海洋学报, 2004, 23(3):78-86. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2004.03.012 [6] Catherine H S W.A review of apatites, iron and manganese minerals and their roles as indicators of biological activity in black shales[J].Precambrian Research, 1993, 38(20):209-229. doi: 10.1016-0301-9268(93)90114-H/ [7] 薛罗.恩平凹陷古近系烃源岩元素地球化学综合评价[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2013. [8] Strakhov N M.The types of iron in sediments of the Black sea[J].Doklady Akademii Nauk Ssr, 1958, 118(4):803-806. [9] 殷鸿福, 谢树成, 秦建中, 等.对地球生物学、生物地质学和地球生物相的一些探讨[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2008, 38(12):1473-1480. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd200812001 [10] 沈俊, 施张燕, 冯庆来.古海洋生产力地球化学指标的研究[J].地质科技情报, 2011, 30(2):69-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.02.012 [11] 王杰.华北北部中上元古界可能烃源岩地球化学特征及生烃潜力[D].兰州: 中国科学院研究生院(兰州地质研究所), 2002. [12] 曹婷婷, 徐思煌, 王约, 等.四川盆地南江杨坝地区下寒武统烃源岩形成的地球生物学条件[J].石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(1):11-16. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201101002 [13] 刘喜停, 颜佳新, 薛武强, 等.华南中二叠统栖霞组海相烃源岩形成的地球生物学过程[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(6):1185-1192. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201406010 [14] Wenhao Li, Zhihuan Zhang.Paleoenvironment and its control of the formation of Oligocene marine source rocks in the deep-water area of the Northern South China Sea[J].Energy & Fuels, 2017, 44(6):10598-10611. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=338a30a1c81365416408fe4406e675a8 [15] Nicholas B H, Katherine H.The character and origin of lacustrine source rocks in the Lower Cretaceous synrift section, Congo Basin, west Africa[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2004, 88(8):1163-1184. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=35e77dd3c9bb9b3b664d1c135f965e43 [16] 范蕊, 李水福, 何生, 等.涠西南凹陷烃源岩地球化学特征及油源对比[J].石油实验地质, 2014, 36(2):238-244. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/sysydz201402019 [17] 孔杰.涠西南凹陷烃源岩有机碳含量测井预测模型优选及应用[J].石化技术, 2018(5):182-184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2018.05.133 [18] 徐新德, 曾少军.基于地化-测井-地震联合反演的研究方法及其应用:以涠西南凹陷为例[J].中国海上油气, 2013, 25(3):13-18. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZHSD201303004.htm [19] 游君君, 徐新德, 李里, 等.涠西南凹陷流沙港组二段烃源岩有机相研究[J].中国矿业, 2012, 21(11):87-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4051.2012.11.022 [20] 杨鹏程, 余学兵, 张传运.涠西南凹陷D次凹流二段优质烃源岩特征[J].海洋石油, 2017, 37(1):1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2017.01.001 [21] 卢林, 汪企浩, 黄建军.北部湾盆地涠西南和海中凹陷新生代局部构造演化史[J].海洋石油, 2007, 27(1):25-29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2007.01.005 [22] 张佰涛, 唐金炎, 王文军, 等.北部湾盆地北部拗陷构造-沉积特征及演化[J].海洋石油, 2014, 34(2):7-12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2336.2014.02.007 [23] 姜平, 张建光, 姚光庆, 等.涠西南凹陷11-7区块流沙港组沉积体系构成及演化特征[J].地质科技情报, 2013, 32(2):97-104. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201302014 [24] 陈亮, 甘华军, 祝春荣, 等.北部湾盆地涠西南凹陷沉降史研究[J].新疆石油学院学报, 2002, 14(4):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2677.2002.04.004 [25] 张强, 吴智平, 颜世永, 等.北部湾盆地北部坳陷古近系构造发育特征及其对沉积的控制作用[J].高校地质学报, 2018, 24(6):787-799. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/gxdzxb201806001 [26] Filippidis A, Geograkopoulos A, Kassoli-Foumaraki A, et al.Trace elements in composited samples of three lignite seams from the central Drama lignite deposit Macedonia, Greece[J].International Journal of Coal Geology, 1996, 29(4):219-234. doi: 10.1016/0166-5162(95)00032-1 [27] Ruud M.Trace element behavior in coal-fired power plants[J].Fuel Processing Technology, 1994, 39(1/3):199-217. doi: 10.1016-0378-3820(94)90180-5/ [28] 杨桂芳, 武法东, 陈正洪, 等.内蒙古磴口河湖相沉积物正构烷烃分布特征及其环境意义[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(2):327-333. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201502013 [29] 唐领余, 毛礼米, 吕新苗, 等.第四纪沉积物中重要蕨类孢子和微体藻类的古生态环境指示意义[J].科学通报, 2013, 58(20):1969-1983. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201320011 [30] 刘士磊, 王启飞, 龚莹杰, 等.渤海海域古近纪微体化石组合特征及油气勘探意义[J].地层学杂志, 2012, 36(4):700-709. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DCXZ201204004.htm [31] 张玉兰, 王开发, 张盛隆.某些海生藻类在陆架沉积中的分布及其古环境意义[J].同济大学学报:自然科学版, 1994, 22(3):340-345. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=QK199400726338 [32] 田景春, 张翔.沉积地球化学[M].北京:地质出版社, 2016. [33] Muller P J, Suess E.Productivity, sedimentation rate and sedimentary organic matter in the oceans.I:Organic carbon preservation[J].Deep Sea Research, 1979, 26(12):1347-1362. doi: 10.1016/0198-0149(79)90003-7 [34] 李守军, 郑德顺, 耿福兰.定量再造湖泊古生产力的尝试[J].高校地质学报, 2002, 8(2):215-219. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2002.02.011 [35] Kelts K.Environments of deposition of lacustrine petroleum source rocks: an introduction[C]//Fleet A J, Kelts K, Talbot M R.Lacustrine petroleum source rocks.Oxford: Geological Society Paper, 1988: 3-26. [36] Harvey H R, Tuttle J H, Bell J T.Kinetics of phytoplankton decay during simulated sedimentation:Changes in biochemical composition and microbial activity under oxic and anoxic conditions[J].Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1995, 59(16):3367-3377. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(95)00217-N [37] Schuhe S, Mangelsdorf K, Rullkoetter J.Organic matter preservation on the Pakistan continental margin as revealed by biomarker geochemistry[J].Organic Geochemistry, 2000, 31(10):1005-1022 doi: 10.1016/S0146-6380(00)00108-X [38] Sebastian S, Edith D K, Roland Z, et al.Organic carbon burial efficiency in lake sediments controlled by oxygen exposure time and sediment source[J].Limnology Oceanography, 2009, 54(6):2243-2254. doi: 10.4319/lo.2009.54.6.2243 [39] 李国山, 王永标.古近纪湖相烃源岩形成的地球生物学过程[J].中国科学:地球科学, 2014, 44(6):1206-1217. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkx-cd201406012 -






 下载:
下载: