A comparative study of shale gas preservation conditions on both sides of Tianyangping fault in Yichang area
-
摘要: 中扬子宜昌地区在天阳坪断裂两侧实施了数口页岩气调查井和参数井,总体上,断裂两侧页岩的含气性差别较大。从页岩构造变形、裂缝发育特征、古流体活动等方面研究了保存条件差异的原因。结果表明:①因黄陵隆起的砥柱作用,天阳坪断裂以北的宜昌斜坡带为一简单的单斜构造,产状平缓,天阳坪断裂以南属于宜都-鹤峰复背斜的北端,断裂、褶皱构造发育,地层产状变化大;②典型井揭示天阳坪断裂以北地区页岩构造裂缝不发育,天阳坪断裂以南页岩构造裂缝非常发育并见多个破碎带,是页岩气逸散的主要通道;③古流体分析揭示天阳坪断裂以北页岩早期封闭体系的裂缝较发育,晚期裂缝不发育,天阳坪断裂以南地区晚期裂缝发育,古大气水下渗深度超过3 500~4 000 m,页岩的封闭性破坏严重;④综合研究表明,宜昌周边的页岩气勘探应围绕宜昌斜坡带向东西两侧巴东-大冶对冲干涉带拓展,天阳坪断裂以南的宜都-鹤峰复背斜北端构造变形最强、保存条件差,勘探风险较大。Abstract: The shale gas content is different in different shale gas survey wells and parameter wells, from both sides of Tianyangping fault in Yichang, Middle Yangtze area. The reasons for the difference of preservation conditions are studied from the aspects of shale tectonic deformation, fracture character and paleo-fluid activity. The following results were obtained: ①Because of the pillar effect of Huangling uplift, the Yichang slope is a simple monoclinic structure with gentle occurrence in the north of Tianyangping fault, and on the other hand, faults and folds are well developed and the occurrence of strata varies greatly of northern part of Yidu-Hefeng anticline in the south of Tianyangping fault. ②Typical wells illustrate that fractures and fracture belts of shale are highly developed in the north of Tianyangping fault, and are the channels for shale gas to escape in the north of Tianyangping fault, while fractures are rare in the south of Tianyangping fault. ③Paleo-fluid reveals that more fractures in the early stage of closed system of shale and fewer in the later stage in the north of Tianyangping fault, while more fractures in the later stage lead to the infiltration depth of ancient meteoric water, over 3 500-4 000 m in the south of Tianyangping fault, and the sealing capacity of the shale get worse. ④The conclusion is that exploration should spread to the Badong-Daye ramp interference fringe, in the east and west of Yichang slope; and there are more exploration risks to spread to the south of Tianyangping fault because of the strong tectonic deformation, and worst protection condition in the north end of Yidu-Hefeng anticlinorium.
-
Key words:
- Tianyangping fault /
- fracture /
- shale gas /
- preservation condition /
- Yichang area
-
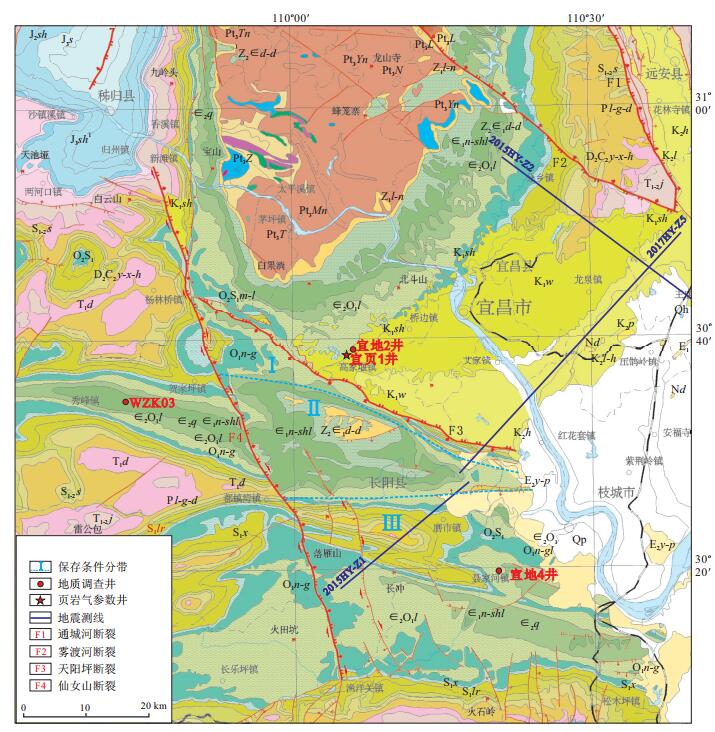
图 1 研究区位置及采样钻井、地震剖面分布图
第四系:Qh.全新统;Qhal.全新统冲积物;Qp.更新统;Nd.新近系掇刀石组;古近系:E2y-p.洋溪组-牌楼口组; E2q.龚家冲组;白垩系:K2p.跑马岗组; K2h.红花套组;K2l.罗镜滩组; K1w.五龙组;K1sh.石门组;侏罗系:J3s.沙镇溪组; J2sh.沙溪庙组;三叠系:T1-2j.嘉陵江祖;T1d.大冶组;二叠系:Pl-g-d.梁山组-孤峰组-大隆组; 泥盆系-石炭系:D2C2y-x-h.云台观组-写经寺组-黄龙组;志留系:S1-2s.纱帽组;S1lr.罗惹坪组;S1x.新滩组;O2S1.中奥陶统-下志留统; O2S1m-l.庙坡组-龙马溪组;O1n-g.下奥陶统南津关组-牯牛潭组;寒武系:∈2O1l.娄山关组;∈2q.覃家庙组;∈1n-shl.牛蹄塘组-石龙洞组;震旦系:Z2∈1d-d.陡山沱组-灯影组;Z1l-n.莲沱组-南沱组;岩浆岩:Pt3Z.总溪仿单元; Pt3T.中坝单元; Pt3Mn.庙湾岩单元; Pt3Yn.鹰子嘴单元; Pt3L.路溪坪单元; Pt3Tn.田家坪单元; Pt3N.内口单元
Figure 1. Location of the study area and sampling wells, seismic sections
表 1 天阳坪断裂两侧页岩气保存条件对比表
Table 1. Comparison of shale gas preservation conditions on both sides of Tianyangping fault
保存条件影响因素 天阳坪断裂以北 天阳坪断裂以南 类别 项目 特点 保存意义 特点 保存意义 构造变形 构造样式 宽缓的单斜,断裂不发育 页岩气逸散弱,保存条件有利 褶皱变形发育、NNW和NEE、NWW断裂发育 页岩气横向散失、垂向散失强,保存不利 变形机制 与黄陵隆起垂向隆升相关 宜昌斜坡具有整体性,保存条件好 黄陵砥柱、NW向推覆共同作用 强变形、碎块化,页岩气强散失 裂缝发育 裂缝类型及密度 发育各种类型裂缝,密度低 页岩气逸散通道相对不发育 发育各种类型裂缝、破碎带,密度大 页岩气逸散通道密集发育 裂缝宽度 宽度小,一般1~5 mm,最宽50 mm 页岩气逸散速度较慢 宽度大,大量大于10 cm,最宽可达50 cm以上 可能导致页岩气急剧逸散 充填物发育 半充填-未充填裂缝不发育 晚期逸散通道不发育,有利于保存 半充填-未充填裂缝、破碎带发育 页岩气持续散失的通道发育,保存不利 古流体活动 包裹体类型 烃类包裹体、高密度甲烷包裹体为主 含气饱和度高,封闭性好 以气液两相包裹体、纯水溶液包裹体为主 高含水饱和度,气藏已破坏 包裹体气相组分 以甲烷为主 来自封闭的页岩气层流体 氮气、甲烷 有大气介入的开放体系 包裹体盐度 高盐度 来自封闭的地层流体 部分低盐度 来自开放体系,淡水渗入 包裹体形成时间 形成较早,以近最大埋深阶段为主 形成于早期封闭体系,后期破坏弱 以浅埋藏阶段为主 形成晚,易形成开放体系 -
[1] Hu Dongfeng, Zhang Hanrong, Ni Kai, et al.Preservation conditions for marine shale gas at the southeastern margin of the Sichuan Basin and their controlling factors[J].Natural Gas Industry B, 2014(1):178-184. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Doaj000004076706 [2] Hao Fang, Zou Huayao, Lu Yongchao.Mechanisms of shale gas storage:Implications for shale gas exploration in China[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(8):1325-1346. doi: 10.1306/02141312091 [3] Zou Caineng, Dong Dazhong, Wang Yuman, et al.Shale gas in China:Characteristics, challenges and prospects (I)[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2015, 42(6):753-767. doi: 10.1016/S1876-3804(15)30072-0 [4] 王濡岳, 丁文龙, 龚大建, 等.黔北地区海相页岩气保存条件:以贵州岑巩区块下寒武统牛蹄塘组为例[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(1):45-55. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/syytrqdz201601007 [5] 雷子慧, 赵安坤, 余谦, 等.贵州北部安场向斜下志留统龙马溪组页岩气保存条件[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(4):121-127. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201604018 [6] 苗凤彬, 谭慧, 王强, 等.湘中涟源凹陷石炭系测水组页岩气保存条件[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(6):90-97. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201606013 [7] 魏肖, 金爱民, 朱蓉, 等.黔南黄平凹陷及周缘古流体特征及其对油气保存的指示[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3):67-74. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201803009 [8] 吴忠锐, 何生, 何希鹏.涟源凹陷上二叠统大隆组泥页岩裂缝方解石脉体流体包裹体特征及其启示[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):70-81. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201904009 [9] 陈孝红, 危凯, 张保民, 等.湖北宜昌寒武系水井沱组页岩气藏主控地质因素和富集模式[J].中国地质, 2018, 45(2):207-226. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgdizhi201802001 [10] 陈孝红, 张保民, 陈林, 等.鄂西宜昌地区晚奥陶世-早志留世页岩气藏的主控地质因素与富集模式[J].地球学报, 2018, 39(3):257-268. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DQXB201803001.htm [11] 魏祥峰, 李宇平, 魏志红, 等.保存条件对四川盆地及周缘海相页岩气富集高产的影响机制[J].石油实验地质, 2017, 39(2):147-153. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201702002 [12] 付宜兴, 张萍, 李志祥, 等.中扬子区构造特征及勘探方向建议[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31(3):308-314. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200703006 [13] 余川, 曾春林, 周洵, 等.大巴山冲断带下寒武统页岩气构造保存单元划分及分区评价[J].天然气地球科学, 2018, 29(6):853-865. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201806011 [14] 汤济广, 李豫, 汪凯明, 等.四川盆地东南地区龙马溪组页岩气有效保存区综合评价[J].天然气工业, 2015, 35(5):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy201505003 [15] Zhang Kun, Song Yan, Jiang Shu et al.Shale gas accumulation mechanism in a syncline setting based on multiplegeological factors:An example of southern Sichuan and the Xiuwu Basin in the Yangtze Region[J].Fuel, 2019a, 241:468-476. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2018.12.060 [16] 丁道桂, 刘光祥.扬子板内递进变形:南方构造问题之二[J].石油实验地质, 2007, 2(3):238-247. http://www.cqvip.com/qk/95265X/200703/24883089.html [17] 梅廉夫, 刘昭茜, 汤济广, 等.湘鄂西-川东中生代陆内递进扩展变形:来自裂变径迹和平衡剖面的证据[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2010, 35(2):161-174. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201002001 [18] Shen Chuanbo, Mei Lianfu, Peng Lei, et al.LA-ICPMS U-Pb zircon age constraints on the provenance of Cretaceous sediments in the Yichang area of the Jianghan Basin, central China[J].Cretacous Research, 2012, 34:172-183. doi: 10.1016/j.cretres.2011.10.016 [19] Ji Wenbin, Lin Wei, Michel F, et al.Origin and tectonic significance of the Huangling massif within the Yangtze craton, South China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 86(2):59-75. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1a86a3b8aa5e94eade10ac54ae45a007 [20] Ge Xiang, Shen Chuanbo, Zhao Yang.Low-temperature thermochronology constraints on the Mesozoic-Cenozoic exhumation of the Huangling Massif in the Middle Yangtze block, Central China[J].Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 24(4):541-552. doi: 10.1007/s12583-013-0348-8 [21] 王平, 刘少峰, 王凯, 等.鄂西弧形构造变形特征及成因机制[J].地质科学, 2012, 47(1):22-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkx201201003 [22] Curtis J B.Fractured shale-gas systems[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2002, 86(11):1921-1938. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a0a945b1e9be609ea86247395927ba7a [23] Jenkins C, Ouenes A, Zellou A, et al.Quantifying and predicting naturally fractured reservoir behavior with continuous fracture models[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2009, 93(11):1597-1608. doi: 10.1306/07130909016 [24] 聂海宽, 包书景, 高波.四川盆地及其周缘下古生界页岩气保存条件研究[J].地学前缘, 2012, 19(3):280-294. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201203030 [25] 曾维特, 丁文龙, 张金川, 等.渝东南-黔北地区下寒武统牛蹄塘组页岩裂缝有效性研究[J].地学前缘, 2016, 23(1):96-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dxqy201601009 [26] Zhang Yuying, He Zhiliang, Jiang Shu, et al.Fracture types in the Lower Cambrian shale and their effect on shale gas accumulation, Upper Yangtze[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019b, 99:282-291. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2018.10.030 [27] Boles J, Eichhubl P, Garven G, et al.Evolution of a hydrocarbon migration pathway along basin-bounding faults:evidence from fault cement[J].AAPG Bulltin, 2004, 88(7):947-970. doi: 10.1306/02090403040 [28] 马永生, 楼章华, 郭彤楼, 等.中国南方海相地层油气保存条件综合评价技术体系探讨[J].地质学报, 2006, 80(3):406-417. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dizhixb200603013 [29] 楼章华, 马永生, 郭彤楼, 等.中国南方海相地层油气保存条件评价[J].天然气工业, 2006, 26(8):8-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqgy200608003 [30] 刘安, 欧文佳, 黄惠兰, 等.湘鄂西地区奥陶系-志留系滑脱带古流体特征及页岩气保存意义[J].天然气工业, 2018, 38(5):34-43. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-TRQG201805006.htm [31] 刘德汉, 戴金星, 肖贤明, 等.普光气田中高密度甲烷包裹体的发现及形成的温度和压力条件[J].科学通报, 2010, 5(4/5):359-366. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=kxtb201004008 [32] 席斌斌, 腾格尔, 俞凌杰.川东南页岩气储层脉体中包裹体古压力特征及其地质意义[J].石油实验地质, 2016, 38(4):473-479. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201604009 [33] Gao Jian, Zhang Jiankun, He Sheng, et al.Overpressure generation and evolution in Lower Paleozoic gas shales of the Jiaoshiba region, China:Implications for shale gas accumulation[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2019, 102:844-859. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2019.01.032 [34] 焦伟伟, 汪生秀, 程礼军, 等.渝东南地区下寒武统页岩气高氮低烃成因[J].天然气地球科学, 2017, 28(12):1882-1890. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=trqdqkx201712011 [35] Liu Yang, Zhang Jinchuan, Ren Jun, et al.Stable isotope geochemistry of the nitrogen-rich gas from lower Cambrian shale in the Yangtze Gorges area, South China[J].Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77:693-7032. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.07.020 [36] 何钦, 张扬.鄂西地区南庄坪重晶石矿地质特征及成矿模式[J].资源环境与工程, 2018, 32(4):528-532. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hbdk201804004 -





 下载:
下载: