Landslide susceptibility evaluation of Sinan County using logistics regression model and 3S technology
-
摘要:
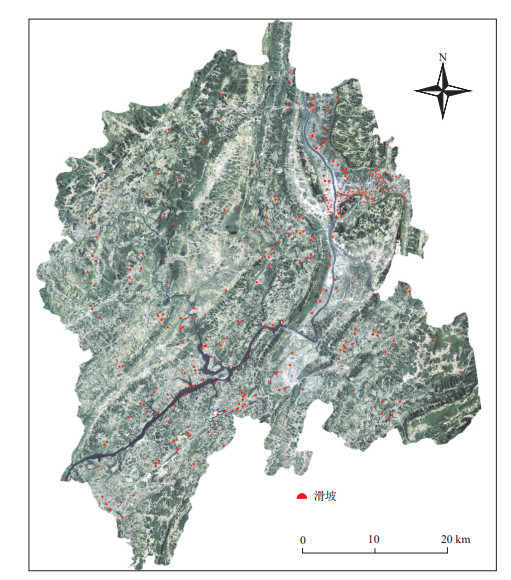
区域滑坡易发性评价对滑坡灾害防治具有重要意义,贵州省思南县由于其特殊的自然地理和地质条件,受滑坡地质灾害的影响非常严重,因此,非常有必要对思南县的滑坡易发性进行评价。在滑坡编录的基础上,采用由RS、GIS和GPS组成的3S技术,获取了思南县的数字高程模型、坡度、坡向、剖面曲率、坡长、岩土类型、地表湿度指数、距离水系的距离、植被覆盖度和地表建筑物指数10个滑坡影响因子;再在频率比和相关性分析的基础上,利用逻辑回归模型对思南县的滑坡易发性进行了评价并绘制了易发性分布图。结果表明:利用逻辑回归模型预测思南县滑坡易发性的准确率(AUC值)达到0.797,较为准确地预测出了思南县滑坡分布规律;极高和高滑坡易发区主要分布在高程低于600 m、地表坡度较大且以软质岩类为主的区域;而极低和低滑坡易发区主要分布在高程较高、地表坡度较小且以硬质岩类为主的区域。
Abstract:The Sinan County of Guizhou Province, due to the specific and complex physical geography and geological conditions, is seriously affected by the landslide hazards. Hence, it is very necessary to conduct regional landslide susceptibility evaluation for landslide prediction and prevention in the area. This study uses 3S technology:remote sensing (RS), globe position system (GPS) and geographic information system (GIS), to evaluate landslide susceptibility based on the logistic regression (LR) model. The 3S technology is applied to obtain the landslide inventory, condition factors of landslides and other related basic data in Sinan County. About 308 landslides and ten affecting factors are acquired digital elevation model (DEM), slope, aspect, profile curvature, rock types, buffer of fracture lines, modified normalized difference water index (MNDWI), distance to river, normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) and normalized difference building index (NDBI), using the 3S technology. Then based on the correlation analysis, LR model is used to calculate the landslide susceptibility indexes and map these indexes. Results show that, the area under the curve (AUC) of receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) is 0.797 using LR model. The landslide distribution characteristics of Sinan County are accurately predicted by the LR model. In addition, the high and very high susceptible areas are mainly distributed in the areas where the DEM are higher than 600 m. In these areas, the slope are relatively great and the rocks are soft. The low and very low susceptible areas are mainly distributed in the areas where the DEM are high, the slopes are relatively low and the rocks are of hard rock class.
-
表 1 滑坡易发性评价的影响因子分级体系
Table 1. Classification system of basic influencing factors of landslides in Sinan County
因子类别 影响因子 因子分级 地形地貌 高程/m < 476;476~ < 568;568~ < 648;648~ < 729;729~ < 815;815~ < 911;911~1 021;>1 021 坡度/(°) < 6.11;6.11~ < 10.88;10.88~ < 15.40;15.40~ < 19.91;19.91~ < 24.95;24.95~ < 31.06;31.06~39.29;>39.29 坡向 平坡;正北;东北;正东;东南;正南;西南;正西;西北 剖面曲率 < 2.2;2.2~ < 4.2;4.2~ < 6.4;6.4~ < 8.7;8.7~ < 11.5;11.5~ < 14.9;14.9~19.9;>19.9 坡长/m < 1.3;1.3~ < 2.7;2.7~ < 4.0;4.0~ < 5.5;5.5~ < 7.2;7.2~ < 9.4;9.4~ < 12.1;>12.1 工程地质 岩土类型 软质岩类;硬质岩类;软硬相间岩类;松散岩类 水文环境 MNDWI < 39;39~ < 61;61~ < 83;83~ < 106;106~ < 132;132~ < 163;163~215;>215 距离水系的距离/m < 300;300~ < 600;600~900;>900 m 地表覆盖因子 NDVI < 38;38~ < 93;93~ < 128;128~ < 154;154~ < 176;176~ < 199;199~224;>224 NDBI < 44;44~ < 73;73~ < 100;100~ < 126;126~ < 154;154~ < 183;183~218;>218 表 2 逻辑回归方程中的相关变量
Table 2. Relative variables of the logistic regression model
变量 影响因子 系数值 S.E. Wals df Sig. X1, j 高程 1.508 0.026 3 344.073 1 0.000 X2, j 坡度 1.500 0.032 2 164.334 1 0.000 X3, j 坡向 -0.109 0.138 22.627 1 0.041 X4, j 剖面曲率 1.717 0.093 340.572 1 0.000 X5, j 坡长 0.655 0.037 317.869 1 0.000 X6, j 岩土类型 0.998 0.015 4 298.464 1 0.000 X7, j MNDWI 0.784 0.093 71.343 1 0.000 X8, j 距离水系的距离 2.714 0.081 1 124.072 1 0.000 X9, j NDBI 0.225 0.088 49.622 1 0.000 X10, j NDVI 0.622 0.038 34.364 1 0.000 C 常量 -11.450 0.241 2 263.122 1 0.000 注:S.E.标准误差;Wals.检验因子;df.自由度;Sig.显著性检验 -
[1] Wang Yang, Liu Jizhixian, Yan Shuangjie, et al.Estimation of probability distribution of shear strength of slip zone soils in Middle Jurassic red beds in Wanzhou of China[J].Landslides, 2017, 14(6):2165-2174. doi: 10.1007/s10346-017-0890-z [2] Jiang S H, Huang J, Huang F, et al.Modelling of spatial variability of soil undrained shear strength by conditional random fields for slope reliability analysis[J].Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2018, 63:374-389. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2018.06.030 [3] 刘磊, 殷坤龙, 王佳佳, 等.降雨影响下的区域滑坡危险性动态评价研究:以三峡库区万州主城区为例[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(3):558-569. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSLX201603013.htm [4] 王芳, 殷坤龙, 桂蕾, 等.不同日降雨工况下万州区滑坡灾害危险性分析[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(1):190-195, 203. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201801026 [5] 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 何涛, 等.库岸滑坡地下水位时间序列混沌特征识别与PSO-LSSVM模型预测[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(6):186-192. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201506027 [6] Huang F M, Yin K L, Huang J S, et al.Landslide susceptibility mapping based on self-organizing-map network and extreme learning machine[J].Engineering Geology, 2017, 223:11-22. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.04.013 [7] Huang F M, Yao C, Liu W P, et al.Landslide susceptibility assessment in the Nantian area of China: A comparison of frequency ratio model and support vector machine[J].Geomatics, Natural Hazards and Risk, 2018, 9(1):919-938. doi: 10.1080/19475705.2018.1482963 [8] Chang Z L, Du Z, Zhang F, et al.Landslide susceptibility prediction based on remote sensing images and GIS:Comparisons of supervised and unsupervised machine learning models[J].Remote Sensing, 2020, 12(3):502. doi: 10.3390/rs12030502 [9] Huang F M, Chen L X, Yin K L, et al.Object-oriented change detection and damage assessment using high-resolution remote sensing images, Tangjiao Landslide, Three Gorges Reservoir, China[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2018, 77(5):183. doi: 10.1007/s12665-018-7334-5 [10] Li Y Y, Huang J S, Jiang S H, et al.A web-based GPS system for displacement monitoring and failure mechanism analysis of reservoir landslide[J].Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1):17171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-17507-7 [11] Huang F M, Wu P, Ziggah Y Y.GPS monitoring landslide deformation signal processing using time-series model[J].International Journal of Signal Processing, Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, 2016, 9(3):321-332. doi: 10.14257/ijsip.2016.9.3.28 [12] 肖鹏, 李安龙.基于GIS的黄河水下三角洲海底滑坡稳定性预测[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(3):221-226. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/201603/669167100.html [13] 管全中, 董大忠, 王玉满, 等.层次分析法在四川盆地页岩气勘探区评价中的应用[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(5):91-97. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201505015.htm [14] 张俊, 殷坤龙, 王佳佳, 等.三峡库区万州区滑坡灾害易发性评价研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(2):284-296. [15] 郭天颂, 张菊清, 韩煜, 等.基于粒子群优化支持向量机的延长县滑坡易发性评价[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):236-243. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20193/7002215554.html [16] Aditian A, Kubota T, Shinohara Y.Comparison of GIS-based landslide susceptibility models using frequency ratio, logistic regression, and artificial neural network in a tertiary region of Ambon, Indonesia[J].Geomorphology, 2018, 318:101-111. doi: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.06.006 [17] Huang F M, Yin K L, Zhang G R, et al.Landslide displacement prediction using discrete wavelet transform and extreme learning machine based on chaos theory[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(20):1-18. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6133-0 [18] Zhou Chao, Yin Kunlong, Huan Faming.Application of the chaotic sequence WA-ELM coupling model in landslide displacement prediction[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(9):2674-2680. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94551X/201509/666084759.html [19] Huang F M, Zhang J, Zhou C B, et al.A deep learning algorithm using a fully connected sparse autoencoder neural network for landslide susceptibility prediction[J].Landslides, 2020, 17(1):217-229. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01274-9 [20] Li D Y, Huang F M, Yan L X, et al.Landslide susceptibility prediction using particle-swarm-optimized multilayer perceptron: Comparisons with multilayer-perceptron-only, BP Neural Network, and Information Value Models[J].Applied Sciences, 2019, 9(18):3664. doi: 10.3390/app9183664 [21] Biswajeet Pradhan.A comparative study on the predictive ability of the decision tree, support vector machine and neuro-fuzzy models in landslide susceptibility mapping using GIS[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2013, 51:350-365. [22] 杨永刚, 殷坤龙, 赵海燕, 等.基于C5.0决策树-快速聚类模型的万州区库岸段乡镇滑坡易发性区划[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):189-197. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201906023.htm [23] 王锐, 张泰丽.基于GIS和逻辑回归法的滑坡易发性评价[J].低温建筑技术, 2018, 40(6):95-97. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10335-1018244309.htm [24] 方教勇, 杨根云.基于GIS与逻辑回归的清平滑坡易发性评价[J].人民珠江, 2018, 39(4):66-70. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RMZJ201804015.htm [25] Akcay O.Landslide fissure inference assessment by ANFIS and logistic regression using UAS-based photogrammetry[J].ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 2015, 4(4):2131-2158. doi: 10.3390/ijgi4042131 [26] 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 蒋水华, 等.基于聚类分析和支持向量机的滑坡易发性评价[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2018, 37(1):156-167. doi: 10.13722/j.cnki.jrme.2017.0824 [27] Li Zhu, Huang L H, Fan L Y, et al.Landslide susceptibility prediction modeling based on remote sensing and a novel deep learning algorithm of a cascade-parallel recurrent neural network[J].Sensors, 2020, 20(6):1576. doi: 10.3390/s20061576 [28] Huang F M, Luo X Y, Liu W P.Stability analysis of hydrodynamic pressure landslides with different permeability coefficients affected by reservoir water level fluctuations and rainstorms[J].Water, 2017, 9(7):450. doi: 10.3390/w9070450 [29] 黄发明, 殷坤龙, 张桂荣, 等.基于相空间重构和小波分析-粒子群向量机的滑坡地下水位预测[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2015, 40(7):1254-1265. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqkx201507013 [30] Chen W, Wang J L, Xie X S, et al.Spatial prediction of landslide susceptibility using integrated frequency ratio with entropy and support vector machines by different kernel functions[J].Environmental Earth Sciences, 2016, 75(20):1344. doi: 10.1007/s12665-016-6162-8 -





 下载:
下载: