Effect of repeated infiltration on permeability characteristics of remolded loess
-
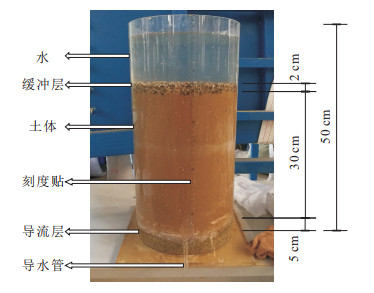
摘要: 甘肃黑方台黄土经历长期的灌溉入渗破坏了其原生结构,改变了不同深度黄土的颗粒级配,影响了土体的力学性质。为研究反复灌溉入渗对坡体的影响,通过室内土柱渗透试验研究了反复入渗对甘肃黑方台黄土渗透特性的影响,并研究了渗透作用下黄土中细颗粒运移的规律与模式。研究表明:①水力梯度对渗透速率影响较小而干密度对渗透速率影响较大;随着入渗次数的增加,重塑黄土的渗透性能变弱;②黄土在渗流力的作用下,存在细颗粒沿渗流方向运移的现象,且细颗粒在土柱中上部聚集最多;③影响细颗粒运移的因素有:水力梯度、干密度和渗透次数;其中细颗粒的运移量与水力梯度、渗透次数呈正相关,与干密度呈负相关,且水力梯度是影响细颗粒运移的主要因素;④在渗透过程中,细颗粒运移堆积,最终填充土体内孔隙,导致黄土的渗透性下降。Abstract: Long-term irrigation infiltration in Heifangtai, Gansu Province, destroys the original structure of loess, changes the particle gradation of loess at different depths, and affects the properties of the soil. In order to study the effect of repeated irrigation infiltration on slope, this paper studies the influence of repeated infiltration on the permeability of loess in Heifangtai, by indoor soil column penetration test, and the regularity and mode of fine particle migration in loess under osmosis. The following conclusions are reaches: ①The hydraulic gradient has little effect on the permeation rate and the dry density has a greater influence on the percolation rate. With the increase of the infiltration times, the permeability of the remolded loess becomes weaker. ②Under the action of seepage force, the loess shows the phenomenon of fine particles moving along the seepage direction, and the fine particles gather most in the upper part of the soil column. ③The factors affecting the migration of fine particles are: hydraulic gradient, dry density and penetration times; and the migration of fine particles is positively correlated with hydraulic gradient and penetration number, negatively correlated with dry density. The hydraulic gradient is the main factor affecting the migration of fine particles. ④During the infiltration process, the fine particles are continuously transported, and finally the pores in the soil are filled, and so the permeability of the loess is lowered.
-
Key words:
- loess /
- repeated infiltration /
- permeability characteristics /
- fine particle migration
-
表 1 试验参数
Table 1. Test parameters
条件 水头/cm 干密度/(g·cm-3) 渗透次数/次 不同水头 7 10 1.42 7 13 不同干密度 1.42 7 1.45 7 1.50 不同渗透次数 7 1.42 7 21 表 2 不同干密度对应的填土质量
Table 2. Filling quality corresponding to different dry densities
干密度ρ/ (g·cm-3) 体积V/cm3 含水率ω /% 公式 质量M/g 1.42 452.39 1.57 M=V·ρ· (1 +ω) 3 262.39 1.45 3 331.32 1.50 3 446.19 -
[1] 刘海娇, 鲁晓兵, 王淑云, 等.细颗粒运移对土体力学特性的影响[C]//中国地质学会, 中国地质学会工程地质专业委员会.2017年全国工程地质学术年会论文集.广西桂林: 《工程地质学报》编辑部, 2017: 5. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GCDZ201710001025.htm [2] 王永焱.中国黄土的结构特征及物理力学性质[M].北京:科技出版社, 1990. [3] 杜丽娜.多孔介质中土壤颗粒运移的试验研究[D].陕西杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10712-1014440319.htm [4] 仵彦卿.多孔介质污染物迁移动力学[M].上海:上海交通大学出版社, 2007. [5] Dikinya O, Hinz C, Aylmore G.Decrease in hydraulic conductivity and particle release associated with self-filtration in saturated soil columns[J].Geoderma, 2008, 146(1):192-200. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0016706108001365 [6] M.G.Hajra L N R L.Effects of ionic strength on fine particle clogging of soil filters[J].Journal of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2002, 128(8):631-639. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/245294184_Effects_of_Ionic_Strength_on_Fine_Particle_Clogging_of_Soil_Filters [7] 蒲春生, 张绍槐.非膨胀黏土的分散和运移[J].石油钻采工艺, 1992, 14(1):63-71. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=978603 [8] 王正波, 岳湘安, 韩冬.黏土矿物及流体对低渗透岩心渗流特性的影响[J].油气地质与采收率, 2007, 14(2):89-92. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/yqdzycsl200702024 [9] 刘杰.土石坝渗流控制理论基础及工程经验教训[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社, 2006. [10] Gavin K, Xue J.A simple method to analyze infiltration into unsaturated soil slopes[J].Computers & Geotechnics, 2008, 35(2):223-230. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-foreign_other_thesis/0204112175420.html [11] 彭淑君.晋中黄土湿陷特性研究[D].西安: 西北大学, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10697-1014242931.htm [12] 茹豪, 张建军, 李玉婷, 等.黄土高原土壤粒径分形特征及其对土壤侵蚀的影响[J].农业机械学报, 2015, 46(4):176-182. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=664418193 [13] 王志兵, 汪稔, 胡明鉴, 等.颗粒运移对蒋家沟土体渗透性影响的试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2011, 32(7):2017-2024. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX201107018.htm [14] 矫滨田, 鲁晓兵, 王淑云, 等.土体降雨滑坡中细颗粒运移及效应[J].地下空间与工程学报, 2005, 1(增刊1):36-38. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=conference&id=6235194 [15] 亓星, 许强, 孙亮, 等.降雨型黄土滑坡预警研究现状综述[J].地质科技情报, 2014, 33(6):219-225. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201406033.htm [16] 亓星, 许强, 朱星, 等.甘肃黑方台陈家8#静态液化型黄土滑坡变形特征及成因机理[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5):234-239. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201805033.htm [17] 张一希, 许强, 刘方洲, 等.不同地区饱和原状黄土静态液化特性试验研究[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5):229-233. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201805031 [18] 王志兵, 麦棠坤, 齐程.泥石流孕育-启动过程的细粒作用[C]//中国地质学会, 中国地质学会工程地质专业委员会.2017年全国工程地质学术年会论文集.广西桂林: 《工程地质学报》编辑部, 2017: 8. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-GCDZ201710001056.htm [19] 宋朋燃.黄土边坡冲刷破坏特征及数值模拟[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2013. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-1013193110.htm [20] 胡炜, 朱立峰, 张茂省, 等.灌溉引起的黄土工程地质性质变化[J].地质通报, 2013, 32(6):875-880. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZQYD201306008.htm [21] 雷祥义.中国黄土的孔隙类型与湿陷性[J].中国科学:化学生物学农学医学地学, 1987(12):1309-1318. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFD1987-JBXK198712008.htm [22] 黄智全.无黏性粗粒土渗透淤堵作用室内模拟试验及机理研究[D].长春: 吉林大学, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10183-2010109608.htm [23] 郭玉文, 加藤诚, 宋菲, 等.黄土高原黄土团粒组成及其与碳酸钙关系的研究[J].土壤学报, 2004, 41(3):362-368. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_trxb200403006.aspx [24] 刘春, 许强, 施斌, 等.岩石颗粒与孔隙系统数字图像识别方法及应用[J].岩土工程学报, 2018, 40(5):925-931. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTGC201805022.htm [25] 赵宽耀, 许强, 张先林, 等.黑方台浅层黄土渗透特性对比试验研究[J].工程地质学报, 2018, 26(2):459-466. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98122X/20182/7000655592.html [26] 郭朝旭, 崔鹏.宽级配弱固结土体内细颗粒迁移规律研究评述[J].山地学报, 2017, 35(2):179-186. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_sdxb201702007.aspx [27] 吴梦喜, 叶发明, 张琦.细颗粒流失对砂砾石土本构关系的影响研究[J].岩土力学, 2017, 38(6):1550-1556. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/94551X/20176/672381343.html [28] 李喜安, 黄润秋, 彭建兵, 等.关于物理潜蚀作用及其概念模型的讨论[J].工程地质学报, 2010, 18(6):880-886. http://www.cqvip.com/Main/Detail.aspx?id=36206059 -





 下载:
下载: