Genetic types and geological features of large scale and extra-large scale layered landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area
-
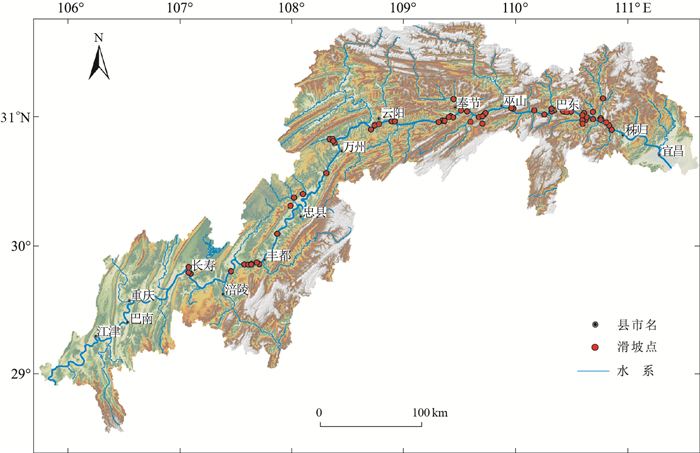
摘要: 三峡库区大型-特大型滑坡发育,尤以层状岩质滑坡的危害性大。因库区各段地质条件差异使得滑坡成因模式各不相同,这影响了滑坡的运动形式和岩土体解体程度。在收集三峡库区51处典型的大型-特大型层状岩质滑坡调查资料基础上,根据堆积岩体结构和区段地质条件反推该段滑坡破坏成因模式,而不同成因模式下的滑坡坡体渗透性不同,分析已有滑坡对库水位变动存在的复活响应差异,据此得出以下结论:①在成因模式上,除顺层滑移型滑坡在库区中均有分布外,从库首至库尾随着岩层倾角的逐渐减缓,滑坡成因模式从崩塌型、反倾弯曲型逐渐过渡到平推式;②在坡体渗透性上,成因模式造成的岩体结构变化与坡体中的泥质含量共同作用,导致顺层滑移型滑坡前后缘渗透性存在较大差异;反倾型滑坡渗透性则整体变化较小;③在库水位变动影响下,不同坡体渗透性与滑面形态共同决定了滑坡的复活变形差异。Abstract: The large-scale and extra-large scale landslides in the Three Gorges Reservoir area have a great impact on the rock landslides. The geological conditions in various sections of the reservoir make the landslide genesis patterns different, resulting in different forms of motion after the damage and the degree of disintegration of the rock masses. With 51 typical large scale or extra-large scale bedrock landslide data collected in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, the cause model of the landslide failure is reversed according to the structure of the stacked rock masses and the geological conditions. The landslides with different genetic models have different permeability characteristics and resurrection responses to reservoir water level changes. The results show that from the head to the tail of the reservoir, along with the decreasing of the rock dips, in addition to the distribution of the full-slide type, the genetic types gradually change from collapse type and anti-tilt type to translation type. In the permeability of the slope, the change of rock mass structure caused by the genetic model and the shale content in the slope body result in a large difference in the permeability of the front and rear edges of the bedding landslide. But the anti-dipping landslides are the opposite, and under the influence of reservoir water fluctuations, the permeability of different slopes and the shape of the slip surface jointly determine the difference of resurrection deformation of the landslides.
-
Key words:
- landslide /
- Three Gorges Reservoir area /
- genetic type /
- rock mass structure /
- permeability
-
表 1 不同成因模式下滑坡基本特征统计表
Table 1. Basic characteristics of landslides with different genetic models
模式类型 滑坡个数/个 主要分布区段 主要地层 岩性 岩层倾角α/(°) 滑面形态 典型滑坡 平推式 9 长寿-万州 J2s,J3s 泥岩、砂质泥岩与厚层长石砂岩互层 3~12 近水平直线 玉皇观滑坡、李家湾滑坡 顺层滑移型 31 全库区 T2b,J1-2z,J2s,J3s,J3p 泥灰岩、泥岩、泥质粉砂岩与石英砂岩、砂岩互层 11~45 波状、直线、靠椅 白衣庵滑坡、木鱼包滑坡 反倾弯曲型 5 巴东,秭归 T2b,J1x 黏土岩、灰岩、泥灰岩 -25~-40 弧形、波状 白家包滑坡 崩塌型 6 秭归 S-P,Z-∈ 灰岩、泥质灰岩、炭质页岩、 35~65 / 作揖沱滑坡 注:Z-∈.震旦系-寒武系;S-P.志留系-二叠系;T2b.中三叠统巴东组;J1x.下侏罗统香溪组;J1-2z.中下侏罗统自流井组;J2s.中侏罗统上沙溪庙组;J3s.上侏罗统遂宁组;J3p.上侏罗统蓬莱镇组 表 2 三峡库区滑坡物质渗透系数等级分类
Table 2. Classification of landslide material permeability coefficient in the Three Gorges Reservoir
渗透性程度 饱和渗透系数k/(m·d-1) 弱透水性 [0, 0.1) 中等透水性 [0.1, 1) 良透水性 [1, 10) 强透水性 [10, +∞) 表 3 典型成因模式下滑坡前中后缘渗透系数及岩体结构
Table 3. Permeability coefficient and rock mass structure of the typical genetic model
k/(m·d-1) 表 4 不同成因模式下滑坡对库水位响应类型及数量统计
Table 4. Response types and quantity statistics of slope to reservoir water level in different genetic models
类型 坡体前缘渗透性 滑面形态 按库水作用类型的滑坡分类 动水压力型 浮托减重型 平推式 弱-中等 直线 9 0 顺层滑移型 弱-中等 波状、直线、靠椅 16 3 反倾弯曲型 中等-强 弧形、波状 5 0 崩塌型 中等-良 直线、折线 3 0 -
[1] 李松林, 许强, 汤明高, 等.库水位升降作用下不同滑面形态老滑坡响应规律[J].工程地质学报, 2017, 25(3):841-852. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GCDZ201703032.htm [2] Varnes D J.Landslide types and processes[J].Landslides-invesitgation and mitigation, 1996, 247:36-75. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=ec2b11d009424f6d2ec584372c9d50dc&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [3] Hungr O, Leroueil S, Picarelli L.The Varnes classification of landslide types, an update[J].Landslides, 2014, 11(2):167-194. doi: 10.1007/s10346-013-0436-y [4] 罗元华, 伍法权, 常中华.三峡库区奉节县新城区T2b3泥质灰岩斜坡变形破坏模式的现象学研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2005, 24(12):2029-2034. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/yslxygcxb200512005 [5] 张学年, 盛祝平, 孙广忠, 等.长江三峡工程库区顺层岸坡研究[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993:71-110. [6] 祁生文, 伍法权, 常中华, 等.三峡地区奉节县城缓倾层状岸坡变形破坏模式及成因机制[J].岩土工程学报, 2006, 28(1):88-91. http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-DZDQ200702001330.htm [7] 任光明, 夏敏, 李果, 等.陡倾顺层岩质斜坡倾倒变形破坏特征研究[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(s1):3193-3193. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSLX2009S1093.htm [8] 单慧媚, 梁合诚, 刘佳伟, 等.饱水过程中松散土体渗透性变化研究[J].水文地质与工程地质, 2010, 37(5):97-101. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SWDG201005021.htm [9] 李泯蒂.三峡库区碎石土组构及渗透特性分析[D].湖北: 三峡大学, 2015. [10] 张国栋, 邓全胜, 李泯蒂.干湿循环对水库滑坡渗透系数影响的试验研究[J].人民长江, 2016, 47 (22):79-82. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-RIVE201622017.htm [11] 肖东辉, 冯文杰, 冯泽, 等.冻融循环作用下黄土渗透性与其结构特征关系研究[J].水文地质工程地, 2015, 42(4):43-49. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SWDG201504009.htm [12] 张夏冉, 殷坤龙, 夏辉, 等.渗透系数与库水位升降对下坪滑坡稳定性的影响研究[J].工程地质学报, 2017, 25(2):488-495. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GCDZ201702028.htm [13] 王力, 王世梅, 向玲.降雨作用下三峡库区某粘质土滑坡优势流分析[J].地下空间与工程学报, 2015, 11(4):1047-1052. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-BASE201504037.htm [14] 常宏, 王旭升.滑坡稳定性变化与地下水非稳定渗流初探:以三峡库区黄蜡石滑坡群石榴树包滑坡为例[J].地质科技情报, 2004, 23(1):94-98. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ200401020.htm [15] 董辉, 罗潇.强降雨作用下堆积碎石土渗流规律研究[J].工程地质学报, 2015, 23(4):616-623. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/98122X/20154/665913913.html [16] 张广成, 唐辉明, 胡斌.非饱和渗流对滑坡稳定性的影响研究[J].岩土力学, 2007, 28 (5):965-970. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX200705021.htm [17] 唐朝晖, 孔涛, 柴波.降雨作用碎石土堆积层滑坡变形规律[J].地质科技情报, 2012, 31(6):168-173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201206028.htm [18] 中国地质调查局.水文地质手册[M].第2版.北京:地质出版社, 2012. [19] 孙一清, 李德营, 殷坤龙, 等.三峡库区堆积层滑坡间歇性滑坡预测:以白水河滑坡为例[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5):195-203. https://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=DZKQ201905021 [20] 邓建辉, 谭国焕, 李焯芬.泄滩滑坡碎块石土饱和与非饱和水力学参数的现场试验研究[J].岩土力学, 2007, 28(2): 327-331. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTLX200702022.htm [21] 张俞, 殷坤龙, 郭子正, 等.库水位变动联合降雨作用下麻柳林滑坡稳定性评价[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):198-205. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZKQ201906024.htm [22] 柴军瑞, 李守义.三峡库区泄滩滑坡渗流场与应力场耦合分析[J].岩石力学与工程学报, 2004, 23(8):1280-1284. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YSLX200408009.htm [23] 油新华, 李晓, 马风山, 等.白衣庵滑坡原状土的渗透性试验研究[J].岩土工程学报, 2001, 23(6):769-770. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YTGC200106026.htm -





 下载:
下载: