Grading evaluation of deep reservoir in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin
-
摘要: 西湖凹陷是东海盆地最有油气潜力、最有勘探难度的沉积盆地,储层类型多样且致密化严重是目前制约资源评价的重点难题之一。现有的储层评价标准并没有充分考虑到多样性储层并存的特征,对于储层的评价依然依托的是常规储层评价标准,并没有系统开展过多类型储层的分类、分级评价。在充分讨论西湖凹陷储层控制因素的基础上,遴选出储层发育的主要控制要素,建立了"微相-成岩-温度"三要素联控下的储层三元分级方案,并在此基础上,对主要目的段储层开展了分级评价,认为花港组储层以低渗特低渗储层为主,占总储层的35%以上,是未来主要的勘探类型。平湖组以常规和低渗储层为主。研究成果为后期资源量分级评价奠定了基础,也为国内外同类型盆地储层评价提供了借鉴。Abstract: Xihu Depression is a sedimentary basin with the most oil and gas potential and exploration difficulty in the East China Sea Basin. The existing reservoir evaluation standard cannot fully take into account the characteristics of reservoir diversity, so the reservoir evaluation relies on the conventional standard, and the systematic reservoir classification and grading evaluation are constrained. This paper, on the basis of discussion reservoir control factors, takes the "Microfacies-Diagenesis-Temperature" as the main evaluation parameters of reservoir classification and evaluates the main reservoirs on this basis. The results show that the Huagang Formation is mainly composed of low-permeability and super-low permeability reservoirs, accounting for more than 35% of the total reservoir, and thus is the main exploration type in the future. The Pinghu Formation is mainly composed of conventional and low-permeability reservoirs. The research results establish a foundation for the later stage of resource quantity grading evaluation and, also to provide some help for same type reservoir in others basin.
-
Key words:
- grading evaluation /
- principle /
- deep reservoir /
- Xihu Depression /
- East China Sea Basin
-
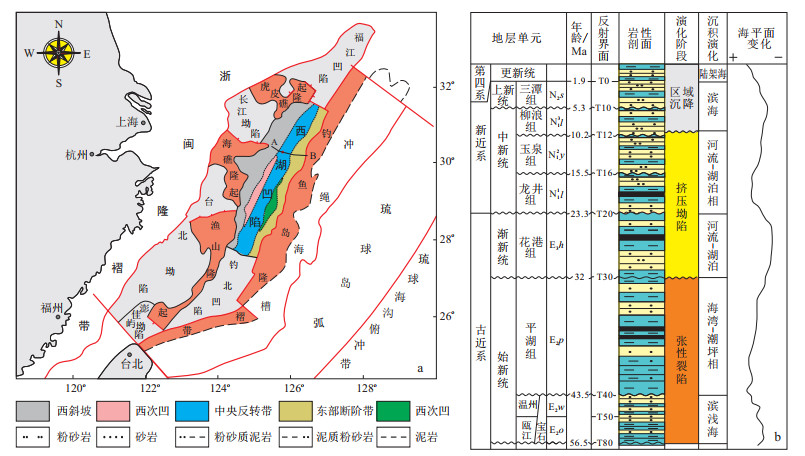
图 1 西湖凹陷区域位置示意图(a)与地层充填序列图(b)(a据文献[9]修改)
Figure 1. Location map (a) and formation filling sequence diagram (b) of Xihu Depression
图 6 西湖凹陷中北部花港组储层酸碱成岩环境发育序列(据文献[15]修改)
Figure 6. Development sequence of diagenetic environment of Huagang Formation in the north-central part of Xihu Depression
图 10 西湖凹陷储层分级大剖面(剖面位置见图 1)
Figure 10. Great profile of reservoir classification in Xihu Depression
表 1 “相-岩-温”三元分级方案
Table 1. Reservoir classification program of "Microfacies-Diagenesis-Temperature"
分级 常规储层 低渗储层 特低渗储层 致密储层 分级参数 沉积微相 心滩砂坝和滞留沉积、河口坝 河道边缘与砂坝顶部 废弃河道与河漫沉积 湖、海相细粒沉积 成岩 成岩阶段 早B-中A1 中A1-中A2 中A2-中B 中B-晚 成岩相 弱压实+绿泥石胶结相+强溶蚀(AAA) 中压实+弱胶结相+强溶蚀(BAA) 强压实+中胶结相+中溶蚀(CBB) 强压实+弱胶结相+中强溶蚀(CBC)(CCC) 温度场/℃ < 140 [140, 160) [160, 180) ≥180 物性特征 渗透率/10-3 μm2 ≥10 (10, 1] (1, 0.1] < 0.1 孔隙度/% ≥15 (15, 12] (12, 6.5] < 6.5 注:压实分为弱(A)、中(B)、强(C)压实; 胶结分为弱胶结(绿泥石)(A)、中胶结(高岭石)(B)、强胶结(钙硅质)(C); 溶蚀分为弱(A)、中(B)、强(C)溶蚀 表 2 西湖凹陷主要目的层段储层分级评价结果
Table 2. Reservoir classification evaluation results of main targets in Xihu Depression
层位 常规储层 低渗储层 特低渗储层 致密储层 总面积/ km2 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% 面积/km2 占比/% H3 1 259.00 2.9 9 958.2 22.96 10 379 23.93 21 774 50.21 43 370.67 H4 1 159.62 3.62 5 174 16.15 8 356.7 26.08 17 351 54.16 42 041.320 H5 852.75 3.49 6 460.2 26.43 6 877.5 28.14 10 250 41.94 24 440.45 花下 2 153.04 5.32 11 191 27.65 3 152.6 7.79 24 057 59.43 40 553.64 平上HST 94.26 0.44 632.62 2.93 1 204.9 5.58 19 661 91.05 21 592.3 平上TST 7 306.78 13.02 7152.7 12.75 3 737.2 6.66 37 909 67.57 56 105.68 平中 4 284.27 6.41 6 867.3 10.28 2 059.3 3.08 53 611 80.23 66 821.87 平下 888.28 2.53 3 956.9 11.28 3 088 8.8 27 158 77.39 35 091.18 -
[1] 刘金水."储保耦合"控藏机制与西湖凹陷大中型油气田勘探实践[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):11-19. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903002 [2] 周心怀.西湖凹陷成盆背景、原型盆地演化及勘探启示[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):1-10. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903001 [3] 高伟中, 孙鹏, 赵洪, 等.西湖凹陷花港组深部储层特征及控制因素[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 43(4):396-404. [4] 钟韬, 李键, 曹冰, 等.西湖凹陷花港组储层致密化及其与油气成藏的关系[J].海洋地质前沿, 2018, 34(1):20-27. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0120180802940887 [5] 张武.西湖凹陷低渗储层成因及优质储层主控因素[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):40-49. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903005 [6] 郑军.西湖凹陷中央背斜带中北部深部优质储层孔隙保存机理[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(3):173-179. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201603022 [7] 苏奥, 陈红汉, 胡飞, 等.西湖凹陷中央构造带中南部油气成藏条件、特征及富集规律[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2):129-135. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201502017 [8] 刘金水, 陆永潮, 秦兰芝.源-汇系统分析方法在大型储集体研究中的应用:以西湖凹陷中央反转带花港组为例[J].石油实验地质, 2019, 41(3):303-310. [9] 周瑞琦, 傅恒, 徐国盛, 等.东海陆架盆地西湖凹陷平湖组-花港组沉积层序[J].沉积学报, 2018, 36(1):135-144. [10] 高伟中.西湖凹陷中央反转构造带圈闭油气充满度差异性原因分析[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):20-28. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903003 [11] 曹冰.西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组致密砂岩储层埋藏史-热史[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 43(4):405-414. [12] 林承焰, 孙小龙, 马存飞, 等.西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组储层物性演化[J].中国矿业大学学报, 2017, 46(4):820-829. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkydxxb201704016 [13] 张武, 侯国伟, 肖晓光, 等.西湖凹陷低渗储层成因及优质储层主控因素[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):40-49. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903005 [14] 黄导武, 段冬平, 刘彬彬, 等.西湖凹陷低渗-致密砂岩气藏储层特征及差异成因[J].中国海上油气, 2019, 31(3):99-107. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zghsyq-gc201903012 [15] 徐国盛, 徐芳艮, 袁海锋, 等.西湖凹陷中央反转构造带花港组致密砂岩储层成岩环境演变与孔隙演化[J].成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 43(4):385-395. [16] 仝志刚, 贺清, 何仕斌, 等.东海西湖凹陷地温场及其对烃源岩的作用[J].石油实验地质, 2009, 31(5):466-471, 484. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz200905006 [17] 高伟中, 杨彩虹, 赵洪.东海盆地西湖凹陷热事件对储层的改造及其机理探讨[J].石油实验地质, 2015, 37(5):548-554. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=sysydz201505005 [18] 侯志强, 于浩, 刘云, 等.西湖凹陷M气田区块低孔渗致密砂岩储层高精度三维孔隙压力场地震预测[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):273-280, 286. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902032 [19] 蒋一鸣.西湖凹陷平湖斜坡带平湖组碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及米兰科维奇旋回:对源-汇系统及沉积演化的约束[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):133-140. [20] 叶加仁, 刘金水, 徐陈杰, 等.东海西湖凹陷西次凹天然气资源分级评价[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb202003001 -





 下载:
下载: