Sedimentary facies characteristics and accumulation systems of Albian-Turonian at the outer shelf-slope area of MSGB Basin
-
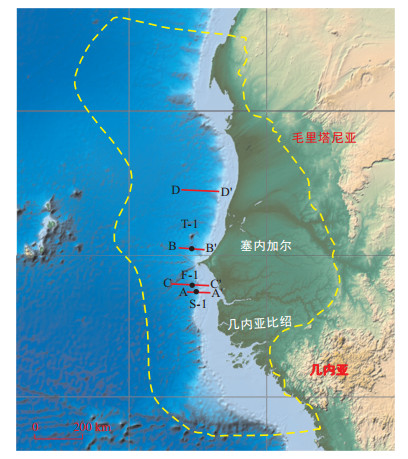
摘要: 近几年来,多个大型油气发现使得毛塞几比盆地成为国际油气勘探的热点区域。基于地震资料和钻测井资料系统开展了沉积相以及沉积模式研究、储层物性分析、烃源岩评价以及成藏体系分析工作。研究结果表明:①盆地中南部外陆架广泛发育多期强制海退三角洲沉积体系,受基准面旋回控制,强制海退三角洲顶积层遭受剥蚀,砂体被搬运到三角洲前部,形成强制海退砂,砂体在陆架边缘附近广泛分布;陆坡类型控制了深水扇差异分布模式,南部断控型陆坡控制了深水扇的分布,深水扇主体发育在陆坡坡脚,距离陆架边缘较近,北部平缓型陆坡下重力流搬运较远,深水扇主体远离陆架边缘,据此建立了南部断控型陆坡控砂模式和北部缓坡型陆坡富砂模式。②外陆架强制海退三角洲和北部缓坡型深水扇储层条件好,测试产能高,受胶结作用和滑塌碎屑影响,南部陡坡型深水扇储层物性差。③油源对比表明,油气主要来自下白垩统阿普第阶-阿尔比阶与上白垩统赛诺曼阶-土伦阶海相烃源岩,阿普第阶-阿尔比阶烃源岩以Ⅱ2型干酪根为主,主要生气;赛诺曼阶-土伦阶海相烃源岩以Ⅰ型干酪根为主,主要生油。④研究区发育3套有利成藏体系,分别为阿尔比阶陆架边缘成藏体系、阿尔比阶-土伦阶陆坡坡脚成藏体系以及赛诺曼阶陆坡远端成藏体系,其中陆架边缘成藏体系与陆坡远端成藏体系勘探潜力更大,是下一步勘探的重点。Abstract: In recent years, several large oil and gas discoveries have made the MSGB Basin a hot spot for international oil and gas explorations. Based on seismic data and drilling and logging data, this paper studies sedimentary facies and sedimentary models, and analyses reservoir physical properties, source rock evaluation and hydrocarbon accumulation models. The results show first that the multi-stage forced regressive delta is widely developed at the southern outer shelf of the basin. Controlled by the base surface cycle, the topset of delta is eroded, and the sand body is transported to the front of the delta to form forced regressive sands. The sand body is widely distributed near the edge of the shelf. Slope type controls the distribution patterns of deep-water fans, and southern faulted slope controls the distribution of the deep-water fans. Fans mainly develop in continental slope foot, close to the shelf edge. Gravity flow is carried far on the northern gentle slope, deep-water fans away from the shelf edge. We established two types of sedimentary models. Then, the results indicate the forced regressive deltas at the outer shelf and northern deep-water fans at gentle slope have good reservoir properties and high test productivity. Southern deep-water fan has poor reservoir properties due to cementation and slump debris. Also, oil-source correlation shows that oil and gas mainly come from Lower Cretaceous Aptian to Albian and Upper Cretaceous Cenomanian to Turonian marine source rocks. Aptian to Albian source rock with Ⅱ2 kerogen type tends to generate gas and Cenomanian to Turonian source rocks with I kerogen type tends to generate oil. Lastly, there are three favorable hydrocarbon accumulation systems in the study area, namely Albian accumulation system at shelf margin, Albian to Turonian hydrocarbon accumulation system at slope foot and Cenomanian hydrocarbon accumulation system at distal slope. Hydrocarbon accumulation system at shelf margin and distal slope have greater exploration potential, a favorable direction for the next exploration.
-
Key words:
- shelf margin /
- delta /
- deep-water fan /
- hydrocarbon accumulation model /
- MSGB Basin
-
图 2 毛塞几比盆地综合地层柱状图(据文献[15])
Figure 2. Generalized stratigraphic chart in MSGB Basin
-
[1] 王大鹏, 殷进垠, 田纳新, 等.塞内加尔盆地成藏组合划分与资源潜力评价[J].现代地质, 2017, 31(6):1201-1213. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xddz201706009 [2] 孙涛, 王建新, 孙玉梅, 等.西非塞内加尔盆地海相优质烃源岩控制因素讨论[J].海洋石油, 2017, 37(4):41-46, 52. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hysy201704007 [3] 孙涛, 王建新, 孙玉梅.西非塞内加尔盆地深水区油气地球化学特征与油气成藏[J].沉积学报, 2017, 35(6):1284-1292. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201706019 [4] Uchupi K O E E.Continental margin off western Africa:Senegal to Portugal[J].AAPG Bulletin, 1976, 60(5):809-878. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/305189870_Continental_Margin_Off_Western_Africa_Senegal_to_Portugal [5] Ruiter P A C D.Structural history of Atlantic margin of Africa[J].AAPG Bulletin, 1977, 61(7):961-981. doi: 10.1306/c1ea43b0-16c9-11d7-8645000102c1865d [6] Ritz M, Bellion Y, Flicoteaux R.Magnetotelluric soundings and the geological structure and tectonics of the Senegalo-Mauritanian Basin in northern Senegal, West Africa[J].Tectonics, 1987, 6(4):395-409. doi: 10.1029/TC006i004p00395/pdf [7] Kinnaird J A, Bowden P.Magmatism in extensional structural settings[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag, 1991. [8] Davison I.Central Atlantic margin basins of North West Africa:Geology and hydrocarbon potential (Morocco to Guinea)[J].Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2005, 43(1/3):254-274. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s1464343x05001196 [9] 熊利平, 王骏, 殷进垠, 等.西非构造演化及其对油气成藏的控制作用[J].石油与天然气地质, 2005, 26(5):641-646. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz200505014 [10] 熊利平, 刘延莉, 霍红.西非海岸南、北两段主要含油气盆地油气成藏特征对比[J].石油与天然气地质, 2010, 31(4):410-419. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201004003 [11] 冯杨伟, 屈红军, 张功成, 等.西非被动大陆边缘构造-沉积演化及其对生储盖的控制作用[J].海相油气地质, 2010, 15(3):45-51. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hxyqdz201003007 [12] 温志新, 徐洪, 王兆明, 等.被动大陆边缘盆地分类及其油气分布规律[J].石油勘探与开发, 2016, 43(5):678-688. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syktykf201605002 [13] Ndiaye M, Ngom P M, Gorin G, et al.A new interpretation of the deep-part of Senegal-Mauritanian Basin in the Diourbel:Thies area by integrating seismic, magnetic, gravimetric and borehole data:Implication for petroleum exploration.[J].Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 121:330-341. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.06.002 [14] 康洪全, 贾怀存, 程涛, 等.南大西洋两岸含盐盆地裂谷层序油气地质特征与油气分布特征对比[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(4):113-119. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201804014 [15] 孔令武, 赵红岩, 韩文明, 等.西非毛塞几比盆地油气成藏差异性分析[J].海洋地质前沿, 2019, 35(5):66-72. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=hydzdt201905009 [16] Plint A G, Nummedal D.The falling stage systems tract:Recognition and importance in sequence stratigraphic analysis[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 172(1):1-17. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.172.01.01 [17] Hansen J P V, Rasmussen E S.Structural, sedimentologic, and sea-level controls on sand distribution in a steep-clinoform asymmetric wave-influenced delta:Miocene Billund Sand, eastern Danish North Sea and Jylland[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2008, 78(2):130-146. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2008.010 [18] Miller L K, Rasmussen E S, Clausen O R.Clinoform migration patterns of a Late Miocene delta complex in the Danish Central Graben: Implications for relative sea-level changes[J].2009, 21(5): 704-720. [19] Posamentier H W, Allen G P, James D P, et al.Forced regressions in a sequence stratigraphic framework:Concepts, examples, and exploration significance[J].AAPG Bulletin, 1992, 76(11):1687-1709. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/30002458593 [20] Fraser C, Hill P R, Allard M.Morphology and facies architecture of a falling sea level strandplain, Umiujaq, Hudson Bay, Canada[J].Sedimentology, 2004, 52(1):141-160. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3091.2004.00680.x [21] Trincardi F, Correggiari A.Quaternary forced regression deposits in the Adriatic Basin and the record of composite sea-level cycles[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 172(1):245-269. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.172.01.12 [22] Zhu Y, Bhattacharya J P, Li W, et al.Milankovitch-scale sequence stratigraphy and stepped forced regressions of the Turonian Ferron Notom deltaic complex, South-Central Utah, U.S.A[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2012, 82(9):723-746. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2012.63 [23] Ainsworth R B, Bosscher H, Newall M J.Forward stratigraphic modelling of forced regressions:Evidence for the genesis of attached and detached lowstand systems[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 172(1):163-176. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.172.01.08 [24] Fitzsimmons R, Johnson S.Forced regressions:Recognition, architecture and genesis in the Campanian of the Bighorn Basin, Wyoming[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 172(1):113-139. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.172.01.06 [25] Haywick D W.Recognition and distinction of normal and forced regression in cyclothemic strata:A Plio-Pleistocene case study from eastern North Island, New Zealand[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 172(1):193-215. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.172.01.10 [26] Postma G.Sedimentary responses to forced regressions[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2001, 144(3):377-379. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=S0016756801414956 [27] Helland-Hansen W, Hampson G J.Trajectory analysis:Concepts and applications[J].Basin Research, 2010, 21(5):454-483. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1177/096466399400300201 [28] Mcmurray L S, Gawthorpe R L.Along-strike variability of forced regressive deposits:Late Quaternary, northern Peloponnesos, Greece[J].Geological Society London Special Publications, 2000, 172(1):363-377. doi: 10.1144/GSL.SP.2000.172.01.16 [29] 柯友亮, 郝杰, 王华, 等.基于叠后地震数据的南堡凹陷高南斜坡带三角洲扇体识别及演化特征[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):95-106. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902011 [30] 胡勇, 黄凯, 徐振华, 等.渤海BZ油田鸟足状浅水三角洲指状砂坝储层剩余油分布特征[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):195-204. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201902022 [31] 王亚辉, 张道军, 陈杨, 等.琼东南盆地三亚组陆架边缘三角洲的发现及其油气勘探意义[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(5):30-36. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201805004 [32] 朱筱敏, 葛家旺, 赵宏超, 等.陆架边缘三角洲研究进展及实例分析[J].沉积学报, 2017, 35(5):945-957. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201705007 [33] 邢作昌, 林畅松, 张忠涛, 等.白云深水区珠海组陆架边缘三角洲沉积演化[J].特种油气藏, 2017, 24(5):15-20. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=tzyqc201705003 [34] 徐强, 王英民, 吕明, 等.陆架边缘三角洲在层序地层格架中的识别及其意义:以南海白云凹陷为例[J].石油与天然气地质, 2011, 32(5):733-742. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/95357X/20115/40011671.html [35] 徐少华, 王英民, 何敏, 等.强制海退体系域的识别特征与成因分析[J].中南大学学报:自然科学版, 2016, 47(2):531-540. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zngydxxb201602026 [36] 刘豪, 王英民, 王媛.浅海陆棚环境下沉积坡折带及其对局部强制海退体系域的控制[J].沉积学报, 2011, 29(5):906-916. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cjxb201105009 [37] 金之钧, 张一伟, 王捷, 等.油气成藏机理与分布规律[M].北京:地质出版社, 2003. [38] 王大鹏, 陆红梅, 陈小亮, 等.海相碳酸盐岩大中型油气田成藏体系及分布特征[J].石油与天然气地质, 2016, 37(3):363-371. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=syytrqdz201603008 -





 下载:
下载: