Laboratory experiment and simulation of solute transport affected by different grades of fissures and water storage of waterlogging in karst depression
-
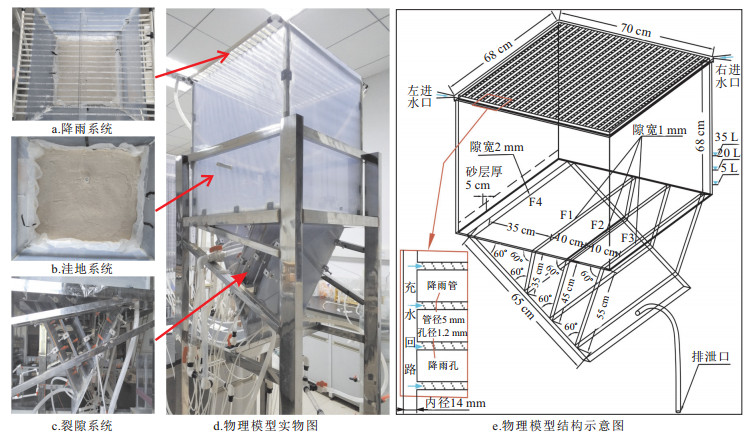
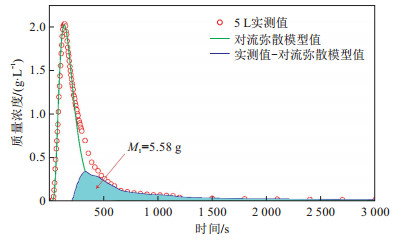
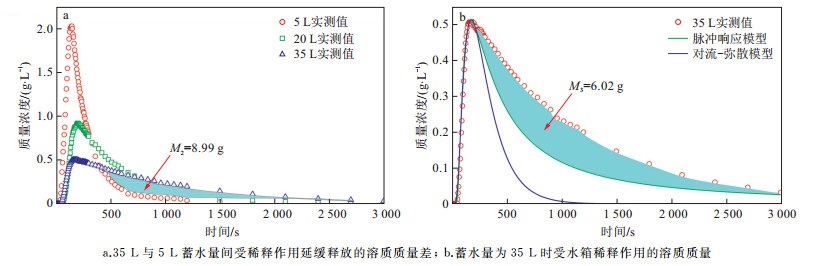
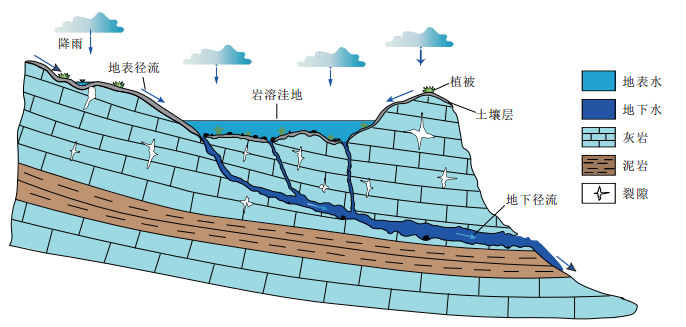
摘要: 岩溶洼地在西南地区分布广泛,岩溶地下水为当地居民生产和生活的主要水源,研究岩溶洼地内涝条件下裂隙系统中的溶质迁移及响应规律可为峰丛洼地区岩溶地下水的污染防控提供科学依据。基于相似原理构建了岩溶洼地-裂隙系统物理模型,采用对流-弥散模型和脉冲响应模型对溶质迁移过程进行了模拟分析,探讨了不同级次裂隙和内涝蓄水量大小对溶质迁移的影响。结果表明:大裂隙作为优先水流通道,对溶质迁移起主要的控制作用;小裂隙对溶质迁移起暂时储存和缓慢释放的调蓄作用,其溶质迁移的叠加过程使总出口溶质迁移的"拖尾"效应更加明显;随着内涝蓄水量的增加,稀释作用增强,导致溶质峰值质量浓度降低、溶质质量浓度回归至本底值的时间延长、延缓释放溶质的质量增加。该物理模型是对复杂岩溶洼地系统内污染物迁移研究的一种新探索,其模拟结果进一步深化了对洼地内涝条件下面源污染物在岩溶水系统中迁移规律的认识。Abstract: The karst depressions are widely distributed in southwest China. In this area, the karst groundwater is the main water resource for the local residents to live and produce. Studying the solute transport and response law in the fissure system under karst waterlogging conditions can provide a scientific basis for karst groundwater pollution prevention and control peak-cluster depression. Based on similarity principle, a laboratory physical model of karst depression-fracture system has been establishea. The solute transport processes were simulated by advection-dispersion model and impulse response model, and the effects of different grades of fissures and water storage of waterlogging in depression on solute transport were discussed. The results indicate that the large fissure is performed as the priority flow channel, which plays a major role in controlling solute transport. The small fissures play an important role in adjusting the transient storage and slowing release in solute transport process, and the superposition processes of solute transport in small fissures makes the trailing more obvious in breakthrough curve at the total outlet. As water storage of waterlogging increases, the dilution effect enhances dramatically, which leads to the gradual decrease of solute peak concentration, the time extension of solute concentration returning to the background value, and the increase of the delay-release solute mass. This physical simulation model is a new exploration of pollutant transport in complex karst depression systems, which deepens the understanding of solute transport process in karst water system under waterlogging conditions in depression with surface pollution.
-
Key words:
- karst depression /
- physical model /
- karst waterlogging /
- solute transport /
- breakthrough curve
-
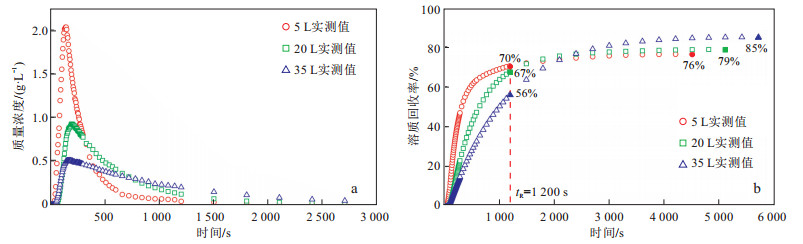
表 1 不同蓄水量下的实验结果对比
Table 1. Comparison of experimental results under different water storage conditions
蓄水量/
L峰值质量
浓度/(g·L-1)峰现时间/
s出口流量/
(mL·s-1)出口流速/
(m·s-1)示踪实验
历时/s示踪历时总
消耗水量/L总回收
质量/g1 200 s时
回收率/%总回收率/
%5 2.032 145 30.54 0.607 4 200 128.27 16.36 70 76 20 0.924 195 30.88 0.614 5 100 157.49 16.86 67 79 35 0.506 185 31.39 0.624 5 700 178.92 18.18 56 85 表 2 不同蓄水量下的计算参数对比
Table 2. Calculation parameters under different water storage conditions
蓄水量/
L等效流速
v/(m·s-1)纵向弥散系数
DL/(m2·s-1)溶质峰值质量浓度
Cmax/(g·L-1)系统时间常数
τ脉冲响应模型
NSE对流-弥散模型
NSE5 0.42 3 2.032 75 0.68 0.97 20 0.28 3 0.924 180 0.96 0.89 35 0.30 4 0.506 240 0.90 0.64 -
[1] 袁道先.中国岩溶学[M].北京:地质出版社, 1994. [2] 袁道先, 蒋勇军, 沈立成, 等.现代岩溶学[M].北京:科学出版社, 2016. [3] 罗明明, 周宏, 陈植华.香溪河流域岩溶水循环规律[M].北京:科学出版社, 2018. [4] 郭芳, 姜光辉, 蒋忠诚.中国南方岩溶石山地区不同岩溶类型的地下水与环境地质问题[J].地质科技情报, 2006, 25(1):83-87. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb200601015 [5] 陈静, 罗明明, 廖春来, 等.中国岩溶湿地生态水文过程研究进展[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6):221-230. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201906026 [6] Sauter M.Quantification and forecasting of regional groundwater flow and transport in a karst aquifer(Gallusquelle, Malm, SW, Germany)[M].Tübingen:Universität Tübingen, 1992. [7] Goldscheider N, Drew D.Methods in karst hydrogeology[M].[S.l.]: Taylor and Francis, 2007. [8] 张蓉蓉, 束龙仓, 闵星, 等.管道流对非均质岩溶含水系统水动力过程影响的模拟[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2012, 42(增刊2):386-392. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/91256B/2012S2/1003447361.html [9] 郭绪磊, 朱静静, 陈乾龙, 等.新型地下水流速流向测量技术及其在岩溶区调查中的应用[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1):243-249. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201901027 [10] White W B.Karst hydrology:Recent developments and open questions[J].Engineering Geology, 2002, 65(2):85-105. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0013795201001168 [11] Enemark T, Peeters L J M, Mallants D, et al.Hydrogeological conceptual model building and testing:A review[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2019, 569:310-329. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.007 [12] Ding H H, Zhang X M, Chu X W, et al.Simulation of groundwater dynamic response to hydrological factors in karst aquifer system[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2020, 587:124995. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124995 [13] 闵佳."渗流-管流耦合模型"的物理模拟及数值模拟[D].北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2019. [14] Morales T, Uriarte J A, Olazar M, et al.Solute transport modelling in karst conduits with slow zones during different hydrologic conditions[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2010, 390:182-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2010.06.041 [15] Field M S, Leij F J.Solute transport in solution conduits exhibiting multi-peaked breakthrough curves[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 440/441:26-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.03.018 [16] 腾强, 王明玉, 王慧芳.裂隙管道网络物理模型水流与溶质运移模拟试验[J].中国科学院大学学报, 2014, 31(1):54-60. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgkxyyjsyxb201401009 [17] 张雪梅, 周小姣, 褚学伟, 等.集中式补给-排泄的组合裂隙溶质运移模拟试验[J].水利科技与经济, 2019, 25(2):34-40. http://kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?dbcode=CJFD&filename=SLKY201902006 [18] 李庆松, 李兆林, 裴建国, 等.马山东部岩溶洼地谷地内涝特征与治理规划[J].中国岩溶, 2008, 27(4):359-365. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=zgyr200804011 [19] 李阳兵, 罗光杰, 白晓永, 等.典型峰丛洼地耕地、聚落及其与喀斯特石漠化的相互关系:案例研究[J].生态学报, 2014, 34(9):2195-2207. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/stxb201409003 [20] 夏青, 姜光辉, 李科, 等.桂林峰丛洼地岩溶动力系统CO2特征及变化规律[J].地质科技情报, 2007, 26(5):79-82. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb200705014 [21] 蒋建清, 程超, 蔡晶垚, 等.一种自循环式人工降雨模拟装置降雨特性的试验研究[J].湖南城市学院学报:自然科学版, 2017, 26(2):1-5. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=huncjgdzkxxxb201702001 [22] 张雪梅.岩溶裂隙-管道水动力弥散特征室内模拟研究[D].贵阳: 贵州大学, 2019. [23] 赵小二, 常勇, 彭伏, 等.水箱-管道系统溶质运移实验研究及其岩溶水文地质意义[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2017, 47(4):1219-1228. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=cckjdxxb201704018 [24] Kreft A, Zuber A.On the physical meaning of the dispersion equation and its solution for different initian and boundary conditions[J].Chemical Engineering Science, 1978, 33(11):1047-1061. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0009250978851963 [25] Criss R E, Winston W E.Hydrograph for small basins following intense storms[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(6):1314-1317. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2002GL016808 [26] Criss R E, Winston W E.Discharge predictions of a rainfall-driven theoretical hydrograph compared to common models and observed data[J].Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(10):1-9. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=1bedc0b8a09f9d6abda545c05edaadab [27] Winston W E, Criss R E.Dynamic hydrologic and geochemical response in a perennial karst spring[J].Water Resources Research, 2004, 40(5):1-11. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=10.1029/2004WR003054 [28] Yang Y, Endreny T A.Watershed hydrograph model based on surface flow diffusion[J].Water Resources Research, 2013, 49(1):507-516. doi: 10.1029/2012WR012186 [29] Predieri S, Norman H A, Krizek D T.et al.Influence of UV-B radiation on membrane lipid composition and ethylene evolution in 'Doyenne d'Hiver' pear shoots grown in vitro under different photosynthetic photon fluxes[J].Environmental and Experimental Botany, 1995, 35(2):151-160. doi: 10.1016/0098-8472(95)00003-2 -





 下载:
下载: