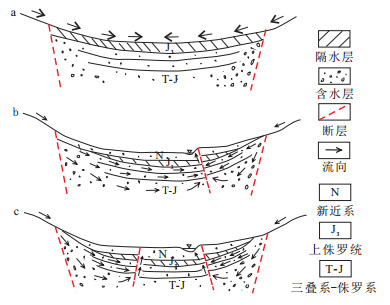
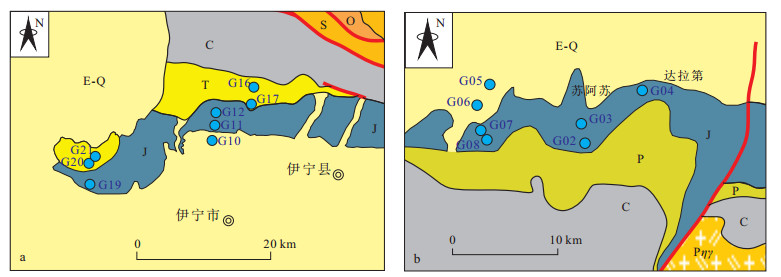
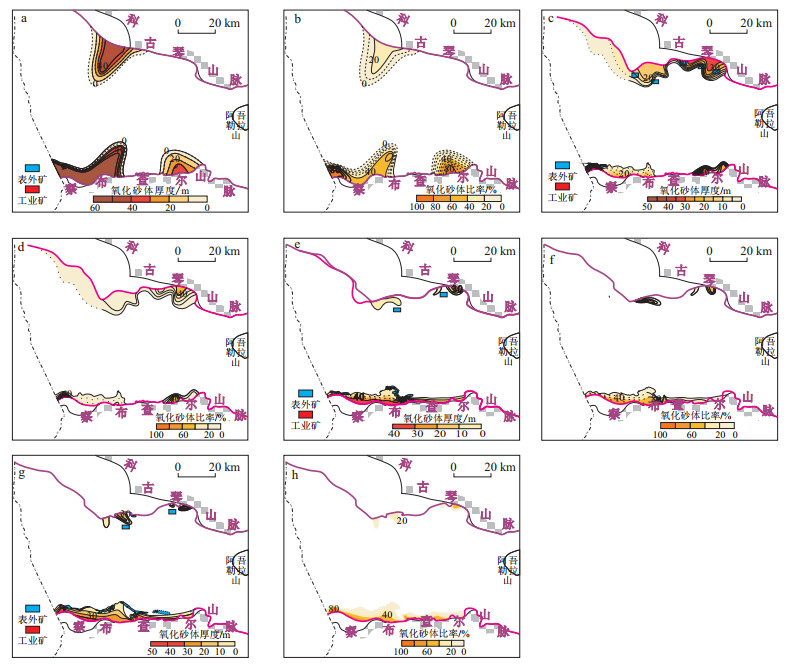
Relationship between uranium mineralization and hydrologic condition in Yili Basin
-
摘要: 砂岩型铀矿是一种水成矿产,研究盆地水文地质条件与铀成矿的关系对揭示铀成矿规律和预测铀成矿靶区十分重要。以伊犁盆地为例,根据盆地地下水系统演化特征分析了不同地质时期铀成矿的水动力条件,运用水文地球化学测试技术分析了地下水化学特征及铀成矿的水化学条件,结合铀矿勘探钻孔资料,统计分析了铀储层及其内部层间氧化带的发育特征与铀矿分布的关系,揭示了盆地内部不同部位、不同时代铀储层的铀成矿水文地质条件的差异以及铀成矿的有利区段。结果表明:空间上,盆地西南部构造稳定,铀储层规模大、连续性好,铀成矿作用的持续性好,具有最有利的铀矿富集的水文地质条件;东南部次之,北部的铀成矿条件最弱。各铀储层中,西山窑组的铀成矿条件最好,八道湾组次之,小泉沟群最弱。Abstract: The sandstone-type uranium deposit is a kind of hydro-sedimentary mineral. It is very important to study the relationship between the hydrogeological conditions and uranium mineralization to reveal the uranium metallogenic regularity and predict the target area of uranium ore.Yili Basin is taken as an example, the hydrodynamic conditions of uranium mineralization in different geological periods are analyzed according to the evolution characteristics of groundwater system. Hydrogeochemical techniques are used to analyze groundwater chemical characteristics and hydrogeochemical conditions of uranium mineralization. The relationship between the distribution of uranium deposits and the development characteristics of uranium reservoirs and interlayer oxidation zones are statistically analyzed according to uranium exploration drilling data. It reveals the spatial differences of uranium ore-forming hydrogeological conditions among uranium deposits of different ages, and the favorable position of uranium mineralization. It indicates that the southwestern basin is the most advantageous part for uranium richness because it has stable geological structure and large-scale uranium reservoir with good continuity, which is beneficial for continual uranium mineralization. The southeast is the second favorable part for uranium richness, and the northern uranium mineralization conditions are the weakest. From the perspective of different uranium reservoirs, the uranium metallogenic conditions of Xishanyao Formation is the best, followed by Badaowan, and the Xiaoquangou group is the weakest.
-
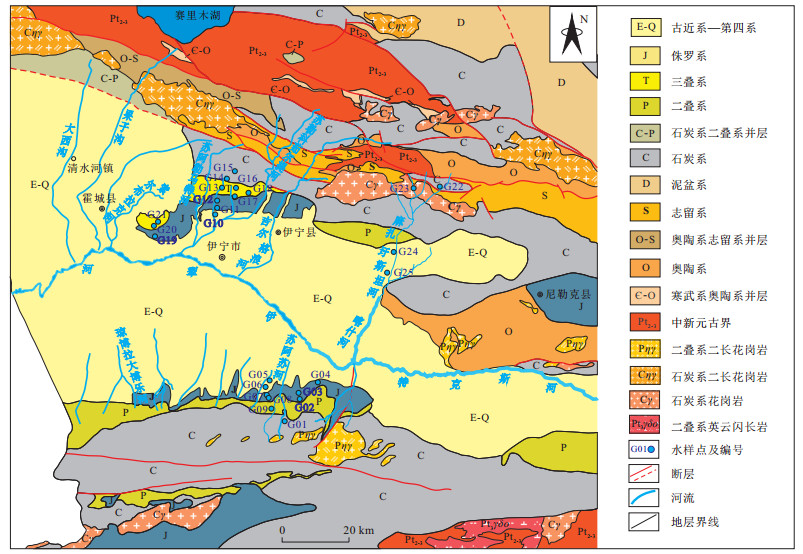
表 1 地下水化学组分特征
Table 1. Chemical composition of groundwater
编号 出露地层 Ca2+ Mg2+ K++Na+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- ρ(TDS)/
(g·L-1)ρ(U6+)/
(μg·L-1)水化学类型 ρB/(mg·L-1) G02 J1s泉水 53.3 8.1 13.6 62.1 165.6 217.8 0.5 15.7 HCO3·SO4-Ca G03 J1s泉水 65.2 19.8 103.9 32.6 611.8 205.0 1.1 24.6 SO4-Na·Ca G11 J1s泉水 72.1 35.7 119.5 252.7 716.0 299.0 1.5 20.2 SO4·Cl-Na·Ca·Mg G07 J2x泉水 69.8 14.6 58.5 144.9 461.1 145.2 1.0 8.4 SO4·Cl-Ca·Na G08 J2x泉水 73.5 15.2 63.8 163.1 498.3 179.4 1.1 6.4 SO4·Cl-Ca·Na G14 C2ysh泉水 20.3 3.1 34.8 22.9 69.0 299.0 0.5 7.9 SO4-Na·Ca G15 C2ysh泉水 56.4 22.8 108.9 174.2 723.1 153.8 1.3 22.2 HCO3-Na·Ca G22 C1d泉水 30.4 6.2 6.6 9.4 52.5 128.1 0.3 3.3 HCO3·SO4-Ca G01 C1d泉水 333.5 75.9 474.8 2 060.0 2 570.0 205.0 5.9 17.5 Cl·SO4-Na·Ca G23 Cηγ泉水 64.0 14.2 56.7 25.6 628.0 213.6 1.0 68.5 SO4-Ca·Na G24 N2d泉水 69.6 43.6 159.1 324.9 1 149.0 187.9 2.0 24.1 SO4·Cl-Na·Mg G25 N2d泉水 64.1 46.4 165.7 236.1 1 399.0 170.9 2.1 28.0 SO4-Na·Mg G13 T2-3X泉水 75.8 34.8 104.4 188.7 781.9 256.3 1.5 15.8 SO4-Na·Ca·Mg G18 T2-3X泉水 84.3 28.4 103.3 204.7 812.3 256.3 1.6 12.4 SO4-Na·Ca G17 T2-3X泉水 127.0 68.6 437.3 745.5 2 748.0 341.7 4.5 28.2 SO4·Cl-Na G16 T2-3X泉水 160.2 76.5 428.7 624.7 3 370.0 205.0 4.9 48.5 SO4-Na G21 T2-3X泉水 333.4 52.5 1 601.9 5 748.0 5 791.0 222.1 13.8 62.1 Cl·SO4-Na G20 T2-3X泉水 276.1 38.1 1 727.0 4 565.0 8 202.0 192.2 15.1 59.1 SO4·Cl-Na G04 J2x煤矿矿坑水 147.5 34.1 113.9 434.5 1 176.0 213.6 2.1 3.6 SO4·Cl-Ca·Na G19 J2x煤矿矿坑水 519.4 165.7 1 874.5 26 577.0 4 313.0 234.9 33.7 5.3 Cl-Na G10 J2x煤矿矿坑水 175.0 119.8 802.8 2 147.0 3 992.0 213.6 7.5 6.6 SO4·Cl-Na G05 J2x煤矿矿井水 105.6 31.0 74.8 181.1 806.9 205.0 1.5 8.6 SO4-Ca·Na G06 J2x煤矿矿井水 77.7 21.2 66.4 155.9 488.8 222.1 1.1 11.3 SO4-Ca·Na G12 J1b井水 53.3 25.7 92.0 156.2 551.3 256.3 1.2 18.8 SO4-Na·Ca G09 T2-3X井水 93.4 26.1 94.2 316.7 651.5 179.4 1.4 21.4 SO4·Cl-Ca·Na 注:C1d为下石炭统大哈拉军山组火山岩和火山碎屑岩;C2ysh为中石炭统伊什基里克组火山岩和火山碎屑岩;Cηγ为石炭系二长花岗岩;T2-3X为中上三叠统小泉沟群;J1b为下侏罗统八道湾组;J1s为下侏罗统三工河组;J2x为中侏罗统西山窑组;N2d为新近系上新统独山子组 -
[1] 潘蔚.伊犁盆地铀成矿时空分布特征与层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿找矿思路分析[J].铀矿地质, 2000, 16(1):19-25. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykdz200001004 [2] 刘红旭, 张晓, 丁波, 等.伊犁盆地南缘砂岩型铀矿成矿模式与找矿方向[J].铀矿地质, 2015, 31(1):198-205. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ykdz2015z1008 [3] 成建军, 郭丽超, 李书海.伊犁盆地南缘铀水文地球化学特征及地下水铀成矿作用[J].现代矿业, 2017, 33(3):73-76. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xdky201703015 [4] Langmuir D, Chatham J.Groundwater prospecting for sandstone-type uranium deposits:A preliminary comparison of the merits of mineral-solution equilibria, and single-element tracer methods[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1980, 13(2/3):201-219. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375674280900072 [5] Bhattacharyya A, Campbell K M, Kelly S D, et al.Biogenic non-crystalline U (IV)revealed as major component in uranium ore deposits[J].Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1):1-8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-016-0009-6 [6] Dai S, Yang J, Ward C R, et al.Geochemical and mineralogical evidence for a coal-hosted uranium deposit in the Yili Basin, Xinjiang, northwestern China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 70:1-30. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.03.010 [7] Wu B L, Liu C Y, Wang J Q.Basical characteristics of fluid geologic process of interlayer oxidation zone sandstone-type uranium deposit[J].Science in China, 2007, 50(2):185-194. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/60111X/2007z2/1000887577.html [8] 邢东旭, 康勇, 王冰, 等.伊犁盆地南缘洪海沟地区铀矿主要含矿含水层及水文地球化学特征[J].新疆地质, 2014, 32(2):240-243. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=xjdz201402020 [9] Miller A W, Rodriguez D R, Honeyman B D.Upscaling sorption/desorption processes in reactive transport models to describe metal/radionuclide transport:A critical review[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2010, 44(21):7996-8007. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20942399 [10] 焦养泉, 吴立群, 荣辉, 等.铀储层结构与成矿流场研究:揭示东胜砂岩型铀矿床成矿机理的一把钥匙[J].地质科技情报, 2012, 31(5):94-104. http://www.cqvip.com/QK/93477A/20125/43592580.html [11] 陈戴生, 王瑞英.伊犁盆地层间氧化带砂岩型铀矿成矿模式[J].铀矿地质, 1997, 13(6):327-335. http://qikan.cqvip.com/Qikan/Article/Detail?id=2857232 [12] 何忧, 荣辉, 黄琨, 等.伊犁盆地地下水水文地球化学特征与铀成矿条件分析[J].安全与环境工程, 2019, 26(1):7-13. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzktaq201901002 [13] 王勇, 陈正乐, 刘健, 等.伊犁盆地南部新构造特征及其对砂岩型铀矿的控制作用[J].大地构造与成矿学, 2006, 30(4):486-494. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ddgzyckx200604011 [14] 焦养泉, 吴立群, 杨琴.铀储层-砂岩型铀矿地质学的新概念[J].地质科技情报, 2007, 26(4):1-7. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzkjqb200704001 [15] Michel F A, Allen D M, Grant M B.Hydrogeochemistry and geothermal characteristics of the White Lake Basin, Southcentral British Columbia, Canada[J].Geothermics, 2002, 31(2):169-194. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6505(01)00009-8 [16] Min M, Peng X, Zhou X, et al.Hydrochemistry and isotope compositions of groundwater from the Shihongtan sandstone-hosted uranium deposit, Xinjiang, NW China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2007, 93(2):91-108. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=d6623a703bbdc8aa9c3489ce8b3d6b86 [17] Cowart J B, Osmond J K.Uranium isotopes in groundwater:Their use in prospecting for sandstone-type uranium deposits[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1977, 8(1/2):365-379. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0375674277900620 [18] Halpern J, Smith J.Kinetics of the oxidation of uranium (IV)by molecular oxygen in aqueous perchloric acid solution[J].Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 1956, 34(10):1419-1427. doi: 10.1139/v56-182 [19] Chapelle F H.The significance of microbial processes in hydrogeology and geochemistry[J].Hydrogeology Journal, 2000, 8(1):41-46. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=a9b313e71c8b6557b07e14dc19600110 [20] Hua B, Xu H F, Terry J, et al.Kinetics of uranium(VI) reduction by hydrogen sulfide in anoxic aqueous systems[J].Environmental Science & Technology, 2006, 40(15):4666-4671. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=179bc67a5f9f76272d9a1e4fc5369588 [21] 苗爱生, 陆琦, 刘惠芳, 等.鄂尔多斯砂岩型铀矿床古层间氧化带中铀石的产状和形成[J].地质科技情报, 2009, 28(4):51-58. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb200904009 [22] 苗爱生, 焦养泉, 常宝成, 等.鄂尔多斯盆地东北部东胜铀矿床古层间氧化带精细解剖[J].地质科技情报, 2010, 29(3):55-61. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=dzkjqb201003008 [23] Jiao Y, Wu L, Yang S, et al.Sedimentology of uranium reservoir:The exploration and production base of sandstone-type uranium deposits[M].Beijing:Geological Publishing House, 2006:248-265. [24] Wu L, Jiao Y, Roger M, et al.Sedimentological setting of sandstone-type uranium deposits in coal measures on the southwest margin of the Turpan-Hami Basin, China[J].Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36(2):223-237. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=622be5c226e4970a946edf18edebb275 -





 下载:
下载: