Diagenetic effect of mantle-derived CO2 charge to clay minerals in the Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin in South China Sea
-
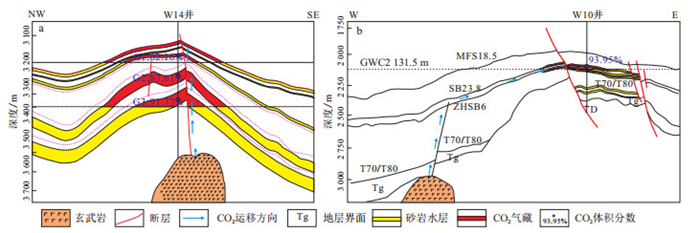
摘要: 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区油气勘探中钻遇大量高含量CO2气层,使得如何规避高CO2风险成为当前面临的挑战。通过工区充注CO2的储层砂岩黏土矿物X射线衍射(XRD)、流体包裹体显微测温和稀有气体同位素组成等分析,明确了幔源无机CO2的成因,并运用黏土矿物特征讨论高温幔源无机CO2充注的黏土矿物成岩响应:有序带倒转和大量自生高岭石的生成。依据CO2气井的XRD全定量分析数据剖面图将幔源无机CO2气层段的黏土矿物组合分为3类:Ⅰ类为I/S混层黏土矿物中S体积分数介于10%~25%之间,有序度处于R2~R3带,高岭石体积分数高;Ⅱ类为I/S混层黏土矿物中S体积分数介于10%~15%,有序度为R2~R3带,自生高岭石体积分数低;Ⅲ类为I/S混层黏土矿物中S体积分数介于50%~60%,有序度为R0带,高岭石体积分数低。总结出幔源CO2在珠江组和珠海组中存在2种运聚模式:一是幔源CO2通过与基性岩浆连通的深大断裂垂直向上运聚;二是垂直向上运移后通过连通砂体侧向长距离运聚。研究结果对珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区下一步油气勘探规避高含量CO2风险具有指导作用。Abstract: During petroleum exploration in the Baiyun-Liwan deep-water area of the Pearl River Mouth Basin (PRMB), South China Sea, a huge number of CO2 gas reservoirs has been met. Therefore, how to avoid the high CO2 risk has become a big challenge now. In this paper, the X-Ray diffraction (XRD) of clay minerals in the sandstone filled with CO2, microthermometry of fluid inclusions and isotopes of noble gas were used for analysis. The results show that the origin of inorganic CO2 is magmatic. The effects of mantle-derived CO2 on clay minerals are the inversion of clay mineral order degree and the formation of a largeamount of authigenic kaolinite. Moreover, the clay mineral assemblage was divided into three types based on the of XRD analysis data in CO2 wells. Finally, two patterns of CO2 migration and accumulation in the Zhujiang and Zhuhai Formations were summarized: (1) the mantle-derived CO2 migrates vertically upward through the deep faults which connected with the mafic igneous rocks, and (2) lateral long-distance migration through connecting sand bodies after vertical upward migration. These results have certain guiding significance for avoiding the risk of high CO2 in the future exploration in the deep-water area of PRMB, South China Sea.
-
图 2 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区天然气中3He/4He-δ13CCO2-PDB关系图(底图据文献[25])
Figure 2. Plot of 3He/4He-δ13CCO2-PDB of the natural gas samples in Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area, PRMB
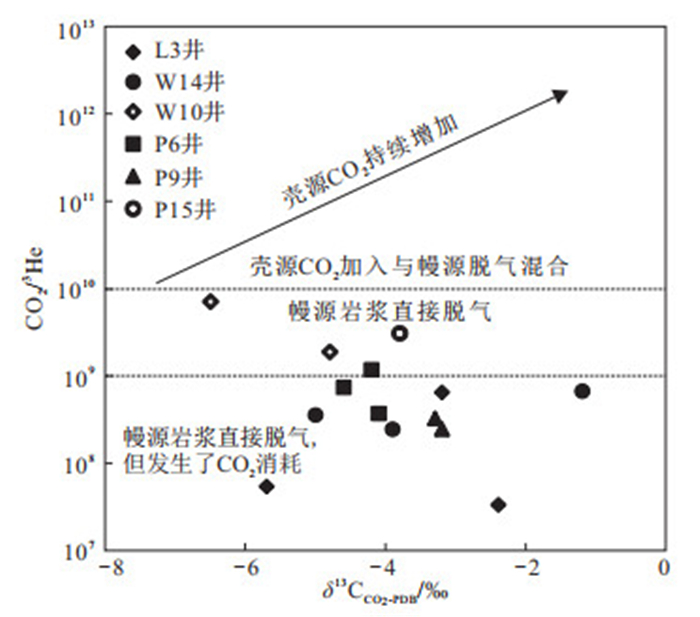
图 3 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区天然气CO2/3He-δ13CCO2-PDB关系图(底图据文献[25])
Figure 3. Plot of CO2/3He-δ13CCO2-PDB of the natural gas samples in Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area, PRMB
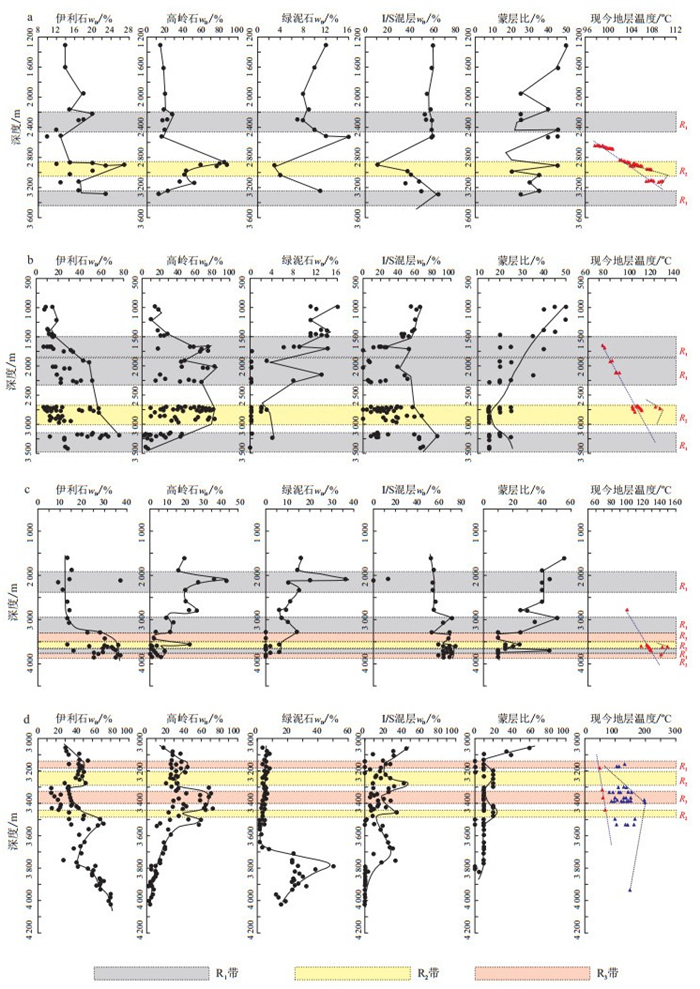
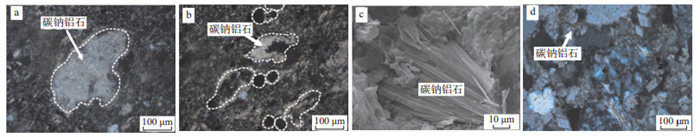
图 6 高含CO2井区单井XRD分析黏土矿物质量分数-深度剖面图
a.P5井,2 836.2~2 912 m为含CO2层段,φ(CO2)为14.00%~16.10%;b.P6、P7、P8井,2 733~2 903.5 m为含CO2层段,φ(CO2)为8.47%~9.00%;c.P11井,3 612~3 820 m为含CO2层段,φ(CO2)为7.67%~58.50%;d.W14井,3 184.9~3 189 m、3 321.2~3 370.1 m为含CO2层段,φ(CO2)分别为59.36%~62.16%、85.75%~92.41%
Figure 6. Cross plots of clay mineral contents-depth for the single well XRD in deepwater area
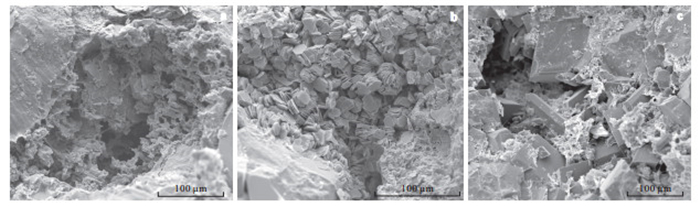
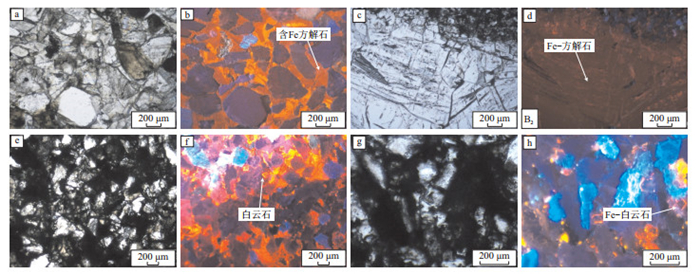
图 9 深水区砂岩粒间孔隙充填方解石、白云石和Fe-白云石胶结物的透射光、阴极光照片
a, b.P13井,3 372.6~3 372.75 m,粗砂岩,粒间孔隙充填大量发桔红色阴极光的含铁方解石胶结物;c, d.L2井,2 196.0~2 196.15 m,极细粉砂岩,充填暗棕色阴极光的铁方解石脉;e, f.L18井,3 440.59 m,细砂岩,粒间孔隙充填发桔黄色阴极光的含铁方解石胶结物和发桔黄色阴极光的粒状白云石,白云石多为菱形自形,可见环带结构;g, h.L11井,2 878 m,砂岩,粒间孔隙充填发暗棕色阴极光的粒状白云石,白云石多为菱形自形,可见环带结构
Figure 9. Transmission and cathodic photographs of intergranular pores of sandstone filled with calcite, dolomite and Fe-dolomite cement in deepwater area
图 10 白云-荔湾深水区温度-方解石胶结物δ18O关系图(底图据文献[7])
Figure 10. Scatter diagram between homogenization temperature and δ18O of aqueous inclusion in in the carbonte cements of Zhuhai and Zhujiang Formations in deepwater area
表 1 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区CO2及稀有气体同位素和体积分数分析结果
Table 1. Concentrations and isotopic of CO2 and rare gases in Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area, PRMB
井号 深度/m φ(CO2)/% δ13CCO2-PDB/‰ 3He/4He CO2/3He 幔源He贡献率/% L11 1 502.0 0.56 -2.4 2.17 3.36×107 26.94 L13 1 763.6 0.96 -5.7 2.22 5.41×107 27.57 L18 2 511.5 4.46 -3.2 1.14 6.48×108 14.04 W14 1 907.3 3.98 -4.1 2.18 3.72×108 27.07 W14 2 249.0 9.00 -4.2 2.18 1.18×109 27.07 W11 3 192.0 3.89 -4.6 1.21 7.42×108 14.91 P4 2 711~2 766 3.81 -3.3 1.70 3.27×108 21.05 P5 2 743~2 758 3.38 -3.2 1.76 2.45×108 21.80 P5 3 249.0 11.84 -3.8 1.30 3.08×109 16.04 P11 2 111.0 97.92 -4.8 5.90 1.88×109 73.65 P11 2 111.0 98.27 -6.5 6.59 7.10×109 82.31 P14 3 189.4 60.11 -5.0 6.92 3.57×108 86.42 P14 3 321.2 85.75 -3.9 6.51 2.46×108 81.30 L11 3 370.1 90.09 -1.2 6.86 6.70×108 85.76 注:取国际公认值空气标准:Ra=(1.40±0.03)×10-6;w(4He)=5.24×10-6;幔源He贡献率(%)=(R测-R壳)/(R幔-R壳),式中,R壳为壳源中3He/4He(R壳=0.02Ra);R测为测试样品中3He/4He值(R测=(8±1)Ra),Ra为大气中3He/4He值 表 2 白云-荔湾深水区流体包裹体均一温度及现今地层温度
Table 2. Homogenization temperature of fluid inclusions and current formation temperature in Baiyun-Liwan deepwater area
井号 深度/m 层位 CO2包裹体
均一温度
ThCO2/℃伴生盐水
包裹体均一
温度Th/℃现今地
层温度
T/℃L1 2 169~2 172 N1z 29.3 136.1 100.0 L11 2 883 N1z 27.7 112.9 103.6 L13 2 722 N1z 33.8 140.4 107.4 L18 3 791 E3z 32.5 170.3 162.4 L18 3 804.98 E3z 27.9 189.9 163.1 W14 3 385 E3z 31.4 194.7 165.8 W14 3 397 E3z 29.7 197.8 166.4 W11 3 270 E3z 29.3 210.4 192.3 P4 3 005 N1z 29.3 160.8 121.1 P5 2 838 N1z 30.7 130.3 104.9 P5 2 859 N1z 29.4 130.5 105.7 P11 3 367 N1z 29.5 167.2 134.4 P14 3 776.5 N1z 32.5 174.2 149.5 P14 3 765 N1z 29.8 187.0 149.1 P14 3 765 N1z 28.8 176.7 149.1 注:N1z.珠海组;E3z.珠江组 表 3 珠江口盆地白云-荔湾深水区自生高岭石含量、黏土矿物有序带及CO2稳定同位素统计表
Table 3. Data of authigenic kaolinite contents, S% and the orders in I/S mixed clay minerals, and natural gas components contents and stable carbon isotopic ratios of CO2
井号 深度/m 层位 岩性 高岭石
wB/%I/S中S
wB/%有序带 黏土矿物
组合类型CH4 CO2 N2 δ13C1-PDB/
‰δ13C2-PDB/
‰δ13C3-PDB/
‰δ13CnC4-PDB/
‰δ13CnC5-PDB/
‰δ13CCO2-PDB/
‰φB/% L4 2 725~2 748 N1z2 砂岩 76.80 10 R3 Ⅰ 88.660 3.570 0.33 -36.70 -26.85 -25.61 -25.01 -7.89 L16 2 372~2 374.5 N1z2 砂岩 23.70 25 R2 Ⅰ 89.44 2.52 0.98 -38.20 -28.40 -27.30 -27.00 -25.40 -8.40 L16 2 471~2 513.5 N1z2 砂岩 42.40 25 R2 Ⅰ 90.33 3.29 0.84 -37.10 -29.20 -26.40 -26.00 -24.90 -9.50 L20 2 976.5~2 990.28 N1z2 砂岩 43.30 25 R2 Ⅰ 87.50 3.98 0.48 -39.10 -29.10 -28.30 -27.60 -25.90 -9.10 L20 3 006.8~3 008.2 N1z2 砂岩 53.70 25 R2 Ⅰ 88.48 3.42 0.16 -39.00 -28.40 -27.70 -27.20 -26.00 -8.20 W14 3 184.9~3 189.4 N1z 砂岩 37.00 10 R3 Ⅰ 35.04 62.16 1.73 -51.10 -34.00 -30.10 -28.40 -4.80 W14 3 321.0~3 321.2 N1z 砂岩 34.00 10 R3 Ⅰ 12.29 87.61 0.00 -53.20 -34.90 -30.20 -27.70 -2.90 W14 3 354.3~3 370.1 E3z 砂岩 64.00 10 R3 Ⅰ 5.74 91.77 2.27 -52.90 -35.10 -30.40 -28.60 -3.20 P5 2 904~2 912 泥质细砂岩 77.00 10 R3 Ⅰ 5.29 2.69 91.70 -34.40 -28.50 -29.90 -7.20 P7 1 727~1 728.7 N1z1 中粗砂岩 67.50 25 R2 Ⅰ 87.70 1.57 4.33 -35.80 -25.40 -26.40 -8.40 P7 2 903~2 903.5 细砂岩 78.50 15 R2 Ⅰ 85.20 3.79 3.44 -36.70 -29.70 -28.90 -5.10 P6 1 907.3~1 917.0 粉-细砂岩 48.00 20 R2 Ⅰ 89.91 4.41 0 -38.10 -29.20 -27.90 -27.60 -27.40 -6.30 P6 2 249 N1h 粉-细砂岩 53.00 25 R2 Ⅰ 85.60 8.47 0 -36.80 -29.30 -28.20 -27.50 -27.60 -6.20 P9 2 711~2 726 N1z2 砂岩 52.70 15 R2 Ⅰ 88.58 4.10 0.57 -35.50 -28.80 -27.20 -26.70 -26.50 -4.50 P9 2 743~2 758 N1z2 砂岩 76.88 15 R2 Ⅰ 89.13 3.94 0.46 -36.90 -28.80 -27.70 -27.50 -27.30 -5.40 P13 3 281 N1z2 灰质细砂岩 24.00 20 R2 Ⅰ 84.37 7.41 0.50 -37.66 -28.96 -26.85 -26.16 0 -3.25 P13 3 313.5 N1z2 粉砂岩 38.00 20 R2 Ⅰ 88.03 4.63 0.07 -37.61 -29.10 -27.44 -26.64 0 -5.12 P13 3 329 N1z2 细砂岩 30.00 20 R2 Ⅰ 90.28 3.45 4.24 -37.24 -29.15 -27.09 -26.33 0 -4.82 P16 3 230~3 238.5 N1z2 细砂岩 73.75 15 R2 Ⅰ 78.09 14.56 0.11 -36.38 -28.07 -26.26 -26.65 -25.59 -4.22 P20 4 055.6~4 056.3 N1z2 粉砂岩 10.00 15 R2 Ⅰ 75.78 18.50 0.09 -35.60 -28.50 -26.90 -25.80 0 -2.50 P11 3 612~3 632.8 N1z2 细砂岩 0.00 15 R2 Ⅱ 80.00 13.80 0.43 -34.60 -27.70 -27.00 0 0 -2.50 P11 3 650~3 660 N1z2 细砂岩 1.00 15 R2 Ⅱ 78.80 13.80 0.61 -36.80 -28.60 -27.40 0 0 -4.70 P15 3 242~3 249 N1z 细砂岩 3.00 15 R2 Ⅱ 82.19 11.91 0.03 -35.90 -29.10 -27.80 -27.10 -26.60 -5.00 W10 2 111.5~2 116.5 E3z 砂岩 3.00 50~60 R0 Ⅲ 2.16 93.95 3.89 -35.71 -26.87 -23.77 0 0 -6.47 注:N1h为韩江组 表 4 W14井岩屑长石砂岩XRD分析结果[26]
Table 4. XRD measurement of debris-arkosic sandstones in Well W14
深度/m 层位 矿物wB/% 石英 钾长石 方解石 白云石 菱铁矿 黄铁矿 碳钠铝石 3 109~3 112 珠江组 29.0 1.4 1.4 27.8 5.7 - - 3 277~3 280 珠江组 41.2 1.9 - 5.3 0.9 3.0 0.3 3 331~3 334 珠江组 63.7 4.2 - 3.1 3.3 1.0 - 3 379~3 382 珠海组 73.9 1.9 - 1.2 3.7 1.5 - 3 475~3 478 珠海组 67.4 - - 0.8 3.1 0.9 0.8 3 646~3 649 恩平组 41.5 - 1.0 3.3 3.2 2.9 - 3 916~3 919 文昌组 44.6 2.7 13.9 3.8 - 0.4 - 注:“-”代表含量微少;样品测试在吉林大学测试科学实验中心完成 -
[1] Eberl D, Hower J. Kinetics of illite formation[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1976, 87(2): 1326-1330. http://bulletin.geoscienceworld.org/content/87/9/1326 [2] Yun J, Wu H, Feng Z, et al. CO2 gas emplacement age in the Songliao Basin: Insight from volcanic quartz 40Ar-39Ar stepwise crushing[J]. Science Bulletin, 2010, 55(17): 1795-1799. doi: 10.1007/s11434-010-3082-y [3] Bethke C M, Vergo N, Altaner S P. Pathways of smectite illitization[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1986, 34(2): 125-135. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1986.0340203 [4] Hoffman J, Hower J. Clay mineral assemblages as low grade metamorphic geothermometers: Application to the thrust faulted disturbed belt of Montana, U.S. A[M]. Oklahoma: SEPM Special Publications, 1979. [5] Hower J, Eslinger E V, Hower M E, et al. Mechanism of burial metamorphism of argillaceous sediment: 1. Mineralogical and chemical evidence[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1976, 87(5): 725-737. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1976)87<725:MOBMOA>2.0.CO;2 [6] Moore D M, Reynolds R C. X-ray diffraction and the identification and analysis of clay minerals[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 1989. [7] Davies G R, Smith L B. Structurally controlled hydrothermal dolomite reservoir facies: An overview[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2011, 90(11): 1641-1690. http://www.nrcresearchpress.com/servlet/linkout?suffix=rg11/ref11&dbid=16&doi=10.1139%2FE09-019&key=10.1306%2F05220605164 [8] 陈红汉, 米立军, 刘妍鷨, 等. 珠江口盆地深水区CO2成因、分布规律与风险带预测[J]. 石油学报, 2017, 38(2): 119-134. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201702001.htmChen H H, Mi L J, Liu Y H, et al. Genesis, distribution and risk belt prediction of CO2 in deep-water area in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2017, 38(2): 119-134(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201702001.htm [9] 张鑫, 陈红汉, 龙昭, 等. 泌阳凹陷北部缓坡带核桃园组油气运聚成藏过程[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 140-149. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003018.htmZhang X, Chen H H, Long Z, et al. Hydrocarbon migration and accumulation of Hetaoyuan Formation in the northern gentle slope of Biyang Depression[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 140-149(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003018.htm [10] 李智, 张志业, 何登发, 等. 南襄盆地泌阳凹陷与南阳凹陷油气地质特征类比及勘探启示[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 79-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202002009.htmLi Z, Zhang Z Y, He D F, et al. Comparison in petroleum geology between Biyang Depression and Nanyang Depression in Nanxiang Basin and its exploration significance[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 79-89(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202002009.htm [11] 刁慧, 邹玮, 李宁, 等. 东海盆地西湖凹陷武云亭构造油气来源与成藏模式[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(3): 110-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003015.htmDiao H, Zou W, Li N, et al. Hydrocarbon origin and reservoir forming model of Wuyunting structure in Xihu Depression, East China Sea Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(3): 110-119(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202003015.htm [12] 刘妍鷨, 陈红汉, 苏奥, 等. 从含油气检测来洞悉琼东南盆地东部发育始新统烃源岩的可能性[J]. 地球科学, 2016, 41(9): 1539-1547. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201609009.htmLiu Y H, Chen H H, Su A, et al. Eocene source rock determination in Qiongdongnan Basin, the South China Sea: a hydrocarbon detection perspective[J]. Earth Science, 2016, 41(9): 1539-1547(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201609009.htm [13] 任建业, 庞雄, 雷超, 等. 被动陆缘洋陆转换带和岩石圈伸展破裂过程分析及其对南海陆缘深水盆地研究的启示[J]. 地学前缘, 2015, 22(1): 102-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501011.htmRen J Y, Pang X, Lei C, et al. Ocean and continent transition in passive continental margins and analysis of lithospheric extension and breakup process: Implication for research of the deepwater basins in the continental margins of South China Sea[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2015, 22(1): 102-114(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201501011.htm [14] 米立军, 柳保军, 何敏, 等. 南海北部陆缘白云深水区油气地质特征与勘探方向[J]. 中国海上油气, 2016, 28(2): 10-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201602002.htmMi L J, Liu B J, He M, et al. Petroleum geology characteristics and exploration direction in Baiyun deep water area, northern continental margin of the South China Sea[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2016, 28(2): 10-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHSD201602002.htm [15] 李平鲁, 梁慧娴. 珠江口盆地新生代岩浆活动与盆地演化、油气聚集的关系[J]. 广东地质, 1994, 9(2): 23-24.Li P L, Liang H X. Relationship between Cenozoic magmatic activity and basin evolution and hydrocarbon accumulation in the Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Guangdong Geology, 1994, 9(2): 23-24(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 倪金龙, 夏斌, 刘海龄. 南海及邻区前中生代构造演化与东特提斯构造域[J]. 海洋地质动态, 2005, 21(10): 11-16. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200510002.htmNi J L, Xia B, Liu H L. Pre-Mesozoic tectonic evolution of the South China Sea and the East Tethys tectonic domain[J]. Marine Geology Letters, 2005, 21(10): 11-16(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDT200510002.htm [17] 张斌, 王璞珺, 张功成, 等. 珠-琼盆地新生界火山岩特征及其油气地质意义[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40(6): 657-665. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201306004.htmZhang B, Wang P J, Zhang G C, et al. Cenozoic volcanic rocks in the Pearl River Mouth and Southeast Hainan Basins of South China Sea and their implications for petroleum geology[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40(6): 657-665(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201306004.htm [18] 邵磊, 孟晓捷, 张功成, 等. 白云凹陷断裂特征对构造与沉积的控制作用[J]. 同济大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 41(9): 1435-1441. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2013.09.025Shao L, Meng X J, Zhang G C, et al. Feature of faults system and its influence on tectonic and sedimentary history of Baiyun Sag[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2013, 41(9): 1435-1441(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-374x.2013.09.025 [19] Sun Q, Cartwright J, Wu S, et al. 3D seismic interpretation of dissolution pipes in the South China Sea: Genesis by subsurface, fluid induced collapse[J]. Marine Geology, 2013, 337(3): 171-181. [20] Lollar B S, O'Nions R K, Ballentine C J. Helium and neon isotope systematics in carbon dioxide-rich and hydrocarbon-rich gas reservoirs[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(23): 5279-5290. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90311-5 [21] Hulston J R, Hilton D R, Kaplan I R. Helium and carbon isotope systematics of natural gases from Taranaki Basin, New Zealand[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 2001, 16(4): 419-436. doi: 10.1016/S0883-2927(00)00045-7 [22] Lupton J E. Terrestrial inert gases: Isotope tracer studies and clues to primordial components in the mantle[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1983, 11(1): 371-414. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ea.11.050183.002103 [23] Poreda R J, Jenden P D, Kaplan I R, et al. Mantle helium in Sacramento basin natural gas wells[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1986, 50(12): 2847-2853. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(86)90231-0 [24] Lollar B S, Ballentine C J, Onions R K. The fate of mantle-derived carbon in a continental sedimentary basin: Integration of C/He relationships and stable isotope signatures[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(11): 2295-2307. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00083-5 [25] Huang B, Tian H, Huang H. Origin and accumulation of CO2 and its natural displacement of oils in the continental margin basins, northern South China Sea[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(7): 1349-1369. doi: 10.1306/02091514125 [26] Li F, Li W. Petrological record of CO2 influx in the Dongying Sag, Bohai Bay Basin, NE China[J]. Applied Geochemistry. 2017, 84: 373-386. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2017.07.015 [27] Zhao S, Liu L, Liu N. Petrographic and stable isotopic evidences of CO2-induced alterations in sandstones in the Lishui sag, East China Sea Basin, China[J]. Applied Geochemistry. 2018, 90: 115-128. doi: 10.1016/j.apgeochem.2018.01.004 [28] 徐思萌. 含有孔虫泥质粉砂岩内片钠铝石纵向分布特征与成因[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2017.Xu S M. The vertical distribution characteristics and genesis of dawsonite in pelitic siltstone with foraminifers: a case studying in LWX well of the eastern South China Sea[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017(in Chinese with English abstract). [29] Hellevang H, Declercq J, Aagaard P. Why is Dawsonite Absent in CO2 Charged Reservoirs?[J]. Oil & Gas Science & Technology, 2011, 66(1): 119-135. [30] Stoessell R K. Regular Solution Site-Mixing Model for Chlorites[J]. Clays and Clay Minerals, 1984, 32(3): 205-212. doi: 10.1346/CCMN.1984.0320308 期刊类型引用(15)
1. 孙健,陈亮,马洪素,郑植. 完整极硬岩TBM施工辅助破岩方法研究现状及展望. 世界核地质科学. 2024(01): 141-163 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 金彤,徐振洋,王雪松,吴怡璇,郭连军. 旋转钻进过程中的破岩能耗特征分析. 矿业研究与开发. 2024(04): 228-236 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 李欣冉,饶珂嘉,苏贺,侯雨函,冯茂根,彭建宇,张凤鹏. 等离子冲击波作用下红砂岩的动态破裂行为试验与数值模拟研究. 有色金属(矿山部分). 2024(03): 170-177+185 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 郭军,米鑫程,冯国瑞,白锦文,文晓泽,朱林俊,王子,皇文博. 基于液电效应的高压电脉冲岩体致裂特征及机理. 煤炭学报. 2024(05): 2270-2282 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 常宏. 油气田开发中分支井压力稳定性的评估与优化. 石油和化工设备. 2024(08): 119-122 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 肖一标,段隆臣,李昌平,康积锋,李傲. 基于高压电脉冲破岩损伤模型的破岩过程研究. 地质科技通报. 2023(03): 323-330 .  本站查看
本站查看7. 祝效华,李瑞,刘伟吉,李枝林,陆灯云. 深层页岩气水平井高效破岩提速技术发展现状. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版). 2023(04): 1-18 .  百度学术
百度学术8. 刘晓丽,孙欢,董勤喜,熊炎林,KUMAR Nawnit,苏岩,周建军. 深埋引水隧洞极硬岩TBM掘进及辅助破岩技术. 清华大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(08): 1292-1301 .  百度学术
百度学术9. 林柏泉,张祥良. 等离子体致裂煤岩增透技术及研究进展. 矿业安全与环保. 2022(04): 12-21 .  百度学术
百度学术10. 马宁,金博,周鹏,钱阳,薛启龙. 基于COMSOL的高压放电破碎岩石仿真研究. 钻探工程. 2022(06): 62-70 .  百度学术
百度学术11. 杨扬,李昌平. 电脉冲破岩实验高压脉冲电源设计. 电力电子技术. 2021(03): 55-57 .  百度学术
百度学术12. 白丽丽,李铮,王营,闫铁,孙文峰,李沼萱,刘师成. 岩石孔隙性质对电脉冲破岩的影响规律. 特种油气藏. 2021(01): 148-153 .  百度学术
百度学术13. 孔二伟,李傲,曾石友,段隆臣,张锋,李昌平. 基于Selfrag高压电脉冲放电破岩试验的仿真模拟. 钻探工程. 2021(08): 40-46 .  百度学术
百度学术14. 梁丽,肖一标,李大鹏,段隆臣,张锋,李昌平. 高压电脉冲破岩试验装置的研制. 钻探工程. 2021(11): 76-82 .  百度学术
百度学术15. 吴敏干,刘毅,林福昌,刘思维,孙建军. 液电脉冲激波特性分析. 强激光与粒子束. 2020(04): 120-126 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(18)
-





 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术


