Numerical simulation of sedimentation in the Central Canyon of Lingshui area, Qiongdongnan Basin
-
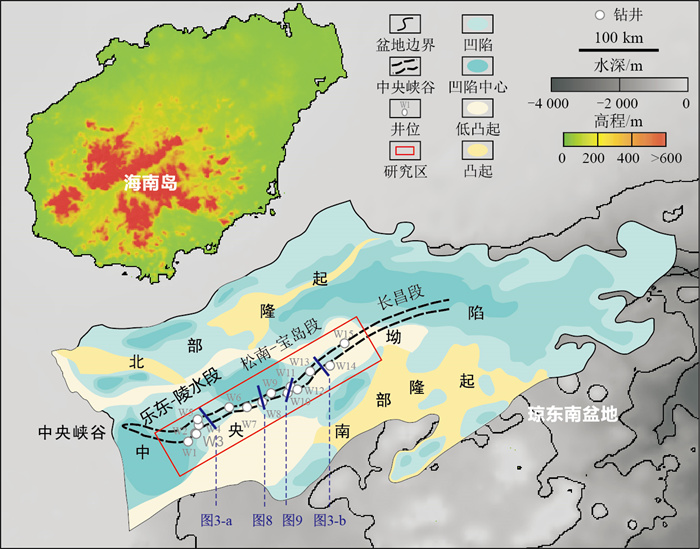
摘要: 深水峡谷是当今海洋油气勘探领域的研究热点。南海西北部琼东南盆地的中央峡谷已部署了多口深水钻井来勘探沉积充填的岩性油气藏,然而,由于这些探井数量相对有限、井间距离大以及地震资料分辨率较低,峡谷内砂体的叠复关系、边界接触关系以及沉积演化等问题尚不清楚,严重制约着储层空间分布与储层物性的精细刻画。对琼东南盆地陵水区中央峡谷开展了沉积数值模拟研究,根据研究区具体地质背景建立了地质模型和数学模型,通过流体动力学软件ANSYS FLUENT正演模拟了多个沉积期次和多套砂组在不同初始条件(如物源和入流速度)下的浊流沉积几何形态,包括砂体平面分布特征和隔夹层分布特征。模拟结果表明:峡谷平直段内,浊流受底床摩擦力的持续影响,流速降低且湍流强度减弱,使得较粗颗粒可沉降于底床,细颗粒可随浊流头部涡流悬浮;峡谷狭窄段内,浊流头部的湍流较强,侵蚀峡谷壁并使峡谷走向发生偏移,悬浮颗粒受离心力作用形成溢岸沉积;峡谷内砂体展布具有垂向分异性,砂体内部泥岩以夹层为主,厚度一般较小且横向连续性差。与现有地震、钻井资料的对比分析显示本次数值模拟结果具有有效性。本研究成果揭示了中央峡谷不同沉积期次和不同砂组的沉积水动力学过程,进而预测了砂体的空间展布特征,为储层物性预测提供了坚实支撑。Abstract: Deepwater canyon is now the focus of the research field of offshore oil and gas exploration.In the Qiongdongnan Basin of the northwestern South China Sea, several deepwater exploration boreholes have been deployed in the Central Canyon to reveal the lithologic hydrocarbon reservoir of sediment infill therein.However, due to the relatively limited number of these boreholes, the large distance between each borehole, as well as the low resolution of seismic data, the issues regarding the superposition relationship between different sandstone bodies within the canyon, their contact relationship with boundaries, and sedimentary evolution remain poorly understood, which severely hinder the delicate characterization of reservoir physical properties.This study investigates the Lingshui area of the Central Canyon from the perspective of numerical simulation of sedimentation.Geological and mathematical models are established based on the specific geological observations.The hydrodynamic simulation software ANSYS FLUENT is used for the forward modeling of multiple sedimentary stages and sandstone bodies with different initial conditions (e.g., provenance and inlet velocity) to reveal the geometry of modeled turbidite sedimentation, including the horizontal and vertical distribution patterns of sandstone bodies.The simulation results show that: Within the straight section of the canyon, the flow rate and intensity of the turbidity current gradually decrease due to the effect of substrate friction; Relatively coarse and fine particles can be deposited on the substrate and suspended along with the vortex at the head of the turbidity flow, respectively; Within the narrow section of the canyon, the turbulence of the head of the turbidity flow is strong enough to erode the canyon wall and also shift the strike of the canyon.Suspended particles can be affected by centrifugation force to form the overflow sedimentation; In addition, the results show a vertical heterogeneity of sandstone bodies distributed within the canyon: sandstone bodies are usually interlayered by mudstone that features a small thickness and poor lateral continuity.A comparison with the available seismic and borehole data shows the validity of the obtained simulation results.This study attempts to reveal the hydrodynamic processes in terms of different sedimentary stages and sandstone bodies, and then to predict the configuration of sandstone bodies that provides a favorable basis for reservoir prediction.
-
Key words:
- Qiongdongnan Basin /
- Lingshui area /
- Central Canyon /
- numerical simulation /
- sedimentary hydrodynamics
-
图 3 琼东南盆地中央峡谷地层格架及本次模拟的6个沉积期次(剖面位置如图 1所示)
Figure 3. Stratigraphic framework of the Central Canyon, Qiongdongnan Basin, showing the six sedimentary stages modeled in this study
图 8 W8井剖面砂组垂向分布特征(剖面位置如图 1所示)
Figure 8. Vertical distribution pattern of sandstone bodies in the profile of Borehole W8
图 9 W10-W11连井剖面砂组垂向分布特征(剖面位置如图 1所示)
Figure 9. Vertical distribution pattern of sandstone bodies in the profile of Boreholes W10-W11
表 1 沉积水动力学模拟主要参数
Table 1. Main parameters for the simulation of sedimentary hydrodynamics
参数 期次1 期次2 期次3 期次4 期次5 期次6 模型长度/m 155 152 152 152 152 152 模型宽度/m 55 50 60 50 50 50 网格最大歪斜度 0.941 01 0.908 78 0.733 68 0.672 31 0.691 16 0.528 31 砂泥相进口速度/(m·s-1) ≈1.5 ≈1 ≈3.5 ≈5 ≈3 ≈6 砂相颗粒直径①/mm 0.047 0.070 0.042 0.050 0.043 0.040 泥相颗粒直径/mm 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 砂泥比② 11%∶9% 11%∶9% 14.6%∶5.4% 14%∶6% 4%∶16% 8%∶12% 海水黏度/(kg·m-1·s-1) 0.001 砂相颗粒黏度/(kg·m-1·s-1) <0.01 泥相颗粒黏度/(kg·m-1·s-1) 0.01 海水密度/(kg·m-3) 998.2 砂相颗粒密度/(kg·m-3) 2 680 泥相颗粒密度/(kg·m-3) 2 720 底面粗糙系数 0.8 底面粗糙高度/mm 与砂相颗粒粒径相同 海水热导率/(W·m-1·K-1) 0.6 海水相对分子质量/(kg·kg-1·mol-1) 18 颗粒热导率/(W·m-1·K-1) 0.024 2 L-J特征长度/(10-8 m) 3.711 L-J能量参数/K 78.6 注:①砂相颗粒粒径为一个沉积期次内岩心、岩屑所测粒度值的加权平均值;②浊流颗粒体积分数一般小于20%;这里将测井资料统计所得砂泥占比进行分配,取20%作为砂泥体积分数之和的上限 -
[1] Carter R. The nature and evolution of deep-sea channel systems[J]. Basin Research, 1988, 1(1): 41-54. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2117.1988.tb00004.x [2] Clark J D, Pickering K T. Architectural elements, and growth patterns of submarine channels: Application to hydrocarbon exploration[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1996, 80(2): 194-220. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/255037078_Architectural_elements_and_growth_patterns_of_submarine_channels_Application_to_hydrocarbon_exploration [3] Posamentier H W, Kolla V. Seismic geomorphology, and stratigraphy of depositional elements in deep-water settings[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2003, 73(3): 367-388. doi: 10.1306/111302730367 [4] Deptuck M E, Sylvester Z, Pirmez C, et al. Migration-aggradation history and 3-D seismic geomorphology of submarine channels in the Pleistocene Benin-major Canyon, western Niger Delta slope[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2007, 24(6/9): 406-433. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/s0264817207000372 [5] Mayall M, Jones E, Casey M. Turbidite channel reservoirs: Key elements in facies prediction and effective development[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(8): 821-841. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2006.08.001 [6] 周蒂, 孙珍, 陈汉宗. 世界著名深水油气盆地的构造特征及对我国南海北部深水油气勘探的启示[J]. 地球科学进展, 2007, 22(6): 561-572. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.06.002Zhou D, Sun Z, Chen H Z, Tectonic features of world's major deep-water oil/gas fields and their enlightenment to deep-water exploration in northern South China Sea[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2007, 22(6): 561-572(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2007.06.002 [7] Antobreh A A, Krastel S. Morphology, seismic characteristics and development of Cap Timiris Canyon, offshore Mauritania: A newly discovered canyon preserved-off a major arid climatic region[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2006, 23(1): 37-59. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2005.06.003 [8] Piper D J, Shaw J, Skene K I. Stratigraphic and sedimentological evidence for late Wisconsinan sub-glacial outburst floods to Laurentian Fan[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2007, 246(1): 101-119. doi: 10.1016/j.palaeo.2006.10.029 [9] Yuan S Q, Lue F L, Wu S G, et al. Seismic stratigraphy of the Qiongdongnan deep sea channel system, northwest South China Sea[J]. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2009, 27(2): 250-259. doi: 10.1007/s00343-009-9177-0 [10] 林畅松, 刘景彦, 蔡世祥, 等. 莺-琼盆地大型下切谷和海底重力流体系的沉积构成和发育背景[J]. 科学通报, 2001, 46(1): 69-72. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.01.018Lin C S, Liu J Y, Cai S X, et al. Depositional architecture and developing settings of large-scale incised valley and submarine gravity flow systems in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins, South China Sea[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2001, 46(1): 69-72(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.01.018 [11] 苏明, 张成, 解习农, 等. 深水峡谷体系控制因素分析: 以南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系为例[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2014, 44(8): 1807-1820. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201408019.htmSu M, Zhang C, Xie X N, et al. Controlling factors on the submarine canyon system: A case study of the central canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 2014, 44(8): 1807-1820(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201408019.htm [12] 许怀智, 蔡东升, 孙志鹏, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷沉积充填特征及油气地质意义[J]. 地质学报, 2012, 86(4): 641-650. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.010Xu H Z, Cai D S, Sun Z P, et al. Filling characters of central submarine canyon of Qiongdongnan Basin and its significance of petroleum geology[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2012, 86(4): 641-650(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2012.04.010 [13] 张道军, 王亚辉, 王振峰, 等. 琼东南盆地深水区中央峡谷沉积微相特征[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6): 1114-1121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306019.htmZhang D J, Wang Y H, Wang Z F, et al. characteristics of sedimentary microfacies in the central canyon within the deep-water area, Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 1114-1121(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306019.htm [14] Gong C, Wang Y, Zhu W, et al. The central submarine canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northwestern South China Sea: Architecture, sequence stratigraphy, and depositional processes[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2011, 28(9): 1690-1702. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2011.06.005 [15] 李华, 何幼斌. 深水重力流水道沉积研究进展[J]. 古地理学报, 2020, 22(1): 161-174. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202001010.htmLi H, He Y B. Research progress on deepwater gravity flow channel deposit[J]. Journal of Paleogeography, 2020, 22(1): 161-174(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX202001010.htm [16] 何家雄, 刘海龄, 姚永坚, 等. 南海北部边缘盆地油气地质及资源前景[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 2008.He J X, Liu H L, Yao Y J, et al. Petroleum geology and resource prospects in the northern marginal basin of the South China Sea[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 2008(in Chinese). [17] Wang P, Li Q. The South China Sea: Paleoceanography and sedimentology[M]. Netherlands: Springer, 2009. [18] Su M, Xie X N, Xie Y, et al. The segmentations and the significances of the central canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2014, 79: 552-563. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.038 [19] 苏明, 解习农, 王振峰, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系沉积演化[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(3): 467-478. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201303008.htmSu M, Xie X N, Wang Z F, et al. Sedimentary evolution of the central canyon system in Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(3): 467-478(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201303008.htm [20] Cao L C, Jiang T, Wang Z F, et al. Provenance of Upper Miocene sediments in the Yinggehai and Qiongdongnan Basins, northwestern South China Sea: Evidence from REE, heavy minerals and zircon U-Pb ages[J]. Marine Geology, 2015, 361: 136-146. doi: 10.1016/j.margeo.2015.01.007 [21] 梁超. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷乐东-宝岛段充填结构及储层差异性[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2020.Liang C. Depositional architecture and reservoir differences in the Ledong-Baodao segments of the central canyon in the Qiongdongnan Basin[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences (Wuhan), 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [22] 王杨君, 尹太举, 邓智浩, 等. 水动力数值模拟的河控三角洲分支河道演化研究[J]. 地质科技情报, 2016, 35(1): 44-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201601007.htmWang Y J, Yin T J, Deng Z H, et al. Terminal distributary channels in fluvial-dominated delta systems from numerical simulation of hydrodynamics[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2016, 35(1): 44-52(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201601007.htm [23] 朱红钧. ANSYS 15.0几何建模与网格划分实战指南[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2014.Zhu H J. ANSYS 15.0 geometry modeling and meshing guide[M]. Beijing: Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2014(in Chinese). [24] Anderson J D, Degrez G, Dick E, et al. Computational fluid dynamics: An introduction[M]. New York: Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. [25] 崔书岳, 康志江, 邸元. 基于多相流模型的缝洞型油藏数值模拟软件研制与应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 97-104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905010.htmCui S Y, Kang Z J, Di Y. Development and application of numerical simulation software platform for fractured-cave reservoir based on multiphase flow model[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 97-104(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905010.htm [26] 甘泉. 远源细粒辫状河心滩坝演化与河流分叉的交互沉积过程: 现代沉积启示与数值模拟分析[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(1): 14-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101002.htmGan Q. Interaction and sedimentary process between the evolution of the bar and bifurcation of the river in the far-source fine-grained braided river: Numerical simulation analysis inspired by modern deposition[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(1): 14-26(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202101002.htm [27] 姜涛, 解习农, 汤苏林. 浊流形成条件的水动力学模拟及其在储层预测方面的作用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2005, 24(2): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200502001.htmJiang T, Xie X N, Tang S L. Hydrodynamic simulation of turbidity and its application for reservoir prediction[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2005, 24(2): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ200502001.htm [28] 唐家鹏. ANSYS FLUENT 16.0超级学习手册[M]. 北京: 人民邮电出版社, 2016.Tang J P. ANSYS FLUENT 16.0 super learning manual[M]. Beijing: Posts and Telecommunications Press, 2016(in Chinese). [29] Huang H Q, Imran J, Pirmez C. Numerical model of turbidity currents with a deforming bottom boundary[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering, 2005, 131(4): 283-293. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9429(2005)131:4(283) [30] 王振峰. 深水重要油气储层: 琼东南盆地中央峡谷体系[J]. 沉积学报, 2012, 30(4): 646-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201204004.htmWang Z F. Important deepwater hydrocarbon reservoirs: The central canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2012, 30(4): 646-653(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201204004.htm [31] 姜涛, 解习农, 汤苏林, 等. 浊流成因海底沉积波形成机理及其数值模拟[J]. 科学通报, 2007, 52(16): 1945-1950. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200716017.htmJiang T, Xie X N, Tang S L, et al. Numerical simulation on the evolution of sediment waves caused by turbidity currents[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2007, 52(16): 2429-2434(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200716017.htm [32] 陈麒玉, 刘刚, 何珍文, 等. 面向地质大数据的结构-属性一体化三维地质建模技术现状与展望[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 51-58. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202004007.htmChen Q Y, Liu G, He Z W, et al. Current situation and prospect of structure-attribute integrated 3D geological modeling technology for geological big data[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 51-58(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ202004007.htm [33] 黄璐, 张家年, 吴昊雨, 等. 弯曲海底峡谷中浊流的三维流动及沉积的初步研究[J]. 沉积学报, 2013, 31(6): 1001-1007. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306006.htmHuang L, Zhang J N, Wu H Y, et al. Preliminary study of three-dimensional flow and deposition of turbidity currents in sinuous submarine canyons[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2013, 31(6): 1001-1007(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201306006.htm [34] 李超, 陈国俊, 沈怀磊, 等. 琼东南盆地中央峡谷沉积充填特征与储层分布规律[J]. 石油学报, 2013, 34(增刊2): 74-82. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S2010.htmLi C, Chen G J, Shen H L, et al. Depositional filling and reservoir distribution patterns of the central canyon in Qiongdongnan Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(S2): 74-82(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2013S2010.htm [35] 张道军, 王亚辉, 赵鹏肖, 等. 南海北部琼东南盆地陵水段峡谷沉积建造及勘探意义[J]. 海洋学报, 2015, 2(2): 25-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201502003.htmZhang D J, Wang Y H, Zhao P X, et al. Sedimentary formation and exploration significance of the Lingshui canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin, northern South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 2(2): 25-35(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SEAC201502003.htm [36] 解习农, 孙志鹏, 张道军, 等. 琼东南盆地深水峡谷体系沉积充填及有利储层预测[C]//第十七届中国科协年会论文集. 广州: [出版社不详], 2015: 1-8.Xie X N, Sun Z P, Zhang D J, et al. Depositional architectures and reservoir prediction of central canyon system in the Qiongdongnan Basin[C]//The 17th China Association for Science Annual Conference Proceedings. Guangzhou: [s. n. ], 2015: 1-8(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: