Reservoir control of tight sandstone provenance system in Xujiahe Formation, Sichuan Basin
-
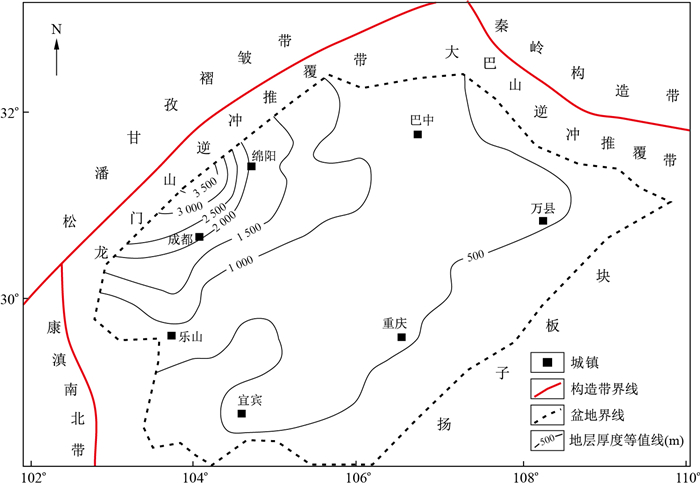
摘要: 为明确四川盆地须家河组致密砂岩物源特征及控储作用,运用储层岩石学测试和镜下分析,研究了物源与储层发育的关系及分布,探讨了物源体系的控制因素。研究结果表明,四川盆地须家河组储层具有成分成熟度较低、物性差异性强、以中-细粒为主、主要为溶蚀孔隙和成岩效应存在两面性5个基本特征;物源控制了储层岩石类型的发育范围,平面展布存在差异性,其可溶矿物组分及含量亦有所不同,导致各地区孔隙发育及规模有所不同;西部龙门山和东北部大巴山是须家河组的主要供源区,前者表现为碳酸盐岩岩屑含量相对较高,后者表现为火山岩岩屑含量相对较高。不同时期造山活动强度的阶段性变化使得物源供应强度及类型也随之变化,储层岩石组分差异分化,进而控制储层垂向非均质性。研究成果可以为该区下一步的油气精细勘探提供借鉴。Abstract: In order to clarify the provenance characteristics and reservoir control of tight sandstone in Xujiahe Formation of Sichuan Basin, by means of reservoir petrology test and microscopic analysis, the relationship and distribution between provenance and reservoir development are studied, and the controlling factors of provenance system are discussed.The results show that the Xujiahe Formation reservoir in Sichuan Basin has five basic characteristics: low composition maturity, strong physical property difference, mainly medium fine grain, mainly dissolution pores and two sides of diagenetic effect; the provenance controls the development range of reservoir rock types, the plane distribution is different, and the composition and content of soluble minerals are also different, which leads to different porosity Longmenshan in the West and Dabashan in the Northeast are the main source areas of Xujiahe Formation.The former shows relatively high content of carbonate cuttings, while the latter shows relatively high content of volcanic cuttings.The stage change of orogenic activity intensity in different periods leads to the change of provenance supply intensity and types, the differentiation of reservoir rock components, and then controls the vertical heterogeneity of reservoir.The research results can provide reference for the next fine oil and gas exploration in this area.
-
Key words:
- Sichuan Basin /
- Xujiahe Formation /
- provenance system /
- tight sandstone /
- reservoir control
-
图 3 须家河组储层镜下特征
a.S1,4 828~4 830 m,须二段,残余粒间孔,(-);b.S2,4 623~4 626 m,须五段,岩屑砂岩中的构造裂缝,(-);c.S3,4 740~4 745 m,须二段,云母被压变形,扫描电镜;d.S4,4 605~4 609 m,须二段,石英颗粒边缘次生加大,阴极发光;e.S5,4 612~4 615 m,须二段,岩屑砂岩中的长石沿解理缝被溶蚀,长石粒内溶孔,(-);f.S6,4 621~4 624 m,须二段,砂岩中的填隙物被溶蚀,粒间溶孔,扫描电镜;g.S7,4 734~4 738 m,须二段,石英砂岩中的颗粒微裂缝、构造裂缝,变质岩岩屑被溶蚀,粒内溶孔,(-);h.S8,4 098.7 m,须三段,岩(钙)屑砂岩,岩屑多为碳酸盐岩岩屑,(+);i.S9,4 701~4 705 m,须四段,砂砾岩中的碳酸盐岩砾石,(-)
Figure 3. Microscopic characteristics of the Xujiahe Formation reservoir
图 4 须家河组二段孔隙类型分布图(据文献[14]修改)
Figure 4. Distribution of pore types in the second member of the Xujiahe Formation
-
[1] 孙玮, 刘树根, 曹俊兴, 等. 四川叠合盆地西部中北段深层-超深层海相大型气田形成条件分析[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(4): 1171-1188. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201704012.htmSun W, Liu S G, Cao J X, et al. Analysis on the formation conditions of large-scale marine deep and super-deep strata gas fields in the middle-northern segments of western Sichuan Superimposed Basin, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(4): 1171-1188(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201704012.htm [2] 朱童, 王鹏, 沈忠民, 等. 四川盆地陆相油型气分布、成因及来源[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 137-144. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502020.htmZhu T, Wang P, Shen Z M, et al. Distribution, origin and source of terrestrial oil-type gas in Sichuan Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 137-144(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502020.htm [3] He D F, Ma Y S, Li Y Q, et al. New directions in an established gas play: Promising dolomite reservoirs in the Middle Triassic Leikoupo Formation of the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2019, 103(1): 1-29. doi: 10.1306/05111816502 [4] Liu Y F, Qiu N S, Yao Q Y, et al. Distribution, origin and evolution of the Upper Triassic overpressures in the central portion of the Sichuan Basin, SW China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2016, 146(10): 1116-1129. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039516430010_80b9.html [5] 汪泽成, 赵文智, 胡素云, 等. 克拉通盆地构造分异对大油气田形成的控制作用: 以四川盆地震旦系-三叠系为例[J]. 天然气工业, 2017, 37(1): 9-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201701003.htmWang Z C, Zhao W Z, Hu S Y, et al. Control of tectonic differentiation on the formation of large oil and gas fields in craton basins: A case study of Sinian-Triassic of the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2017, 37(1): 9-23(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201701003.htm [6] 冯增昭, 鲍志东, 李尚武. 从岩相古地理论中国南方中下三叠统油气潜景[J]. 石油大学学报: 自然科学版, 1997, 21(3): 3-8. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX703.000.htmFeng Z Z, Bao Z D, Li S W. Potential of oil and gas of the Middle and Lower Triassic of South China from the viewpoint of lithofacies paleogeography[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum, 1997, 21(3): 3-8(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX703.000.htm [7] 周家云, 龚大兴, 李萌. 四川盆地三叠纪蒸发岩特征、盐盆迁移及其构造控制[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(11): 1945-1952. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201511006.htmZhou J Y, Gong D X, Li M. The characteristic of evaporite, migration of salt basins and its tectonic control in Triassic Sichuan Basin[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(11): 1945-1952(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201511006.htm [8] Xu C M, Gehenn J M, Zhao D H, et al. The fluvial and lacustrine sedimentary systems and stratigraphic correlation in the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2015, 99(11): 2023-2041. doi: 10.1306/07061514236 [9] Plesch A, Shaw J H, Kronman D. Mechanics of low-relief detachment folding in the Bajiaochang Field, Sichuan Basin, China[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(11): 1559-1575. doi: 10.1306/06200706072 [10] Zeng L B. Microfracturing in the Upper Triassic Sichuan Basin tight-gas sandstones: Tectonic, overpressure, and diagenetic origins[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2010, 94(12): 1811-1825. doi: 10.1306/06301009191 [11] 林小兵, 刘莉萍, 田景春, 等. 川西坳陷中部须家河组五段致密砂岩储层特征及主控因素[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 2014, 35(2): 224-230. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201402010.htmLin X B, Liu L P, Tian J C, et al. Characteristics and controlling factors of tight sandstone reservoirs in the 5th Member of Xujiahe Formation in the central of Western Sichuan Depression[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2014, 35(2): 224-230(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYYT201402010.htm [12] 余瑜, 林良彪, 高健, 等. Q型聚类分析在四川盆地南部上三叠统须二段成岩相研究中的应用[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(2): 133-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201702017.htmYu Y, Lin L B, Gao J, et al. Application of Q type cluster analysis in the study of quantitative diagenetic facies of Member 2 of Xujiahe Formation in Southern Sichuan[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(2): 133-140(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201702017.htm [13] 杨光, 李国辉, 李楠, 等. 四川盆地多层系油气成藏特征与富集规律[J]. 天然气工业, 2016, 36(11): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201611002.htmYang G, Li G H, Li N, et al. Hydrocarbon accumulation characteristics and enrichment laws of multi-layered reservoirs in the Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2016, 36(11): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201611002.htm [14] 张浩然, 姜华, 陈志勇, 等. 四川盆地及周缘地区加里东运动幕次研究现状综述[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 118-126. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10057.shtmlZhang H R, Jiang H, Chen Z Y, et al. A review of the research status of Caledonian movement stages in Sichuan Basin and surrounding areas[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 118-126(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10057.shtml [15] Liu Y F, Qiu N S, Xie Z Y, et al. Overpressure compartments in the central paleo-uplift, Sichuan Basin, Southwest China[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science & Engineering, 2016, 100(5): 867-888. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1875510015302201/pdfft?md5=5604f9152053212759c03ed7b085f8aa&pid=1-s2.0-S1875510015302201-main.pdf [16] 岳勇, 陈孝红, 张国涛, 等. 宜昌斜坡区南华系-震旦系断坳结构发现及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2): 1-9. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9969.shtmlYue Y, Chen X H, Zhang G T, et al. Discovery and geological significance of Nanhua Sinian fault-depression, Yichang slope[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(2): 1-9(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9969.shtml [17] 余世花. 四川盆地西部晚三叠世须家河组物源分析及其构造意义[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2016.Yu S H. Provenance analysis of Late Triassic Xujiahe Formation in western Sichuan Basin and its tectonic significance[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [18] Wan T F, Wang Y M, Liu J L. Detachments and magmatic source depth in lithosphere of Eastern China during Yanshanian and Sichuanian Stages[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2008, 15(3): 1-35. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035535009010_5330.html [19] 施振生, 王秀芹, 吴长江. 四川盆地上三叠统须家河组重矿物特征及物源区意义[J]. 天然气地球科学, 2011, 22(4): 619-627. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201104009.htmShi Z S, Wang X Q, Wu C J. The heavy minerals and provenances of the Upper Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2011, 22(4): 619-627(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TDKX201104009.htm [20] 张连进, 黄家强, 罗强, 等. 川西北前陆双鱼石地区砂箱物理模拟及其油气地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2021, 40(2): 156-166. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10126.shtmlZhang L J, Huang J Q, Luo Q, et al. Analogue experiments for the Shuangyushi area in the northwestern Sichuan Foreland Basin and their implications[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2021, 40(2): 156-166(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10126.shtml [21] 王丽宁, 陈竹新, 李本亮, 等. 龙门山冲断带北段构造解析及有利区带预测[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2014, 41(5): 539-545. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201405005.htmWang L N, Chen Z X, Li B L, et al. Structural characteristics of the northern Longmenshan fold-thrust belt and the favorable exploration areas, Sichuan Basin, Southwest China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2014, 41(5): 539-545(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201405005.htm -





 下载:
下载: