Effect of long-term immersion in static water on the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of sliding zone soil in the Three Gorges Reservoir area
-
摘要:
三峡水库蓄水使得库岸大量土体长期处于浸泡状态,导致土体软化从而诱发滑坡失稳。为研究长期浸泡对滑坡土体物理-化学-力学性质的影响,以马家沟滑坡原状滑带土为对象开展了浸泡软化试验,通过比较不同浸泡时间滑带土的粒度分布、界限含水率、化学与矿物成分、剪切特性等特征,探讨了滑带土浸泡软化机理。研究结果表明:浸泡过程中滑带土中Ca2+、Mg2+等离子流失较多,但矿物成分无变化;浸泡后滑带土出现阶段性粒度细化现象,液塑限和塑性指数均随黏粒含量增加而增大;随着浸泡时间增加,滑带土应力应变关系在低法向应力下由强软化型变为弱软化型,在高法向应力下由软化型变为硬化型;滑带土抗剪强度参数随着浸泡时间增加呈指数形式降低,黏聚力c降低程度大于内摩擦角φ。研究成果可以为水库滑坡稳定性评价提供理论依据。
Abstract:The impoundment of the Three Gorges Reservoir has caused a large amount of soil on the bank to be immersed for a long time, which may cause the soil softened and induce instability of landslide.In order to study the effect of long-term immersion on the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of the landslide soil, the immersion softening test is carried out on the undisturbed sliding zone soil of Majiagou landslide.By comparing the particle size distribution, limit moisture content, the characteristics of chemical and mineral composition, shear characteristics, etc., this paper discusses the immersion softening mechanism of sliding zone soil.The results show that ions, such as Ca2+, Mg2+ in the sliding zone soil are largely lost during the immersion process, but the mineral composition does not change.After the immersion, the sliding zone soil appears staged particle size refinement, with which the liquid limit, plastic limit and plasticity index increase.As the immersion time increases, the stress-strain relationship of the sliding zone soil changes from a strong softening type to a weakly softening type under low normal stress, and from a softening type to a hardening type under high normal stress.The shear strength parameters decrease exponentially with the increase of immersion time, and the decrease of cohesion is greater than internal friction angle.The research results can provide a theoretical basis for the stability evaluation of reservoir landslide.
-
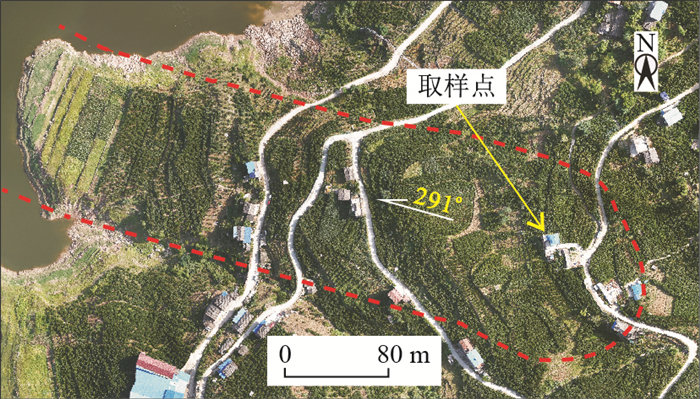
图 1 马家沟滑坡全貌图[1]
Figure 1. Boundary of the Majiagou landslide
图 2 马家沟滑坡剖面图[2]
Figure 2. Profile of the Majiagou landslide
表 1 滑带土基本物理力学参数
Table 1. Physical properties of sliding zone soil
干密度ρd/(g·cm-3) 天然含水率ω/% 相对密度Gs 塑限ωP/% 液限ωL/% 1.97 15.42 2.62 16.03 29.76 表 2 不同浸泡时间上清液所含阳离子及pH(浸泡时间0 d为去离子水)
Table 2. Cationic and pH of supernatant with different durations of immersion
浸泡时间/d Ag+ Ba2+ Ca2+ K+ Mg2+ Na+ Si pH ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% ρB/(mg·L-1) 占比/% 0 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 4.69 98.12 0.07 1.46 0.02 0.42 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 7.18 1 0.05 0.33 0.06 0.39 9.62 62.88 0.65 4.25 0.96 6.27 2.27 14.84 1.69 11.05 7.34 4 0.07 0.24 0.09 0.31 17.00 58.95 1.12 3.88 1.70 5.89 5.89 20.42 2.97 10.30 7.26 7 0.01 0.04 0.09 0.33 18.78 68.99 0.48 1.76 1.95 7.16 3.74 13.74 2.17 7.97 7.44 10 0.05 0.14 0.12 0.34 23.81 68.07 0.65 1.86 2.43 6.95 4.92 14.07 3.00 8.58 6.71 14 0.05 0.13 0.18 0.46 26.35 67.43 0.86 2.20 2.69 6.88 5.56 14.23 3.39 8.67 7.59 18 0.02 0.05 0.18 0.44 27.53 66.98 1.04 2.53 2.89 7.03 6.05 14.72 3.39 8.25 6.94 24 0.01 0.02 0.20 0.48 29.08 69.82 0.76 1.82 3.05 7.32 5.59 13.42 2.96 7.11 7.14 30 0.03 0.07 0.21 0.48 30.22 68.37 0.89 2.01 3.28 7.42 6.10 13.80 3.47 7.85 6.68 表 3 不同浸泡时间滑带土矿物成分
Table 3. Mineral composition of sliding zone soil with different durations of immersion
浸泡时间/d 方解石 蒙脱石 绿泥石 伊利石 高岭石 石英 长石 wB/% 0 7.41 26.74 5.26 28.32 6.27 13.44 12.56 1 8.04 26.22 6.84 27.35 6.84 14.89 9.83 4 5.42 27.76 4.66 28.65 6.75 12.07 14.69 7 6.91 25.98 5.50 29.63 6.71 16.70 8.57 10 7.54 25.61 6.08 25.28 5.17 19.98 10.34 14 5.78 25.08 3.67 27.18 3.67 20.19 14.43 18 6.25 25.61 8.45 20.20 8.45 20.89 10.14 24 8.71 27.76 9.00 27.29 3.03 14.92 9.30 30 8.76 27.92 9.44 26.50 3.05 15.01 9.33 表 4 地下水水质分析
Table 4. Quality analysis of the groundwater
水类型 离子成分ρB/(mg·L-1) pH 含盐量ρB/
(mg·L-1)Ca2+ Mg+ Na+ K+ Cl- SO42- HCO3- 地下水 67.22 8.51 7.84 1.85 14.18 3.84 249.57 7.50 360.17 表 5 化学反应方程式
Table 5. Chemical reaction equation
现象 化学方程式 胶结物溶解 CaCO3+CO2+H2O→Ca2++HCO3-
MgCO3+CO2+H2O→Mg2++HCO3-离子交换 土粒-Ca2++2Na+→土粒-2Na++Ca2+
土粒-Ca2++2K+→土粒-2K++Ca2+
蒙脱石-Ca2++2H+→蒙脱石-2H2++Ca2+表 6 不同浸泡时间滑带土抗剪强度参数
Table 6. Shear strength parameters of sliding zone soil with different durations of immersion
浸泡时间/d 黏聚力c/kPa 内摩擦角φ/(°) 0 75.46 19.34 1 71.85 18.58 4 66.28 17.66 7 59.30 16.44 10 57.10 15.98 14 55.45 15.75 18 54.65 15.71 24 53.97 15.63 30 53.66 15.58 -
[1] Hu X, He C, Zhou C, et al. Model test and numerical analysis on the deformation and stability of a landslide subjected to reservoir filling[J]. Geofluids, 2019, 2019: 1-15. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/334490099_Model_Test_and_Numerical_Analysis_on_the_Deformation_and_Stability_of_a_Landslide_Subjected_to_Reservoir_Filling [2] Zhang Y, Hu X, Tannant D D, et al. Field monitoring and deformation characteristics of a landslide with piles in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. Landslides, 2018, 15(3): 581-592. doi: 10.1007/s10346-018-0945-9 [3] Hu X, Zhou C, Xu C, et al. Model tests of the response of landslide-stabilizing piles to piles with different stiffness[J]. Landslides, 2019, 16(11): 2187-2200. doi: 10.1007/s10346-019-01233-4 [4] Liu D, Hu X, Zhou C, et al. Deformation mechanisms and evolution of a pile-reinforced landslide under long-term reservoir operation[J]. Engineering Geology, 2020, 275: 105747. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105747 [5] 张景昱, 宛良朋, 潘洪月, 等. 考虑水-岩作用特点的典型岸坡长期稳定性分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2017, 39(10): 1851-1858. doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710013Zhang J Y, Wan L P, Pan H Y, et al. Long-term stability of bank slope considering characteristics of water-rock interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2017, 39(10): 1851-1858(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.11779/CJGE201710013 [6] 邓华锋, 周美玲, 李建林, 等. 水-岩作用下红层软岩力学特性劣化规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2016, 35(增刊2): 3481-3491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2016S2005.htmDeng H F, Zhou M L, Li J L, et al. Mechanical properties deteriorating change rule research of red-layer soft rock under water-rock interaction[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2016, 35(S2): 3481-3491(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2016S2005.htm [7] 王旋, 胡新丽, 周昌, 等. 基于物理模型试验的滑坡-抗滑桩位移场变化特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4): 103-108. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10005.shtmlWang X, Hu X L, Zhou C, et al. Model test on the displacement field characteristics of the landslide stabilizing piles[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(4): 103-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10005.shtml [8] 赵宇, 崔鹏, 胡良博. 黏土抗剪强度演化与酸雨引发滑坡的关系: 以三峡库区滑坡为例[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2009, 28(3): 576-582. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.03.017Zhao Y, Cui P, Hu L B. Relation between evolution of clay shear strength and landslide induced by acid rain: Taking landslides in Three Gorges Reservoir area for example[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(3): 576-582(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2009.03.017 [9] 刘林洁, 向喜琼, 喻兴, 等. 炭质泥岩抗剪强度的饱水软化特性及工程应用研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(8): 244-247. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.08.042Liu L J, Xiang X Q, Yu X, et al. Characteristics of softening shear strength of carbonaceous mudstone and its engineering application[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2017, 17(8): 244-247(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.08.042 [10] 张晓奇, 胡新丽, 刘忠绪, 等. 呷爬滑坡滑带土蠕变特性及其稳定性[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 145-153. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10080.shtmlZhang X Q, Hu X L, Liu Z X, et al. Creep properties and stability of sliding zone soil in Gapa landslide[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 145-153(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10080.shtml [11] 吴恒, 张信贵, 易念平, 等. 城市环境下的水土作用对土强度的影响[J]. 岩土力学, 1999, 20(4): 25-30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.1999.04.005Wu H, Zhang X G, Yi N P, et al. Influence of water-soil interaction on soil strength in urban areas[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 1999, 20(4): 25-30(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.1999.04.005 [12] 张信贵, 吴恒, 方崇, 等. 水土化学体系中钙镁对土体结构强度贡献的试验研究[J]. 地球与环境, 2005, 33(4): 58-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200504012.htmZhang X G, Wu H, Fang C, et al. Experimental research on Ca2+ and Mg2+ contributions to structural strength in soil body-hydrochemistry environment[J]. Earth and Environment, 2005, 33(4): 58-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZDQ200504012.htm [13] 张信贵, 易念平, 吴恒. 不同pH水环境下土变形特性的试验研究[J]. 高校地质学报, 2006, 12(2): 242-248. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.02.012Zhang X G, Yi N P, Wu H. Laboratory test for soil deformation properties in solutions with various pH values[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2006, 12(2): 242-248(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2006.02.012 [14] 刘剑, 崔鹏. 水土化学作用对土体黏聚力的影响: 以蒙脱石-石英砂重塑土为例[J]. 岩土力学, 2017, 38(2): 419-427, 434. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201702016.htmLiu J, Cui P. Influence of water-soil chemical interaction on cohesive force: A case study of montmorillonite-quartz remolded soil[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2017, 38(2): 419-427, 434(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTLX201702016.htm [15] 梁学战. 三峡库区水位升降作用下岸坡破坏机制研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2013.Liang X Z. Failure mechanism research on bank slope under water level fluctuation in the Three Gorges Reservoir area[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [16] 刘虎虎, 缪海波, 陈志伟, 等. 含水率和离子浓度对滑带土抗剪强度的影响[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(1): 228-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901025.htmLiu H H, Mou H B, Chen Z W, et al. Effect of water content and ion concentration on shear strength of sliding zone soil[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(1): 228-234(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201901025.htm [17] 汤连生. 水-土化学作用的力学效应及机理分析[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2000, 39(4): 104-109. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2000.04.024Tang L S. Mechanical effect of chemical action of water on soil and analysis on its mechanism[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2000, 39(4): 104-109(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2000.04.024 [18] 王洋, 汤连生, 高全臣, 等. 水土作用模式对残积红黏土力学性质的影响分析[J]. 中山大学学报: 自然科学版, 2007, 46(1): 128-132. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2007.01.028Wang Y, Tang L S, Gao Q C, et al. Effects of water-soil interaction on mechanical strength of residual red clay[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2007, 46(1): 128-132(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0529-6579.2007.01.028 [19] 王绪民, 陈善雄, 程昌炳. 酸性溶液浸泡下原状黄土物理力学特性试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2013, 35(9): 1619-1626. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201309009.htmWang X M, Chen S X, Cheng C B. Experimental study on physico-mechanical characteristics of undisturbed loess soaked in acid solution[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(9): 1619-1626(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YTGC201309009.htm [20] Ying C, Hu X, Zhou C, et al. Analysis of chemo-mechanical behavior of silty soil under long-term immersion in saline reservoir water[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment, 2020, 80(1): 627-640. doi: 10.1007/s10064-020-01928-2 [21] 李江, 许强, 胡泽铭, 等. 川东红层原状滑带土饱水软化试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2015, 34(增刊2): 4333-4342. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2015S2084.htmLi J, Xu Q, Hu Z M, et al. Experimental research on softening of undisturbed saturated slip soil in eastern of Sichuan Province red bed[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2015, 34(S2): 4333-4342(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSLX2015S2084.htm [22] 住房和城乡建设部. JGJ/T87-2012建筑工程地质勘探与取样技术规程[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. JGJ/T87-2012 Technical specification for engineering geological prospecting and sampling of constructions[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2012(in Chinese). [23] Fan X, Xu Q, Scaringi G, et al. A chemo-mechanical insight into the failure mechanism of frequently occurred landslides in the Loess Plateau, Gansu Province, China[J]. Engineering Geology, 2017, 228: 337-345. doi: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.09.003 [24] 住房和城乡建设部. GB/T50123-2019土工试验方法标准[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2019.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. GB/T50123-2019 Standard for geotechnical testing method[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2019(in Chinese). [25] 庄雅婷, 黄炎和, 林金石, 等. 崩岗红土层土壤液塑限特性及影响因素研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 2014, 21(3): 208-211, 216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201403039.htmZhuang Y T, Huang Y H, Lin J S, et al. Study on liquid limit and plastic limit characteristics and factors of Benggang in red soil layer[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 2014, 21(3): 208-211, 216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-STBY201403039.htm [26] 花可可, 魏朝富, 任镇江. 土壤液限和抗剪强度特征值及其影响因素研究: 基于紫色土区[J]. 农机化研究, 2011, 33(6): 105-110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2011.06.028Hua K K, Wei C F, Ren Z J. Characters and effects of soil liquid limit and shear strength in purple hilly-mountainous region[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2011, 33(6): 105-110(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-188X.2011.06.028 [27] 王成华, 李广信. 土体应力-应变关系转型问题分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2004, 25(8): 1185-1190. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2004.08.002Wang C H, Li G X. Analysis of problem of pattern transition in stress-strain relations of soils[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2004, 25(8): 1185-1190(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2004.08.002 [28] 魏厚振, 汪稔, 胡明鉴, 等. 蒋家沟砾石土不同粗粒含量直剪强度特征[J]. 岩土力学, 2008, 29(1): 48-51, 57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.01.010Wei H Z, Wang R, Hu M J, et al. Strength behaviour of gravelly soil with different coarse-grained contents in Jiangjiagou Ravine[J]. Rockand Soil Mechanics, 2008, 29(1): 48-51, 57(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.01.010 [29] 李振, 邢义川. 干密度和细粒含量对砂卵石及碎石抗剪强度的影响[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(12): 2255-2260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.12.032Li Z, Xing Y C. Effects of dry density and percent fines on shearing strength of sandy cobble and broken stone[J]. Rockand Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(12): 2255-2260(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2006.12.032 [30] 郭子正, 殷坤龙, 唐扬, 等. 库水位下降及降雨作用下麻柳林滑坡稳定性评价与预测[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(4): 260-265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704035.htmGuo Z Z, Yin K L, Tang Y, et al. Stability evaluation and prediction of Maliulin Landslide under reservoir water level decline and rainfall[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(4): 260-265(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201704035.htm [31] 魏学勇, 欧阳祖熙, 董东林, 等. 库水位涨落条件下滑坡渗流场特征及稳定性分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(6): 128-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.06.019Wei X Y, Ouyang Z X, Dong D L, et al. Analysis of landslide seepage and stability under the conditions of reservoir water level fluctuation[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(6): 128-132(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.06.019 -





 下载:
下载: