Diagenetic and metallogenic ages, and geological significance of the Fujiashan skarn-type(Cu-) W Deposit, southeastern Hubei Province
-
摘要: 付家山(Cu-)W矿床是鄂东南地区新近发现的大型矽卡岩型矿床之一,成矿与花岗闪长斑岩关系密切。为了精确获得该矿床成岩成矿年龄,利用LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os同位素定年法对其进行了系统的成岩成矿年代学研究,并基于长江中下游成矿带晚中生代沉积地层及构造变形、地球物理和岩石地球化学等证据探讨了其成岩成矿构造背景。结果显示:花岗闪长斑岩锆石U-Pb加权平均年龄为(144±3)Ma,而辉钼矿Re-Os模式年龄为(146±2)Ma,成岩与成矿作用均形成于晚侏罗世-早白垩世。付家山(Cu-)W矿床形成时代与长江中下游地区大规模岩浆成矿事件时间一致,包括鄂东南地区在内的长江中下游地区的构造演化历史及最新的年代学数据表明,付家山(Cu-)W矿床极有可能形成于岩石圈伸展减薄构造背景。付家山等晚侏罗世-早白垩世矽卡岩型(Cu-)W矿床的发现及厘定指示了鄂东南矿集区具有良好的钨矿找矿前景。Abstract: The Fujiashan(Cu-) W Deposit, which is discovered recently, is one of the typical skarn deposit in southeastern Hubei.The(Cu-) W mineralization is closely associated with the Fujiashan granodiorite porphyry.In order to accurately determine the diagenetic and metallogenic ages of the deposit, ages of the granodiorite porphyry and (Cu-) W mineralization are studied by using LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating in this paper. In addition, the tectonic setting of diagenesis and mineralization is discussed based on the sedimentary strata, structural deformation, geophysical and geochemical evidences in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River during the Late Mesozoic.The results show that the granodiorite porphyry yields a weighted average 206Pb/238U age of (144±3) Ma, whereas a Re-Os model age of molybdenite of (146±2) Ma is obtained for mineralization.These isotopic ages indicate that the granodiorite porphyry and(Cu-) W mineralization at Fujiashan both formed during Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous.In addition, the diagenesis and mineralization ages of the Fujiashan(Cu-) W Deposit are also consistent with the time of large-scale magmatic and metallogenic events for skarn Fe-Cu-Au-Mo deposits in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River.According to the history of tectonic evolution and the latest chronological data in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, including southeastern Hubei, it is considered that the Fujiashan(Cu-) W Deposit is likely to be formed in a tectonic setting of lithospheric extension and thinning.The discovery and determination of Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous skarn(Cu-) W Deposits including the Fujiashan indicate that the ore concentration area in southeastern Hubei has a good explorational prospect for tungsten deposits.
-
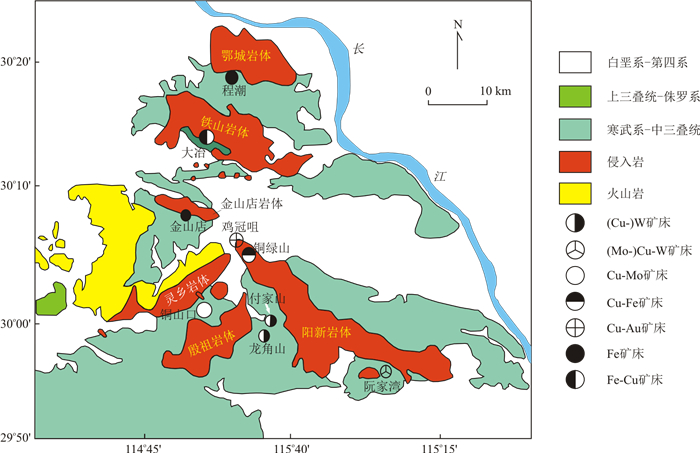
图 1 鄂东南矿集区典型岩体及矽卡岩型矿床分布图(据文献[21]修改)
Figure 1. Distribution map of magmatism and skarn-type deposits in the southeastern Hubei Province
图 2 付家山(Cu-)W矿床地质简图(据文献[12]修改)
Figure 2. Geological map of the Fujiashan (Cu-)W deposit
图 3 付家山(Cu-)W矿床西侧矿区1011线(a)和东侧矿区17线(b)地质剖面图(据文献[13])
Figure 3. Geological profiles of Line 1011(a) in the western section and Line 17(b) in the eastern section of the Fujiashan(Cu-)W district
表 1 付家山花岗闪长斑岩(FJS-26)LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb同位素数据
Table 1. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb isotopic data of the Fujiashan granodiorite porphyry(sample FJS-26)
分析点号 元素wB/10-6 Th/U 同位素比值 年龄/Ma Th U 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ 207Pb/206Pb 1σ 207Pb/235U 1σ 206Pb/238U 1σ FJS-26-01 225.2 445.1 0.51 0.051 9 0.003 3 0.153 7 0.009 8 0.021 6 0.000 5 283 153 145 9 138 3 FJS-26-03 1 022.6 838.6 1.22 0.052 6 0.002 0 0.162 6 0.006 2 0.022 3 0.000 3 322 81 153 5 142 2 FJS-26-05 413.6 479.3 0.86 0.056 2 0.002 4 0.179 0 0.007 5 0.023 2 0.000 3 461 94 167 6 148 2 FJS-26-06 469.3 620.6 0.76 0.047 8 0.001 7 0.146 6 0.005 2 0.022 2 0.000 3 100 -114 139 5 141 2 FJS-26-07 254.7 384.1 0.66 0.047 9 0.003 2 0.159 6 0.010 7 0.024 0 0.000 4 98 152 150 9 153 2 FJS-26-08 238.7 319.5 0.75 0.048 8 0.002 2 0.154 6 0.006 5 0.023 2 0.000 3 200 104 146 6 148 2 FJS-26-09 246.4 381.6 0.65 0.046 6 0.002 3 0.147 8 0.007 0 0.023 2 0.000 3 32 111 140 6 148 2 FJS-26-10 869.0 657.8 1.32 0.050 5 0.002 1 0.152 0 0.006 1 0.021 9 0.000 3 220 101 144 5 140 2 FJS-26-11 156.3 238.4 0.66 0.052 8 0.003 3 0.173 1 0.010 8 0.023 8 0.000 4 317 141 162 9 152 3 FJS-26-12 1 039.4 749.6 1.39 0.048 3 0.001 8 0.147 1 0.005 5 0.022 1 0.000 3 117 89 139 5 141 2 FJS-26-13 303.1 240.4 1.26 0.051 1 0.003 1 0.163 6 0.008 8 0.023 6 0.000 4 256 137 154 8 150 2 FJS-26-14 473.0 529.1 0.89 0.050 1 0.002 0 0.162 1 0.006 6 0.023 4 0.000 3 198 99 153 6 149 2 FJS-26-15 390.1 513.7 0.76 0.050 5 0.002 1 0.157 2 0.006 3 0.022 6 0.000 3 217 94 148 6 144 2 FJS-26-16 590.7 831.7 0.71 0.049 1 0.001 7 0.145 4 0.005 0 0.021 5 0.000 3 150 77 138 4 137 2 FJS-26-18 515.0 657.6 0.78 0.048 8 0.001 7 0.152 4 0.005 6 0.022 6 0.000 3 200 85 144 5 144 2 FJS-26-19 689.9 659.9 1.05 0.050 3 0.001 9 0.148 8 0.005 7 0.021 4 0.000 2 209 90 141 5 136 2 FJS-26-20 307.9 357.1 0.86 0.049 2 0.002 5 0.162 1 0.008 2 0.024 1 0.000 4 167 120 153 7 154 3 表 2 付家山(Cu-)W矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素组成
Table 2. Re-Os isotopic composition of Molybdenite from the Fujiashan(Cu-)W deposit
样品编号 质量/g w(Re)/10-6 w(Os普)/ 10-6 w(187Re)/10-6 w(187Os)/10-6 模式年龄t/Ma FJS-31 0.002 06 267.5±2.4 5.151±0.162 168.1±1.5 409.1±2.4 146±2 表 3 鄂东南地区典型矽卡岩型矿床成岩成矿年龄统计
Table 3. Statistics of diagenetic and metallogenic ages of typical skarn deposits in southeastern Hubei Province
岩体名称 岩石名称 成岩时代/Ma 测试对象 成矿或蚀变年龄/Ma 测试方法 资料来源 付家山 花岗闪长斑岩 144±3 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 本文 矿体 146±2 辉钼矿Re-Os 龙角山 花岗闪长斑岩 144±1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 文献[11] 矿体 144.7±2.9 辉钼矿Re-Os 鸡冠咀 石英正长闪长玢岩 146±2 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[37] 闪长岩 132±4 SHRIMP U-Pb 矿体 138.2±2.2 辉钼矿Re-Os 文献[19] 蚀变岩 140.3±1.1 金云母40Ar/39Ar 桃花咀 矿体 138.3±2 辉钼矿Re-Os 文献[19] 矽卡岩 139.9±1.1 金云母40Ar/39Ar 铜绿山 石英正长闪长玢岩 146±1 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[38] 石英闪长岩 140±2 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[19] 矿体 137.8±1.7 辉钼矿Re-Os 文献[15] 矿体 138.1±1.8 辉钼矿Re-Os 矿体 137.3±2.4 辉钼矿Re-Os 文献[19] 矽卡岩 136.0±1.3 LA-ICP-MS榍石U-Pb 文献[35] 姜桥 花岗闪长岩 144±1 LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb 文献[39] 铜山口 花岗闪长岩 140.6±2.4 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[30] 矿体 143.8±2.6 辉钼矿Re-Os 阮家湾 花岗闪长岩 143±1 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[40] 矿体 143.6±1.7 辉钼矿Re-Os 文献[15] 犀牛山 花岗闪长斑岩 147±1 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[40] 丰山 花岗闪长斑岩 137±2 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[37] 矿体 144±2.1 辉钼矿Re-Os 文献[15] 鸡笼山 花岗闪长斑岩 138±2 SHRIMP U-Pb 文献[37] 岩体 151.8±0.7 锆石U-Pb 文献[41] 矿体 150.7±0.8 辉钼矿Re-Os -
[1] 周涛发, 范裕, 袁峰, 等. 长江中下游成矿带地质与矿产研究进展[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(10): 3051-3066. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210003.htmZhou T F, Fan Y, Yuan F, et al. Progress of geological study in the middle-lower Yangtze River valley metallogenic belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(10): 3051-3066(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210003.htm [2] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Li R L, et al. Re-Os molybdenite and Ar-Ar phlogopite dating of Cu-Fe-Au-Mo(W) deposits in southeastern Hubei, China[J]. Contribution to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2007, 90: 249-270. doi: 10.1007/s00710-006-0176-y [3] 翟裕生, 姚书振, 林新多, 等. 长江中下游地区铁、铜等成矿规律研究[J]. 矿床地质, 1992, 11(1): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199201000.htmZhai Y S, Yao S Z, Lin X D, et al. Metallogenic regularity of iron and copper in the middle-lower Yangtze River valley metallogenic belt[J]. Mineral Deposits, 1992, 11(1): 1-12(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ199201000.htm [4] 周涛发, 宋明义, 范裕, 等. 安徽庐枞盆地中巴家滩岩体的年代学研究及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2007, 23(10): 2379-2386. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.006Zhou T F, Song M Y, Fan Y, et al. Chronology of the Bajiatan in the Luzong Basin, Anhui, and its significance[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2007, 23(10): 2379-2386(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.10.006 [5] Li J W, Zhao X F, Zhou M F, et al. Late Mesozoic magmatism from the Daye region, eastern China: U-Pb ages, petrogenesis, and geodynamic implications[J]. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 2009, 157: 383-409. doi: 10.1007/s00410-008-0341-x [6] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Zhao H J. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic intrusions in the southeast Hubei Province, middle-lower Yangtze River belt(MLYRB), East China[J]. Lithos, 2011, 125(1/2): 693-710. [7] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Zhao H J, et al. Zircon U-Pb and phlogopite 40Ar-39Ar age of the Chengchao and Jinshandian skarn Fe deposits, southeast Hubei Province, middle-lower Yangtze River valley metallogenic belt, China[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2012, 47(6): 633-652. doi: 10.1007/s00126-011-0367-2 [8] 孙家富. 大冶-阳新地区矽卡岩型白钨矿床的成矿特点[J]. 地质与勘探, 1984, 28(8): 9-11, 29. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198408001.htmSun J F. Metallogenic characteristics of skarn type scheelite deposits in Daye-Yangxin area[J]. Geology and Exploration, 1984, 28(8): 9-11, 29(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT198408001.htm [9] 赵一鸣, 吴良士. 中国铜矿矿产资源图(1: 500万)说明书[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006: 1-55.Zhao Y M, Wu L S. Description of China's copper mineral resources map(1: 5000000)[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006: 1-55(in Chinese). [10] Deng X D, Li J W, Zhou M F, et al. In-situ LA-ICPMS trace elements and U-Pb analysis of titanite from the Mesozoic Ruanjiawan W-Cu-Mo skarn deposit, Daye district, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 65: 990-1004. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.011 [11] 丁丽雪, 黄圭成, 夏金龙. 鄂东南地区龙角山-付家山斑岩体成因及其对成矿作用的指示[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(8): 1513-1527. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201408013.htmDing L X, Huang G C, Xia J L. Petrogenesis of the Longjiaoshan-Fujiashan porphyritic intrusion in southeastern Hubei Province and implications for Cu-W mineralization[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(8): 1513-1527(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201408013.htm [12] 纪云昊, 谢桂青, 朱乔乔, 等. 含碳质地层对矽卡岩钨矿的影响: 以鄂东付家山钨矿床为例[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(4): 917-934. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201904015.htmJi Y H, Xie G Q, Zhu Q Q, et al. Influence of carbonaceous strata on skarn tungsten deposits: A case study of Fujiashan deposit in eastern Hubei Province[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(4): 917-934(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCDZ201904015.htm [13] 纪云昊. 鄂东矿集区付家山-龙角山矽卡岩W-Cu矿成矿机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2020.Ji Y H. Metallogenic mechanism of Fujiashan-Longjiaoshan skarn W-Cu deposit, Edong ore cluster[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2020(in Chinese with English abstract). [14] Lei X F, Duan D F, Jiang S Y, et al. Ore-forming fluids and isotopic(H-O-C-S-Pb) characteristics of the Fujiashan-Longjiaoshan skarn W-Cu-(Mo) deposit in the Edong district of Hubei Province, China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 102: 386-405. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2018.09.019 [15] 谢桂青, 毛景文, 李瑞玲, 等. 鄂东南地区Cu-Au-Mo-(W)矿床的成矿时代及其成矿地球动力学背景探讨: 辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(1): 43-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.01.006Xie G Q, Mao J W, Li Q L, et al. Metallogenic epoch and geodynamic framework of Cu-Au-Mo-(W) deposits in southeastern Hubei Province: Constraints from Re-Os molybdenite ages[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(1): 43-52(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.01.006 [16] 毛景文, 邵拥军, 谢桂青, 等. 长江中下游成矿带铜陵矿集区铜多金属矿床模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2009, 28(2): 109-119. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.02.001Mao J W, Shao Y J, Xie G Q, et al. Mineral deposit model for porphyry-skarn polymetallic copper deposits in Tongling ore dense district of middle-lower Yangtze valley metallogenic belt[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2009, 28(2): 109-119(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2009.02.001 [17] Mao J W, Pirajno F, Cook N. Mesozoic metallogeny in East China and corresponding geodynamic settings: An introduction to the special issue[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43: 1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.09.003 [18] Pan Y M, Dong P. The lower Changjiang(Yangzi/Yangtze River) metallogenic belt, eastcentral China: Intrusion and wall rock-hosted Cu-Fe-Au, Mo, Zn, Pb, Ag deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 1999, 15: 177-242. doi: 10.1016/S0169-1368(99)00022-0 [19] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Zhao H J, et al. Timing of skarn deposit formation of the Tonglushan ore district, southeastern Hubei Province, middle-lower Yangtze River valley metallogenic belt and its implications[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2011, 43: 62-77. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2011.05.005 [20] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Li R L, et al. Geochemistry and Nd-Sr isotopic studies of Late Mesozoic granitoids in the southeastern Hubei Province, middle-lower Yangtze River belt, eastern China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting[J]. Lithos, 2008, 104: 216-230. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.008 [21] 谢桂青, 朱乔乔, 姚磊, 等. 鄂东南地区晚中生代铜铁金多金属矿的区域成矿模型探讨[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2013, 32(4): 418-426. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.04.005Xie G Q, Zhu Q Q, Yao L, et al. Discussion on regional metal mineral deposit model of Late Mesozoic Cu-Fe-Au polymetallic deposits in the southeast Hubei Province[J]. Bulletin of Mineeralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2013, 32(4): 418-426(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2013.04.005 [22] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Zhou S D, et al. SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating for volcanic rocks of the Dasi Formation in southeast Hubei Province, middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River and its implications[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2006, 51: 3000-3009. doi: 10.1007/s11434-006-2187-9 [23] Wang Q, Wyman D A, Xu J F, et al. Petrogenesis of Cretaceous adakitic and shoshonitic igneous rocks in the Luzong area, Anhui Province(eastern China): Implications for geodynamics and Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Lithos, 2006, 89: 424-446. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2005.12.010 [24] Andersen T. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb[J]. Chemical Geology, 2002, 192: 59-79. doi: 10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X [25] 杜安道, 赵敦敏, 王淑贤, 等. Carius管溶样-负离子热表面电离质谱准确测定辉钼矿铼-锇同位素地质年龄[J]. 岩矿测试, 2001, 20(4): 247-252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.04.002Du A D, Zhao D M, Wang S X, et al. Precise Re-Os dating for molybdenite by ID-NTIMS with Carius tube sample preparation[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2001, 20(4): 247-252(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2001.04.002 [26] 屈文俊, 杜安道. 高温密闭溶样电感耦合等离子体质谱准确测定辉钼矿铼-锇地质年龄[J]. 岩矿测试, 2003, 22(4): 254-257, 262. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2003.04.003Qu W J, Du A D. Highly Precise Re-Os dating of molybdenite by ICP-MS with Carius tube sample digestion[J]. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 2003, 22(4): 254-257, 262(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2003.04.003 [27] Griffin W L, Belousova E A, Shee S R, et al. Archean crustal evolution in the northern Yilgarn Craton: U-Pb and Hf-isotope evidence from detrital zircons[J]. Precambrian Research, 2004, 131: 231-282. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2003.12.011 [28] Hoskin P W O, Schaltegger U. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2003, 53: 27-62. doi: 10.2113/0530027 [29] Smoliar M I, Walker R J, Morgan J W. Re-Os ages of group ⅡA, ⅢA, ⅣA and ⅥB iron meteorites[J]. Science, 1996, 271: 1099-1102. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5252.1099 [30] Li J W, Zhao X F, Zhou M F, et al. Origin of the Tongshankou prophyry-skarn Cu-Mo deposit, eastern Yangtze Craton, eastern China: Geochronological, geochemical, and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints[J]. Mineralium Deposita, 2008, 43(3): 315-336. doi: 10.1007/s00126-007-0161-3 [31] Selby D, Creaser R A, Hart C J, et al. Absolute timing of sulfide and gold mineralization: A comparison of Re-Os molybdenite and Ar-Ar mica methods from the Tintina Gold Belt, Alaska[J]. Geology, 2002, 30: 791-794. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<0791:ATOSAG>2.0.CO;2 [32] 赵岩岩, 谭俊, 刘晓阳, 等. 湖北大冶铜绿山矽卡岩型铜铁(金)矿床包裹体特征及其地质意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 64-74. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10072.shtmlZhao Y Y, Tan J, Liu X Y, et al. Inclusion features and geological significance of the Tonglüshan skarn-type copper-iron(gold) deposit in Daye, Hubei[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 64-74(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10072.shtml [33] 何迪, 谭俊, 刘晓阳, 等. 湖北大冶铜山口斑岩-矽卡岩型铜钼矿床包裹体特征及流体演化意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(5): 97-108. https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10055.shtmlHe D, Tan J, Liu X Y, et al. Significance of inclusions and fluid evolution of the porphyry-skarn copper-molybdenum deposit in Tongshankou, Daye, Hubei[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(5): 97-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract10055.shtml [34] Xie G Q, Mao J W, Li X W, et al. Late Mesozoic bimodal volcanic rocks in the Jinniu Basin, middle-lower Yangtze River belt(MLYRB), East China: Age, petrogenesis and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2011, 127: 144-164. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2011.08.012 [35] Li J W, Deng X D, Zhou M F, et al. Laser ablation ICP-MS titanite U-Th-Pb dating of hydrothermal ore deposits: A case study of the Tonglushan Cu-Fe-Au skarn deposit, SE Hubei Province, China[J]. Chemical Geology, 2010, 270: 56-67. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.11.005 [36] 瞿泓滢, 王浩琳, 裴荣富, 等. 鄂东南地区与铁山和金山店铁矿有关的花岗质岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS年龄和Hf同位素组成及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(1): 147-165. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201201014.htmQu H Y, Wang H L, Pei R F, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of Tieshan and Jinshandian plutons in the southeastern Hubei Province[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(1): 147-165(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201201014.htm [37] 陈富文, 梅玉萍, 李华芹. 鄂东丰山矿田花岗闪长斑岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其意义[J]. 地质学报, 2011, 85(1): 88-96. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.01.014Chen F W, Mei Y P, Li H Q. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating for granodiorite porphyry of the Fengshan Orefield in eastern Hubei Province and its geological significance[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85(1): 88-96(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.01.014 [38] 梅玉萍, 李华芹, 陈富文. 鄂东铜绿山矿区石英正长闪长玢岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其地质意义[J]. 地球学报, 2008, 29(6): 805-810. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.06.023Mei Y P, Li H Q, Chen F W. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the quartz-orthoclase diorite porphyrite from the Tonglushan orefield in eastern Hubei Province and its geological implication[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2008, 29(6): 805-810(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2008.06.023 [39] 丁丽雪, 黄圭成, 夏金龙, 等. 鄂东南地区姜桥花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2013, 32(3): 275-290. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.03.001Ding L X, Huang G C, Xia J L, et al. U-Pb ages and Hf isotope characteristics of zircons from Jiangqiao granodiorite in southeastern Hubei Province and their geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2013, 32(3): 275-290(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.03.001 [40] 颜代蓉, 邓晓东, 李建威, 等. 鄂东南地区阮家湾和犀牛山花岗闪长岩的时代、成因及成矿和找矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2012, 28(10): 3373-3388. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210025.htmYan D R, Deng X D, Li J W, et al. U-Pb age and petrogenesis of the Ruanjiawan granodiorite pluton and Xiniushan granodiorite porphyry, southeast Hubei Province: Implications for Cu-Mo mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2012, 28(10): 3373-3388(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201210025.htm [41] 贾宝剑, 李胜荣, 杨庆雨, 等. 湖北鸡笼山矽卡岩型金铜矿床铅同位素地球化学研究[J]. 现代地质, 2012, 26(3): 471-477, 488. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.03.006Jia B J, Li S R, Yang Q Y, et al. Pb isotope geochemistry of the Jilongshan skarn-host Au-Cu deposit in Hubei Province[J]. Geoscience, 2012, 26(3): 471-477, 488(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8527.2012.03.006 [42] 李华芹, 陈富文, 梅玉萍. 鄂东鸡冠嘴矿区成矿岩体锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2009, 33(3): 411-417. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.012Li H Q, Chen F W, Mei Y P. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of the mineralized intrusion from Jiguanzui ore field in eastern Hubei Province and its geological significance[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2009, 33(3): 411-417(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2009.03.012 [43] 常印佛, 刘湘培, 吴言昌. 长江中下游铜铁成矿带[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 1991.Chang Y F, Liu X P, Wu Y C. Copper-iron deposits in the middle-lower Yangtze valley metallogenic belt[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1991(in Chinese). [44] 翟裕生, 姚书振, 陈华慧, 等. 长江中下游鄂城-铜陵一带遥感地质及成矿规律研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1992.Zhai Y S, Yao S Z, Chen H H, et al. Remote sensing geology and metallogenic regularity in Echeng-Tongling area, middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1992(in Chinese). [45] 闫峻, 陈江峰, 谢智, 等. 长江中下游地区蝌蚪山晚中生代玄武岩的地球化学研究: 岩石圈地幔性质与演化的制约[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(5): 455-469. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.05.004Yan J, Chen J F, Xie Z, et al. Geochemistry of Late Mesozoic basalts from Kedoushan in the middle and lower Yangtze regions: Constraints on characteristics and evolution of the lithospheric mantle[J]. Geochimica, 2005, 34(5): 455-469(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.05.004 [46] 谢智, 李全忠, 陈江峰, 等. 庐枞早白垩世火山岩的地球化学特征及其源区意义[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(2): 235-249. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.008Xie Z, Li Q Z, Chen J F, et al. The geochemical characteristics of the Early-Cretaceous volcanics in Luzhong region and their source significances[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(2): 235-249(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2007.02.008 [47] 吴利仁, 齐进英, 王听渡, 等. 中国东部中生代火山岩[J]. 地质学报, 1982, 61(3): 223-234. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198203003.htmWu L R, Qi J Y, Wang T D, et al. Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the eastern part of China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1982, 61(3): 223-234(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE198203003.htm [48] 汪洋, 邓晋福, 姬广义. 长江中下游地区早白垩世埃达克质岩的大地构造背景及其成矿意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2004, 20(2): 297-314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402010.htmWang Y, Deng J F, Ji G Y. A perspective on the geotectonic setting of Early Cretaceous adakite-like rocks in the lower reaches of Yangtze River and its significance for copper-gold mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2004, 20(2): 297-314(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200402010.htm [49] Sun W D, Ding X, Hu Y H, et al. The golden transformation of the Cretaceous Plate subduction in the west Pacific[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2007, 262: 533-542. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2007.08.021 [50] 孙卫东, 凌明星, 汪方跃, 等. 太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2008, 27(3): 218-225. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.03.002Sun W D, Ling M X, Wang F Y, et al. Pacific Plate subduction and Mesozoic geological event in eastern China[J]. Bulletin of Mineeralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2008, 27(3): 218-225(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.03.002 [51] Mao J W, Wang Y T, Lehmann B, et al. Molybdenite Re-Os and albit 40Ar/39Ar dating of Cu-Au-Mo and magnetite porphyry systems in the Yangtze River valley and metallogenic implications[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2006, 29: 307-324. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2005.11.001 [52] Zhai Y S, Xiong Y L, Yao S Z, et al. Metallogeny of copper and iron deposits in the eastern Yangtze Carton, east-central China[J]. Ore Geology Review, 1996, 11: 229-248. doi: 10.1016/0169-1368(96)00003-0 [53] Li Z, Liu S F, Zhang J F, et al. Typical basin-fill sequences and basin migration in Yanshan, North China: Response to Mesozoic tectonic transition[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2004, 47: 181-192. [54] 付明希, 胡圣标, 汪集旸. 华北东部中生代热体制转换及其构造意义[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2004, 34(6): 514-520. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200406002.htmFu M X, Hu S B, Wang J Y. Mesozoic thermal regime transition and its tectonic significance in eastern North China[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2004, 34(6): 514-520(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200406002.htm [55] 吕庆田, 侯增谦, 杨竹森, 等. 长江中下游地区的底侵作用及动力学演化模式: 来自地球物理资料的约束[J]. 中国科学: D辑, 2004, 34(9): 783-794. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200409000.htmHou Z Q, Yang Z S, et al. Underplating and its dynamic evolution model in the middle-lower reaches of Yangtze River: Constraints from geophysical data[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2004, 34(9): 783-794(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK200409000.htm [56] Defant M J, Drummond M S. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere[J]. Nature, 1990, 347: 662-665. doi: 10.1038/347662a0 [57] Richards S, Lister G, Kennett B. A slab in depth: Three-dimensional geometry and evolution of the Indo-Australian Plate[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2007, 8(12): 1-11. [58] Xu J F, Shinjo R, Defant M J, et al. Origin of Mesozoic adakitic intrusive rocks in the Ningzhen area of East China: Partial melting of delaminated lower continental crust?[J]. Geology, 2002, 30: 1111-1114. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2002)030<1111:OOMAIR>2.0.CO;2 [59] Wang Q, Zhao Z H, Xu J F, et al. Petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Yanshanian adakite-like rocks in the eastern Yangtze Block[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2003, 46: 164-176. [60] Chen J F, Yan J, Xie Z, et al. Nd and Sr isotopic compositions of igneous rocks from the lower Yangtze region in eastern China: Constraints on sources[J]. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth(A), 2001, 26: 719-731. doi: 10.1016/S1464-1895(01)00122-3 [61] Wu C Z, Gu L X, Ren Z W, et al. Transition from plate margin to intraplate environment: Geochemistry of basalts in Paleogene Liaohe Basin, northeastern China[J]. Science in China: Series D, 2005, 48(12): 2069-2080. [62] 马昌前, 杨坤光, 唐仲华, 等. 花岗岩类岩浆动力学: 理论方法及鄂东花岗岩类例析[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1994.Ma C Q, Yang K G, Tang Z H, et al. Magmatic dynamics of granitoids: Theoretical method and case study of granitoids in eastern Hubei[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1994(in Chinese). [63] 董峻麟, 贾宗勇, 刘群, 等. 鄂东南大冶地区中生代火山岩时代及意义[J]. 青海大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 31(6): 61-65. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201306012.htmDong J L, Jia Z Y, Liu Q, et al. The formation age and indication of Mesozoic volcanic rocks from Daye, southeast Hubei[J]. Journal of Qinghai University: Natural Science Edition, 2013, 31(6): 61-65(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXZ201306012.htm [64] 谢桂青, 李瑞玲, 蒋国豪, 等. 鄂东南地区晚中生代侵入岩的地球化学和成因及对岩石圈减薄时限的制约[J]. 岩石学报, 2008, 24(8): 1703-1714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200808004.htmXie G Q, Li R L, Jiang G H, et al. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of Late Mesozoic granitoids in southeastern Hubei Province and constrains on the timing of lithospheric thinning, middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River, eastern China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2008, 24(8): 1703-1714(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB200808004.htm [65] 张世涛, 陈华勇, 韩金生, 等. 鄂东南铜绿山大型铜铁金矿床成矿岩体年代学、地球化学特征及成矿意义[J]. 地球化学, 2018, 47(3): 240-256. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201803002.htmZhang S T, Chen H Y, Han J S, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, and mineralization of quartz monzodiorite and quartz monzodiorite porphyry in Tonglüshan Cu-Fe-Au deposit, Edongnan ore district, China[J]. Geochimica, 2018, 47(3): 240-256(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQHX201803002.htm [66] 王登红, 陈郑辉, 黄国成, 等. 华南"南钨北扩"、"东钨西扩"及其找矿方向探讨[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2012, 36(3): 322-329. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.003Wang D H, Chen Z H, Huang G C, et al. Northwards and westwards prospecting for Tungsten and its significance in South China[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2012, 36(3): 322-329(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2012.03.003 [67] 聂利青, 周涛发, 汪方跃, 等. 安徽庐枞矿集区东顾山钨矿床成矿流体来源与演化: 来自H、O、S同位素和流体包裹体的证据[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(12): 3825-3837. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.16Nie L Q, Zhou T F, Wang F Y, et al. Study of fluid inclusions and H-O-S isotopic compositions of Donggushan tungsten skarn deposit, Anhui Province, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(12): 3825-3837(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.12.16 [68] 肖鑫, 周涛发, 袁峰, 等. 安徽青阳高家塝钨钼矿床成岩成矿时代及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(3): 859-872. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201703014.htmXiao X, Zhou T F, Yuan F, et al. The geochronology of the Qingyang Gaojiabang tungsten-molybdenum deposit and its geological significance, Anhui Province, East China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(3): 859-872(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201703014.htm [69] 陈雪锋, 周涛发, 张达玉, 等. 皖南池州桂林郑钼矿床成矿岩体的年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2017, 33(10): 3200-3216. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201710015.htmChen X F, Zhou T F, Zhang D Y, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and geological characteristics of the granite porphyry beneath Guilinzheng Mo deposit, Chizhou, southern Anhui[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2017, 33(10): 3200-3216(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201710015.htm [70] 聂利青, 周涛发, 范裕, 等. 长江中下游成矿带庐枞矿集区首例钨矿床成岩成矿时代及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(2): 303-318. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201602003.htmNie L Q, Zhou T F, Fan Y, et al. LA-ICPMS U-Pb zircon age and molybdenite Re-Os dating of Donggushan, the first tungsten deposit found in the Luzong Orefield, middle-lower Yangtze River valley metallogenic belt[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(2): 303-318(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201602003.htm [71] 周涛发, 聂利青, 王世伟, 等. 长江中下游成矿带钨矿床[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(12): 3592-3608. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201912003.htmZhou T F, Nie L Q, Wang S W, et al. Tungsten deposits in the middle-lower Yangtze metallogenic belt, China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(12): 3592-3608(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201912003.htm -





 下载:
下载: