Failure mechanism of cavitation-induced shear of the plugging layer in high-temperature high-pressure fractured gas reservoirs in the Tazhong block, NW China
-
摘要:
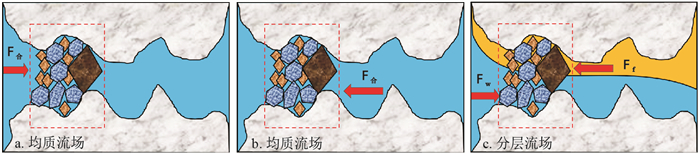
为了深入了解塔中区块高温高压裂缝性气藏封堵层失效问题, 基于储层特征和流体特性的深入分析, 结合封堵层微尺度物理结构特征, 对高温高压裂缝性气藏封堵层失效特征进行了研究, 提出了封堵层气蚀剪切失效概念, 构建了封堵层气蚀剪切失效的物理模型, 并借助颗粒物质力学和液桥理论, 对封堵层气蚀剪切失效过程进行了深入研究, 并基于反向气蚀原理, 开展了室内反向承压实验研究。研究结果表明, 裂缝性封堵层"气蚀剪切"失效作为一种气藏封堵层特有的失效模式, 其发生过程分为3个阶段: 气体扩散降黏破坏、气蚀剪切剥离破坏和气液置换错位剪切破坏; 正向承压6 MPa的统一封堵层, 对于不同属性的流体其抗剪切破坏能力不同, 当反向驱替流体由柴油转变为氮气时, 封堵层的反向承压值由原来的2.0 MPa(22 min)和2.5 MPa(30 min)分别减小到后来的1.5 MPa(10 min)和1.0 MPa(12 min), 综合抗剪切性能降低了约50%, 表明气体具有与液体不同的破坏能力和机制。
Abstract:To profoundly understand the plugging layer failure behavior of high-temperature high-pressure fractured gas reservoirs in the Tazhong block, the failure characteristics of high-temperature high-pressure fractured gas reservoirs were studied and analyzed based on the combination of reservoir characteristics, fluid properties and the microscaled physical structure of the plugging layer. The concept of cavitation-induced shear failure is proposed, and the physical model of cavitation-induced shear failure is established. The cavitation-induced shear failure process of the plugging layer is systematically studied with the aid of granular material mechanics and liquid bridge theory. In addition, laboratory experiments of reversed pressure-bearing were carried out based on the principle of reversed cavitation. Results show that the cavitation-induced shear failure of the fractured sealing layer is a special kind of failure modes of the plugging layerin gas reservoirs. This process can be divided into three steps: viscosity reduction because of gas diffusion, cavitation-induced shear stripping and fluids displacement mismatch shearing destructions. In addition, the experimental results show that the plugging layer with a positive pressure of 6 MPa has different shear failure resistances for different fluids. With the displacement medium changing from liquid to gas, the reversed pressure-bearing value of the plugging layer decreases from 2.0 MPa (22 min) and 2.5 MPa (30 min) to 1.5 MPa (10 min) and 1.0 MPa (12 min), respectively. The comprehensive shear resistance is reduced by approximately 50%, indicating that gas has different destructive ability and destructive mechanism compared to liquid.
-
表 1 塔中区块试验井储层段岩心全烃含量统计结果
Table 1. Statistical results of total hydrocarbon content in cores collected from tested wells in the Tazhong block
井深/m 钻时效率/(min·m-1) TG C1 C2 C3 iC4 nC4 iC5 nC5 wB/% 7 319 76 61.013 53.909 5 0.077 6 0.004 1 0.000 6 0.005 6 0.000 6 0.001 5 7 320 54 54.779 48.323 4 0.073 8 0.005 5 0.001 1 0.001 9 0.000 6 0.004 1 7 321 28 55.049 48.533 7 0.075 4 0.005 6 0.000 6 0.003 1 0.000 6 0.003 3 7 322 37 55.822 49.516 2 0.076 0 0.007 0 0.000 6 0.002 8 0.001 1 0.005 3 7 323 34 59.339 52.684 1 0.079 1 0.005 9 0.000 6 0.003 0 0.002 4 0.005 3 7 324 30 66.133 58.868 7 0.086 0 0.007 3 0.000 9 0.004 9 0.002 3 0.004 7 7 325 26 66.226 61.030 8 0.091 4 0.007 2 0.001 0 0.001 4 0.000 9 0.005 2 表 2 裂缝正向承压封堵实验
Table 2. Fracture forward pressure-bearing plugging experiment
裂缝形状 裂缝宽度/mm 正向承压值/MPa 累计漏失量/mL 临界封堵时间/min 平行缝 2×2 6 16 17 楔形缝 2×1.5 6 10 15 平行缝 2×2 6 14 19 楔形缝 2×1.5 6 12 13 注:正向承压值是指封堵层形成的承压值(MPa);临界封堵时间是指完全形成封堵层不再发生漏失时的时间(min) 表 3 封堵层反向承压评价实验
Table 3. Reversed pressure-bearing evaluation experiment of the plugging layer
反向驱替流体 裂缝形状 裂缝宽度/mm 反向承压值/MPa 临界时间/min 0#柴油 平行缝 2×2 2.0 22 楔形缝 2×1.5 2.5 30 氮气(N2) 平行缝 2×2 1.5 10 楔形缝 2×1.5 1.0 12 注:反向承压值是指进行反向驱替时封堵层所能承受的最大压力值(MPa);临界时间是反向驱替过程中封堵层发生破坏时的时间 -
[1] 闫丰明, 康毅力, 孙凯, 等. 裂缝-孔洞型碳酸盐岩储层暂堵性堵漏机理研究[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2011, 39(2): 81-85. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZT201102018.htmYan F M, Kang Y L, Sun K, et al. Mechanism of temporary sealing for fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoir[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2011, 39(2): 81-85(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZT201102018.htm [2] 杨枝. 塔中地区裂缝性碳酸盐岩储层保护技术研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2010.Yang Z. The research on protection technology of fractured carbonate reservoir in Tarim Basin[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2010(in Chinese with English abstract). [3] 许成元, 闫霄鹏, 康毅力, 等. 深层裂缝性储集层封堵层结构失稳机理与强化方法[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2020, 47(2): 399-408. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002021.htmXu C Y, Yan X P, Kang Y L, et al. Structural failure mechanism and strengthening method of fracture plugging zone for lost circulation control in deep naturally fractured reservoirs[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2020, 47(2): 399-408(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK202002021.htm [4] 苏晓明, 练章华, 方俊伟, 等. 适用于塔中区块碳酸盐岩缝洞型异常高温高压储集层的钻井液承压堵漏材料[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 2019, 46(1): 168-175. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901017.htmSu X M, Lian Z H, Fang J W, et al. Lost circulation material for abnormally high temperature and pressure fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoirs in Tazhong block, Tarim Basin, NW China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2019, 46(1): 168-175(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201901017.htm [5] Zhang R, Bo K, Liu Z. A method of sizing plugging nanoparticles to prevent water invasion for shale wellbore stability based on CFD-DEM simulation[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2021, 196: 107733. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2020.107733 [6] Li Z Y, Li X G, Du K, et al. Development of a new high-temperature and high-strength polymer gel for plugging fractured reservoirs[J]. Upstream Oil and Gas Technology, 2020, 5: 100014. doi: 10.1016/j.upstre.2020.100014 [7] Yan X, Kang Y, Xu C, et al. Fracture plugging zone for lost circulation control in fractured reservoirs: Multiscale structure and structure characterization methods[J]. Powder Technology, 2020, 370: 159-175. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.05.026 [8] Yang M, Chen Y. Investigation of LCM soaking process on fracture plugging for fluid loss remediation and formation damage control[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2020, 81: 103444 doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2020.103444 [9] 李大奇, 康毅力, 刘修善, 等. 基于漏失机理的碳酸盐岩地层漏失压力模型[J]. 石油学报, 2011, 32(5): 900-904. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201105027.htmLi D Q, Kang Y L, Liu X S, et al. The lost circulation pressure of carbonate formations on the basis of leakage mechanisms[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(5): 900-904(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201105027.htm [10] 吕开河, 邱正松, 魏慧明, 等. 自适应防漏堵漏钻井液技术研究[J]. 石油学报, 2008, 29(5): 757-760, 765. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.05.023Lü K H, Qiu Z S, Wei H M, et al. Study on techniques of auto-adapting lost circulation resistance and control for drilling fluid[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2008, 29(5): 757-760, 765(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2697.2008.05.023 [11] 牛磊星, 孙平贺. 丙烯酸高吸水膨胀树脂在深部钻探中的堵漏试验[J]. 地质科技情报, 2017, 36(1): 208-212. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201701026.htmNiu L X, Sun P H. Experimental study on the plugging of acrylic acid high water absorbing resin in deep drilling[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2017, 36(1): 208-212(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201701026.htm [12] 王新新, 朱永峰, 杨鹏飞, 等. 塔里木盆地哈拉哈塘油田A-B区块二叠系火成岩漏失原因与应对措施[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2): 136-142. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902015.htmWang X X, Zhu Y F, Yang P F, et al. Lost circulation reason and solutions of Permian igneous rock in Halahatang Oilfield A-B area, Tarim Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(2): 136-142(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902015.htm [13] 邱正松, 刘均一, 周宝义, 等. 钻井液致密承压封堵裂缝机理与优化设计[J]. 石油学报, 2016, 37(2): 137-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2016S2017.htmQiu Z S, Liu J Y, Zhou B Y, et al. Tight fracture-plugging mechanism and optimized design for plugging drilling fluid[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2016, 37(2): 137-143(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB2016S2017.htm [14] 许成元. 裂缝性储层强化封堵承压能力模型与方法[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2015.Xu C Y. Models and methods to strengthen wellbore pressure containment by fracture plugging in fractured reservoirs[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2015(in Chinese with English abstract). [15] 邱正松, 暴丹, 刘均一, 等. 裂缝封堵失稳微观机理及致密承压封堵实验[J]. 石油学报, 2018, 39(5): 587-596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201805010.htmQiu Z S, Bao D, Liu J Y, et al. Microcosmic mechanism of fracture-plugging instability and experimental study on pressure bearing and tight plugging[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2018, 39(5): 587-596(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201805010.htm [16] Peter E C, Saeed S, Raj K. Lost circulation and filter cake evolution: Impact of dynamic wellbore conditions and wellbore strengthening implications[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 171: 1326-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.08.063 [17] 康毅力, 余海峰, 许成元, 等. 毫米级宽度裂缝封堵层优化设计[J]. 天然气工业, 2014, 34(11): 88-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201411019.htmKang Y L, Yu H F, Xu C Y, et al. An optimal design for millimeter-wide fracture-plugged zones[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2014, 34(11): 88-94(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TRQG201411019.htm [18] Shamlooh M, Hamza A, Hussein I A, et al. Investigation of the rheological properties of nanosilica-reinforced PAM /PEI gels for wellbore strengthening at high reservoir temperatures[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2019, 33(1): 6829-6836. [19] 王贵, 蒲晓林. 提高地层承压能力的钻井液堵漏作用机理[J]. 石油学报, 2010, 31(6): 1009-1012. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201006026.htmWang G, Pu X L. Plugging mechanism of drilling fluid by enhancing wellbore pressure[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2010, 31(6): 1009-1012(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201006026.htm [20] 王平全, 李再钧, 聂勋勇, 等. 用于钻井堵漏和封堵的特种凝胶抗冲稀性能[J]. 石油学报, 2012, 33(4): 697-701. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201204025.htmWang P Q, Li Z J, Nie X Y, et al. Anti-dilution properties of a special gel applied to loss circulation control in drilling[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2012, 33(4): 697-701(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201204025.htm [21] 暴丹, 邱正松, 邱维清, 等. 高温地层钻井堵漏材料特性实验[J]. 石油学报, 2019, 40(7): 846-857. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201907010.htmBao D, Qiu Z S, Qiu W Q, et al. Experiment on properties of lost circulation materials in high temperature formation[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2019, 40(7): 846-857(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYXB201907010.htm [22] 佘继平. 页岩井周地层—封堵带系统突变失稳机理[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2016.She J P. Catastrophic instability mechanism to system consisted of plugging zone and rock in shale formation[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). [23] 王贵. 提高地层承压能力的钻井液封堵理论与技术研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2012.Wang G. Theory and technology on drilling fluids for wellborestrenthening[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2012(in Chinese with English abstract). [24] 李大奇, 康毅力, 刘修善, 等. 裂缝性地层钻井液漏失动力学模型研究进展[J]. 石油钻探技术, 2013, 41(4): 42-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZT201304011.htmLi D Q, Kang Y L, Liu X S, et al. Progress in drilling fluid loss dynamics model for fractured formations[J]. Petroleum Drilling Techniques, 2013, 41(4): 42-47(in Chinese with English abstract https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZT201304011.htm [25] 孙其诚, 王光谦. 颗粒物质力学导论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.Sun Q C, Wang G Q. Introduction to granular material mechanics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2009(in Chinese). [26] 张韵洋. 薄弱地层封堵承压能力研究[D]. 成都: 西南石油大学, 2016.Zhang Y Y. Study on sealing and bearing capacity of weak formation[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Petroleum University, 2016(in Chinese with English abstract). -





 下载:
下载: