Characterization and evaluation of fractal dimension of intersalt shale oil reservoirs in Qianjiang Depression
-
摘要:
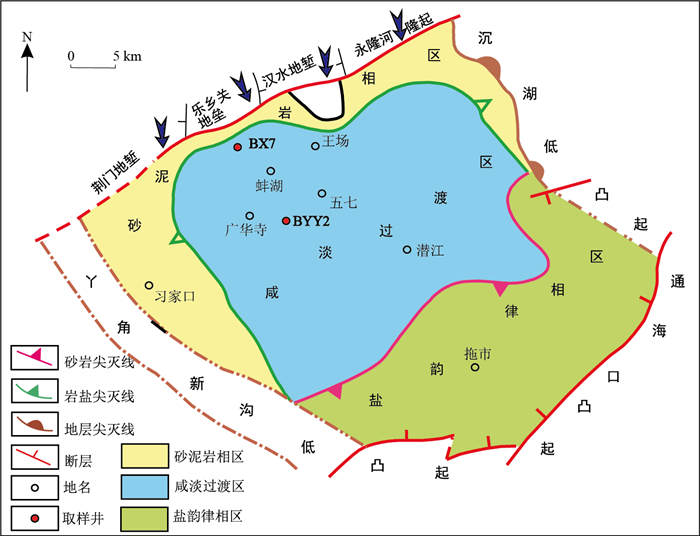
目前, 众多学者从地球化学特征、储层物性特征等方面对潜江凹陷潜江组页岩展开了较多研究, 并取得了一定的进展, 但对其孔隙的复杂性、形成孔喉的主要矿物及其影响因素的分析存在盲点。依据分形理论, 结合氮气吸附实验、高压压汞实验, 选取沉积位置不同的BX7井以及BYY2井, 分别对潜三段第四亚段(E
q 34-10)页岩的比表面分形特征、孔隙结构分形特征以及孔喉分形特征进行了评价, 分析了其影响因素。结果表明, 该地区的孔隙表面较为平整, 比表面分形维数D 1趋近于2, 孔隙表面的粗糙程度主要受黏土矿物本身特性影响。相较于沉积边缘的BX7井, 位于沉积中心的BYY2井储层孔隙结构分形特征更为简单。小孔径孔隙的孔体积所占比例越大, 孔隙结构分形特征越复杂。BX7井储层孔隙结构分形维数D 2主要受黏土矿物以及石英的影响, 而BYY2井储层孔隙结构分形维数D 2主要受白云石的影响。白云石为构成BX7井储层孔喉的主要矿物, 随白云石增加, 孔喉特征复杂, 连通性变差。BYY2井储层中石英形成的孔喉直径较小, 石英的增加会使孔隙连通性变差; 方解石形成的孔喉直径较大。页岩油的赋存会使孔隙的分形维数变小, 对孔喉分形特征的影响较小。盐类矿物的存在会阻塞孔隙, 使孔隙连通性变差。Abstract:At present, studies of the shales in Qianjiang Formation from the Qianjiang Depression has been widely documented and significant progress has been made in the aspects of geochemical characteristics and reservoir physical properties.However, the complexity of pores, the main minerals forming pore throats and their influencing factors is still poorly understood. In this work, based on fractal theory and combined with nitrogen adsorption and high-pressure mercury injection experiments, Wells BX7 and BYY2 at different deposition locations were selected to evaluate the specific surface fractal characteristics, pore structure fractal characteristics and pore throat fractal characteristics of the E
q 34-10 rhythmic shale of the Qianjiang Formation and analyses the influencing factors.The results show that the pore surface of shale in study are a is relatively flat, with the fractal dimension D1 being close to 2, and the roughness of the pore surface is mainly affected by the characteristics of the clay minerals. Compared with Well BX7 at the sedimentary edge, Well BYY2 at the sedimentary center has simpler fractal characteristics of reservoir pore structure. The larger the proportion of pore volume with a small pore size is, the more complex the fractal characteristics of the pore structure are. The fractal dimensionD 2 of the reservoir pore structure in Well BX7 is mainly affected by clay minerals and quartz, while dolomiteis the dominant controlling factor for the fractal dimensionD 2 of the reservoir pore structure in Well BYY2. Dolomite is the main mineral that constitutes the pore throat of the Well BX7 reservoir. With the increase in dolomite, the pore throat features are complex, and the pore connectivity becomes poor. The pore throat diameter formed by quartz in the Well BYY2 reservoir is small.The increase in quartz will worsen the pore connectivity, and the pore throat diameter formed by calcite is large. The occurrence of shale oil will reduce the fractal dimension of pores and have little influence on the fractal characteristics of pore throats. The presence of salt minerals can block the pores and make the pore connectivity poor.-
Key words:
- fractal characteristics /
- shale reservoir /
- Qianjiang Formation /
- Qianjiang Depression
-
图 2 潜江凹陷潜江组Eq34-10韵律页岩样品孔隙类型及有机质赋存状态
A.层间孔,粒间孔,BX7井,3 046.98 m;B.层间孔,粒间孔,BX7井,3 055.32 m;C.溶蚀孔,BX7井,3 046.98 m;D.有机质在粒间孔以及层间孔内赋存,BX7井,3 055.32 m;E.白云石晶间孔,BYY2井,2 817.11 m;F.粒间孔,BYY2井,2 817.51 m;G.白云石晶间孔,BYY2井,2 817.51 m;H.有机质在白云石晶间孔内赋存,BYY2井,2 814.67 m;I.有机质在粒间孔内赋存,BYY2井,2 817.11 m
Figure 2. Pore types and organic matter occurrence state of Qianjiang Formation Eq34-10 rhythmic shale samples in Qianjiang Depression
表 1 BX7井以及BYY2井样品矿物成分特征
Table 1. Mineral composition characteristics of samples from Wells BX7 and BYY2
样品 深度/m w(TOC)/% 黏土 石英 长石 方解石 白云石 黄铁矿 石膏 硬石膏 石盐 钙芒硝 wB/% BX7-1 3 046.490 2.070 21.96 12.60 16.53 14.59 31.90 2.43 \ \ \ \ BX7-2 3 046.980 2.870 13.47 18.88 17.42 20.22 27.32 2.69 \ \ \ \ BX7-6 3 049.020 1.400 18.13 22.47 13.02 30.27 14.43 1.68 \ \ \ \ BX7-11 3 051.820 1.010 6.44 9.58 4.79 10.19 66.08 2.92 \ \ \ \ BX7-15 3 053.720 2.430 37.87 25.42 10.27 8.74 11.56 3.72 2.43 \ \ \ BX7-18 3 055.320 0.815 5.53 17.11 16.28 25.78 33.36 1.94 \ \ \ \ BX7-25 3 060.110 0.969 8.24 8.11 20.47 13.65 46.73 2.80 \ \ \ \ BYY2-21 2 814.450 1.830 9.13 13.87 21.37 36.25 15.17 1.94 \ \ 2.27 \ BYY2-90 2 817.105 2.440 19.96 8.60 28.35 5.17 29.71 2.68 \ 3.59 1.95 \ BYY2-101 2 817.505 2.050 19.64 8.40 30.39 13.49 22.13 1.68 \ \ 0.85 3.43 BYY2-161 2 820.230 1.150 15.50 9.52 20.54 1.60 44.38 1.70 2.43 2.11 2.22 \ 表 2 基于N2气体吸附以及高压压汞数据重建计算分形维数值
Table 2. Calculation of fractal dimension values based on N2 gas adsorption and high-pressure mercury injection data
样品 氮气吸附实验 高压压汞实验 D1 D2 D3 BX7-1 抽提前 2.100 5 2.284 9 2.829 抽提后 2.358 4 2.579 0 2.898 BX7-2 抽提前 2.097 0 2.383 8 2.824 抽提后 2.348 5 2.641 7 2.828 BX7-6 抽提前 1.743 6 2.513 3 2.883 抽提后 2.407 2 2.659 5 2.886 BX7-11 抽提前 / / 2.844 抽提后 / / 2.955 BX7-15 抽提前 1.807 6 2.491 8 2.745 抽提后 2.483 9 2.676 3 2.790 BX7-18 抽提前 1.975 9 2.269 6 2.811 抽提后 2.241 3 2.561 9 2.821 BX7-25 抽提前 1.736 4 2.283 4 / 抽提后 2.359 6 2.538 0 / 样品 氮气吸附实验 高压压汞实验 D1 D2 D3-1 D3-2 BYY2-21 抽提前 1.792 1 2.258 5 2.89 2.76 抽提后 2.386 4 2.344 1 2.96 2.89 BYY2-90 抽提前 1.861 2 2.272 6 2.98 2.71 抽提后 2.384 1 2.384 8 2.88 2.80 BYY2-101 抽提前 2.033 1 2.190 0 2.77 2.84 抽提后 2.415 1 2.345 6 2.80 2.88 BYY2-161 抽提前 1.744 9 2.326 6 2.90 2.88 抽提后 2.286 1 2.403 1 2.91 2.78 -
[1] Chen S B, Zhu Y M, Wang H Y, et al. Shale gas reservoir characterisation: A typical case in the southern Sichuan Basin of China[J]. Energy, 2011, 36: 6609-6616. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2011.09.001 [2] Clarkson C R, Jensen J L, Chiooerfield S. Unconventional gas reservoir evaluation: What do we have to consider?[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2012, 8: 9-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2012.01.001 [3] Ji L, Qiu J, Xia Y, et al. Micropore characteristics and methane adsorption properties of common clay minerals by electron microscope scanning[J]. Acta Petroleum Sinica, 2012, 33(2): 249-256. [4] Milliken K L, Esch W L, Reed R M, et al. Grain assemblages and strong diagenetic overprinting in siliceous mudrocks, Barnett Shale(Mississippian), Fort Worth Basin, Texas, U.S. A[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96: 1553-1578. doi: 10.1306/12011111129 [5] Milliken K L, Rudnicki M, Awwiller D N, et al. Organic matter-hosted pore system, Marcellus Formation(Devonian), Pennsylvania[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97: 177-200. doi: 10.1306/07231212048 [6] Wang P F, Jiang Z X, Chen L, et al. Pore structure characterization for the Longmaxi and Niutitang shales in the Upper Yangtze Platform, South China: Evidence from focused ion beam-He ion microscopy, nano-computerized tomography and gas adsorption analysis[J]. Marine Petroleum Geology, 2016, 77: 1323-1337. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2016.09.001 [7] 孙中良, 王芙蓉, 侯宇光, 等. 潜江凹陷潜江组页岩中可溶有机质赋存空间表征及影响因素分析[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(6): 81-90. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906011.htmSun Z L, Wang F R, Hou Y G, et al. Spatial characterization and influence factors of soluble organic matter in shale of Qianjiang Formation in Qianjiang Depression[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(6): 81-90(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201906011.htm [8] Ross D J K, Bustin R M. The importance of shale composition and pore structure upon gas storage potential of shale gas reservoirs[J]. Marine Petroleum Geology, 2009, 26(6): 916-927. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2008.06.004 [9] Mastalerz M, Schimmelmann A, Drobniak A, et al. Porosity of Devonian and Mississippian New Albany shale across a maturation gradient: Insights from organic petrology, gas adsorption, and mercury intrusion[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97: 1621-1643. doi: 10.1306/04011312194 [10] Zhao H W, Ning Z F, Zhao T Y, et al. Effects of mineralogy on petrophysical properties and permeability estimation of the Upper Triassic Yanchang tight oil sandstones in Ordos Basin, northern China[J]. Fuel, 2016, 186: 328-338. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2016.08.096 [11] Mandelbrot B B. On the geometry of homogeneous turbulence, with stress on the fractal dimension of the iso-surfaces of scalars[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 1975, 72(3): 401-416. doi: 10.1017/S0022112075003047 [12] Li P, Zheng M, Bi H, et al. Pore throat structure and fractal characteristics of tight oil sandstone: A case study in the Ordos Basin, China[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science Engineering, 2017, 149: 665-674. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.11.015 [13] Huang W, Lu S, Hersi O S, et al. Reservoir spaces in tight sandstones: Classification, fractal characters, and heterogeneity[J]. Journal of National Gas Science Engineering, 2017, 46: 80-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2017.07.006 [14] 赵会涛, 郭英涛, 杜小伟, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地高桥地区本溪组砂岩储层微观孔隙多重分形特征[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(6): 175-184. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0614Zhao H T, Guo Y T, Du X W, et al. Micro-pore multifractal characteristics of Benxi Formation sandstone reservoir in Gaoqiao area, Ordos Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(6): 175-184(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0614 [15] Yin T, Liu D, Cai Y, et al. Size distribution and fractal characteristics of coal pores through nuclear magnetic resonance cryoporometry[J]. Energy Fuels, 2017, 31(8): 7746-7757. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.7b00389 [16] Lai J, Wang G. Fractal analysis of tight gas sandstones using high-pressure mercury intrusion techniques[J]. Journal of National Gas Science Engineering, 2015, 24: 185-196. doi: 10.1016/j.jngse.2015.03.027 [17] Wang Z, Pan M, Shi Y, et al. Fractal analysis of Donghetang sandstones using NMR measurements[J]. Energy & Fuels, 2018, 32: 2973-2982. [18] Zhao P, Wang Z, Sun Z, et al. Investigation on the pore structure and multifractal characteristics of tight oil reservoirs using NMR measurements: Permian Lucaogou Formation in Jimusaer Sag, Junggar Basin[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2017, 86: 1067-1081. doi: 10.1016/j.marpetgeo.2017.07.011 [19] Jiang F J, Chen D, Chen J, et al. Fractal analysis of shale pore structure of continental gas shale reservoir in the Ordos Basin, NW China[J]. Energy Fuels, 2016, 30: 4676-4689. doi: 10.1021/acs.energyfuels.6b00574 [20] Yang F, Ning Z F, Liu H Q. Fractal characteristics of shales from a shale gas reservoir in the Sichuan Basin, China[J]. Fuel, 2014, 115: 378-384. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2013.07.040 [21] Sun M D, Yu B S, Hu Q H, et al. Nanoscale pore characteristics of the Lower Cambrian Niutitang Formation shale: A case study from Well Yuke #1 in the Southeast of Chongqing, China[J]. International Journal of Coal Geology, 2016, 154: 16-29. [22] Hu Q H, Zhang Y X, Meng X H, et al. Characterization of micro-nano pore networks in shale oil reservoirs of Paleogene Shahejie Formation in Dongying Sag of Bohai Bay Basin, East China[J]. Petoleum Exploration and Development, 2017, 44(5): 1-10. [23] 王国力, 杨玉卿, 张永生, 等. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷王场地区古近系潜江组沉积微相及其演变[J]. 古地理学报, 2004, 6(2): 140-150. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200402001.htmWang G L, Wang Y Q, Zhang Y S, et al. Sedimentary microfacies and evolution of the Qianjiang Formation of Paleogene at Wangchang area in Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of Palaeography, 2004, 6(2): 140-150(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX200402001.htm [24] 熊智勇, 吴世强, 王洋, 等. 江汉盐湖盆地盐间泥质白云岩油藏地质特征与实践[J]. 地质科技情报, 2015, 34(2): 181-187. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502027.htmXiong Z Y, Wu S Q, Wang Y, et al. Geological characteristics and practice for intersalt argillaceous dolomite reservoir in the Qianjiang Depression of Jianghan Salt Lake Basin[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2015, 34(2): 181-187(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201502027.htm [25] 聂海宽, 张培先, 边瑞康, 等. 中国陆相页岩油富集特征[J]. 地学前缘, 2016, 23(2): 55-62. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602009.htmNie H K, Zhang P X, Bian R K, et al. Oil accumulation characteristics of China continental shale[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2016, 23(2): 55-62(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201602009.htm [26] 肖枫, 张士万, 何幼斌, 等. 潜江凹陷潜三段盐间页岩油特征及油源研究[J]. 能源与环保, 2017, 39(7): 96-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT201707018.htmXiao F, Zhang S W, He Y B, et al. Geochemistry and oil-source study of inter-salt shale oil of Eq3 in Qianjiang Depression[J]. China Energy and Environmental Protection, 2017, 39(7): 96-108(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZMT201707018.htm [27] 陶国亮, 刘鹏, 钱门辉, 等. 潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩含油性及其勘探意义[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2019, 48(6): 1256-1265. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201906011.htmTao G L, Liu P, Qian M H, et al. Oil-bearing characteristics and exploration significance of inter-salt shale in Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Depression, Jianghan Basin[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2019, 48(6): 1256-1265(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGKD201906011.htm [28] 龙玉梅, 陈曼霏, 陈风玲, 等. 潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩油储层发育特征及影响因素[J]. 油气地质与采收率, 2019, 26(1): 59-64. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901006.htmLong Y M, Chen M F, Chen F L, et al. Characteristics and influencing factors of inter-salt shale oil reservoirs in Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2019, 26(1): 59-64(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YQCS201901006.htm [29] 徐二社, 陶国亮, 李志明, 等. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷盐间页岩油储层不同岩相微观储集特征: 以古近系潜江组三段4亚段10韵律为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2020, 42(2): 193-201. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202002006.htmXu E S, Tao G L, Li Z M, et al. Microscopic reservoir characteristics of different lithofacies from inter-salt shale oil reservoir in Qianjiang Sag, Jianghan Basin: A case study of Paleogene Eq34-10 rhythm[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2020, 42(2): 193-201(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD202002006.htm [30] 徐崇凯, 刘池洋, 郭佩, 等. 潜江凹陷古近系潜江组盐间泥岩地球化学特征及地质意义[J]. 沉积学报, 2018, 36(3): 617-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201803017.htmXu C K, Liu C Y, Guo P, et al. Geochemical characteristics and their geological significance of intrasalt mudstones from the Paleogene Qianjiang Formation in the Qianjiang Graben, Jianghan Basin, China[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2018, 36(3): 617-629(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201803017.htm [31] 刘刚, 周东升. 微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用: 以江汉盆地潜江组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(2): 307-310. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200703016.htmLiu G, Zhou D S. Application of microelements analysis in identifying sediment environment: Taking Qianjiang Formation in the Jianghan Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(2): 307-310(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD200703016.htm [32] 戴世昭. 江汉盐湖盆地石油地质[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1997: 57-108.Dai S Z. Petroleum geology of Jianghan Salt Lake Basin[M]. Beijing: Petroleum Industry Press, 1997: 57-108(in Chinese). [33] 王芙蓉, 何生, 郑有恒, 等. 江汉盆地潜江凹陷潜江组盐间页岩油储层矿物组成与脆性特征研究[J]. 石油实验地质, 2016, 38(2): 211-218. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201602011.htmWang F R, He S, Zheng Y H, et al. Mineral composition and brittleness characteristics of the inter-salt shale oil reservoirs in the Qianjiang Formation, Qianjiang Sag[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2016, 38(2): 211-218(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYSD201602011.htm [34] Pfeifer P, Avnir D. Chemistry in noninteger dimensions between two and three[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1983, 79(7), 3369-3558. [35] Liu X J, Xiong J, Liang L X. Investigation of pore structure and fractal characteristics of organic rich Yanchang Formation shale in central China by nitrogen adsorption/desorption analysis[J]. Journal of National Gas Science Engineering, 2015, 22: 62-72. [36] Li Z Q, Shen X, Qi Z Y, et al. Study on the pore structure and fractal characteristics of marine and continental shale based on mercury porosimetry, N2 adsorption and NMR methods[J]. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering, 2018, 53: 12-21. [37] Khalili N R, Pan M, Sandí G. Determination of fractal dimension of solid carbons from gas and liquid phase adsorption isotherms[J]. Carbon, 2000, 38: 573-588. [38] Sing K S W. Characterization of porous materials: Past, present and future[J]. Colloids & Surfaces A Physicochemical & Engineering Aspects, 2004, 241(1/3): 3-7. [39] Yao Y B, Liu D M, Tang D Z, et al. Fractal characterization of adsorption-pores of coals from North China: An investigation on CH4 adsorption capacity of coals[J]. Science Direct, 2008, 73: 27-42. [40] Brunauer S, Emmett P H, Teller E. On a theory of the van der waals adsorption of gases[J]. American Chemical Society, 1940, 62(7): 1723-1732. [41] Giri A, Tarafdar S, Gouze P, et al. Fractal pore structure of sedimentary rocks: Simulation in 2-D using a relaxed bidisperse ballistic deposition model[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2012, 87: 40-45. [42] Petrov O V, Furó I. NMR cryoporometry: Principles, applications and potential[J]. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer, 2009, 54: 97-122. [43] Sun Z L, He Z L, Wang F R, et al. Occurrence characteristics of saline-lacustrine shale-oil in the Qianjiang Depression, Jianghan Basin, Central China[J/OL]. Journal of Earth Science, 2020. [2020-10-2](2021-01-21). https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1788.P.20201027.1150.006.html. -





 下载:
下载: