Geological, geochemical and sulfur isotopic characteristics of critical metal-enriched pyritic ore in the Puyi area, northwest Guizhou Province: Constraints on the genesis of the deposit
-
摘要:
探讨黔西北普宜地区富关键金属元素硫铁矿的同位素地球化学特征、元素地球化学特征及成因, 可以为硫铁矿资源开发、伴生有益元素综合利用与评价及理解富关键金属元素硫铁矿聚集机制提供更为丰富的信息。在全面收集已有地质、矿产资料的基础上, 结合野外实地调查, 应用元素地球化学及硫同位素分析等方法, 对该区硫铁矿地球化学特征及成因做了较为深入研究, 并初步建立成矿模式。结果表明: 富关键金属元素硫铁矿主要赋存于中二叠统龙潭组(P2
l )底部的晶屑凝灰岩中, 矿体形态简单, 呈层状分布, 硫铁矿中共(伴)生的稀土, Li, Nb, Zr, Ga等有益元素均可综合利用。w (ΣREE)平均为431.24×10-6, 最大值为1 634.57×10-6, 一般在180×10-6~1 630×10-6之间;w (Ga)平均为32.51×10-6, 一般为25×10-6~120×10-6, 最大为120.00×10-6;w (Nd)平均为103.29×10-6, 一般为40×10-6~380×10-6, 最大为380.00×10-6;w (Li)最大值为1 366.00×10-6;w (Al2O3)最大值为42.17%。硫铁矿稀土元素配分模式表现为轻稀土元素富集、重稀土元素相对亏损的右倾型。矿石中成矿元素Ga, Li, Zr, Ti, Se, Cd, Nb, V, Hg等元素相对富集, Ba, Sr, Zn, Te等元素相对贫化。硫铁矿石中黄铁矿硫同位素δ 34S变化范围主要在-33.90‰~-18.60‰之间, 平均值-16.04‰, 为轻硫富集型, 富关键金属元素硫铁矿的硫源受生物细菌还原作用影响较大。硫铁矿主要是在沉积阶段通过微生物铁还原、微生物硫酸盐还原和化学铁还原驱动下形成的。初步认为赋存于硫铁矿中的稀土主要以类质同象替代形式赋存于黏土矿物中, 形成过程可分为风化搬运阶段、沉积成矿阶段和成岩后生作用阶段。Abstract:The study of the isotopic and elemental geochemical characteristics and genesis of critical metal-enriched pyritic ore in the Puyi area of Northwest Guizhou provides more abundant information for the exploitation of pyritic ore resources, comprehensive utilization and evaluation of associated beneficial elements, and understanding the mechanism of critical metal-enriched pyritic ore. Based on the comprehensive collection of existing geological and mineral data, combined with field investigation, the geochemical characteristics and genesis of pyrite in this area are studied by using element geochemistry and sulfur isotope analysis, and the metallogenic model is preliminarily established. The study shows that the critical metal-enriched pyritic ore mainly occurs in the crystalline tuff at the bottom of the Longtan Formation of the middle Permian(P2
l ), and the ore body is simple in shape and distributed in layers. The beneficial elements, such as REEs, Li, Nb, Zr, Li, Nb, Zr, Ga, can be comprehensively utilized. The results show that ΣREE usually ranges from 180×10-6 to 1 630×10-6, with an average of 431.24×10-6 and up to 1 634.57×10-6; Ga usually ranges from 25×10-6 to 120×10-6, with an average of 32.51×10-6 and up to 120.00×10-6; Nd generally ranges from 40×10-6 to 380×10-6, with an average of 103.29×10-6 and up to 380.00×10-6; and the maximum values of Li and Al2O3 are 1 366.00×10-6 and 42.17%. The REE distribution pattern of pyritic ore is characterized by enrichment in LREEs and relative depletion in HREEs. The ore-forming elements Ga, Li, Zr, Ti, Se, Cd, Nb, V and Hg are relatively enriched, while Ba, Sr, Zn and Te are relatively depleted. Theδ 34S of pyrite in pyritic ore mainly range from -33.90‰ to -18.60‰(on average of -16.04‰), which shows the characteristics of the enrichment of light sulfur. The sulfur source of critical metal-enriched pyritic ore was greatly affected by the reduction of biological bacteria. Pyritic ore is mainly formed in the sedimentary stage by microbial iron reduction, microbial sulfate reduction and chemical iron reduction. It is suggested that REEs in pyritic ore mainly occur in clay minerals in the form of similar isomorphic substitution, and the formation process can be divided into the weathering transportation stage, sedimentary mineralization stage and diagenetic epigenetic stage.-
Key words:
- pyritic ore /
- sulfur isotope /
- critical metal /
- genesis /
- Puyi area /
- northwestern Guizhou
-
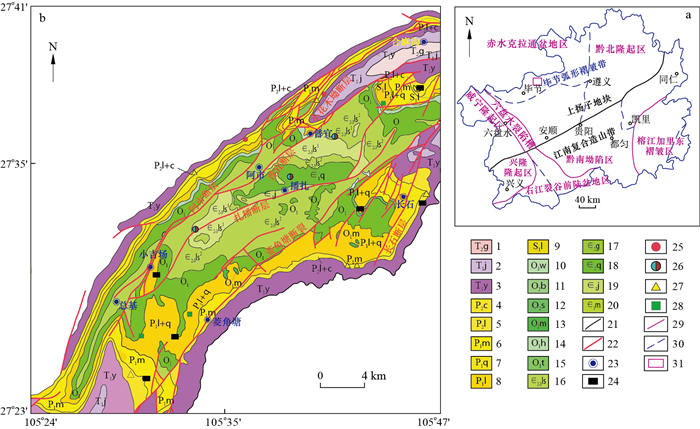
图 1 普宜地区地质简图[21]
1.关岭组;2.嘉陵江组;3.夜郎组;4.长兴组;5.龙潭组;6.茅口组;7.栖霞组;8.梁山组;9.龙马溪组;10.五峰组;11.宝塔组;12.十字铺组;13.湄潭组;14.红花园组;15.桐梓组;16.娄山关组;17.高台组;18.清虚洞组;19.金顶山组;20.明心寺组;21.地质界线;22.断层;23.地点及地名;24.煤;25.铁矿;26.铅锌矿;27.硫铁矿;28.黏土矿; 29.三级构造单元界线;30.四级构造单元界线;31.研究区
Figure 1. Simplified geological map of the Puyi area
图 3 研究区硫铁矿稀土元素分配模式(球粒陨石标准化数据引自文献[25])
Figure 3. Chondrite-normalized REE patterns in the study area
图 5 研究区w(B)-w(Ga)(a)和w(Ba)-w(Sr)(b)图解[29]
Figure 5. B-Ga(a) and Ba-Sr(b) diagrams in the study area
图 6 限定物源区特征图解(底图据文献[24]修改)
Figure 6. Characteristic diagram of limited source area
图 7 研究区硫同位素与地球上重要物质及各类硫铁矿床硫同位素组成对比图(底图据文献[49]修改)
TRS.硫酸盐热化学还原;BRS.细菌硫酸盐还原
Figure 7. Comparison of sulfur isotopes in the study area with important substances on the earth and sulfur isotopic compositions of various pyrite deposits
表 1 普宜地区硫铁矿石主量元素、微量元素组成及元素比值特征
Table 1. Characteristics of major elements, trace elements and element ratios of pyritic ore in the Puyi area
编号 D4601-1QY D4630-1QY D4670-1QY D4671-1QY D4672-1QY D4624-1Y D4625-1Y D4630-1Y D4654-1Y D4670-1Y D4671-2Y D4672-1Y D4685-1Y 地壳丰度 SiO2 33.97 29.04 19.78 18.41 36.76 29.27 11.94 40.65 46.58 45.19 32.34 46.88 41.77 28.3 Al2O3 29.67 25.32 15.16 14.44 20.94 19.86 7.32 26.10 32.50 31.95 21.06 32.08 29.63 8.41 TFe2O3 12.35 13.74 38.72 33.14 15.34 18.83 25.80 13.97 10.30 10.29 19.35 8.72 13.50 5.31 TiO2 3.43 1.87 2.82 2.24 4.70 1.51 0.26 2.04 1.73 0.99 0.83 2.54 1.16 0.42 CaO wB/% 0.053 0.055 0.049 0.075 0.075 - - - - - - - - 4.75 MgO 0.078 0.041 0.11 0.087 0.069 - - - - - - - - 2.83 Na2O 0.030 0.120 0.048 0.029 0.039 - - - - - - - - 2.3 K2O 0.260 0.450 0.440 0.046 0.150 - - - - - - - - 1.49 P2O5 0.057 0.020 0.037 0.061 0.033 - - - - - - - - 0.044 烧失量 17.36 27.20 18.88 27.35 18.06 - - - - - - - - - Ni 62.0 35.2 49.5 62.7 49.5 42.5 29.9 45.3 43.7 57.2 76.5 31.2 89.6 59 Co 9.56 23.60 3.61 13.40 11.30 6.54 2.79 3.77 4.79 55.30 13.10 2.43 14.40 27 Cu 62.2 73.4 61.2 158.0 78.2 144.0 36.9 58.9 97.3 61.1 160.0 45.2 104.0 27 Pb 48.6 30.5 47.6 53.8 48.3 129.0 41.9 41.7 34.9 46.5 51.8 30.5 27.5 11 As 4.12 7.82 7.34 4.76 6.44 3.79 < 1.00 15.40 1.04 11.10 4.04 6.40 1.89 2.5 Te 0.28 < 0.20 0.28 0.32 0.84 1.19 0.35 0.75 0.40 0.30 < 0.20 0.38 0.37 - Se 0.38 0.24 1.54 0.18 3.34 0.76 0.40 1.65 1.57 0.26 0.11 2.32 0.31 0.13 Cr wB/10-6 273.0 160.0 148.0 124.0 281.0 185.0 35.6 236.0 197.0 97.3 107.0 636.0 176.0 135 V 280 391 145 261 612 624 104 594 197 129 185 856 266 138 Ga 42.80 41.30 31.60 23.40 32.00 36.90 7.49 40.00 42.40 35.70 28.20 40.80 27.20 16 In 0.380 0.360 0.230 0.140 0.230 0.390 0.078 0.280 0.410 0.058 0.140 0.410 0.320 0.05 Th 8.67 10.40 14.80 9.88 19.10 14.90 2.77 21.80 26.10 13.80 9.53 35.40 20.70 5.6 Zr 1 814 766 1 976 588 1 099 640 116 1 054 1 270 1 830 461 1 430 956 132 Nb 183.0 53.6 194.0 43.2 112.0 42.6 < 5.0 74.4 177.0 168.0 29.7 192.0 64.0 8 U 8.36 5.77 5.62 3.02 8.34 8.63 1.21 7.94 8.39 4.94 1.97 13.40 6.82 1.3 Li 474.0 385.0 150.0 180.0 130.0 133.0 72.4 221.0 723.0 25.5 147.0 200.0 870.0 16 Sr 84.7 41.8 30.9 196.0 27.0 32.7 18.1 47.7 87.5 28.9 177.0 30.0 34.9 320 Cd 0.090 2.220 0.100 1.240 0.460 0.270 0.050 0.130 0.083 2.120 1.410 0.086 0.080 0.08 Ge 2.00 1.12 0.66 0.96 1.14 0.94 0.27 1.10 1.66 1.02 0.79 1.47 1.26 1.3 Ba 30.6 39.8 52.6 157.0 56.2 < 50.0 < 50.0 118.0 70.6 106.0 99.6 99.7 83.0 456 F 370 414 512 410 312 438 368 220 536 571 609 344 817 553 Zn wB/10-6 - - - - - < 15.0 18.2 < 15.0 < 15.0 75.3 18.7 < 15.0 < 15.0 72 Ag - - - - - 0.070 0.033 0.031 < 0.020 0.029 0.076 < 0.020 0.034 0.056 Sb - - - - - 2.49 0.36 2.62 1.03 0.98 1.36 3.10 1.11 0.2 Hg - - - - - 0.83 0.10 0.77 0.26 0.37 0.43 0.36 0.12 30 B 39.1 42.6 29.8 10.2 12.2 11.7 < 5.00 42.0 45.6 28.9 9.94 25.5 53.4 11 Rb 8.66 7.62 7.98 1.16 2.66 - - - - - - - - 49 Sc 23.7 22.6 18.5 18.6 24.4 - - - - - - - - 22 B/Ga 0.91 1.03 0.94 0.44 0.38 0.32 0.67 1.05 1.08 0.81 0.35 0.63 1.96 Sr/Ba 2.77 1.05 0.59 1.25 0.48 0.65 0.36 0.40 1.24 0.27 1.78 0.30 0.42 Th/U 1.04 1.80 2.63 3.27 2.29 1.73 2.29 2.75 3.11 2.79 4.84 2.64 3.04 Rb/K 0.003 3 0.001 7 0.001 8 0.002 5 0.001 8 - - - - - - - - Sr/Cu 1.36 0.57 0.50 1.24 0.35 0.23 0.49 0.81 0.90 0.47 1.11 0.66 0.34 V/Cr 1.03 2.44 0.98 2.10 2.18 3.37 2.92 2.52 1.00 1.33 1.73 1.35 1.51 Ni/Co 6.49 1.49 13.71 4.68 4.38 6.50 10.72 12.02 9.12 1.03 5.84 12.84 6.22 Ni/V 0.22 0.09 0.34 0.24 0.08 0.07 0.29 0.08 0.22 0.44 0.41 0.04 0.34 CIA/% 99.03 97.17 96.46 99.40 98.66 Funtion1 11.83 12.88 23.88 20.76 6.72 Funtion2 -6.00 -6.90 -13.63 -13.10 -6.91 注:“-”为未分析项;地壳丰度引自文献[23]; 其中,CIA=[(Al2O3)/(Al2O3+CaO+Na2O+K2O)]×100[22]; Funtion1=-1.773w(TiO2)+0.607w(Al2O3)+0.76w(TFe2O3)-1.5w(MgO)+0.616w(CaO)+0.509w(Na2O)-1.244w(K2O)-9.09;Funtion2=0.445w(TiO2)+0.07w(Al2O3)-0.25w(TFe2O3)-1.142w(MgO)+0.438w(CaO)+1.475w(Na2O)+1.426w(K2O)-6.861[24] 表 2 普宜地区硫铁矿石稀土元素含量及特征参数
Table 2. REE content and characteristic parameters of pyritic ore in the Puyi area
样品编号 D4601-1QY D4630-1QY D4670-1QY D4671-1QY D4672-1QY D4624-1Y D4630-1Y D4654-1Y D4670-1Y D4671-2Y D4672-1Y D4685-1Y La 104.0 49.4 93.1 65.6 39.6 78.4 109.0 106.0 86.6 83.5 69.7 43.8 Ce 81.0 39.4 148.0 93.4 79.8 153.0 181.0 172.0 175.0 113.0 177.0 60.1 Pr 14.60 9.43 12.40 14.60 7.49 12.2 15.2 13.6 21.1 21.2 12.3 7.51 Nd 41.20 33.50 31.60 54.40 21.90 33.8 40.0 34.5 83.3 77.6 34.5 25.5 Sm 7.14 11.00 4.06 12.20 4.94 4.68 5.69 5.64 18.2 11.7 10.1 6.62 Eu 1.95 3.33 0.96 3.40 1.22 1.09 1.41 1.62 4.47 2.62 2.59 1.79 Gd 10.10 20.70 5.04 10.30 6.44 4.19 6.87 7.55 16.3 9.23 12.7 8.9 Tb 1.93 3.86 1.10 1.67 1.44 0.83 1.54 1.55 2.81 1.69 2.78 2.06 Dy 11.60 21.40 7.48 9.73 9.44 5.72 10.30 9.28 15.90 10.80 17.60 14.10 Ho wB/10-6 2.18 3.92 1.50 1.90 1.90 1.23 2.06 1.68 2.86 2.14 3.4 2.94 Er 6.02 10.60 4.42 5.56 5.84 3.85 6.01 4.56 7.85 6.43 10.1 9.39 Tm 0.80 1.44 0.65 0.81 0.90 0.59 0.9 0.64 1.13 0.94 1.54 1.48 Yb 4.78 8.59 4.24 5.12 6.05 3.98 5.68 3.81 6.92 5.89 9.85 9.62 Lu 0.71 1.30 0.63 0.72 0.91 0.62 0.87 0.57 1.02 0.92 1.51 1.51 Y 56.40 113.00 42.50 54.00 41.40 30.80 54.60 39.10 64.00 65.40 72.70 66.20 ΣREE 344.41 330.87 357.68 333.41 229.27 334.98 441.13 402.10 507.46 413.06 438.37 261.52 LREE 249.89 146.06 290.12 243.60 154.95 283.17 352.30 333.36 388.67 309.62 306.19 145.32 HREE 94.52 184.81 67.56 89.81 74.32 51.81 88.83 68.74 118.79 103.44 132.18 116.20 LREE/HREE 2.64 0.79 4.29 2.71 2.08 5.47 3.97 4.85 3.27 2.99 2.32 1.25 (La/Yb)N 14.70 3.89 14.84 8.66 4.42 13.31 12.97 18.80 8.46 9.58 4.78 3.08 δEu 0.70 0.66 0.65 0.90 0.66 0.74 0.69 0.76 0.78 0.75 0.70 0.71 δCe 0.43 0.40 0.90 0.68 1.03 1.06 0.93 0.93 0.94 0.62 1.32 0.72 (La/Sm)N 9.17 2.83 14.43 3.38 5.05 10.54 12.06 11.83 2.99 4.49 4.34 4.16 (Gd/Yb)N 1.71 1.95 0.96 1.63 0.86 0.85 0.98 1.61 1.91 1.27 1.04 0.75 (La/Ce)N 3.35 3.27 1.64 1.83 1.29 1.34 1.57 1.61 1.29 1.93 1.03 1.90 表 3 研究区硫铁矿硫同位素组成
Table 3. Sulfur isotopic composition of pyrite in the study area
样号 矿物 δ34SV-CDT/‰ TCP05-10TW 黄铁矿 -29.20 D1070-1TW 黄铁矿 -27.40 D3035-1TW 黄铁矿 -33.90 D4601-1TW 黄铁矿 -8.15 D4624-1TW 黄铁矿 6.73 D4625-1TW 黄铁矿 -24.45 D4630-1TW 黄铁矿 -31.43 D4654-1TW 黄铁矿 -18.60 D4661-1TW 黄铁矿 -6.68 D4685-1TW 黄铁矿 9.56 D4729-1TW 黄铁矿 -12.89 -
[1] 雷灵芳, 郭江波, 余敏华, 等. 贵州省硫铁矿资源利用现状调查成果汇总报告[R]. 贵阳: 中化地质矿山总局贵州地质勘查院, 2013.Lei L F, Guo J B, Yu M H, et al. Summary report on investigation results of utilization status of pyrite resources in Guizhou Province[R]. Guiyang: Guizhou Geological Exploration Institute of Sinochem General Administration of Geology and Mines, 2013(in Chinese). [2] 胡瑞忠, 温汉捷, 叶霖, 等. 扬子地块西南部关键金属元素成矿作用[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(33): 3700-3714. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202033007.htmHu R Z, Wen H J, Ye L, et al. Metallogeny of critical metals in the southwestern Yangtze Block[J]. China Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(33): 3700-3714(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB202033007.htm [3] 戎嘉余, 陈旭, 王怿, 等. 奥陶-志留纪之交黔中古陆的变迁: 证据与启示[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41(10): 1407-1415. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201110003.htmRong J Y, Chen X, Wang Y, et al. Northward expansion of Central Guizhou Oldland through the Ordovician and Silurian transition: Evidence and implications[J]. China Science: Earth Science, 2011, 41(10): 1407-1415(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201110003.htm [4] Dai S, Zeng R, Sun Y. Enrichment of arsenic, antimony, mercury, and thallium in a Late Permian anthracite from Xingren, Guizhou, Southwest China[J]. International Journal Coal Geology, 2006, 66: 217-226. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2005.09.001 [5] Yu W, Algeo T J, Yan J, et al. Climatic and hydrologic controls on Upper Paleozoic bauxite deposits in South China[J]. Earth-Science Review, 2018, 189: 159-176. [6] 温汉捷, 罗重光, 杜胜江, 等. 碳酸盐岩黏土型锂资源的发现及意义[J]. 科学通报, 2020, 65(1): 53-59.Wen H J, Luo C G, Du S J, et al. Carbonate-hosted clay-type lithium deposit and its prospecting significance[J]. China Science Bulletin, 2020, 65(1): 53-59(in Chinese with English abstract). [7] Bárdossy G. Developments ineconomic geology 14: Karst bauxites, bauxite deposits on carbonate rocks[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1982. [8] Liu X, Wang Q, Feng Y, et al. Genesis of the Guangou karstic bauxite deposit in western Henan, China[J]. Ore Geology Review, 2013, 55: 162-175. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.002 [9] 王登红, 李沛刚, 屈文俊, 等. 贵州大竹园铝土矿中钨和锂的发现与综合评价[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2013, 43(1): 145-152. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201301004.htmWang D H, Li P G, Qu W J, et al. Discovery and preliminary study of the high tungsten and lithium contents in the Dazhuyuan bauxite deposit, Guizhou, China[J]. Science China: Earth Science, 2013, 43(1): 145-152(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK201301004.htm [10] Dai S, Zhou Y, Zhang M, et al. A new type of Nb(Ta)-Zr(Hf)-REE-Ga polymetallic deposit in the Late Permian coal-bearing strata, eastern Yunnan, southwestern China: Possible economic significance and genetic implications[J]. International Journal Coal Geology, 2010, 83: 55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.coal.2010.04.002 [11] 代世峰, 任徳贻, 周义平, 等. 煤型稀有金属矿床: 成因类型、赋存状态和利用评价[J]. 煤炭学报, 2014, 39(8): 1707-1715. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201408044.htmDai S F, Ren D Y, Zhou Y P, et al. Coal-hosted rare metal deposits: Genetic types, modes of occurrence, and utilization evaluation[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2014, 39(8): 1707-1715(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MTXB201408044.htm [12] Zhang Z, Zheng G, Takahashi Y, et al. Extreme enrichment of rare earth elements in hard clay rocks and its potential as a resource[J]. Ore Geology Review, 2016, 72: 191-212. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.018 [13] Zhong H, Campbell I H, Zhu W G, et al. Timing and source constraints on the relationship between mafic and felsic intrusions in the Emeishan large igneous province[J]. Geochimca et Cosmochimca Acta, 2011, 75(5): 1374-1395. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2010.12.016 [14] Deconinck J F, Crasquin S, Bruneau L, et al. Diagenesis of clay minerals and K-bentonites in Late Permian/Early Triassic sediments of the Sichuan Basin(Chaotian section, Central China)[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2014, 81: 28-37. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2013.11.018 [15] He B, Xu Y G, Huang X L, et al. Age and duration of the Emeishan flood volcanism, SW China: Geochemistry and SHRIMP zircon U-Pb dating of silicic ignimbrites, post-volcanic Xuanwei Formation and clay tuff at the Chaotian section[J]. Earth Planetery Science Letter, 2007, 255: 306-323. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.021 [16] Xu Y G, Chung S L, Shao H, et al. Silicic magmas from the Emeishan large igneous province, Southwest China: Petrogenesis and their link with the end-Guadalupian biological crisis[J]. Lithos, 2010, 119: 47-60. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2010.04.013 [17] 贵州地质区调大队一分队. 1∶20万威信幅区域地质调查报告[R]. 贵阳: 有色金属矿产地质调查中心, 1989.The First Unit of the Guizhou Geological District Survey Team. 1∶200 000 prestige sheet regional geological survey report[R]. Guiyang: Geological Survey Center for Nonferrous Metals, 1989(in Chinese). [18] 何熙琦, 刘爱民, 肖加飞, 等. 1∶25万毕节幅区域地质调查成果报告[R]. 贵阳: 贵州省地质调查院, 2004.He X Q, Liu A M, Xiao J F, et al. 1∶250 000 Bijie sheet regional geological survey results report[R]. Guiyang: Guizhou Geological Survey Institute, 2004, 1-254(in Chinese). [19] 王常微, 邓毅, 晓芳, 等. 贵州省矿产资源潜力评价综合信息集成[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018.Wang C W, Deng Y, Xiao F, et al. Comprehensive information integration of mineral resources potential evaluation in Guizhou Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018(in Chinese). [20] 张慧, 王常微, 熊兴国, 等. 贵州省矿产资源潜力评价成矿地质背景研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018.Zhang H, Wang C W, Xiong X G, et al. Study on the metallogenic geological background of mineral resources potential evaluation in Guizhou Province[M]. Wuhan: China University of China Press, 2018(in Chinese). [21] 贵州省地质调查院. 中国区域地质志: 贵州志[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2017: 939-941.Guizhou Geological Survey Institute. The regional geology of China: Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2017: 939-941(in Chinese). [22] Nesbitt H W, Markovics G. Weathering of granodioritic crust, long-term storage of elements in weathering profiles, and petrogenesis of siliciclastic sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(8): 1653-1670. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00031-8 [23] Rudnick R L, Gao S. Composition of the continental crust[C]//Holland H D, Turekian K K. Treatise on geochemistry. Oxford: Elsevier-Pergaman, 2003. [24] Rollinson H R. Using geochemical data: Evaluation, presentation, interpretation[M]. [S. l.]: Longman Singapur Press, 1993. [25] Taylor S R, Mclennan S M. The continental crust: Its composition and evolution[M]. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publication, 1985. [26] Chaussidon M, Lorand J P. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege(North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): An ion microprobe study[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1990, 54(10) : 2835-2846. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(90)90018-G [27] Ohmoto H. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 1972, 67(5) : 551-578. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.67.5.551 [28] Zhou J X, Huang Z L, Bao G P, et al. Sources and thermo-chemical sulfate reduction for reduced sulfur in the hydrothermal fluids, southeastern SYG Pb-Zn metallogenic province, SW China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2013, 24(5) : 759 -771. doi: 10.1007/s12583-013-0372-8 [29] 金中国, 刘辰生, 邹林, 等. 贵州务-正-道地区二叠纪铝土矿沉积环境地球化学证据[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(4): 817-827. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.04.011Jin Z G, Liu C S, Zou L, et al. Geochemical evidence of sedimentary environment of Permian bauxite in the Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen area, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(4): 817-827(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.04.011 [30] 杜远生, 周琦, 金中国, 等. 黔北务正道地区铝土矿基础地质与成矿作用研究进展[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(1): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.01.001Du Y S, Zhou Q, Jin Z G, et al. Advances in basic geology and metallogenic regularity study of bauxite in Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen area, northern Guizhou Province[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(1): 1-6(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2013.01.001 [31] Adams J A S, Weaver C E. Thorium-touranium ratios as indictatiors of sedimentary processes an example of geochemical facies[J]. Bulletin America Assocation Petroleum Geologists, 1958, 42: 387-430. [32] Laukas T C. Origin of bauxite at Eufaula Alabama[J]. USA Clay Minerals, 1983, 18(2): 350-361. [33] Campbell F A, Williams G D. Chemical composition of shale of Mannvill Group(Lower Cretaceous) of central Alberta[J]. AAPG Bulletin, 1965, 49(1): 29-56. [34] Jones B J, Manning A C. Comparison of geochemical indices used for the interpretation of palaeoredox conditions in ancient mudstones[J]. Chemical Geology, 1994, 111(1/4): 111-129. [35] 黄建国. 黔西南二叠系龙潭组含金建造的初步研究[D]. 贵阳: 贵州大学, 2007.Huang J G. Preliminary study on gold bearing formation of Permian Longtan Formation in Southwest Guizhou[D]. Guiyang: Guizhou University, 2007(in Chinese with English abstract). [36] Davidson C J. Hydrothermal geochemistry and ore genesis of seafloor volcanogenic copper-bearing oxide ores[J]. Economic Geology, 1992, 87(3): 889-912. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.87.3.889 [37] 宋明水. 东营凹陷南斜坡沙四段沉积环境的地球化学特征[J]. 矿物岩石, 2005, 25(1): 67-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200501013.htmSong M S. Sedimentary environment geochemistry in the Shasi section of southern ramp, Dongying Depression[J]. Journal Mineral Petrology, 2005, 25(1): 67-73(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200501013.htm [38] 刘刚, 周东升. 微量元素分析在判别沉积环境中的应用: 以江汉盆地潜江组为例[J]. 石油实验地质, 2007, 29(3): 308-310.Liu G, Zhou D S. Application of microelements analysis in identifying sedimentary environment: Taking Qianjiang Formation in the Jianghan Basin as an example[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2007, 29(3): 308-310(in Chinese with English abstract). [39] 刘成英, 朱日祥. 试论峨眉山玄武岩的地球动力学含义[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2): 52-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.003Liu C Y, Zhu R X. Discussion on geodynamic significance of the Emeishan basalts[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(2): 52-69(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.003 [40] Wang J D, Li H M. Paleo-latitude variation of Guizhou terrain from Devonian to Cretaceous[J]. Chinese Journal of Geochemistry, 1998, 17(4), 356-361. doi: 10.1007/BF02837987 [41] 金中国, 刘玲, 黄智龙, 等. 贵州务正道地区铝土矿床稀土元素组成及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2012, 48(6): 1067-1076. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201206003.htmJin Z G, Liu L, Huang Z L, et al. REE composition of the bauxite deposits in the Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen area, Guizhou Province and its geological significance[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2012, 48(6): 1067-1076(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201206003.htm [42] 张海. 黔西北地区稀土矿床地质地球化学特征及其成矿机制研究[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2014.Zhang H. Geological and geochemical characteristics and metallogenic mechanism of REE deposits, Northwestern Guizhou[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese with English abstract). [43] 洪汉烈. 黏土矿物古气候意义研究的现状与展望[J]. 地质科技情报, 2010, 29(1): 1-7. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201001000.htmHong H L. A review on paleoclimate interpretation of clay minerals[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2010, 29(1): 1-7(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201001000.htm [44] Thamdrup B. Bacterial manganese and iron reduction in aquatic sediments[J]. Advances in Microbial Ecology, 2000, 16(1) : 41-84. [45] Flynn T M, O'Loughlin E J, Mishra B, et al. Sulfur-mediated electron shuttling during bacterial iron reduction[J]. Science, 2014, 344: 1039-1042. doi: 10.1126/science.1252066 [46] Huang Q H, Wang Z J, Wang C X, et al. Phosphorus release in response to pH variation in the lake sediments with different ratios of iron-bound P to calcium-bound P[J]. Chemical Speciation & Bioavailability, 2005, 17(2): 55-61. [47] Ding S M, Wang Y, Wang D, et al. In situ, high-resolution evidence for iron-coupled mobilization of phosphorus in sediments[J]. Scientific Reports, 2016, 6: 24341. doi: 10.1038/srep24341 [48] 张莹华, 凌文黎, 吴慧, 等. 黔北铝土矿不同类型矿石地球化学特征及其对成矿作用的指示[J]. 地质科技情报, 2013, 32(1): 71-79. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201301016.htmZhang Y H, Ling W L, Wu H, et al. Geochemistry of varied type ores of northern Guizhou bauxites and its implication for mineralization[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2013, 32(1): 71-79(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201301016.htm [49] 陈杰, 段士刚, 张作衡, 等. 新疆西天山式可布台铁矿地质、矿物化学和S同位素特征及其对矿床成因的约束[J]. 中国地质, 2014, 41(6): 1833-1852. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.006Chen J, Duan S G, Zhang Z H, et al. Geology, mineral chemistry and sulfur isotope geochemistry of the Shikebutai iron deposit in West Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang: Constraints on genesis of the deposit[J]. Geology in China, 2014, 41(6): 1833-1852(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.06.006 [50] 燕长海, 刘国印. 豫西南铅锌多金属矿控矿条件及找矿方向[J]. 地质通报, 2004, 23(11): 1143-1148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.016Yan C H, Liu G Y. Metallogenic characteristics and ore-prospection suggestions of lead-zinc polymetallic deposits in southwestern Henan Province of China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2004, 23(11): 1143-1148(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.11.016 [51] 徐兆文, 方长泉, 蒋少涌, 等. 安徽青阳峙门口层状硫铁矿矿床地质特征及成因研究[J]. 地质找矿论丛, 2006, 21(1): 10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2006.01.002Xu Z W, Fang C Q, Jiang S Y, et al. Study on geological characteristics and genesis of stratified pyritic deposit in Shimenkou, Anhui Province[J]. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 2006, 21(1): 10-14(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1412.2006.01.002 [52] 李占轲. 华北克拉通南缘中生代银-铅-锌矿床成矿作用研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 2013.Li Z K. Metallogenesis of the silver-lead-zinc deposits along the southern margin of the North China Craton[D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences(Beijing), 2013(in Chinese with English abstract). [53] Canfield D E, Teske A. Late Proterozoic rise in atmospheric oxygen concent ration inferred from phylogenetic and sulphur-isotope studies[J]. Nature, 1996, 382: 127-132. doi: 10.1038/382127a0 [54] Habicht K S, Canfield D E. Sulfur isotope fractionation during bacterial sulfate reduction in organic-rich sediments[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(24): 5351-5361. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00311-6 [55] Canfield D E, Thamdrup B. The production of 34S-depleted sulfide during bacterial disproportionation of elemental sulfur[J]. Science, 1994, 266: 1973-197. doi: 10.1126/science.11540246 [56] 陈兴, 薛春纪. 西天山乌拉根大规模铅锌成矿中H2S成因: 菌生结构和硫同位素组成约束[J]. 岩石学报, 2016, 32(5): 1301-1314. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201605004.htmChen X, Xue C J. Origin of H2S in Uragen large-scale Zn-Pb mineralization, western Tien Shan: Bacteriogenic structure and S-isotopic constraints[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2016, 32(5): 1301-1314(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YSXB201605004.htm [57] Colwell F S, Onstott T C, Delwiche M E, et al. Microorganisms from deep, high temperature sandstones: Constraints on microbial colonization[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews, 1997, 20(3/4): 425-435. [58] Head I M, Jones D M, Larter S R. Biological activity in the deep subsurface and the origin of heavy oil[J]. Nature, 2003, 426: 344-352. doi: 10.1038/nature02134 [59] Elsgaard L, Isaksen M F, Jorgensen B B, et al. Microbial sulfate reduction in deep-sea sediments at the Guaymas Basin hydrothermal vent area: Influence of temperature and substrates[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1994, 58(16): 3335-3343. doi: 10.1016/0016-7037(94)90089-2 [60] Southam G, Saunders J A. The geomicrobiology of ore deposits[J]. Economic Geology, 2005, 100(6): 1067-1084. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.100.6.1067 [61] Zak D, Rossoll T, Exner H, et al. Mitigation of sulfate pollution by rewetting of fens: A conflict with restoring their phosphorus sink function Wetlands[J]. Wetlands, 2009, 29(4): 1093-1103. doi: 10.1672/09-102D.1 [62] Paerl H W, Paul V J. Climate change: Links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria[J]. Water Research, 2012, 46(5): 1349-1363. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2011.08.002 [63] Yu T, Zhang Y, Wu F C, et al. Six-decade change in water chemistry of large freshwater Lake Taihu, China[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013, 47(16): 9093-9101. [64] Luther G W, Church T M, Scudlark J R, et al. Inorganic and organic sulfur cycling in salt-marsh pore waters[J]. Science, 1986, 232: 746-749. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4751.746 [65] Wang J Z, Jiang X, Zheng B H, et al. Effects of electron acceptors on soluble reactive phosphorus in the overlying water dur-ing algal decomposition[J]. Environmental Science & Pollution Research International, 2015, 22(24): 19507-19517. [66] 徐莉, 张成君, 贾松海, 等. 河南济源大峪槐圪塔岭二叠-三叠系元素地球化学特征及古环境[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(1): 137-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201501011.htmXu L, Zhang C J, Jia S H, et al. Element geochemistry and palaeoenvironment of Permian-Triassic stratum in the Huaigeda Hill of Dayu Town, Jiyuan, Henan Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(1): 137-148(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZXE201501011.htm [67] 金中国, 周家喜, 黄智龙, 等. 贵州务川-正安-道真地区铝土矿碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地学前缘, 2013, 20(6): 226-239. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201306031.htmJin Z G, Zhou J X, Huang Z L, et al. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating and its geological significance for the bauxitein Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen Al metallogenic province, Guizhou, SW China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2013, 20(6): 226-239(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201306031.htm [68] 叶霖, 潘自平, 程增涛. 贵州修文小山坝铝土矿中镓等伴生元素分布规律研究[J]. 矿物学报, 2008, 28(2): 105-111. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2008.02.001Ye L, Pan Z P, Cheng Z T. The regularities of distribution of associated elementsin Xiaoshanba bauxite deposit, Guizhou[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 2008, 28(2): 105-111(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4734.2008.02.001 [69] 刘英俊, 曹励明, 李兆麟, 等. 元素地球化学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1986.Liu Y J, Cao L M, Li Z L, et al. Element geochemistry[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1986(in Chinese). [70] 吴松峻, 汪旋, 季秋忆, 等. 太湖西岸典型区域沉积物的硫铁分布特征及环境意义[J]. 湖泊科学, 2019, 31(4): 950-960. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201904006.htmWu S J, Wang X, Ji Q Y, et al. Iron-sulfur distribution and its environmental significance in three typical areas of western Lake Taihu[J]. Journal of Lake Sciences, 2019, 31(4): 950-960(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FLKX201904006.htm [71] Sun M, Xiao T, Ning Z, et al. Microbial community analysis in rice paddy soils irrigated by acid mine drainage contaminated water[J]. Applied Microbiology & Biotechnology, 2015, 99(6): 2911-2922. [72] Nakagawa M, Ueno Y, Hattori S, et al. Seasonal change in microbial sulfur cycling in monomictic Lake Fukamiike, Japan[J]. Limnology and Oceanography, 2012, 57(4): 974-988. doi: 10.4319/lo.2012.57.4.0974 [73] Hansel C M, Lentini C J, Tang Y, et al. Dominance of sulfur-fueled iron oxide reduction in low-sulfate freshwater sediments[J]. Isme Journal, 2015, 9(11): 2400-2412. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2015.50 [74] Feng Z Y, Fan C X, Huang W Y, et al. Microorganisms and typical organic matter responsible for lacustrine "black bloom"[J]. Science of the Total Environment, 2014, 470/471: 1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.09.022 [75] Rabus R, Hansen T A, Widdel F. Dissimilatory sulfate- and sulfur-reducing prokaryotes[M]. New York: Springer, 2006: 659-768. [76] Chen M, Li X H, He Y H, et al. Increasing sulfate concentrations result in higher sulfide production and phosphorous mobilization in a shallow eutrophic freshwater lake[J]. Water Research, 2016, 96: 94-104. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2016.03.030 [77] Lohmayer R, Kappler A. Lsekannbehrens T, et al. Sulfur species as redox partners and electron shuttles for ferrihydrite re-duction by sulfurospirillum deleyianum[J]. Applied & Environmental Microbiology, 2014, 80(10): 3141-3149. [78] Man J K, Boyanov M I, Antonopoulos D A, et al. Effects of dissimilatory sulfate reduction on FeⅢ(hydr) oxide reduction and microbial community development[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 129(15): 177-190. [79] 金中国, 刘玲, 黄智龙, 等. 贵州务-正-道地区铝土矿含矿岩系中三稀元素赋存状态、富集机理及资源潜力[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(11): 2847-2861. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.010Jin Z G, Liu L, Huang Z L, et al. Occurrence state, enrichment mechanism and resource potential of rare earth, rare metal and rare-scattered elements in ore-bearing rocksin the Wuchuan-Zheng'an-Daozhen bauxite deposit, Guizhou Province[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(11): 2847-2861(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.010 [80] 赵振华. 副矿物微量元素地球化学特征在成岩成矿作用研究中的应用[J]. 地学前缘, 2010, 17(1): 267-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001027.htmZhao Z H. Trace element geochemistry of accessory minerals and its applications in petrogenesis and metallogenesis[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2010, 17(1): 267-286(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY201001027.htm [81] 刘平, 廖友常. 试论遵义高铁铝土矿与低铁铝土矿的分带性及形成机制[J]. 中国地质, 2013, 40(3): 949-966. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.03.025Liu P, Liao Y C. The zonation and genetic mechanism of Zunyi high-and low-ferrous bauxites[J]. Geology in China, 2013, 40(3): 949-966(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.03.025 [82] 杨军臣, 王凤玲, 李德胜, 等. 铝土矿中伴生稀有稀土元素赋存状态及走向查定[J]. 矿山冶金, 2004, 13(2): 89-92. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ200402024.htmYang J C, Wang F L, Li D S, et al. Investigation on occurrence and trend of rare and rare-earth elements associated in bauxite[J]. Mining & Metallurgy, 2004, 13(2): 89-92(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYZZ200402024.htm [83] 庹必阳, 王建丽, 张覃. 稀土元素在铝土矿中的赋存状态及利用现状[J]. 稀土, 2007, 1: 117-119. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ200701033.htmTuo B Y, Wang J L, Zhang Q. Occurrence and utilization of rare earth element in bauxite[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2007, 1: 117-119(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTZZ200701033.htm [84] 李沛刚, 王登红, 赵芝, 等. 贵州大竹园铝土矿矿床地质、地球化学与成矿规律[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014.Li P G, Wang D H, Zhao Z, et al. Geology, geochemistry and metallogenic regularity of Dazhuyuan bauxite deposit in Guizhou Province[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014(in Chinese). [85] Li Z H, Din J, Xu J S, et al. Disovery of the REE minerals in the Wulong- Nanchuan bauxite deposits, Chongqing, China: Insights on conditions of formation and processes[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 133: 88-102. [86] 寇洪立. 一种野外勘查离子型稀土的快速测试方法: 中国, CN 106353316 A[P]. 2017-01-25.Kou H L. A fast testing method of ionic rare earth in field exploration: China, Patent application publication number: CN 106353316 A[P]. 2017-01-25(in Chinese). [87] 徐璐, 李元坤, 惠博, 等. 一种选择性浸出沉积型稀土矿的方法: 中国, CN 109266839 B[P]. 2019-01-25.Xu L, Li Y K, Hui B, et al. A selective leaching method of sedimentary rare earth ore: China, Patent application publication number: CN 109266839 B[P]. 2019-01-25(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: