Identification of the geochemical anomalies using the catchment basin analysis: A case study of 1∶50000 geochemical survey of stream sediments in Wulasitai region, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt
-
摘要:
水系沉积物地球化学测量是卓有成效的找矿技术方法, 基于汇水盆地的水系沉积物地球化学异常提取有助于追溯异常源头、指明找矿方向。基于SCB法提出了汇水盆地法, 该方法以自然汇水盆地为预测单元, 将各样品点的地球化学属性特征赋予各自所在区域, 预测结果较为符合地形地貌特征, 且对于采样密度较高的1∶5万水系沉积物地球化学测量数据有较好的应用效果。以东昆仑乌拉斯太地区为研究区, 使用高精度DEM划分汇水盆地, 利用该方法对1∶5万水系沉积物Au、Ag、Pb因子得分进行了异常信息提取, 在提取过程中利用多种地貌参数(干流坡度、地形起伏比、汇水盆地面积)作为泥沙输移比进行残差校正计算, 并在此基础上, 利用C-A分形法分离了地球化学背景与异常。异常提取结果表明, 汇水盆地面积参数最适合用作乌拉斯太地区的泥沙输移比参与顺流衰减校正, 使用汇水盆地法可以有效识别和提取该地区地球化学异常信息。使用汇水盆地法提取的化探异常范围与矿床空间位置吻合度高, 可以为进一步找矿工作提供有利的信息。
Abstract:Geochemical survey of stream sediments is an effective technology for mineral prospecting. The extraction of geochemical anomalies in stream sediments based on catchment basins has always been one of the research hotspots.The catchment basin analysis method is proposed based on Sample Catchment Basin Analysis (SCBA)in this paper, and it is used to identify geochemical anomalies in the Wulasitai region, East Kunlun Orogenic Belt in Qinghai Province.Catchment basins are divided by a high-precision DEM, and the Au, Ag, and Pb factor loadings of 1∶50000 stream sediments are measured by the catchment basin analysis. During the extraction process, a variety of geomorphic parameters such as main stream slope, relief ratio, catchment basin area, are used as the sediment delivery ratios for residual correction calculation, and the geochemical background and anomalies are separated by the C-A fractal modeling. The anomaly extraction results show that the area of the catchment basin is the most suitable parameter as the sediment delivery ratio to participate in the downstream attenuation correction. The catchment basin method can effectively identify and extract geochemical anomaly information.Anomalies correspond well to the spatial location of ore deposits, and can provide beneficial information for the next step of mineral prospecting.
-
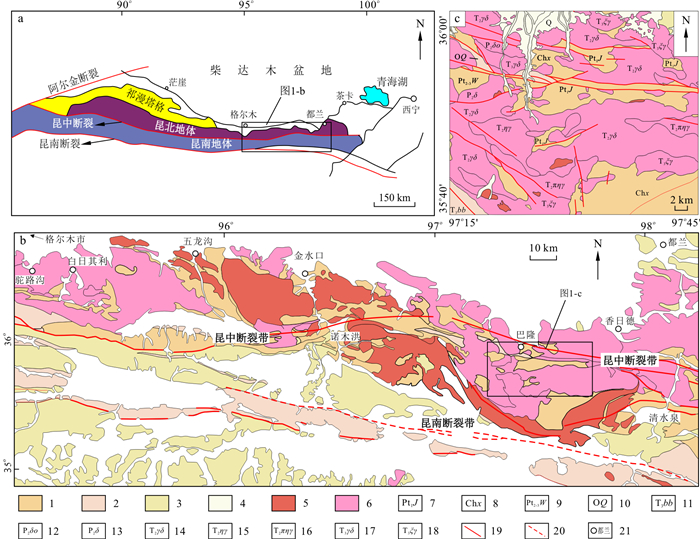
图 1 东昆仑构造单元划分图(a)和地质简图(b)及乌拉斯太地区地质简图(c)
a据文献[34];b据文献[35];c修编自1∶25万阿拉克湖幅、冬给措纳湖幅地质矿产图;1.元古宙地层;2.古生代地层;3.中生代地层;4.新生代地层;5.早古生代侵入岩;6.晚古生代-中生代侵入岩;7.古元古界金水口群;8.长城系小庙组;9.中-新元古界万宝沟群;10.奥陶系祁漫塔格群;11.上三叠统八宝山组;12.中二叠世石英闪长岩;13.中二叠世闪长岩;14.中三叠世花岗闪长岩;15.中三叠世二长花岗岩;16.中三叠世似斑状二长花岗岩;17.晚三叠世花岗闪长岩;18.晚三叠世正长花岗岩;19.断层;20.推测断层; 21.地名
Figure 1. Geotectonic frame work (a), geological map of the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt (b) and simplified geological map of the Wulasitai region (c)
图 7 青海乌拉斯太地区地质体地球化学背景含量分布图(a)与汇水盆地残差值分布图(b)
1.中-新元古界万宝沟群; 2.上三叠统八宝山组; 3.中二叠世石英闪长岩; 4.中二叠世闪长岩; 5.晚三叠世正长花岗岩; 6.中三叠世花岗闪长岩; 7.古元古界金水口群; 8.长城系小庙组; 9.中三叠世二长花岗岩; 10.中三叠世似斑状二长花岗岩; 11.晚三叠世花岗闪长岩; 12.断层
Figure 7. Distribution of the geochemical background of geological bodies (a) and the residual values of catchment basins (b) in the Wulasitai region, Qinghai Province
图 9 青海乌拉斯太地区Au-Ag-Pb元素组合各方法异常提取对比图
a.累计频率法;b.基于干流坡度的汇水盆地法; c.基于流域起伏比的汇水盆地法; d.基于盆地面积的汇水盆地法。1.一级水系;2.二级水系;3.三级水系;4.四级水系;5.五级水系;6.金多金属矿床(点);7.铜(金)多金属矿床(点);8.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合低背景区;9.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合高背景区;10.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合低异常区;11.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合高异常区;12.金单元素异常区;13.银单元素异常区;14.铅单元素异常区
Figure 9. Comparison of geochemical anomalies of Au, Ag, and Pb elements based the accumulative frequency method (a), and catchment basin analysis including MSS(b), RR(c) and Aa(d) in the Wulasitai region, Qinghai Province
图 10 巴隆地区和托克妥地区异常剖析图
a.巴隆地区地质图;b.巴隆地区累计频率法Au-Ag-Pb组合异常图;c.巴隆地区汇水盆地法异常图;d.托克妥地区地质图;e.托克妥地区累计频率法Au-Ag-Pb组合异常图;f.托克妥地区汇水盆地法异常图。1.元古宙地层;2.古生代地层;3.中生代地层;4.新生代地层;5.早古生代侵入岩;6.晚古生代-中生代侵入岩;7.古元古界金水口群;8.长城系小庙组;9.中-新元古界万宝沟群;10.奥陶系祁漫塔格群;11.晚三叠世八宝山组;12.中二叠世石英闪长岩;13.中二叠世闪长岩;14.晚二叠世英云闪长岩;15.中三叠世花岗闪长岩;16.中三叠世二长花岗岩;17.中三叠世似斑状二长花岗岩;18.晚三叠世花岗闪长岩;19.晚三叠世正长花岗岩;20.断层;21.推测断层;22.一级水系;23.二级水系;24.三级水系;25.四级水系;26.五级水系;27.金多金属矿床(点);28.铜(金)多金属矿床(点);29.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合低背景区;30.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合高背景区;31.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合低异常区;32.Au-Ag-Pb元素组合高异常区;33.金单元素异常区;34.银单元素异常区;35.铅单元素异常区。图a~c矿床(点): ①瑙木浑西金矿点;②巴隆金矿床;③瑙木浑沟口金矿床;④瑙木浑东金矿点;⑤诺木洪沟金矿点;⑥瑙木浑河中游金矿点;图d~f矿床(点):①托克妥北金银矿床;②大洪山金铜矿点;③浩来图北山铜矿点;④浩来图北山金矿点;⑤浩来图金矿床;⑥托克妥金铜矿床;⑦科尔西金矿点;⑧巴力根特铜矿点;⑨尕熊沟金矿点
Figure 10. Geochemical anomalies of stream sediments in the Balong and Tuoketuo areas
表 1 乌拉斯太地区水系沉积物元素地球化学参数统计(样品数为5 831)
Table 1. Statistics of elemental geochemical parameters of stream sediments in the Wulasitai region
元素 平均值X 中位数 标准差 方差 偏度 峰度 最大值 东昆仑背景值S[40] X/S 变异系数Cv Au wB/10-9 1.71 1.14 5.79 33.50 22.66 686.07 238.30 1.21 1.41 3.38 Ag 75.23 62.51 99.70 9 939.81 27.51 1 056.97 4 586.51 67.02 1.12 1.33 Cu wB/10-6 22.51 19.24 15.76 248.31 9.60 231.71 498.18 0.75 30.02 0.70 Pb 22.86 19.43 25.04 627.00 17.42 451.23 911.56 0.75 30.48 1.10 Zn 67.61 59.90 39.79 1 583.59 11.85 292.75 1 329.20 0.66 102.44 0.59 Mo 1.05 0.85 2.85 8.13 35.60 1447.72 127.08 1.36 0.77 2.72 W 1.86 1.47 2.51 6.32 10.43 153.76 54.93 0.52 3.57 1.35 Sn 3.15 2.75 3.36 11.28 39.31 2193.41 202.64 2.61 1.21 1.07 表 2 相似系数矩阵
Table 2. Matrix of similarity coefficients
元素 Au Ag Cu Pb Zn Mo W Sn Au 1.000 Ag 0.364 1.000 Cu 0.043 0.147 1.000 Pb 0.207 0.142 0.189 1.000 Zn 0.024 0.138 0.310 0.176 1.000 Mo 0.035 0.042 0.171 0.081 0.148 1.000 W 0.043 0.083 0.183 0.076 0.109 0.112 1.000 Sn -0.002 0.078 0.397 0.188 0.129 0.139 0.072 1.000 表 3 因子成分分析矩阵(旋转后)
Table 3. Matrix of factor components analysis (after rotation)
主因子 1 2 Au -0.143 0.589 Ag -0.035 0.520 Cu 0.424 -0.033 Pb 0.152 0.259 Zn 0.304 0.020 Mo 0.261 -0.061 W 0.197 0.022 Sn 0.376 -0.092 特征根λ 2.009 1.305 方差贡献率/% 22.886 18.544 累计方差贡献率/% 22.886 41.430 表 4 青海乌拉斯太地区汇水盆地泥沙输移比参数统计
Table 4. Summary statistics of sediment delivery proxies in the Wulasitai region, Qinghai Province
干流坡度MSS/% 地形起伏比RR 汇水盆地面积Aa/(km2)-0.2 汇水盆地数量 1 803 1 803 1 803 平均值 13.56 0.12 1.15 中位数 11.02 0.09 1.06 标准差 9.26 0.09 0.45 极小值 1.38 0.01 1.61 极大值 83.43 0.88 5.02 表 5 不同泥沙输移比的校正残差值相似系数矩阵
Table 5. Similarity coefficients matrix of corrected residual values for different sediment transport ratios
MSS RR Aa MSS 1.000 RR 0.999 1.000 Aa 0.919 0.905 1.000 表 6 累计频率法与汇水盆地法圈定异常对比表
Table 6. Comparison of anomalous delineation using the accumulative frequency method and catchment basin analysis
异常提取方法 类型 金多金属矿床(点)总数量/个 铜(金)多金属矿床(点)总数量/个 异常占研究区面积比例/% 落入异常的金多金属矿床(点)数量/个 落入异常的金多金属矿床(点)比例/% 落入异常的铜(金)多金属矿床(点)数量/个 落入异常的铜(金)多金属矿床(点)比例/% 累计频率法 Au 16 7 8.55 9 56.25 3 42.86 Ag 16 7 8.91 5 31.25 0 0.00 Pb 16 7 6.42 5 31.25 1 14.29 Au+Ag+Pb 16 7 20.06 12 75.00 4 57.14 汇水盆地法 MSS 16 7 19.84 14 87.50 5 71.43 RR 16 7 19.63 13 81.25 5 71.43 Aa 16 7 19.82 15 93.75 5 71.43 -
[1] 陈绍强, 庞保成, 张冠清. 地质子区地球化学异常衬度值法在广西百色地区的应用[J]. 矿产与地质, 2019, 33(6): 1057-1061. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2019.06.016Chen S Q, Pang B C, Zhang G Q. The application of geochemical anomaly contrast value method for geological subinterval areas in Baise City of Guangxi[J]. Mineral Resources and Geology, 2019, 33(6): 1057-1061(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2019.06.016 [2] 魏俊浩. 初论成矿场与矿产勘查意义[J]. 地质科技通报, 2020, 39(1): 114-129. doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0113Wei J H. Preliminary discussion on the theory of ore-forming field and its significant role for mineral exploration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2020, 39(1): 114-129(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.19509/j.cnki.dzkq.2020.0113 [3] 石文杰, 魏俊浩, 谭俊, 等. 基于滑动窗口对数标准离差法的地球化学异常识别: 以青海多彩地区1: 5万水系沉积物地球化学测量为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5): 81-89. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905008.htmShi W J, Wei J H, Tan J, et al. Identifying the geochemical anomalies using Logarithmic Standard Deviation Statistics Method based on sliding window: The geochemical survey of 1: 50000 water sediments in Duocai region of Qinghai Province as an example[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(5): 81-89(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905008.htm [4] 王治华, 谭俊, 王凤林, 等. 多种区域化探数据处理方法及异常提取效果对比研究: 以青海小河坝地区水系沉积物测量为例[J]. 矿产勘查, 2019, 10(2): 321-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.02.024Wang Z H, Tan J, Wang F L, et al. A comparative study of several regional geochemical data processing methods and extraction effects of anomalies: A case study of stream system sediments in Xiaoheba area of Qinghai Province[J]. Mineral Exploration, 2019, 10(2): 321-332(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2019.02.024 [5] 石文杰, 魏俊浩, 王启, 等. 分区上异点校正法在干旱地区1: 5万地球化学异常圈定中的应用: 以我国西北某地区为例[J]. 地质科技情报, 2011, 30(1): 34-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.01.006Shi W J, Wei J H, Wang Q, et al. Delineation of 1: 50000 geochemical anomalies based on the method of unit-wise adjustment of outliers in gobigeomorphologic landscape: An example of an arid area from Northwestern China[J]. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2011, 30(1): 34-41(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2011.01.006 [6] 赵宁博, 傅锦, 张川, 等. 子区中位数衬值滤波法在地球化学异常识别中的应用[J]. 世界核地质科学, 2012, 29(1): 47-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2012.01.008Zhao N B, Fu J, Zhang C, et al. Application of subinterval area median contrast filtering method in the recognizing of geochemical anomalies[J]. World Nuclear Geoscience, 2012, 29(1): 47-51(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0636.2012.01.008 [7] 史长义, 张金华, 黄笑梅. 子区中位数衬值滤波法及弱小异常识别[J]. 物探与化探, 1999, 23(4): 11-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH904.001.htmShi C Y, Zhang J H, Huang X M. Subregion median contrast filtering method and recognition of weak anomalies[J]. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 23(4): 11-18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-WTYH904.001.htm [8] Cao M, Lu L. Application of the multivariate canonical trend surface method to the identification of geochemical combination anomalies[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 153: 1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2014.11.006 [9] Davis J C, Sampson R J. Statistics and data analysis in geology[M]. New York: Wiley, 1986. [10] 成秋明, 张生元, 左仁广, 等. 多重分形滤波方法和地球化学信息提取技术研究与进展[J]. 地学前缘, 2009, 16(2): 185-198. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.014Cheng Q M, Zhang S Y, Zuo R G, et al. Progress of multifractal filtering techniques and their applications in geochemical information extraction[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2009, 16(2): 185-198(in Chinese with English abstract). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.02.014 [11] Cheng Q M, Agterberg F P, Ballantyne S B. The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 51(2): 109-130. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2 [12] 左仁广, 彭勇, 李童, 等. 基于深度学习的地质找矿大数据挖掘与集成的挑战[J]. 地球科学, 2020, 46(1): 350-358. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202101028.htmZuo R G, Peng Y, Li T, et al. Challenges of geological prospecting big data mining and integration using deep learning algorithms[J]. Earth Science, 2020, 46(1): 350-358(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202101028.htm [13] Rose A W, Dahlberg E C, Keith M. A multiple regression technique for adjusting background values in stream sediment geochemistry[J]. Economic Geology, 1970, 65(2): 156-165. doi: 10.2113/gsecongeo.65.2.156 [14] Hawkes H E. The downstream dilution of stream sediment anomalies[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1976, 6(1/2): 345-358. [15] Bonham-Carter G, Rogers P, Ellwood D. Catchment basin analysis applied tosurficial geochemical data, Cobequid Highlands, Nova Scotia[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1987, 29(1/3): 259-278. [16] Bonham-Carter G F, Goodfellow W D. Autocorrelation structure of stream-sediment geochemical data: interpretation of zinc and lead anomalies, Nahanni river area, Yukon-Northwest Territories, Canada[C]//Anon. Geostatistics for natural resources characterization. NATO advanced Study Institute, 1984: 817-829. [17] Moon C J. Towards a quantitative model of downstream dilution of point source geochemical anomalies[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1999, 65(2): 111-132. doi: 10.1016/S0375-6742(98)00065-X [18] Carranza E J M. Usefulness of stream order to detect stream sediment geochemical anomalies[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2004, 4(4): 341-352. doi: 10.1144/1467-7873/03-040 [19] Yousefi M, Carranza E J M, Kamkar-Rouhani A. Weighted drainage catchment basin mapping of geochemical anomalies using stream sediment data for mineral potential modeling[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2013, 128: 88-96. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2013.01.013 [20] Farahbakhsh E, Chandra R, Eslamkish T, et al. Modeling geochemical anomalies of stream sediment data through a weighted drainage catchment basin method for detecting porphyry Cu-Au mineralization[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2019, 204: 12-32. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2019.05.003 [21] Carranza E J M. Mapping of anomalies in continuous and discrete fields of stream sediment geochemical landscapes[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2010, 10(2): 171-187. doi: 10.1144/1467-7873/09-223 [22] Carranza E J M. Catchment basinmodelling of stream sediment anomalies revisited: Incorporation of EDA and fractal analysis[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2010, 10(4): 365-381. doi: 10.1144/1467-7873/09-224 [23] Spadoni M. Geochemical mapping using a geomorphologic approach based on catchments[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2006, 90(3): 183-196. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2005.12.001 [24] Mokhtari A R, Garousi Nezhad S. A modified equation for the downstream dilution of stream sediment anomalies[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2015, 159: 185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.09.007 [25] Shahrestani S, Mokhtari A R. Dilution correction equation revisited: The impact of stream slope, relief ratio and area size of basin on geochemical anomalies[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2017, 128: 16-26. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2016.06.019 [26] Shahrestani S, Mokhtari A R. Improved detection of anomalous catchment basins by incorporating drainage density in dilution correction of geochemical residuals[J]. Geochemistry: Exploration, Environment, Analysis, 2017, 17(3): 194-203. doi: 10.1144/geochem2016-015 [27] Garousi N S, Mokhtari A R, Roshani Rodsari P. The true sample catchment basin approach in the analysis of stream sediment geochemical data[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 83: 127-134. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.008 [28] Spadoni M, Cavarretta G, Patera A. Cartographic techniques for mapping the geochemical data of stream sediments: The "Sample Catchment Basin" approach[J]. Environmental Geology, 2004, 45(5): 593-599. doi: 10.1007/s00254-003-0926-7 [29] 黄啸坤, 魏俊浩, 李欢, 等. 东昆仑巴隆地区晚三叠世石英闪长岩成因: U-Pb年代学、地球化学及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约[J]. 地球科学, 2021, 46(6): 1-27. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202106008.htmHuang X K, Wei J H, Li H, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronological, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on petrogenesis of late Triassic quartz diorite in Balong region, East Kunlun Orogen[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(6): 1-27(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX202106008.htm [30] 徐晓波, 王连训, 马昌前, 等. 东昆仑造山带巴隆地区羊粪沟中酸性岩脉成因及其地质意义[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2021, 40(3): 653-676. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202103010.htmXu X B, Wang L X, Ma C Q, et al. Petrogenesis and geological implications of the Yangfengou intermediate-felsic dykes in the Balong area within the Eastern Kunlun Orogen[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 2021, 40(3): 653-676(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH202103010.htm [31] 管祥波, 李军. 青海省都兰县巴隆岩金矿床地质特征及找矿标志[J]. 山东国土资源, 2016, 32(12): 14-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201612003.htmGuan X B, Li J. Geological characteristics and prospecting marks of Balong rock gold deposit in Dulan County of Qinghai Province[J]. Shandong Land and Resources, 2016, 32(12): 14-18(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDDI201612003.htm [32] 邱瑜, 卢佳, 田滔, 等. 1: 2.5万地球化学测量在东昆仑巴隆地区找矿中的应用[J]. 中国锰业, 2019, 37(4): 47-51. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201904010.htmQiu Y, Lu J, Tian T, et al. An application of 1: 25000 geochemical survey to ore prospecting in Balong area of East Kunlun[J]. China's Manganese Industry, 2019, 37(4): 47-51(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGMM201904010.htm [33] 杨经绥, 许志琴, 马昌前, 等. 复合造山作用和中国中央造山带的科学问题[J]. 中国地质, 2010, 37(1): 1-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201001004.htmYang J S, Xu Z Q, Ma C Q, et al. Compound orogeny and scientific problems concerning the Central Orogenic Belt of China[J]. Geology in China, 2010, 37(1): 1-11(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DIZI201001004.htm [34] Hu Y, Niu Y L, Li J Y, et al. Petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Late Triassic mafic dikes and felsic volcanic rocks in the East Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Northern Tibet Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2016, 245: 205-222. [35] Zhang J Y, Ma C Q, Xiong F H, et al. Early Paleozoic high-Mg diorite-granodiorite in the eastern Kunlun Orogen, Western China: Response to continental collision and slab break-off[J]. Lithos, 2014, 210/211: 129-146. [36] Matte P, Tapponnier P, Arnaud N, et al. Tectonics of western Tibet, between the Tarim and the Indus[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1996, 142(3/4): 311-330. [37] 陈加杰, 付乐兵, 魏俊浩, 等. 东昆仑沟里地区晚奥陶世花岗闪长岩地球化学特征及其对原特提斯洋演化的制约[J]. 地球科学: 中国地质大学学报, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201611004.htmChen J J, Fu L B, Wei J H, et al. Geochemical characteristics of late Ordovician granodiorite in Gouli Area, Eastern Kunlun Orogenic Belt, Qinghai Province: Implications on the evolution of Proto-Tethys Ocean[J]. Earth Science: Journal of China University of Geosciences, 2016, 41(11): 1863-1882(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201611004.htm [38] 莫宣学, 罗照华, 邓晋福, 等. 东昆仑造山带花岗岩及地壳生长[J]. 高校地质学报, 2007, 13(3): 403-414. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703005.htmMo X X, Luo Z H, Deng J F, et al. Granitoids and crustal growth in the East-Kunlun Orogenic Belt[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2007, 13(3): 403-414(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXDX200703005.htm [39] Xiong F H, Ma C Q, Zhang J Y, et al. The origin of mafic microgranular enclaves and their host granodiorites from East Kunlun, Northern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Implications for magma mixing during subduction of Paleo-Tethyan lithosphere[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 104(3/4): 211-224. [40] 陈世顺, 樊双虎, 杨小斌. 青海省都兰县沟里地区1: 5万矿产地质、水系沉积物测量综合调查项目成果报告[R]. 西宁: 青海省有色地质勘查局, 2011.Chen S S, Fan S H, Yang X B. Achievement report of the 1: 50000 comprehensive survey project of mineral geology and stream sediments survey in Gouli, Dulan, Qinghai Province[R]. Xining: Qinghai Provincial Non-ferrous Metal Geological and Minerals Exploration Bureau, 2011. [41] 李照会, 郭良, 刘荣华, 等. 基于DEM数字河网提取时集水面积阈值与河源密度关系的研究[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 2018, 20(9): 1244-1251. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX201809006.htmLi Z H, Guo L, Liu R H, et al. The relationship between the threshold of catchment area for extraction of digital river network from DEM and the river source density[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science, 2018, 20(9): 1244-1251(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQXX201809006.htm [42] 吴泰兵, 夏达忠, 张行南. 基于改进适度指数法的流域流水网阈值确定研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2011, 29(4): 18-20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201104005.htmWu T B, Xia D Z, Zhang X N. Identification of critical contributing area based on improved fitness index method[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2011, 29(4): 18-20(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY201104005.htm [43] 马永明, 张利华, 朱志儒, 等. 堵河子流域划分及其NDVI特征分析[J]. 云南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 42(2): 290-298. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDZ202002014.htmMa Y M, Zhang L H, Zhu Z R, et al. Division of Duhe River Basin and analysis of its NDVI characteristics[J]. Journal of Yunnan University: Natural Sciences Edition, 2020, 42(2): 290-298(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YNDZ202002014.htm [44] 杨邦, 任立良. 集水面积阈值确定方法的比较研究[J]. 水电能源科学, 2009, 27(5): 11-14, 171. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY200905005.htmYang B, Ren L L. Identification and comparison of critical support area in extracting drainage network from DEM[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2009, 27(5): 11-14, 171(in Chinese with English abstract). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDNY200905005.htm [45] Pike R J, Wilson S E. Elevation-relief ratio, hypsometric integral, and geomorphic area-altitude analysis[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1971, 82(4): 1079-1084. [46] Carranza E J M. Geochemical anomaly and mineral prospectivity mapping in GIS[M].: Elsevier, 2008. [47] Carranza E J M, Hale M. A catchment basin approach to the analysis of reconnaissance geochemical-geological data fromAlbay Province, Philippines[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1997, 60(2): 157-171. [48] Yuan Y, Jiang Y, Taguas E V, et al. Sediment loss and its cause in Puerto Rico watersheds[J]. Soil, 2015, 1(2): 595-602. [49] Ranasinghe P N, Fernando G W A R, Dissanayake C B, et al. Statistical evaluation of stream sediment geochemistry in interpreting the river catchment of high-grade metamorphic terrains[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2009, 103(2): 97-114. [50] Zhang X, Wu S, Cao W, et al. Dependence of the sediment delivery ratio on scale and its fractal characteristics[J]. International Journal of Sediment Research, 2015, 30(4): 338-343. [51] Williams J R, Berndt H D. Sediment yield computed with universal equation[J]. Journal of the Hydraulics Division, 1972, 98(12): 2087-2098. [52] Schumm S A. Evolution of drainage systems and slopes in Badlands at Perth Amboy, New Jersey[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 1956, 67(5): 597-646. [53] Lu H, Moran C J, Prosser I P. Modelling sediment delivery ratio over the Murray Darling Basin[J]. Environmental Modelling & Software, 2006, 21(9): 1297-1308. [54] Shi Z H, Ai L, Li X, et al. Partial least-squares regression for linking land-cover patterns to soil erosion and sediment yield in watersheds[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 2013, 498: 165-176. [55] Boyce R. Sediment routing with sediment delivery ratios[J]. Present and Prospective Technology for Prediction Sediment, Sediment Yields and Sources, 1975: 61-65. [56] Vanoni V A. Sedimentation engineering[M].: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2006. [57] Carranza E J M. Controls on mineral deposit occurrence inferred from analysis of their spatial pattern and spatial association with geological features[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2009, 35(3/4): 383-400. -





 下载:
下载: