Interaction and sedimentary process between the evolution of the bar and bifurcation of the river in the far-source fine-grained braided river: Numerical simulation analysis inspired by modern deposition
-
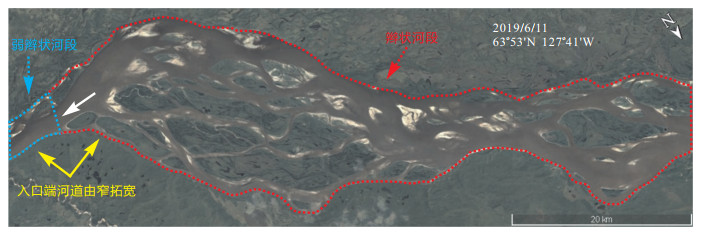
摘要: 远源细粒辫状河广泛发育于河流的中下游,其形成的致密储层是深入挖潜油气面临的挑战。结合现代远源细粒辫状河演变的遥感记录影像,运用基于泥沙水动力学的沉积过程数值模拟软件Delft3D正演远源细粒辫状河的生长演化过程,并探讨物源供给对远源细粒辫状河形态的影响,深入剖析和解释远源细粒辫状河心滩坝演化与河流分叉的交互作用和沉积过程,并进行了现代沉积验证。研究表明:①河道沿下游方向由窄变宽是触发远源细粒辫状河形成的主要地形条件。河流流速和河岸牢固程度是决定河流宽度的重要因素。②远源细粒辫状河心滩坝演化与河流分叉的交互沉积过程是心滩坝泥沙与河流流水交互作用的沉积演化过程。心滩坝泥沙与河流流水交互作用具体包括泥沙在河流中的沉积作用和河流对泥沙的侵蚀作用。③远源细粒辫状河心滩坝演化与河流分叉的交互沉积过程包括3种:河道内心滩坝加积导致河流分叉、心滩坝与河岸分离导致河流分叉、心滩坝的局部冲裂分解导致河流分叉。该研究丰富了远源细粒辫状河沉积理论,并且有助于分析远源细粒辫状河沉积相的储层空间展布规律并应用于油气的深入勘探开发。
-
关键词:
- 远源细粒辫状河 /
- Delft3D沉积数值模拟 /
- Google Earth /
- 物源供给 /
- 河流分叉
Abstract: The far-source fine-grained braided river is widely distributed in the middle and lower reaches of the river.The tight oil and gas reservoir formed by the far-source fine-grained braided river is hard for further exploration of potential oil and gas.Combined with the remote sensing image of the modern far-source fine-grained braided river, the growth and evolution process of the far-source fine-grained braided river was modeled by the numerical simulation software Delft3D based on sediment hydrodynamics.The influences of the river discharge and the supply of mud and sand on the morphology of the far-source fine-grained braided river are simulated.The interaction and sedimentary process between the evolution of the bar and the bifurcation of the river in the far-source fine-grained braided river are analyzed and verified.The main findings are as follows:①The widening of the channel along the downstream direction is the main topographic condition that triggers the formation of the far-source fine-grained braided river.The flow velocity and bank firmness are important factors to determine the river width.②The interaction and sedimentary process between the evolution of the bar and bifurcation of the river in the far-source fine-grained braided river are a sedimentary evolution process of the interaction between the sediment of the bar and the flowing water of the river.The interaction between the sediment of the bar and the flowing water of the river includes deposition of sediment in the river and erosion of sediment by the river.③The aggradation of the bar in the river, the separation of the bar and bank, and the river avulsion are the three main forms of the interaction and sedimentary process between the evolution of the bar and the bifurcation of the river in the far-source fine-grained braided river.This paper enriches the theory of sedimentation of the far-source fine-grained braided river.This study is helpful to analyze the spatial distribution of reservoirs in the far-source fine-grained braided river sedimentary facies and to apply it to the in-depth exploration and development of oil and gas. -
表 1 模型基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters for all models
参数 设定值 网格单元大小/m 50×50 河流总长度/km 30 河流宽度/m 1 900,3 000 河流深度/m 3 初始水位/m 0 网格规模/个 35 758 模拟时长/d 365 时间步长/s 30 地貌演化系数 60 重力加速度/(m·s-2) 9.81 泥质组分初始浓度/(kg·m-3) 500 砂质组分初始浓度/(kg·m-3) 1 600 砂质组分初始厚度/m 10 表 2 不同模型组别的河流流量及泥沙供给情况
Table 2. Discharge and sediment supply in different model scenarios
模拟序号 河流流量/(m3·s-1) 砂质组分中值粒径D50/μm 200 300 400 500 600 700 沉积物供给量/(kg·m-3) 砂质组分 S1 13 500 0.1 - - - - - S2 14 500 0.1 0.09 - - - - S3 15 500 0.1 0.09 0.08 - - - S4 16 500 0.1 0.09 0.08 0.07 - - S5 17 500 0.1 0.09 0.08 0.07 0.06 - S6 18 500 0.1 0.09 0.08 0.07 0.06 0.05 泥质组分 S1-S6 - 0.06 -
[1] Yang H, Lin B, Sun J, et al.Simulating laboratory braided rivers with bed-load sediment transport[J].Water, 2017, 9(9):686-704. doi: 10.3390/w9090686 [2] 张昌民, 尹太举, 赵磊, 等.辫状河储层内部建筑结构分析[J].地质科技情报, 2013, 32(4):7-13. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201304003.htm [3] 廖保方, 薛培华, 李列, 等.辫状河现代沉积研究与相模式:中国永定河剖析[J].沉积学报, 1998, 16(1):34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB199801005.htm [4] Yang H, Lin B, Zhou J.Avulsions in a simulated large lowland braided river[J].Water Resources Management, 2018, 32(7):2301-2314. doi: 10.1007/s11269-018-1930-8 [5] Yang H, Lin B, Zhou J.Physics-based numerical modelling of large braided rivers dominated by suspended sediment[J].Hydrological Processes, 2015, 29(8):1925-1941. doi: 10.1002/hyp.10314 [6] 张可, 吴胜和, 冯文杰, 等.砂质辫状河心滩坝的发育演化过程探讨:沉积数值模拟与现代沉积分析启示[J].沉积学报, 2018, 36(1):81-91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201801009.htm [7] Nicholas A P.Modelling the continuum of river channel patterns[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2013, 38(10):1187-1196. doi: 10.1002/esp.3431 [8] Schuurman F, Marra W A, Kleinhans M G.Physics-based modeling of large braided sand-bed rivers:Bar pattern formation, dynamics, and sensitivity[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, 2013, 118(4):2509-2527. doi: 10.1002/2013JF002896 [9] Sun J, Lin B, Yang H.Development and application of a braided river model with non-uniform sediment transport[J].Advances in Water Resources, 2015, 81:62-74. doi: 10.1016/j.advwatres.2014.12.012 [10] 陈仕臻, 林承焰, 任丽华, 等.砂质辫状河沉积模式的建立:以委内瑞拉奥里诺科重油带H区块为例[J].沉积学报, 2015, 33(5):965-971. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201505012.htm [11] Kleinhans M G, Hardy R J.River bifurcations and avulsion[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2013, 38(3):317-318. doi: 10.1002/esp.3354 [12] Melman F C R.Navigability at an unstable bifurcation: The Montaño-Murindó bifurcation of the Atrato River in Colombia[D].Delft: Delft University of Technology, 2011. [13] Struiksma N.RIVCOM: A summary of results of some test computations[R].Report Q794, Delft Hydraulics, 1988. [14] Lesser G R, Roelvink J A, Van Kester J, et al.Development and validation of a three-dimensional morphological model[J].Coastal Engineering, 2004, 51(8/9):883-915. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2004.07.014 [15] 王杨君, 尹太举, 邓智浩, 等.水动力数值模拟的河控三角洲分支河道演化研究[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(1):44-52. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201601007.htm [16] Edmonds D A, Slingerland R L.Mechanics of river mouth bar formation:Implications for the morphodynamics of delta distributary networks[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Earth Surface, 2007, 112(F2):1-14. doi: 10.1029/2006JF000574/full [17] Deltares D.Delft3D-FLOW simulation of multi-dimensional hydrodynamic flows and transport phenomena including sediments, user manual[M].Delft:Deltares, 2009. [18] 张文彪, 段太忠, 刘彦锋, 等.定量地质建模技术应用现状与发展趋势[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):264-275. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903029.htm [19] 曾灿, 尹太举, 宋亚开.湖平面升降对浅水三角洲影响的沉积数值模拟实验[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2017, 42(11):2095-2104. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201711018.htm [20] Schuurman F, Kleinhans M G.Self-formed braided bar pattern in a numerical model[C]//Proceedings of the 7th IAHR conference on river, estuarine and coastal morphodynamics.Beijing, China.2011: 1647-1657. [21] 中华人民共和国水利部.中国河流泥沙公报[M].北京:中国水利水电出版社, 2018. [22] Schuurman F, Kleinhans M G.Bar dynamics and bifurcation evolution in a modelled braided sand-bed river[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2015, 40(10):1318-1333. doi: 10.1002/esp.3722 [23] Schuurman F, Kleinhans M G, Middelkoop H.Network response to disturbances in large sand-bed braided rivers[J].Earth Surface Dynamics, 2016, 4(1):25-45. doi: 10.5194/esurf-4-25-2016 [24] 冯文杰, 吴胜和, 张可, 等.曲流河浅水三角洲沉积过程与沉积模式探讨:沉积过程数值模拟与现代沉积分析的启示[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(9):2047-2064. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.09.009 [25] 乔雨朋, 邵先杰, 接敬涛, 等.远源砂质辫状河储层构型及控制因素:以秦皇岛32-6油田为例[J].油气地质与采收率, 2016, 23(1):46-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9603.2016.01.007 [26] Walter B.River Bifurcations[D].Trento: University of Trento, 2004. [27] Miori S, Hardy R J, Lane S N.Topographic forcing of flow partition and flow structures at river bifurcations[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2012, 37(6):666-679. doi: 10.1002/esp.3204 [28] Kleinhans M G, Ferguson R I, Lane S N, et al.Splitting rivers at their seams:Bifurcations and avulsion[J].Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2013, 38(1):47-61. doi: 10.1002/esp.3268 [29] Zolezzi G, Bertoldi W, Tubino M, et al.Morphological analysis and prediction of river bifurcations[J].Braided Rivers:Process, Deposits, Ecology and Management, 2006, 36:233-256. doi: 10.1002/9781444304374.ch11/summary [30] Miori S, Repetto R, Tubino M.A one-dimensional model of bifurcations in gravel bed channels with erodible banks[J].Water Resources Research, 2006, 42(11):1-12. doi: 10.1029/2006WR004863 [31] Edmonds D A, Slingerland R L.Stability of delta distributary networks and their bifurcations[J].Water Resources Research, 2008, 44(9):1-13. doi: 10.1029/2008WR006992 [32] Ashmore P E.How do gravel-bed rivers braid?[J].Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 1991, 28(3):326-341. doi: 10.1139/e91-030 [33] 于兴河, 马兴祥, 穆龙新, 等.辫状河储层地质模式及层次界面分析[M].北京:石油工业出版社, 2004. [34] Slingerland R, Smith N D.River avulsions and their deposits[J].Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 2004, 32(1):257-285. doi: 10.1146/annurev.earth.32.101802.120201 [35] Yang H.Development of a physics-based morphodynamic model and its application to braided rivers[D].Cardiff: Cardiff University, 2013. -





 下载:
下载: