Logging identification and prediction of lithofacies of lacustrine shale system in Shichang Sub-Sag, Nanpu Depression
-
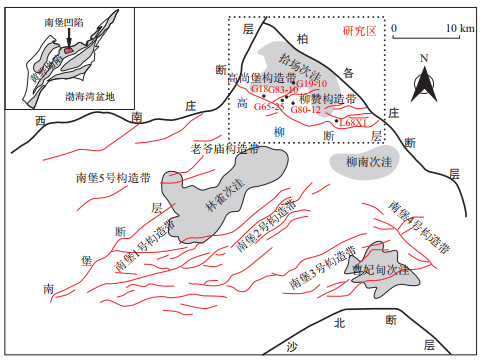
摘要: 泥页岩层系岩相研究是页岩油勘探的基础工作,由于钻井取心较为困难且陆相湖盆范围小,相变快,使岩相精细识别与预测较为困难。测井曲线精确度高,纵向连续性好,可以准确识别与预测岩相。利用全岩X衍射(XRD)、薄片鉴定及地球化学分析测试等实验数据,将岩相按"三级次-三单元"划分方案进行划分,将测井曲线与TOC值、矿物含量等参数进行拟合,综合识别岩相,最后在高分辨率层序格架下建立岩相旋回叠加模式,从而进行岩相展布研究。结果表明该地区为一套以Ⅰ型和Ⅱ1型干酪根为主生油湖相烃源岩,可划分为18种岩相,其中富有机质黏土质层状泥岩、富有机质混合质纹层状泥岩、页岩为页岩油优势岩相。岩相各评价指标可通过测井曲线计算与预测。岩相与层序存在耦合关系,在等时地层格架下具可预测性。沙三4亚段泥页岩层系岩相在此格架下,形成了MSC1中部与MSC2两个有机质富集层,以及SQ5~SQ8上升半旋回4个沉积构造发育带。Abstract: The study of the lithofacies of shale formation is the basic work for shale oil exploration.Due to the limited distribution of the continental lacustrine basin and the fast variations of lithofacies, it is difficult to accurately identify and predict the lithofacies.With high precision and good continuity in vertical direction, the logging curve can be used to accurately identify and predict the lithofacies.Based on the experimental data of whole-rock X-ray diffraction(XRD), thin-section identification and geochemical analysis data, the lithofacies can be divided according to the division scheme named three classes & ternary plots.Fitting logging data with TOC value and mineral content, the lithofacies can be comprehensively identified.Finally, the cycle superposition model of lithofacies is established under the high-resolution sequence frame to study the distribution of lithofacies.The results show that the area is a set of oil-bearing lacustrine source rocks with Ⅰ and Ⅱ1 kerogen, which can be divided into 18 types of lithofacies, among which organic-rich argillaceous lamellar shale and organic-rich mixed lamellar shale are the dominant lithofacies.The evaluation indexes of the lithofacies can be calculated and predicted through the logging curve.There is a coupling relationship between the lithofacies and the sequence so that the lithofacies are predictable under the isochronous stratigraphic framework.The lithofacies of shale formation of the Es34 sub-member are under this framework, forming two organic-rich layers located in the middle of MSC1 and MSC2 middle cycles and four sedimentary tectonic development zones corresponding to the SQ5-SQ8 ascending semi-cycling.
-
Key words:
- Nanpu Depression /
- shale system /
- lithofacies /
- logging /
- isochrono stratigraphic frame
-
图 5 岩相微观沉积构造特征
a.富有机质黏土质块状泥岩,G65-25井, 3 501.73 m;b.有机质混合质块状泥岩,G65-25井,3 519.86 m;c.有机质混合质层状页岩,G65-25井,3 473.60 m;d.有机质混合质纹层状页岩,G65-25井,3 484.44 m;e.有机质黏土质层状泥岩,G65-25井,3 481.83 m;f.有机质黏土质层状页岩,G83-10井,3 661.37 m;g.有机质碳酸盐质层状页岩,G65-25井,3 512.15 m;h.有机质长英质块状泥岩,G65-25井,3 482.98 m;i.贫有机质碳酸盐质块状页岩,G27井,3 564.63 m
Figure 5. Microscopic sedimentary structural features of lithofacies
表 1 岩相类型与特征
Table 1. Types and characteristics of lithofacies
大类 亚类 小类 w(TOC)/% 黏土质矿物质量分数/% 长英质矿物质量分数/% 碳酸盐质矿物质量分数/% 富有机质 黏土质 块状泥岩 2.5~5 >50 25~40 < 12 层状页岩 2.5~3.5 >50 < 25 12~25 混合质 块状泥岩 2.5~3.5 35~50 25~45 12~25 纹层状页岩 2.5~3.5 30~50 25~45 12~25 碳酸盐质 块状泥岩 2.5~3.0 12~25 < 12 >50 中有机质 黏土质 块状泥岩 1.4~2.5 >50 25~40 < 12 层状泥岩 1.0~2.5 >50 25~40 12~25 层状页岩 1.0~2.5 >50 25~40 12~25 混合质 块状泥岩 1.2~2.5 30~50 10~50 10~50 层状页岩 1.0~2.5 30~50 25~50 12~40 纹层状页岩 1.0~2.5 40~50 40~50 < 12 长英质 块状泥岩 1.0~1.8 25~40 >50 < 15 碳酸盐质 层状页岩 1.0~2.3 25~40 < 25 >50 贫有机质 黏土质 块状泥岩 < 1.1 >50 25~50 < 10 层状泥岩 < 1.1 >50 25~50 10~20 混合质 块状泥岩 < 1.1 25~40 15~30 30~50 层状页岩 < 1.1 35~50 10~50 10~50 碳酸盐质 块状泥岩 < 1.1 10~25 < 10 >50 表 2 样品各组分真实质量分数及测井响应值
Table 2. Samples of mineral content and log responses
编号 深度 黏土矿物 长英质矿物 碳酸盐矿物 AC/(μm·ft-1) PE/(b·e-1) DEN/(g·cm-3) RLLD/(Ω·m) SP/mV GR/API wB/% 1 3 472.12 39.10 29.10 19.10 96.38 11.53 2.34 2.06 51.35 91.60 2 3 473.73 37.97 32.55 18.08 91.29 11.36 2.43 2.35 50.75 87.80 3 3 476.62 36.08 39.69 13.53 83.57 10.39 2.43 2.67 50.77 96.57 4 3 477.47 40.98 39.20 8.02 92.14 8.92 2.43 2.37 51.19 92.76 5 3 478.35 49.32 28.31 11.87 92.27 7.19 2.46 2.39 51.18 91.18 6 3 479.31 44.15 33.34 10.81 94.39 9.87 2.45 2.69 50.73 88.52 7 3 480.59 42.62 36.38 10.40 92.29 7.14 2.47 2.70 51.27 97.26 8 3 481.16 49.14 34.19 4.27 89.05 5.98 2.45 2.94 51.19 102.42 9 3 483.24 30.37 51.53 9.20 83.25 7.95 2.51 3.37 51.61 82.32 10 3 484.67 37.80 35.86 17.44 82.01 7.56 2.43 3.75 50.88 86.11 11 3 486.5 49.41 35.43 7.46 99.53 9.93 2.29 4.49 50.96 83.24 12 3 488.39 55.73 26.94 7.43 97.92 7.47 2.46 2.56 50.49 79.58 13 3 489.24 52.08 28.73 6.29 102.13 10.46 2.38 2.18 50.94 86.66 14 3 491.24 38.47 19.70 30.03 110.13 5.84 2.45 2.11 51.19 91.20 15 3 492.16 35.23 22.85 29.52 100.86 5.01 2.45 2.01 51.56 78.65 16 3 495.28 40.73 27.15 21.72 104.60 6.04 2.48 2.80 49.76 76.15 17 3 499.02 29.63 15.29 47.78 114.03 7.97 2.35 2.50 49.74 90.12 18 3 502.25 48.01 35.08 8.31 106.21 5.55 2.40 6.28 50.29 82.07 19 3 503.15 45.36 32.13 15.12 115.67 6.85 2.38 4.08 50.89 72.87 20 3 505.31 42.95 23.97 22.97 111.54 5.46 2.42 3.00 50.68 87.12 21 3 508.18 47.03 33.20 11.07 99.90 4.91 2.49 2.76 50.70 85.29 22 3 512.15 23.23 19.35 50.32 107.40 4.59 2.49 3.70 49.17 76.63 23 3 518.19 30.31 25.72 33.07 100.35 5.88 2.45 2.40 50.17 92.31 24 3 519.01 30.63 27.85 33.42 105.43 6.13 2.50 2.29 50.53 88.51 测试单位:中国石油化工股份有限公司胜利油田分公司勘探开发研究院石油地质测试中心 表 3 矿物含量与各测井响应值相关系数
Table 3. Correlation coefficient of mineral content and responses value of different logging data
测井曲线 相关性系数(R2) 黏土质矿物 长英质矿物 碳酸盐质矿物 AC 0.006 8 0.519 6 0.274 6 SP 0.140 3 0.263 7 0.356 0 PE 0.008 4 0.122 0 0.134 8 DEN 0.143 1 0.016 6 0.007 8 RLLD 0.034 4 0.087 1 0.040 2 CNL 0.022 3 0.022 9 0.014 2 GR 0.009 6 0.114 0 0.032 8 表 4 主要矿物多元线性拟合结果
Table 4. Multiple linear fit results of the dominating minerals
长英质矿物 R2 y=-0.002AC+0.054 9SP+0.018 8PE+ 0.768 0DEN+0.053 19RLLD-4.430 6 0.85 碳酸盐质矿物 R2 y=0.001 1AC-0.120 5SP-0.022 2PE-0.557 6DEN-0.063 0RLLD+7.868 5 0.60 黏土质矿物 R2 y=0.050 8SP-0.288 5DEN+0.016 0RLLD+0.000 7CNL-0.000 2GR-1.516 5 0.42 表 5 不同岩性测井响应平均值统计
Table 5. Statistics of average responses of different lithofacies
泥岩 页岩 泥质粉砂岩 粉砂岩 AC/(μs·ft-1) 99.29 97.16 71.28 75.3 GR/API 79.6 59.06 57 53.64 RLLD/(Ω·m) 3.71 3.5 15.94 19.09 -
[1] 贾承造, 郑民, 张永峰.中国非常规油气资源与勘探开发前景[J].石油勘探与开发, 2012, 39(2):129-136. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201202002.htm [2] 邹才能, 董大忠, 王社教, 等, 中国页岩气形成机理、地质特征及资源潜力[J].石油勘探与开发, 2010, 37(6):641-653. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201006003.htm [3] Zhu H, Kong X, Long H, et al.Duvernay shale lithofacies distribution analysis in the West Canadian Sedimentary Basin[J].IOP Conference Series Earth and Environmental Science, 2018, 121(5):1-8. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/121/5/052007 [4] Bowker K A.Recent development of the Barnett shale play, Fort Worth Basin[J].West Texas Geological Society Bulletin, 2003, 42(6):1-11. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/285699986_Recent_development_of_the_Barnett_Shale_play_Fort_Worth_Basin [5] Hichey J J, Henk B.Lithofacies summary of the Mississippian Barnett Shale, Mitchell 2 TP Sims well, Wise County Texas[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 91(4):437-443. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/249897891_Lithofacies_summary_of_the_Mississippian_Barnett_Shale_Mitchell_2_TP_Sims_well_Wise_County_Texas [6] Zhao Xianzheng, Zhou Lihong, Pu Xiugang, et al.Geological characteristics of shale rock system and shale oil exploration in a lacustrine basin:A case study from the Paleogene 1st sub-member of Kong 2 Member in Cangdong sag, Bohai Bay Basin, China[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2018, 45(3):361-372. http://www.zhangqiaokeyan.com/academic-journal-cn_petroleum-exploration-development_thesis/0201248774953.html [7] Ou Chenghua, Li Chaochu, Rui Zhenhua, et al.Lithofacies distribution and gas-controlling characteristics of the Wufeng-Longmaxi black shales in the southeastern region of the Sichuan Basin, China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2018, 165:269-283. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2018.02.024 [8] Wang G C, Catt T R.Organic-rich marcellus shale lithofacies modeling and distribution pattern analysis in the Appalachian Basin[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2013, 97(12):2173-2205. doi: 10.1306/05141312135 [9] Daniel M J, Ronald J H, Tim E R, et al.Unconventional shale-gas system:The Mississippian barnett shale of north-central Texas as one model for thermogenic shale-gas assessment[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):475-499. doi: 10.1306/12190606068 [10] Loucks R G, Ruppel S C.Mississippian Barnett Shale:Lithofacies and depositional setting of a deep-water shale-gas succession in the Fort Worth Basin, Texas[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2007, 91(4):579-601. doi: 10.1306/11020606059 [11] Qiu Zhen, Tao Huifei, Zou Cainen, et al.Lithofacies and organic geochemistry of the Middle Permian Lucaogou Formation in the Jimusar Sag of the Junggar Basin, NW China[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2016, 140:97-107. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2016.01.014 [12] 王宏语, 杨润泽, 张峰, 等.富含有机质泥页岩岩相表征的研究现状与趋势[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2):141-148. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802020.htm [13] 孟令箭, 吴建楠, 汤建荣, 等.南堡凹陷地层压力演化及成因[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(5):110-117. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201605015.htm [14] 曹宇.南堡凹陷断裂系统类型及其控藏作用[J].大庆石油地质与开发, 2016, 35(4):22-27. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-3754.2016.04.004 [15] 万里明, 吴均, 卢军凯, 等.基于Adam-神经网络的致密砂岩脆性评价方法:以南堡凹陷高北边坡为例[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2):94-103. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9978.shtml [16] Mohamed O, Abouelresh, Roger M S.Lithofacies and sequence stratigraphy of the Barnet Shale in east-central Fort Worth Basin, Texas[J].AAPG Bulletin, 2012, 96(1):34-43. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/264332984_lithofacies_and_sequence_stratigraphy_of_the_barnett_shale_in_east-central_fort_worth_basin_texas [17] 董春梅, 马存飞, 林承焰, 等.一种泥页岩层系岩相划分方法[J].中国石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2015, 39(3):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5005.2015.03.001 [18] Wang Pengfei, Jiang Zhenxue, Yin Lishi, et al.Lithofacies classification and its effect on pore structure of the Cambrian marine shale in the Upper Yangtze Platform, South China:Evidence from FE-SEM and gas adsorption analysis[J].Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering, 2017, 156:307-321. doi: 10.1016/j.petrol.2017.06.011 [19] Wang Chao, ZhangBaiqiao, Lu Yingchao, et al.Lithofacies distribution characteristics and its controlling factors ofshale in Wufeng Formation-Member 1 of Longmaxi Formation in the Jiaoshiba area[J].Petroleum Research, 2018, 3:306-319. doi: 10.1016/j.ptlrs.2018.11.005 [20] Lazar O R, Bohacs K M, Macquaker J H, et al.Capturing key attributes of fine-grained sedimentary rocks in outcrops, cores, and thin sections:Nomenclature and description guidelines[J].Journal of Sedimentary Research, 2015, 85(3):230-246. doi: 10.2110/jsr.2015.11 [21] 柳波, 石佳欣, 付晓飞, 等.陆相泥页岩层系岩相特征与页岩油富集条件:以松辽盆地古龙凹陷白垩系青山口组一段富有机质泥页岩为例[J].石油勘探与开发, 2018, 45(5):84-94. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SKYK201805009.htm [22] 赵显令, 王贵文, 周正龙, 等.地球物理测井岩性解释方法综述[J].地球物理学进展, 2015, 30(3):1278-1287. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQWJ201503038.htm [23] Huang Chuanyan, Zhang Jinchuan, Wang Hua, et al.Lower Es3 in Zhanhua Sag, Jiyang Depression:A case study for lithofacies classification in lacustrine mud shale.[J].Applied Geophysics, 2018, 15(2):151-164. doi: 10.1007/s11770-018-0678-5 [24] 马淼, 孙卫, 白云云, 等.姬塬地区长6储层成岩相特征及测井响应[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3):177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803023.htm [25] 时志强, 曾德勇, 熊兆军, 等.三叠纪巨型季风在上扬子地区的沉积学记录[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2010, 29(2):164-172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2010.02.008 [26] 宋明水.东营凹陷南斜坡沙四段沉积环境的地球化学特征[J].矿物岩石, 2005, 25(1):67-73. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KWYS200501013.htm [27] 许璟, 蒲仁海, 杨林, 等.塔里木盆地石炭系泥岩沉积时的古盐度分析[J].沉积学报, 2010, 28(3):509-517. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CJXB201003014.htm [28] 张廷山, 彭志, 祝海华, 等.海安凹陷曲塘次凹阜二段页岩油形成条件及勘探潜力[J].地质科技情报, 2016, 35(2):177-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201602035.htm [29] 王贵文, 徐敬领, 杨宁, 等.小波分频分析法在沉积层序划分及等时对比中的应用[J].高校地质学报, 2013, 19(1):70-77. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2013.01.011 [30] 李峰峰, 郭睿, 余义常.层序地层划分方法进展及展望[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):215-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904022.htm -





 下载:
下载: