Advances in the application of machine learning methods in mineral prospectivity mapping
-
摘要: 回顾了国内外在矿产资源定量预测研究领域的发展历程,对近十年来国外相关方向的文献进行了统计对比分析,结果显示机器学习方法已经成为矿产资源定量预测研究领域的热点方向,并主要在如下3个方面发挥了积极的作用:①提取和挖掘复杂数据中隐藏的难以识别的矿化信息;②致矿异常信息关联与转换;③多源地学数据的致矿异常信息融合、预测和发现矿床。对逻辑回归、人工神经网络、随机森林与支持向量机等主要机器学习算法与模型在矿产资源定量预测实践中的应用效果进行了评述,并探讨了在实际应用过程中存在的样本选择、错分代价、不确定性评价以及模型性能评价等主要问题及目前的解决方案。最后提出基于大数据与机器学习的矿产资源定量预测是未来发展的重要趋势。Abstract: This paper reviews the development of mineral prospectivity mapping at home and abroad, and conducts statistical comparative analysis of relevant foreign literature in the past decade.It shows that machine learning methods have become a hot topic in the field of mineral prospectivity mapping, and have played an active role in the following three aspects: ① extraction and mining of hidden and unrecognizable mineralization information in complex data; ② association and transformation of ore-forming anomaly information; ③ fusion, prediction and discovery of ore-forming anomaly information from multi-source geological data.Firstly, the application effects of major machine learning algorithms and models, such as logistic regression, artificial neural networks, random forests, and support vector machines, in mineral prospectivity mapping are reviewed.Secondly, it discusses the main problems in the application process, such as sample selection, misclassification cost, uncertainty evaluation, and model performance evaluation, as well as the current solutions.Finally, it is proposed that quantitative prediction of mineral resources based on big data and machine learning is an important trend in the future.
-
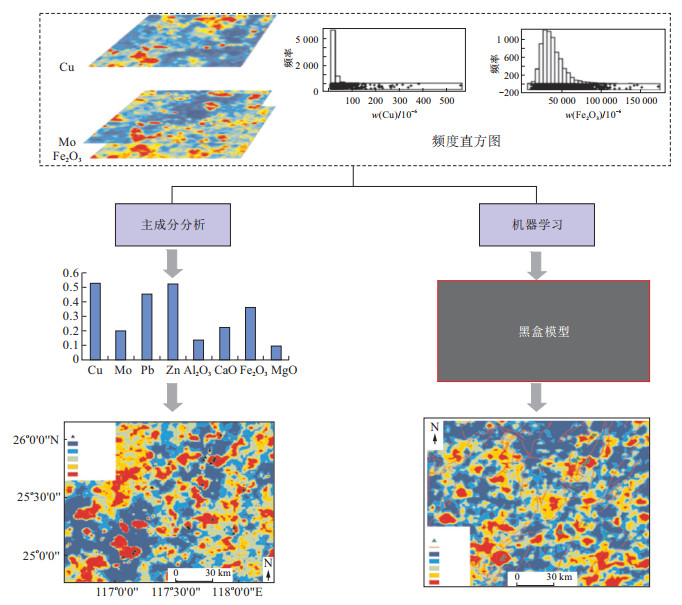
图 1 多元统计方法与机器学习方法挖掘地球化学致矿异常信息对比图解[24]
Figure 1. Comparison between multivariate statistical methods and machine learning methods in geochemical anomaly identification
表 1 矿产资源定量预测模型分类
Table 1. Mineral prospectivity mapping predication models
类型 模型参数 实例 数据驱动 统计矿化指标与已知矿床的关联 逻辑回归、证据权
人工神经网络、随机森林
证据信念函数、支持向量机
似然比分析、判别分析
有利度分析、贝叶斯网络分类知识驱动 由专家评估 布尔逻辑、标志叠加模型
模糊逻辑、证据信念函数
Dempster-Shafer理论表 2 机器学习不同类别划分[26]
Table 2. Categories of machine learning
类别 特征 评价 优化 代表算法 符号主义 使用符号、规则和逻辑来表征知识和进行逻辑推理 准确度 逆向演绎 决策树 联结主义 使用概率矩阵和加权神经元来动态地识别和归纳模式 平方误差 梯度下降 神经网络 进化主义 生成变化,为特定目标获取最优 适应度 遗传搜索 遗传算法 贝叶斯主义 获取发生的可能性来进行概率推理 后验概率 概率推理 朴素贝叶斯、马尔科夫 类推主义 根据约束条件优化函数 间距 约束优化 支持向量机 -
[1] 赵鹏大."三联式"资源定量预测与评价:数字找矿理论与实践探讨[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2002, 27(5):482-489. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2002.05.002 [2] 赵鹏大, 陈永清, 刘吉平, 等.地质异常成矿预测理论与实践[M].武汉:中国地质大学出版社, 1999. [3] 赵鹏大.大数据时代数字找矿与定量评价[J].地质通报, 2015, 34(7):5-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZQYD201507001.htm [4] 成秋明.非线性成矿预测理论:多重分形奇异性-广义自相似性-分形谱系模型与方法[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2006, 31(3):337-348. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2006.03.009 [5] 赵鹏大, 夏庆霖.中国学者在数学地质学科发展中的成就与贡献[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2009, 34(2):225-231. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-2383.2009.02.001 [6] 赵鹏大.矿产资源定量预测及评价模型研究的新进展[J].地质科技情报, 1987, 6(1):1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ198701000.htm [7] 曹新志, 张旺生, 孙华山.我国深部找矿研究进展综述[J].地质科技情报, 2009, 28(2):104-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2009.02.019 [8] Porwal A, Carranza E J M.Introduction to the special issue:GIS-based mineral potential modelling and geological data analyses for mineral exploration[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71:477-483. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.04.017 [9] 赵鹏大.成矿定量预测与深部找矿[J].地学前缘, 2007, 14(5):3-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DXQY200705002.htm [10] Cheng Q, Agterberg F P, Ballantyne S B.The separation of geochemical anomalies from background by fractal methods[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1994, 51(2):109-130. doi: 10.1016/0375-6742(94)90013-2 [11] Cheng Q.The perimeter-area fractal model and its application to geology[J].Mathematical Geology, 1995, 27(1):69-82. doi: 10.1007/BF02083568 [12] Cheng Q, Xu Y, Grunsky E.Integrated spatial and spectrum method for geochemical anomaly separation[J].Natural Resources Research, 2000, 9(1):43-52. doi: 10.1023/A:1010109829861 [13] Cheng Q.Mapping singularities with stream sediment geochemical data for prediction of undiscovered mineral deposits in Gejiu, Yunnan Province, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32(1/2):314-324. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0169136806001119 [14] 张夏林, 吴冲龙, 周琦, 等.基于勘查大数据和数据集市的锰矿床三维地质建模[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4):113-121. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9994.shtml [15] Sprague K, Kemp E D, Wong W, et al.Spatial targeting using queries in a 3-D GIS environment with application to mineral exploration[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2006, 32(3):396-418. doi: 10.1016/j.cageo.2005.07.008 [16] 赵鹏大, 胡旺亮, 李紫金.矿床统计预测[M].北京:地质出版社, 1994. [17] 左仁广, 夏庆霖, 张道军, 等.基于地质过程的闽西南马坑式铁多金属矿定量预测[J].地球科学:中国地质大学学报, 2012, 37(6):1183-1190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DQKX201206015.htm [18] Bonham-Carter G F.Geographic information systems for geoscientists:Modelling with GIS[M].London:Pergamon, 1994. [19] Carranza E J M.Natural resources research publications on geochemical anomaly and mineral potential mapping, and introduction to the special issue of papers in these fields[J].Natural Resources Research, 2017, 26(788):1-32. doi: 10.1007/s11053-017-9348-1 [20] Bishop C M.Pattern recognition and machine learning[M].Boston, MA:Springer, 2006. [21] Stuart J R, Peter N.Artificial intelligence:A modern approach[M].New York:Pearson Education, Inc., 2020. [22] Domingos P.The master algorithm:How the quest for the ultimate learning machine will remake our world[M].England:Reed Business Information Ltd., 2015. [23] Kussul N, Lavreniuk M, Skakun S, et al.Deep learning classification of land cover and crop types using remote sensing data[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(5):778-782. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2017.2681128 [24] 左仁广.基于深度学习的深层次矿化信息挖掘与集成[J].矿物岩石地球化学通报, 2019, 38(1):53-60. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KYDH201901005.htm [25] Zuo R.Machine learning of mineralization-related geochemical anomalies:A review of potential methods[J].Natural Resources Research, 2017, 26(4):457-464. doi: 10.1007/s11053-017-9345-4 [26] Chung C F, Agterberg F P.Regression models for estimating mineral resources from geological map data[J].Journal of the International Association for Mathematical Geology, 1980, 12(5):473-488. doi: 10.1007/BF01028881 [27] Hosmer D H W, Lemeshow S.Applied logistic regression[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2004, 85(411):81-82. [28] 胡涛, 樊鑫, 王硕, 等.基于逻辑回归模型和3S技术的思南县滑坡易发性评价[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(2):113-121. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9980.shtml [29] Chen C, Dai H, Liu Y, et al.Mineral prospectivity mapping integrating multi-source geology spatial data sets and logistic regression modelling[C]//IEEE international conference on spatial data mining and geographical knowledge services.IEEE, 2011. [30] Porwal A, González-Álvarez I, Markwitz V, et al.Weights-of-evidence and logistic regression modeling of magmatic nickel sulfide prospectivity in the Yilgarn Craton, Western Australia[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2010, 38(3):184-196. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2010.04.002 [31] 周曙光, 周可法, 崔遥, 等.基于逻辑回归模型的化探异常信息识别研究:以克拉玛依地区为例[J].西北地质, 2016, 49(1):234-240. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2016.01.024 [32] Müller B, Reinhardt J, Strickland M T.Neural networks[J].Physics of Neural Networks, 1992, 293(4):2588-2592. [33] Nykänen V.Radial basis functional link nets used as a arospectivity mapping tool for orogenic gold deposits within the Central Lapland Greenstone Belt, Northern Fennoscandian Shield[J].Natural Resources Research, 2008, 17(1):29-48. doi: 10.1007/s11053-008-9062-0 [34] Oh H J, Lee S.Application of artificial neural network for gold-silver deposits potential mapping:A case study of Korea[J].Natural Resources Research, 2010, 19(2):103-124. doi: 10.1007/s11053-010-9112-2 [35] Zhao J, Chen S, Zuo R.Identifying geochemical anomalies associated with Au-Cu mineralization using multifractal and artificial neural network models in the Ningqiang district, Shaanxi, China[J].Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 164:54-64. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.06.018 [36] Breiman L.Machine learn[J].Machine Learning, 2001, 45:5-32. doi: 10.1023/A:1010933404324 [37] Hariharan S, Tirodkar S, Porwal A, et al.Random forest-based prospectivity modelling of greenfield terrains using sparse deposit data:An example from the Tanami region, western Australia[J].Natural Resources Research, 2017, 26(1):1-19. doi: 10.1007/s11053-016-9319-y [38] Carranza E J M, Laborte A G.Data-driven predictive modeling of mineral prospectivity using random forests:A case study in Catanduanes Island(Philippines)[J].Natural Resources Research, 2015, 25(1):1-16. [39] Rodriguez-Galiano V F, Chica-Olmo M, Chica-Rivas M.Predictive modelling of gold potential with the integration of multisource information based on random forest:A case study on the Rodalquilar area, Southern Spain[J].International Journal of Geographical Information Science, 2014, 28(7):1336-1354. doi: 10.1080/13658816.2014.885527 [40] Vapnik V.The nature of statistical learning theory springer new york google scholar[M].New York:Springer-verlag, 1995. [41] Burges C J C.A tutorial on support vector machines for pattern recognition[J].Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 1998, 2(2):121-167. doi: 10.1023/A:1009715923555 [42] Vapnik V.Pattern recognition using generalized portrait method[J].Automation & Remote Control, 2008, 24(24):774-780. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10030529499 [43] Cortes C, Vapnik V.Support-vector networks[J].Machine Learning, 1995, 20(3):273-297. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/naid/10020879413 [44] Zuo R, Carranza E J M.Support vector machine:A tool for mapping mineral prospectivity[J].Computers &Geosciences, 2011, 37(12):1967-1975. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2073002 [45] 韩创益, 王恩德, 夏建明, 等.基于贝叶斯推理的LS-SVM矿产资源定量预测[J].东北大学学报:自然科学版, 2017, 38(11):1633-1636. doi: 10.12068/j.issn.1005-3026.2017.11.023 [46] Wang J, Zuo R, Xiong Y.Mapping mineral prospectivity via semi-supervised random forest[J].Natural Resources Research, 2020, 29(1):189-202. doi: 10.1007/s11053-019-09510-8 [47] Granek J, Haber E.Data mining for real mining: A robust algorithm for prospectivity mapping with uncertainties[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 SIAM International Conference on Data Mining.Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2015. [48] Shahshahani B M, Landgrebe D A.The effect of unlabeled samples in reducing the small sample size problem and mitigating the Hughes phenomenon[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and remote sensing, 1994, 32(5):1087-1095. doi: 10.1109/36.312897 [49] Joachims T.Transductive inference for text classification using support vector machines[C]//Proceedings of the sixteenth international conference on machine learning.San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann, 1999. [50] Grandvalet Y, Bengio Y.Semi-supervised learning by entropy minimization[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.2004, 17:529-536. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2976040.2976107 [51] Blum A, Chawla S.Learning from labeled and unlabeled data using graph mincuts[C]//Anon.Proceedings of the 18th international conference on machine learning(ICML), Williamston, MA: Morgan Kaufmann, 2001. [52] Nykänen V, Lahti I, Niiranen T, et al.Receiver operating characteristics(ROC) as validation tool for prospectivity models:A magmatic Ni-Cu case study from the Central Lapland Greenstone Belt, Northern Finland[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71:853-860. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.007 [53] Carranza E J M.Data-driven evidential belief modeling of mineral potential using few prospects and evidence with missing values[J].Natural Resources Research, 2015, 24(3):291-304. doi: 10.1007/s11053-014-9250-z [54] Zhou Z H, Liu X Y.Training cost-sensitive neural networks with methods addressing the class imbalance problem[J].IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2005, 18(1):63-77. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/1549828/citations?tabFilter=papers [55] Berardi V L, Zhang G P.The effect of misclassification costs on neural network classifiers[J].Decision Sciences, 1999, 30(3):659-682. doi: 10.1111/j.1540-5915.1999.tb00902.x [56] Viaene S, Dedene G.Cost-sensitive learning and decision making revisited[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 2005, 166(1):212-220. doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2004.03.031 [57] Kukar M, Kononenko I.Cost-sensitive learning with neural networks[M]//Brighton, UK: ECAI, 1998. [58] Xu J, Cao Y, Li H, et al.Cost-sensitive learning of SVM for ranking[C]//Anon.European conference on machine learning.Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2006. [59] Jiang L, Li C, Cai Z, et al.Sampled bayesian network classifiers for class-imbalance and cost-sensitive learning[C]//Anon.2013 IEEE 25th International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence.Herndon, VA, USA: IEEE, 2013. [60] Zadrozny B, Langford J, Abe N.Cost-sensitive learning by cost-proportionate example weighting[M]//Melbourne, F L, USA: IEEE, 2003. [61] Jiang L, Li C, Wang S.Cost-sensitive Bayesian network classifiers[J].Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 45:211-216. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2014.04.017 [62] Xiong Y, Zuo R.Effects of misclassification costs on mapping mineral prospectivity[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2017, 82:1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.11.014 [63] Zuo R, Zhang Z, Zhang D, et al.Evaluation of uncertainty in mineral prospectivity mapping due to missing evidence:A case study with skarn-type Fe deposits in Southwestern Fujian Province, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2015, 71:502-515. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.024 [64] An P, Moon W M, Bonham-Carter G F.Uncertainty management in integration of exploration data using the belief function[J].Nonrenewable Resources, 1994, 3(1):60-71. doi: 10.1007/BF02261716 [65] Bárdossy G, Fodor J.Review of the main uncertainties and risks in geology[C]//Anon.Evaluation of uncertainties and risks in geology.Berlin: Springer, 2004. [66] Kraipeerapun P, Fung C C, Brown W.Assessment of uncertainty in mineral prospectivity prediction using interval neutrosophic set[C]//Anon.International conference on computational and information science.Berlin: Springer, 2005. [67] 左仁广.基于地质异常的矿产资源定量化预测与不确定性评价[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2009. [68] Yousefi M, Kreuzer O P, Nykänen V, et al.Exploration information systems-a proposal for the future use of GIS in mineral exploration targeting[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 111:103005. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103005 [69] Mihalasky M J, Bonham-Carter G F.Lithodiversity and its spatial association with metallic mineral sites, Great Basin of Nevada[J].Natural Resources Research, 2001, 10(3):209-226. doi: 10.1023/A:1012569225111 [70] Yousefi M, Carranza E J M.Prediction-area(P-A) plot and C-A fractal analysis to classify and evaluate evidential maps for mineral prospectivity modeling[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2015, 79:69-81. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300415000564 [71] Roshanravan B, Aghajani H, Yousefi M, et al.An improved prediction area plot for prospectivity analysis of mineral deposits[J].Natural Resources Research, 2019, 28(3):1089-1105. doi: 10.1007/s11053-018-9439-7 [72] Parsa M, Maghsoudi A, Yousefi M, et al.Prospectivity modeling of porphyry-Cu deposits by identification and integration of efficient mono-elemental geochemical signatures[J].Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2016, 114:228-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jafrearsci.2015.12.007 [73] Xiong Y, Zuo R.GIS-based rare events logistic regression for mineral prospectivity mapping[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2018, 111:18-25. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300417305447 [74] Ross Z E, Meier M A, Hauksson E.P wave arrival picking and first-motion polarity determination with deep learning[J].Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth, 2018, 123(6):5120-5129. doi: 10.1029/2017JB015251 [75] Jiang G Q, Xu J, Wei J.A deep learning algorithm of neural network for the parameterization of typhoon-ocean feedback in typhoon forecast models[J].Geophysical Research Letters, 2018, 45(8):3706-3716. doi: 10.1002/2018GL077004 [76] Xiong Y, Zuo R.Recognition of geochemical anomalies using a deep autoencoder network[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2016, 86:75-82. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0098300415300728 [77] Zuo R, Xiong Y.Big data analytics of identifying geochemical anomalies supported by machine learning methods[J].Natural Resources Research, 2018, 27(1):5-13. doi: 10.1007/s11053-017-9357-0 [78] 周密.福建省崇(安)浦(城)地区火山岩型铀矿致矿信息提取与远景预测[D].武汉: 中国地质大学(武汉), 2012. [79] Zhao J, Chen S, Zuo R, et al.Controls on and prospectivity mapping of volcanic-type uranium mineralization in the Pucheng district, NW Fujian, China[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2019, 112:103028. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103028 -





 下载:
下载: