| [1] |
胡雪峰, 鹿化煜.黄土高原古土壤成土过程的特异性及发生学意义[J].土壤学报, 2004, 41(5):669-675. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0564-3929.2004.05.002
|
| [2] |
Guo Z T, Ruddiman W F, Hao Q Z, et al.Onset of Asian desertification by 22 Myr ago inferred from loess deposits in China[J].Nature, 2002, 416:159-163. doi: 10.1038/416159a
|
| [3] |
丁仲礼, 孙继敏, 刘东生.联系沙漠-黄土演变过程中耦合关系的沉积学指标[J].中国科学:地球科学, 1999, 29(1):82-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JDXK199901012.htm
|
| [4] |
丁仲礼, 任剑璋.最后两个冰期旋回季风-沙漠系统不稳定性的高分辨率黄土记录[J].第四纪研究, 1999, 19(1):49-58. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.1999.01.006
|
| [5] |
鹿化煜, 安芷生.洛川黄土粒度组成的古气候意义[J].科学通报, 1997, 42(1):66-69. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1997.01.020
|
| [6] |
鹿化煜, Ko van Huissteden, 周杰, 等.中国北方更新世极端冷期冬季风的快速变化[J].中国沙漠, 2000, 20(2):192-196. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-694X.2000.02.017
|
| [7] |
Chen F H, Bloemendal J, Feng Z D, et al.East Asian monsoon variations during Oxygen Isotope Stage 5:Evidence from the northwestern margin of the Chinese loess plateau[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 1999, 18(8/9):1127-1135. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/resolve/reference/ADS?id=1999QSRv...18.1127C
|
| [8] |
Boulay S, Colin C, Trentesaux A, et al.Mineralogy and sedimentology of Pleistocene sediment in the South China Sea(ODP Site 1144)[J].Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results, 2003(184):1-21.
|
| [9] |
Weltje G J.End-member modeling of compositional data:Numerical-statistical algorithms for solving the explicit mixing problem[J].Mathematical Geology, 1997, 29(4):503-549. doi: 10.1007/BF02775085
|
| [10] |
李帅.青藏高原东部黄土粒度端元分析及其指示意义[D].兰州: 兰州大学, 2018.
|
| [11] |
刘浩, 贾佳, 路彩晨, 等.则克台黄土粒度组分分离及其记录的末次冰期气候波动[J].干旱区地理, 2018, 41(6):120-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GHDL201806013.htm
|
| [12] |
牟雪松, 马俊, 王永达, 等.粒度分布的端元建模分析及检验:以"吉兰泰-河套"盆地西部DK-12钻孔晚第四纪沉积物为例[J].古地理学报, 2018, 20(3):145-156. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GDLX201803012.htm
|
| [13] |
韩鹏, 刘兴起.内蒙古中东部查干淖尔湖流域7000年以来的气候演变[J].第四纪研究, 2017, 37(6):1381-1390.
|
| [14] |
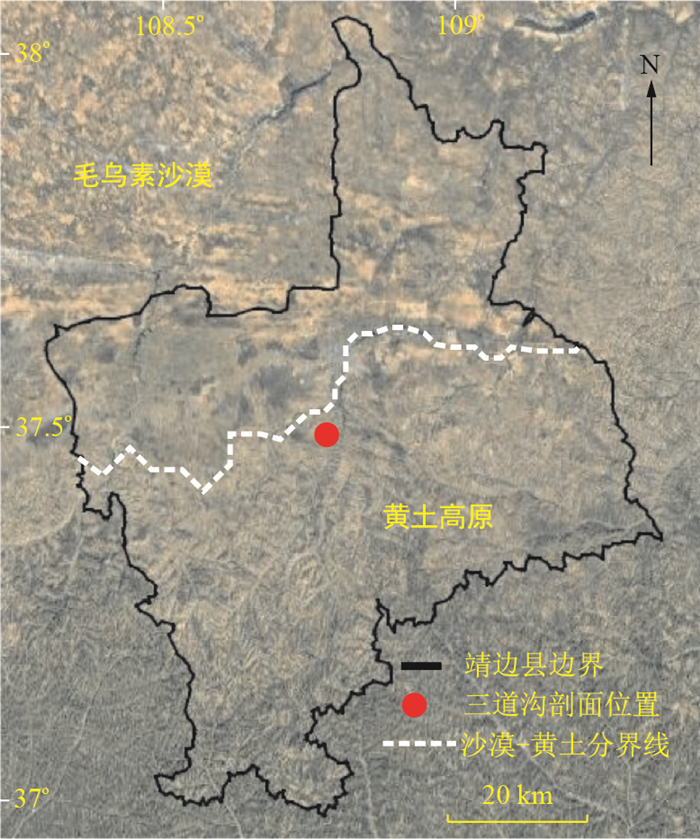
王攀, 张培新, 杨振京, 等.靖边黄土剖面记录的末次冰期以来的气候变化[J].海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2019, 39(3):162-170. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HYDZ201903016.htm
|
| [15] |
张培新, 王攀, 杨振京, 等.陕北靖边三道沟黄土剖面常量元素地球化学特征[J].科学技术与工程, 2019, 19(28):56-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.28.007
|
| [16] |
Paterson G A, Heslop D.New methods for unmixing sediment grain size data[J].Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2015, 16:4494-4506. doi: 10.1002/2015GC006070
|
| [17] |
鹿化煜, Stevens T, 弋双文, 等.高密度光释光测年揭示的距今约15~10 ka黄土高原侵蚀事件[J].科学通报, 2006, 51(23):2767-2772. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2006.23.011
|
| [18] |
秦小光, 蔡炳贵, 穆燕, 等.黄土粉尘搬运过程的动力学物理模型[J].第四纪研究, 2009, 29(6):1154-1161. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DSJJ200906020.htm
|
| [19] |
Pye K, Zhou L P.Late Pleistocene and Holocene aeolian dust deposition in North China and the Northwest Pacific Ocean[J].Palaeogeography Palaeoclimatology Palaeoecology, 1989, 73(1/2):11-23.
|
| [20] |
Patterson E M, Gillette D A.Commonalities in measured size distributions for aerosols having a soil-derived component[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1977, 82(15):2074-2082. doi: 10.1029/JC082i015p02074
|
| [21] |
Vandenberghe J.Grain size of fine-grained windblown sediment:A powerful proxy for process identification[J].Earth-Science Reviews, 2013, 121:18-30. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.03.001
|
| [22] |
Sun D H, Chen F H, Bloemendal J, et al.Seasonal variability of modern dust over the Loess Plateau of China[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 2003, 108(D21):4665. doi: 10.1029/2003JD003382/epdf
|
| [23] |
Sun D H, Bloemendal J, Rea D, et al.Bimodal grain-size distribution of Chinese loess, and its palaeoclimatic implications[J].Catena, 2004, 55(3):325-340. doi: 10.1016/S0341-8162(03)00109-7
|
| [24] |
Vriend M, Prins M A, Buylaert J P, et al.Contrasting dust supply patterns across the north-western Chinese Loess Plateau during the last glacial-interglacial cycle[J].Quaternary International, 2011, 240(1/2):167-180. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1040618210004386
|
| [25] |
Prins M A, Zheng H B, Beets K, et al.Dust supply from river floodplains:The case of the lower Huang He(Yellow River) recorded in a loess-palaeosol sequence from the Mangshan Plateau[J].Journal of Quaternary Science, 2009, 24(1):75-84. doi: 10.1002/jqs.1167
|
| [26] |
Ijmker J, Stauch G, Dietze E, et al.Characterisation of transport processes and sedimentary deposits by statistical end-member mixing analysis of terrestrial sediments in the Donggi Cona lake catchment, NE Tibetan Plateau[J].Sedimentary Geology, 2012, 281:166-179. doi: 10.1016/j.sedgeo.2012.09.006
|
| [27] |
Nottebaum V, Stauch G, Hartmann K, et al.Unmixed loess grain size populations along the northern Qilian Shan(China):Relationships between geomorphologic, sedimentologic and climatic controls[J].Quaternary International, 2015, 372:151-166. doi: 10.1016/j.quaint.2014.12.071
|
| [28] |
Prins M A, Vriend M, Nugteren G, et al.Late Quaternary aeolian dust input variability on the Chinese Loess Plateau:Inferences from unmixing of loess grain-size records[J].Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(1/2):230-242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0277379106002241
|
| [29] |
Vriend M, Prins M A.Calibration of modelled mixing patterns in loess grain-size distributions:An example from the north-astern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, China[J].Sedimentology, 2005, 52(6):1361-1374. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034778948310_2f54.html
|
| [30] |
何俊蓉, 谢先军, 池泽涌, 等.古气候变化对大同盆地第四纪沉积物中砷富集过程的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(5):212-219. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201905023.htm
|
| [31] |
张慧娟, 杨桂芳, 陈正洪, 等.北京延庆古湖沉积物粒度敏感组分记录的区域冬季风演化历史[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(3):81-86. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201803011.htm
|
| [32] |
鲁瑞洁, 王亚军, 张登山.毛乌素沙漠15 ka以来气候变化及沙漠演化研究[J].中国沙漠, 2010, 30(2):273-277. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS201002009.htm
|
| [33] |
刘东生.黄土与环境[M].北京:科学出版社, 1985.
|
| [34] |
An Z S, Kukla G, Porter S C, et al.Late quaternary dust flow on the Chinese Loess Plateau[J].Catena, 1991, 18(2):125-132. doi: 10.1016/0341-8162(91)90012-M
|
| [35] |
Ding Z L, Rutter N, Han J T, et al.A coupled environmental syst EM formed at about 2.5 Ma in East-Asia[J].Paleogeograpy, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology, 1992, 94(1/4):223-242. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/003101829290120t
|
| [36] |
Vandenberghe J, An Z S, Nugteren G, et al.New absolute time scale for the Quaternary climate in the Chinese Loess region by grain size analysis[J].Geology, 1997, 25(1):35-38. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0035:NATSFT>2.3.CO;2
|
| [37] |
Ding Z L, Derbyshire E, Yang S L, et al.Stepwise expansion of desert environment across northern China in the past 3.5 Ma and implications for monsoon evolution[J].Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2005, 237(1/2):45-55. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0012821X05004206
|
| [38] |
Ding Z L, Sun J M, Rutter N W, et al.Changes in Sand Content of Loess Deposits along a North-South Transect of the Chinese Loess Plateau and the Implications for Desert Variations[J].Quaternary Research, 1999, 52(1):56-62. doi: 10.1006/qres.1999.2045
|
| [39] |
楚纯洁, 赵景波, 吴楠楠, 等.毛乌素沙地晚第四纪地层特征与沙漠化研究综述[J].地质科技情报, 2017, 36(5):14-21. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201705003.htm
|
| [40] |
靳鹤龄, 董光荣, 苏志珠, 等.全新世沙漠-黄土边界带空间格局的重建[J].科学通报, 2001, 46(7):538-543. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2001.07.003
|
| [41] |
杨帆, 靳鹤龄, 李孝泽, 等.中晚全新世毛乌素沙漠东南部气候变化过程[J].中国沙漠, 2017, 37(3):431-438. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS201703004.htm
|
| [42] |
舒培仙, 李保生, 牛东风, 等.毛乌素沙漠东南缘滴哨沟湾剖面DGS1层段粒度特征及其指示的全新世气候变化[J].地理科学, 2016, 36(3):448-457. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLKX201603017.htm
|
| [43] |
刘冰, 靳鹤龄, 孙忠.近6 ka以来科尔沁沙地东部气候变化记录[J].中国沙漠, 2011, 31(6):1398-1405. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGSS201106010.htm
|
| [44] |
Sun A Z, Feng Z D.Holocene climatic reconstructions from the fossil pollen record at Qigai Nuur in the southern Mongolian Plateau[J].The Holocene, 2013, 23(10):1391-1402. doi: 10.1177/0959683613489581
|
| [45] |
Huang C L, Zhou J, Pang J L, et al.A regional aridity phase and its possible cultural impact during the Holocene Megathermal in the Guanzhong Basin, China[J].The Holocene, 2000, 10(1):135-142. doi: 10.1191/095968300673103181
|





 下载:
下载: