Factors affecting high temperature rheological properties of polymers used in drilling fluid
-
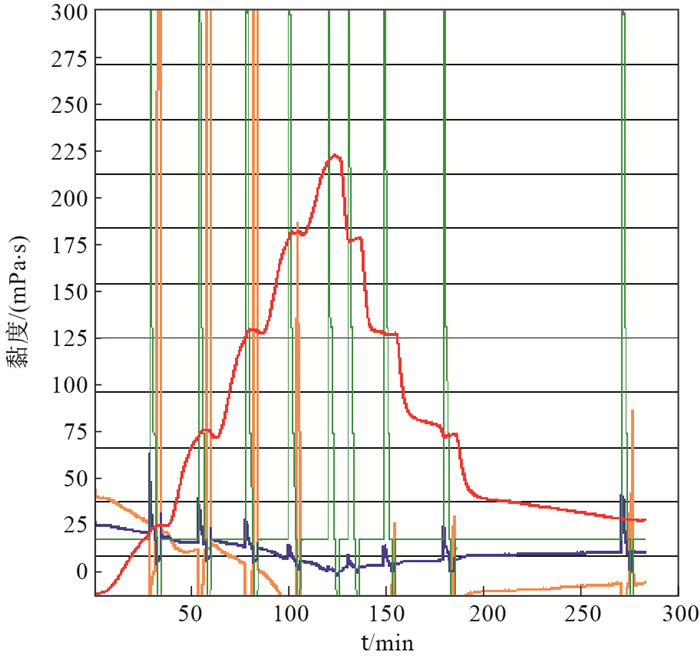
摘要: 聚合物对钻井液的高温流变特性具有重要影响。对比了聚合物种类、加量、剪切时间、盐、造浆黏土等对聚合物溶液高温流变性的影响,并对不同温度下的剪切速率-剪切应力关系进行了流变模型拟合。结果表明,温度升高、剪切时间及盐量增加均导致黏度降低,超过190℃后黏度下降速率加剧;含5%甲酸盐与5%卤盐的样品黏度在降温阶段的黏度恢复率分别为86.8%和2.7%;以宾汉模式对造浆黏土与聚合物混合液进行拟合,220℃时的动切力最高达到5.47 Pa。温度升高使得聚合物溶液由假塑性向牛顿性演变的趋势增强。高于130℃时,长时间剪切导致黏度下降的趋势明显,此时含甲酸盐的聚合物溶液黏度较含卤盐的高,且降温阶段的黏度恢复率也较高。黏土的存在增强了混合液的网间结构,有利于高温下携带岩屑。Abstract: Polymer has a significant effect on the high temperature rheology of drilling fluid.The effects of polymer type, addition amount, shear time, salt and clay on the HTHP rheological properties were compared and analyzed, and the relationship of shear rate and shear stress was fitted to different rheological models.The increase of temperature, shear time and salt amount all led to the decrease of viscosity, especially when the temperature exceeded 190℃.In the cooling progress, the viscosity recovery rates of polymer solutions containing 5% HCOONa and 5% NaCl are 86.8% and 2.7%, respectively.Bingham model was used to characterize the mixture of polymer and clays, and the maximum yield point was 5.47 Pa at 220℃.Heating increases the tendency of the polymer solution to change from pseudoplastic to Newtonian.Above 130℃, the tendency of viscosity to decrease is obvious duedue to shear time.Meanwhile, the viscosity of the formate-containing polymer salt solution is higher than that of the chlorinated salt, and the viscosity retention rate of the former in the cooling process is also higher.The presence of clay enhances the structure force of the polymer solution, which is helpful for cuttings transportation at high temperatures.
-
Key words:
- drilling fluid /
- polymer /
- high temperature rheology /
- rheological model /
- viscosity
-
表 1 造浆黏土+聚合物F的流变参数拟合
Table 1. Rheological parameters fitting of different clay suspensions
温度/℃ PV/(mPa·s) YP/Pa NV-1+聚合物 40 67.01 11.69 100 58.90 10.93 160 49.05 8.41 220 25.06 5.47 SEP+聚合物 40 62.96 11.11 100 51.76 10.12 160 44.60 9.24 220 21.72 4.18 ATTP+聚合物 40 58.95 8.86 100 46.09 6.76 160 28.13 3.24 220 16.24 2.35 -
[1] Caenn R, Darley H C H, Gray G R.Compositions and properties of drilling and completion fluids[M].Sixth edition.USA:Gulf Professional Publishing, 2011. [2] Kelessidis V C, Maglione R, Tsamantaki C, et al.Optimal determination of rheological parameters for Herschel-Bulkley drilling fluids and impact on pressure drop, velocity profiles and penetration rates during drilling[J].Journal of Petroleum Science & Engineering, 2006, 53(3/4):203-224. [3] Nasiri M, Ashrafizadeh S N.Novel equation for the prediction of rheological parameters of drilling fluids in an annulus[J].Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(7):3374-3385. [4] 易灿, 闫振来, 赵怀珍.超深井水基钻井液高温高压流变性试验研究[J].石油钻探技术, 2009, 37(1):10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2009.01.003 [5] 方俊伟, 苏晓明, 熊汉桥, 等.塔中区块成膜封缝堵气钻井液体系[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(2):297-302. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201902036.htm [6] 董文辉, 鄢捷年, 朱墨.两性离子聚合物泥浆高温流变性能的实验研究[J].石油大学学报:自然科学版, 1995, 19(1):39-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYDX501.006.htm [7] 张翼, 方俊伟, 于培志, 等.塔里木盆地顺北一区柯吐尔组失稳特征及钻井液技术研究[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(4):281-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201904030.htm [8] 吕开河, 高锦屏, 孙明波.多元醇钻井液高温流变性研究[J].石油钻探技术, 2000, 28(6):23-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2000.06.009 [9] Wang Fuhua, Tan Xuechao, Wang Ruihe.High temperature and high pressure rheological properties of high-density water-based drilling fluids for deep wells[J].Petroleum Science, 2012, 9(3):354-362. doi: 10.1007/s12182-012-0219-4 [10] 齐佳佳.大庆油田有机硅钻井液高温流变性研究[D].大庆: 大庆石油学院, 2010. [11] Fisk J V, Jamison D E.Physical properties of drilling fluids at high temperature and pressures[J].Spe Drilling Engineering, 1989, 4(4):341-346. doi: 10.2118/17200-PA [12] Arabi A S, Dewu B B M, Funtua I I, et al.Morphology, rheology and thermal stability of drilling fluid formulated from locally beneficiated clays of Pindiga Formation, Northeastern Nigeria[J].Applied Clay Science, 2018, 161:90-102. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2018.03.034 [13] Sinha B K.A new technique to determine the equivalent viscosity of drilling fluids under high temperature and high pressures[J].Society of Petroleum Engineers Journal, 1970, 10(1):33-40. doi: 10.2118/2384-PA [14] 韩博, 鲁光银, 曹涵, 等.基于图像处理技术的聚合物水基钻井液微观结构分形研究[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(2):221-228. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201802030.htm [15] 周欣, 宁伏龙, 孙嘉鑫, 等.实验尺度下钻井液在含水合物地层流动数值模拟[J].地质科技情报, 2015, 34(5):190-198. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201505030.htm [16] 施里宇, 李天太, 张喜凤, 等.温度和膨润土含量对水基钻井液流变性的影响[J].石油钻探技术, 2008, 36(1):20-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0890.2008.01.006 [17] Benna M, Kbir-Ariguib N, Magnin A et al.Effect of pH on rheological properties of purified sodium bentonite suspensions[J].Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 1999, 218(2):442-455. [18] Vryzas Z, Kelessidis V C, Nalbantian L, et al.Effect of temperature on the rheological properties of neat aqueous Wyoming sodium bentonite dispersions[J].Applied Clay Science, 2016, 136:26-36. [19] Hiller K H.Rheological measurements on clay suspensions and drilling fluids at high temperatures and pressures[J].Journal of Petroleum Technology, 1963, 15(7):779-789. doi: 10.2118/489-PA [20] Alderman N J, Gavignet A, Guillot D, et al.High-temperature, high-pressure rheology of water-based muds[C]//Paper 18035-MS presented at the SPE annual technical conference and exhibition, 2-5 October 1988, Houston, Texas, USA. [21] Choo K Y, Bai K.Effects of bentonite concentration and solution pH on the rheological properties and long-term stabilities of bentonite suspensions[J].Applied Clay Science, 2015, 108:182-190. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2015.02.023 [22] Magzoub M I, Nasser M S, Hussein I A, et al.Effects of sodium carbonate addition, heat and agitation on swelling and rheological behavior of Ca-bentonite[J].Applied Clay Science, 2017, 147:176-183. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.07.032 [23] Lin Yuan, Cheah L K J, Phan T N, et al.Effect of temperature on rheological behavior of kaolinite and bentonite suspensions[J].Colloids and Surfaces A:Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2016, 506:1-5. [24] 王中华.国内钻井液及处理剂发展评述[J].中外能源, 2013, 18(10):34-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYZW201310010.htm [25] 张磊.驱油聚合物的降解与稳定性研究[D].济南: 山东大学, 2011. [26] 史雪冬.耐高温聚合物粘弹特性及稳定性研究[D].大庆: 东北石油大学, 2015. [27] 陈跃章, 张柱, 陈明华, 等.聚合物溶液黏度的主要影响因素分析[J].辽宁化工, 2004, 33(5):258-260. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0935.2004.05.004 [28] 方道斌, 郭睿威, 哈润华.丙烯酰胺聚合物[M].北京:化学工业出版社, 2006 [29] 吴其晔, 巫静安.高分子材料流变学[M].北京:高等教育出版社, 2002 [30] 陈乐亮, 汪桂娟.甲酸盐基钻井液完井液体系综述[J].钻井液与完井液, 2003, 20(1):34-39. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJYW200301011.htm [31] 赵春花.低分子量水溶性聚合物与蒙脱土的相互作用及其环境响应行为[D].济南: 山东大学, 2014. -





 下载:
下载: