Extraction of iron meteorites from the Barringer Meteor Crater based on remote sensing alteration information
-
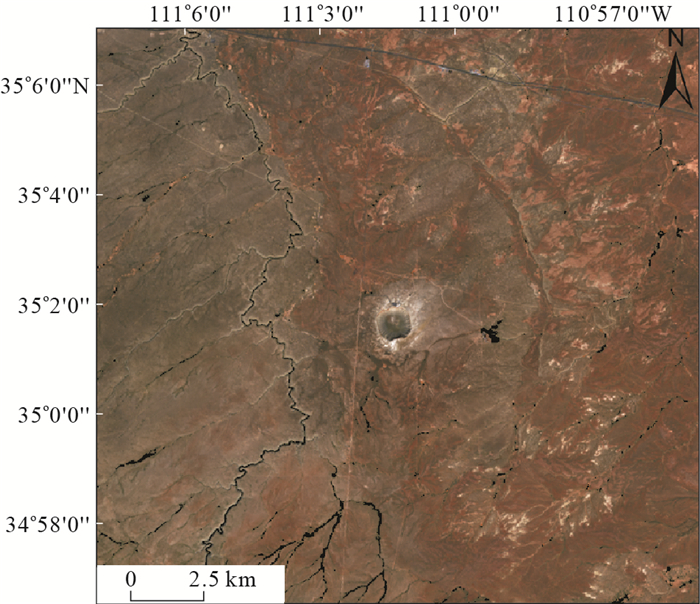
摘要: 目前地球上已经得到确认的撞击坑有190余个,其中直径小于1 km的简单撞击坑绝大部分是由铁质撞击体撞击形成的。由铁质撞击体撞击而成的撞击坑周边存在大量的铁陨石物质,这些铁陨石物质的空间分布特征对研究撞击坑的撞击过程和机理具有重要意义。铁元素的异常富集也可作为探寻地球表面疑似撞击坑的重要信息。为了获取撞击坑周围的铁陨石残片,早期主要通过人工方式进行实地调查,但这种方法效率低下且需要投入大量人力物力。基于铁陨石独特的光谱特征,利用遥感蚀变信息提取手段可以很方便地获取撞击坑周边的铁陨石物质。根据铁陨石矿物的波谱特征,以美国亚利桑那州巴林格撞击坑(Barringer Meteor Crater)为研究对象,基于Landsat 8 OLI数据,采用目前提取蚀变信息的常用方法:波段比值(BandMath)—主成分分析法进行撞击坑周边铁陨石信息的提取。提取结果与前人实地调查获取的铁陨石分布情况契合程度较好。撞击坑东侧、东南侧、西南侧等处的铁陨石聚集区在提取结果图上均有较好的反映。表明利用波段比值-主成分分析方法提取巴林格撞击坑周边铁陨石信息是可行的,实验结果准确地获得了该撞击坑周围的铁陨石空间分布信息,为探寻地球表面撞击成因的环形构造提供了可行方案,同时为未来同类撞击坑信息提取提供了重要的方法参考。
-
关键词:
- 巴林格撞击坑 /
- 铁陨石 /
- Landsat-8 /
- 波段比值-主成分分析 /
- 蚀变信息提取
Abstract: At present, there are more than 190 craters have been confirmed on the earth, and most of the simple impact craters with a diameter of less than 1 km are formed by iron impactor.There is a large amount of iron meteorite material around the impact crater struck by the iron impactor.The spatial distribution characteristics of iron meteorite are of great significance for studying the impact process and mechanism of the crater.The enrichment of iron can also be used as important information to explore suspected impact craters on the Earth's surface.In order to obtain iron meteorite fragments around the impact crater, field investigations were mainly conducted manually in the early days, but this method was inefficient and required a lot of manpower and material resources.Based on the unique spectral characteristics of the meteorite, the spatial distribution characteristics of the meteorite material around the impact crater can be easily obtained by using the remote sensing alteration information extraction method.This paper selects Barringer Meteor Crater in Arizona, USA as the research object, considering of the spectral characteristics of iron meteorite, and using Band Math-PCA(principal components analysis).The extraction results fit well with the field survey of the distribution of iron meteorites by the predecessors.The iron meteorite aggregation area on the east, southeast and southwest sides of the impact crater was well reflected in the extraction results.The iron meteorite around the impact crater was well extracted, and the iron meteorite gathering areas on the east, southeast and southwest sides were well reflected on the extraction result map.It shows that it is feasible to use the principal component analysis-band ratio method to extract the iron meteorite information around the Barringer crater.The experimental results accurately obtained the spatial distribution information of iron meteorite around the impact crater.This paper provides a feasible plan for exploring the ring structure of the impact on the earth's surface, and provides an important method reference for the extraction of similar impact craters in the future.-
Key words:
- Barringer Meteor Crater /
- iron meteorite /
- Landsat-8 /
- bandMath-PCA /
- alteration information extraction
-
表 1 Landsat 8卫星波段
Table 1. Landsat 8 satellite bands
波段名称 波段范围/μm 空间分辨率/m Band1 Coastal 0.433~0.453 30 Band 2 Blue 0.450~0.515 30 Band 3 Green 0.525~0.600 30 Band 4 Red 0.630~0.680 30 Band 5 NIR 0.845~0.885 30 Band 6 SWIR 1 1.560~1.660 30 Band 7 SWIR 2 2.100~2.300 30 Band 8 Pan 0.500~0.680 15 Band 9 Cirrus 1.360~1.390 30 表 2 波段比值-主成分特征分量
Table 2. BandMath ratio and principal component feature subscales
主成分 OLI2 OLI4 OLI5 OLI6/OLI5 PC1 -0.252 946 -0.556 328 0.791 529 -0.000 123 PC2 -0.182 423 -0.776 034 0.603 733 -0.000 282 PC3 -0.950 126 0.297 105 0.094 807 -0.001 083 PC4 -0.001 112 0.000 034 0.001 760 0.999 999 -
[1] Kring D A.Guidebook to the geology of Barringer Crater, Arizona[M].Houston:Meteoritical Society Press, 2017. [2] Craddock R A, Maxwell T A, Howard A D.Crater morphometry and modification in the Sinus Sabaeus and Margaritifer Sinus regions on Mars[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 1997, 102(E6):13321-13340. doi: 10.1029/97JE01084 [3] Barlow N G, Bradley T L.Martian impact craters:Correlations of Ejecta and interior morphologies with diameter, latitude, and terrain[J].Icarus, 1990, 87(1):156-179. doi: 10.1016/0019-1035(90)90026-6 [4] 陈鸣, 肖万生, 谢先德, 等.岫岩陨石撞击坑的证实[J].科学通报, 2009, 54(22):3507-3511. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXTB200922013.htm [5] Chao E C T.Shock effects in certain rock-forming minerals[J].Science, 1967, 156:192-202. doi: 10.1126/science.156.3772.192 [6] French B M, Short N M.Shock Metamorphism of natural materials[J].Science, 1966, 153:903-906. [7] Stöffler D.Deformation and transformation of rock-forming minerals by natural and experimental shock processes:1.Behaviour of minerals under shock compression[J].Fortschr Mineral, 1972, 49:50-113. [8] Stöffler D.Deformation and transformation of rock-forming minerals by natural and experimental processes:2.Physical properties of shocked minerals[J].Fortschr Mineral, 1974, 51:256-289. [9] Grieve R A F, Langenhorst F, Stöffler D.Shock metamorphism in nature and experiment:Ⅱ.Significance in geoscience[J].Meteorit Planet Sci, 1996, 31(1):6-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1945-5100.1996.tb02049.x [10] Keoberl C.Mineralogical and geochemical aspects of impact craters[J].Mineral Mag., 2002, 66(5):745-768. doi: 10.1180/0026461026650059 [11] D'oraziom, Folco L, et al.Gebel Kamil:The iron meteorite that formed the Kamil crater(Egypt)[J].Meteoritics & Planetary Science, 2011, 46(8):1179-1196. [12] Rowan L C, Goetz A F H, Ashley R P.Discrimination of hydrothemally altered and unaltered rocks in visible and near-infrared multispectral images[J].Geophysics, 1977, 42:522-535. doi: 10.1190/1.1440723 [13] 成功, 曾令瑶, 陈松岭.OLI与ETM+数据在豫西沉积型铝土矿找矿中的对比研究[J].国轻金属, 2014(11):7-11. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QJSS201411004.htm [14] 杨长保, 姜琦刚, 刘万崧, 等.基于ASTER数据的内蒙古东乌珠穆沁北部地区遥感蚀变信息提取[J].吉林大学学报:地球科学版, 2009, 39(6):1163-1167. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CCDZ200906035.htm [15] 王爱云, 王安建, 李丽辉.基于最大噪声分量变换(MNF)和矿物标识的植被区蚀变信息提取[J].地质与勘探, 2011, 47(4):710-718. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKT201104022.htm [16] Abrams M J.Landsat-4 thermatic mapper and thematic mapper simulator data for a porphyry copper deposit[J].Photogrammet ric Engineering and Remote Sensing, 1984, 50(8):1171-1173. [17] Gabr S, Ghulan A, Kusky T.Detecting areas of high-potential copper mineralization using ASTER data[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2010, 38(1/2):59-69. [18] 刘燕君.矿产信息的遥感地面模式[M].北京:地质出版社, 1993. [19] Jin M S, Wang H, Zhang W, el al.Method for extraction of ferric contamination anomly from high-resoulusensing data and its application[J].Remote Sensing for Land Resourses, 2015, 27(3):122-127. [20] Kusky T M, Talaat M R.Structural controls on Neoproterozoic min eralization in the South Eastern Desert, Egypt:An integrated field, Landsat TM, and SIR-C/X SAR approach[J].Journal of African Earth Sciences, 2002, 35(1):107-121. doi: 10.1016/S0899-5362(02)00029-5 [21] Rajesh H M.Mapping Proterozoic unconformity-related uranium deposits in the Rockhole area, Northern Territory, Australia using Landsat ETM+[J].Ore Geology Reviews, 2008, 33(3/4):382-396. [22] Adiri Z, El Harti A, Jellouli A, et al.Lithological mapping using Landsat 8 OLI and Terra ASTER multispectral data in the Bas Draa in the lier, Moroccean Anti Atlas[J].Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2016, 10(1):016005. doi: 10.1117/1.JRS.10.016005 [23] 赵元洪, 张福祥, 陈南峰.波段比值的主成份复合在热液蚀变信息提取中的应用[J].国土资源遥感, 1991, 9(3):12-18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG199103002.htm [24] 高景刚, 薛春纪, 吴淦国, 等.基于知识的蚀变遥感异常信息快速提取及找矿应用实践[J].遥感学报, 2008, 12(1):186-192. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXB200801024.htm [25] 王乐.西藏尼雄地区遥感成矿信息提取与找矿远景分析[D].成都: 成都理工大学, 2011. [26] 郭艳, 赵忠海, 曲晖, 等.黑龙江多宝山地区遥感找矿蚀变异常提取方法研究[J].地质科技情报, 2011, 30(2):117-121. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201102020.htm [27] 唐超, 周可法, 张楠楠, 等.基于Landsat-8 OLI和ASTER数据集成和融合和融合的矿化蚀变信息提取[J].地质科技情报, 2018, 37(6):211-217. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201806026.htm [28] Wright S P, Ramsey M S.Thermal infrared data analyses of Meteor Crater, Arizona:Implications for Mars spaceborne data from the thermal emission imaging system[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 2006, 111(E2):1-16. [29] Ramsey M S.Ejecta distribution patterns at Meteor Crater, Arizona:On the applicability of lithologic end-member deconvolution for spaceborne thermal infrared data of Earth and Mars[J].Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(E8):3-1-3-14. [30] Garvin J B, Bufton J L, Campell B A, et al.Terrain analysis of Meteor Crater ejecta blanket[J].Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 1989, 20:332-334. [31] A Myers S A, Cygan R T, Assink R A, et al.29Si MAS NMR relaxation study of shocked Coconino sandstone from Meteor Crater, Arizona[J].Phy.Chem.Minerals, 1988, 25:313-317. [32] 李旭文, 牛志春, 姜晟.Landsat 8卫星OLI遥感影像在生态环境监测中的应用研究[J].环境监控与预警, 2013, 5(6):1-5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6732.2013.06.001 [33] Moore F, Rastmanesh F, Asadi H, et al.Mapping mineralogical alteration using principal component analysis and matched filter processing in the Takab area, Northwest Iran, from ASTER Data[J].Internation Journal of Remote Sensing, 2008, 29(10):2851-2867. doi: 10.1080/01431160701418989 [34] 张玉君, 杨建民.基岩裸露区蚀变岩遥感信息的提取方法[J].国土资源遥感, 1998, 38(2):46-53. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GTYG802.006.htm [35] 马威.基于多时相遥感数据融合的矿化蚀变信息提取研究[D].昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2016. [36] 薛云, 戴塔根, 邹艳红, 等.基于主成分分析的SVM矿化信息提取研究:以青海黄南州阿哇地区为例[J].遥感应用, 2007, 6(6):32-35. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YGXX200706007.htm [37] 张玉君, 曾朝铭, 陈微.ETM+(TM)蚀变遥感异常提取方法研究与应用:方法选择和技术流程[J].国土资源遥感, 2003, 4(2):44-49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-070X.2003.02.011 [38] 梁丹迪, 周可法, 王珊珊, 等.不同空间分辨率高光谱遥感数据对蚀变矿物信息提取的影响[J].地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3):282-289. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DZKQ201903031.htm [39] 荆凤, 陈建平.矿化蚀变信息的遥感提取方法综述[J].遥感信息, 2005, 6(2):62-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3177.2005.02.016 [40] 徐凯, 袁良军, 杨炳南, 等.黔东北伴生-次生矿物遥感数据组合式挖掘与隐伏锰矿信息提取[J].地质科技通报, 2020, 39(4):37-43. http://dzkjqb.cug.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract9997.shtml -





 下载:
下载: